Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 22916-47-8
Miconazole is a broad-spectrum azole antifungal with some activity against Gram-positive bacteria as well. It is widely used to treat mucosal yeast infections, including both oral and vaginal infections; although intravenous miconazole is no longer available, a wide variety of suppositories, creams, gels, and tablet-based products are available. Miconazole is thought to act primarily through the inhibition of fungal CYP450 14α-lanosterol demethylase activity. Miconazole was first synthesized in 1969 and first granted FDA approval on January 8, 1974, for sale by INSIGHT Pharmaceuticals as a topical cream. It is currently available as a variety of prescription and over the counter products. Despite having been in clinical use for an extended period, resistance to miconazole among susceptible organisms is relatively low.
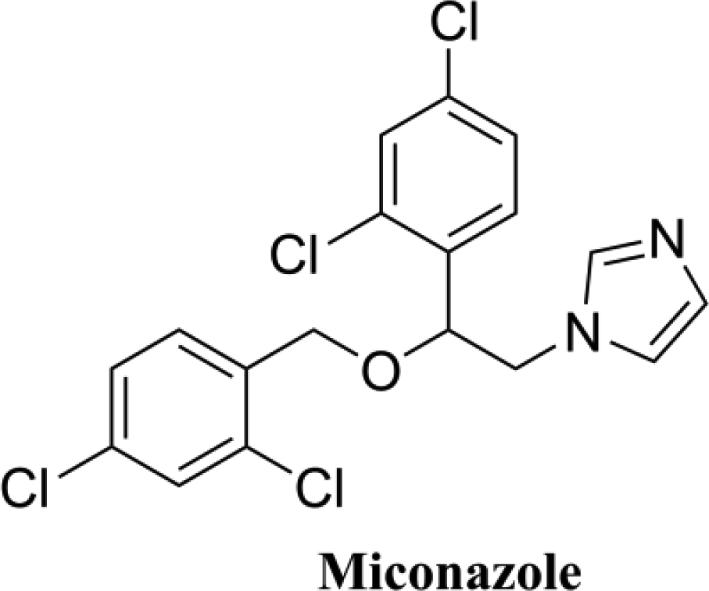
The structure of miconazole.
CAS number: 2309-07-1
Trans-methylferulate is a cinnamate ester that is the methyl ester of ferulic acid. It has been isolated from Pisonia aculeata. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is a cinnamate ester, a methyl ester and a member of guaiacols. It is functionally related to a trans-ferulic acid.
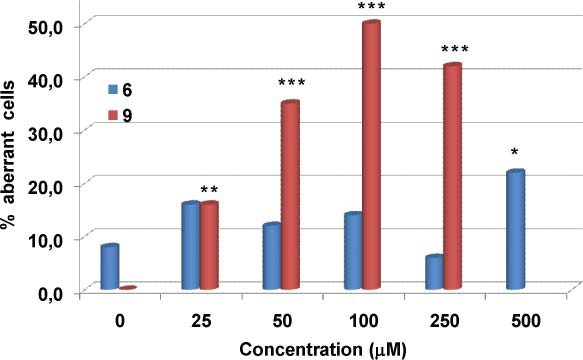
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the monolignol methyl ferulate 6 and its catechol derivative methyl caffeate 9 in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 23094-69-1
Corilagin, a gallotannin, is one of the major active components of many ethnopharmacological plants. It was isolated from Caesalpinia coriaria (Jacq.)
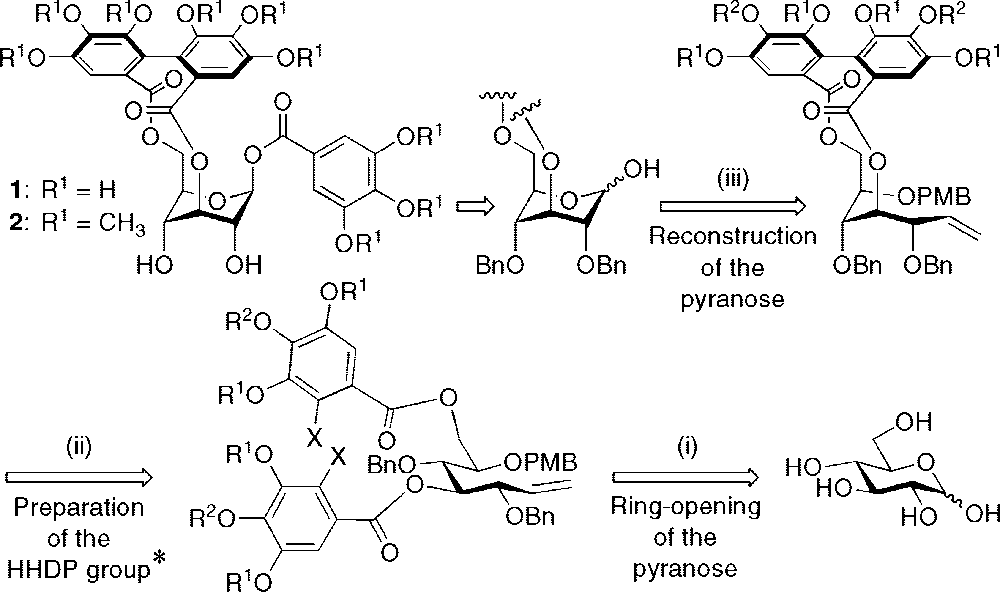
Retrosynthetic Approach to Corilagin (1)
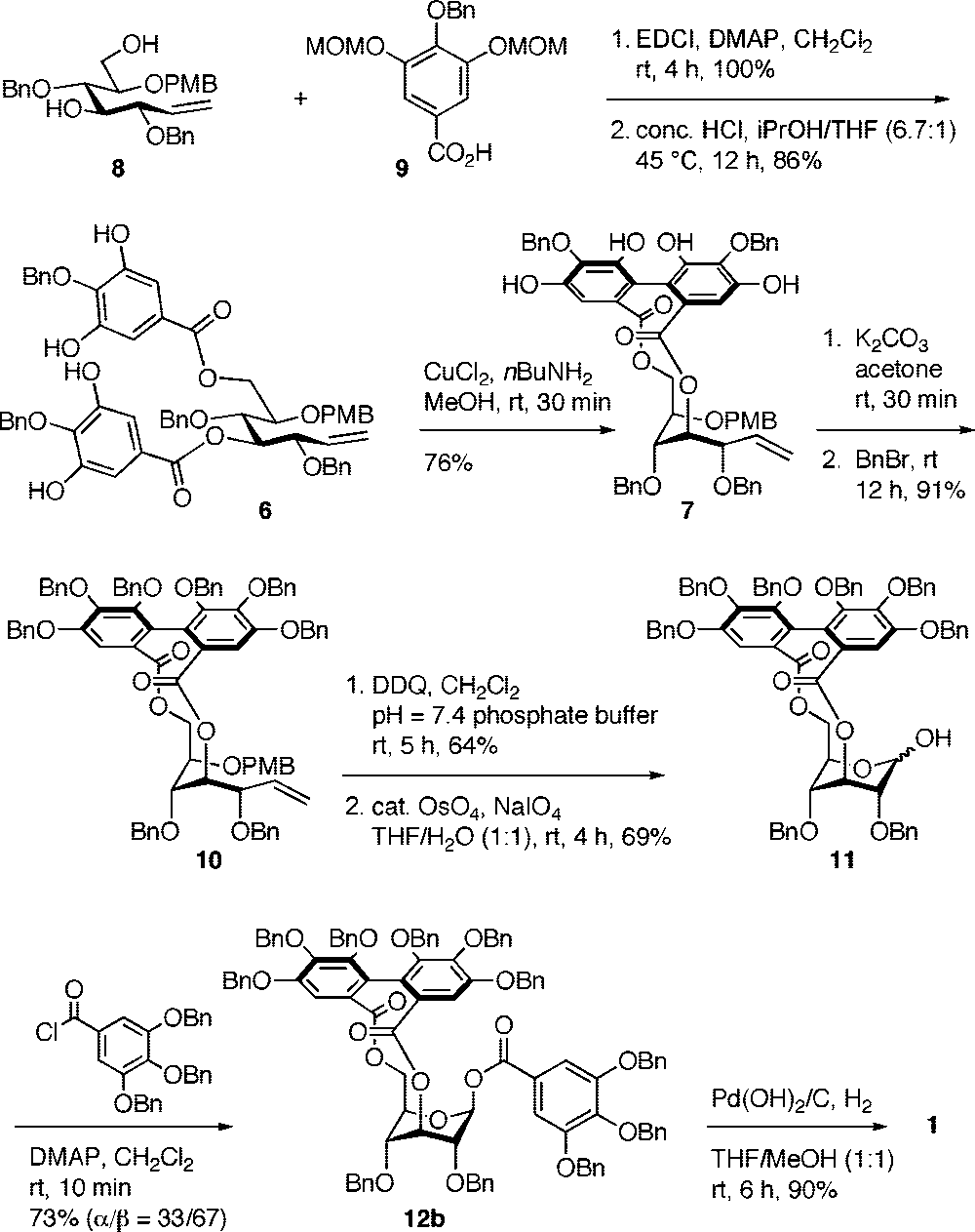
Synthesis of Corilagin (1)
CAS number: 231277-92-2
Lapatinib is an organofluorine compound, an organochlorine compound, a member of quinazolines and a member of furans. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It is functionally related to a monofluorobenzene.
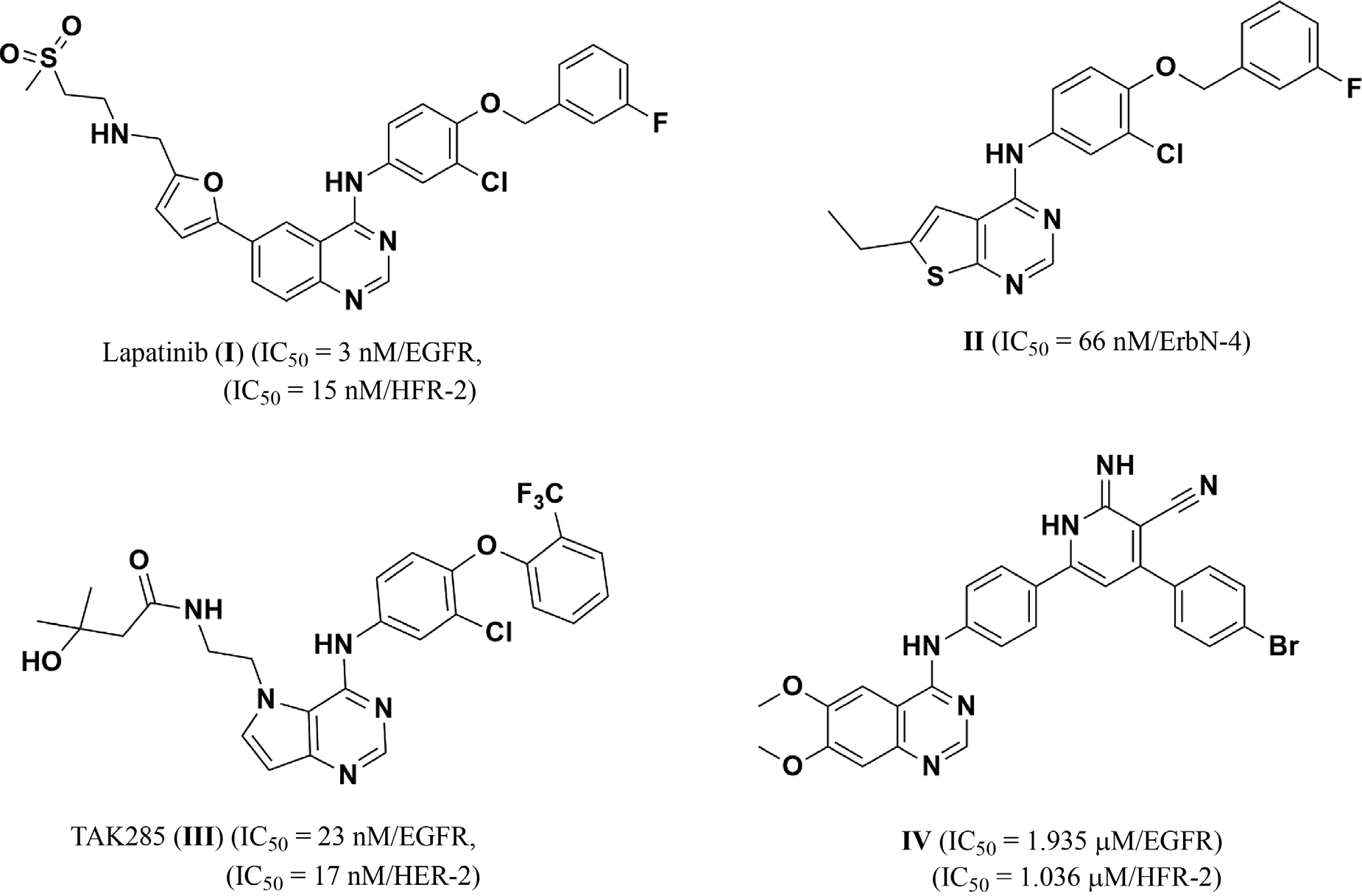
Structures of some approved and reported ErbB family inhibitors: Lapatinib, TAK-285
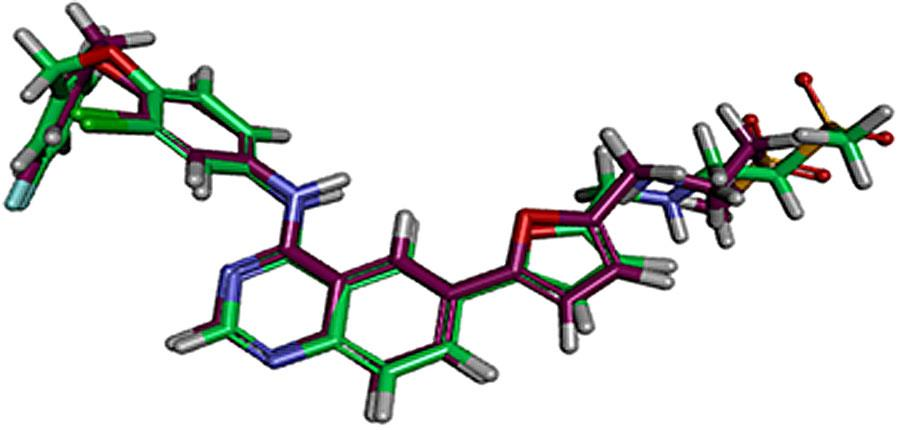
The alignment between the bioactive conformer of lapatinib (I) (colored in violet) and the docked pose (colored in green) at EGFR binding site.
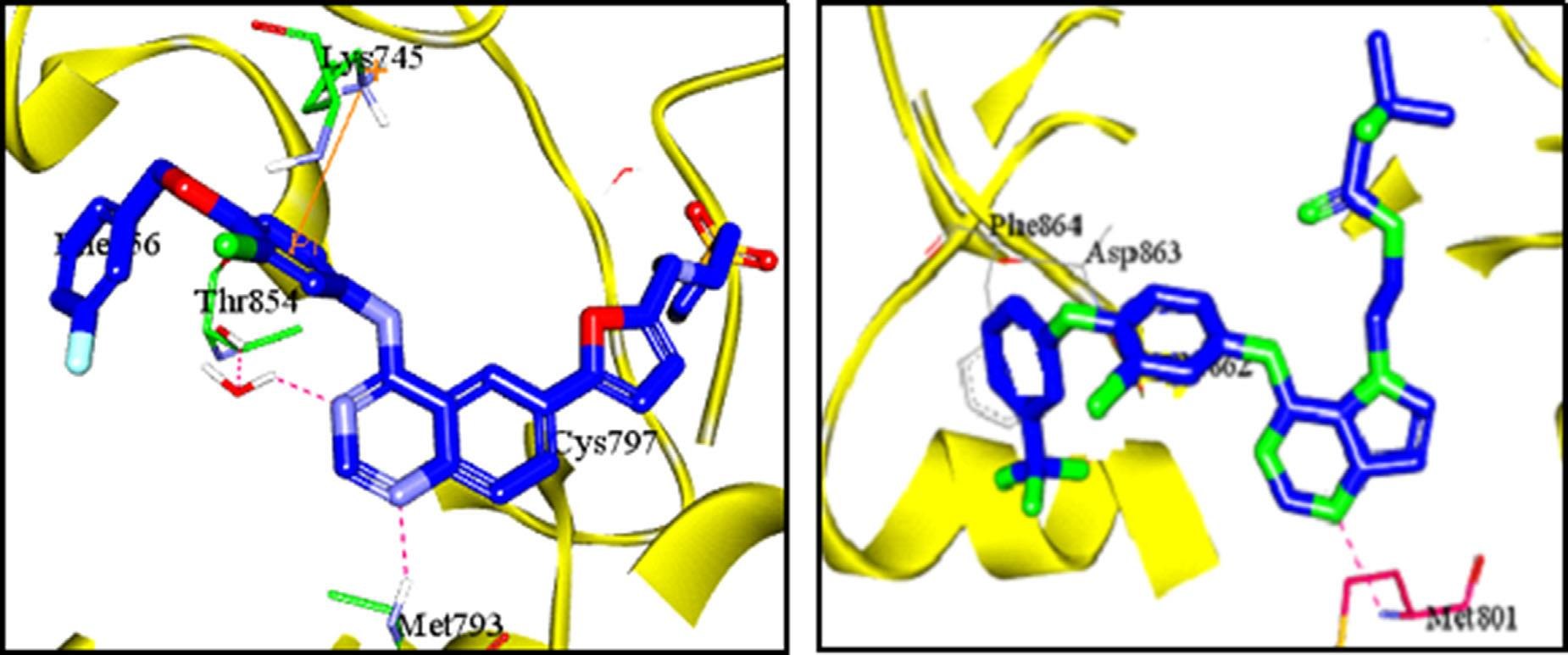
Left: Docking of lapatinib (I) in EGFR binding site (PDB code: 1XKK) showing H bonds with met793 and π interaction with Lys 745. Right: Docking of (TAK285) (III) in HER-2 binding site (PDB code: 3RCD) showing H bond with met801.
CAS number: 23214-92-8
Doxorubicin is a deoxy hexoside, an anthracycline, an anthracycline antibiotic, an aminoglycoside, a member of tetracenequinones, a member of p-quinones, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a doxorubicin(1+). It derives from a hydride of a tetracene.
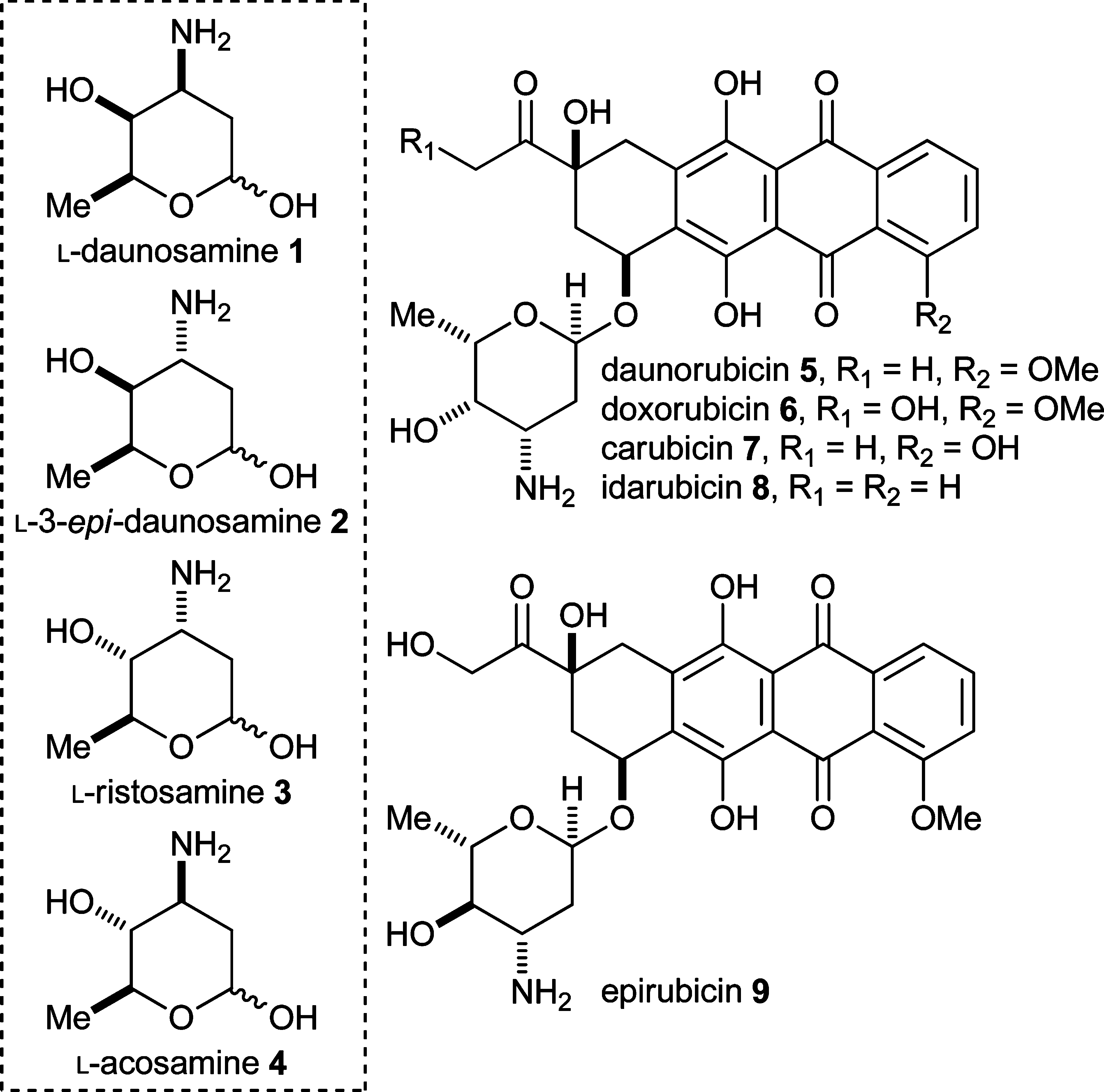
Structures of L-daunosamine 1, L-3-epi-daunosamine 2, L-ristosamine 3, L-acosamine 4, and the anthracycline antibiotics daunorubicin 5, doxorubicin 6, carubicin 7, idarubicin 8, and epirubicin 9.
CAS number: 232925-18-7
Thymectacin, a phosphoramidate derivative of (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine, is a novel small molecule anticancer agent. Thymectacin is selectively active against tumor cells expressing high levels of thymidylate synthase (TS), a critical enzyme in DNA biosynthesis. Thymectacin was as efficacious as irinotecan, a drug recently approved for the treatment of 5-fluorouracil-resistant colon cancer.
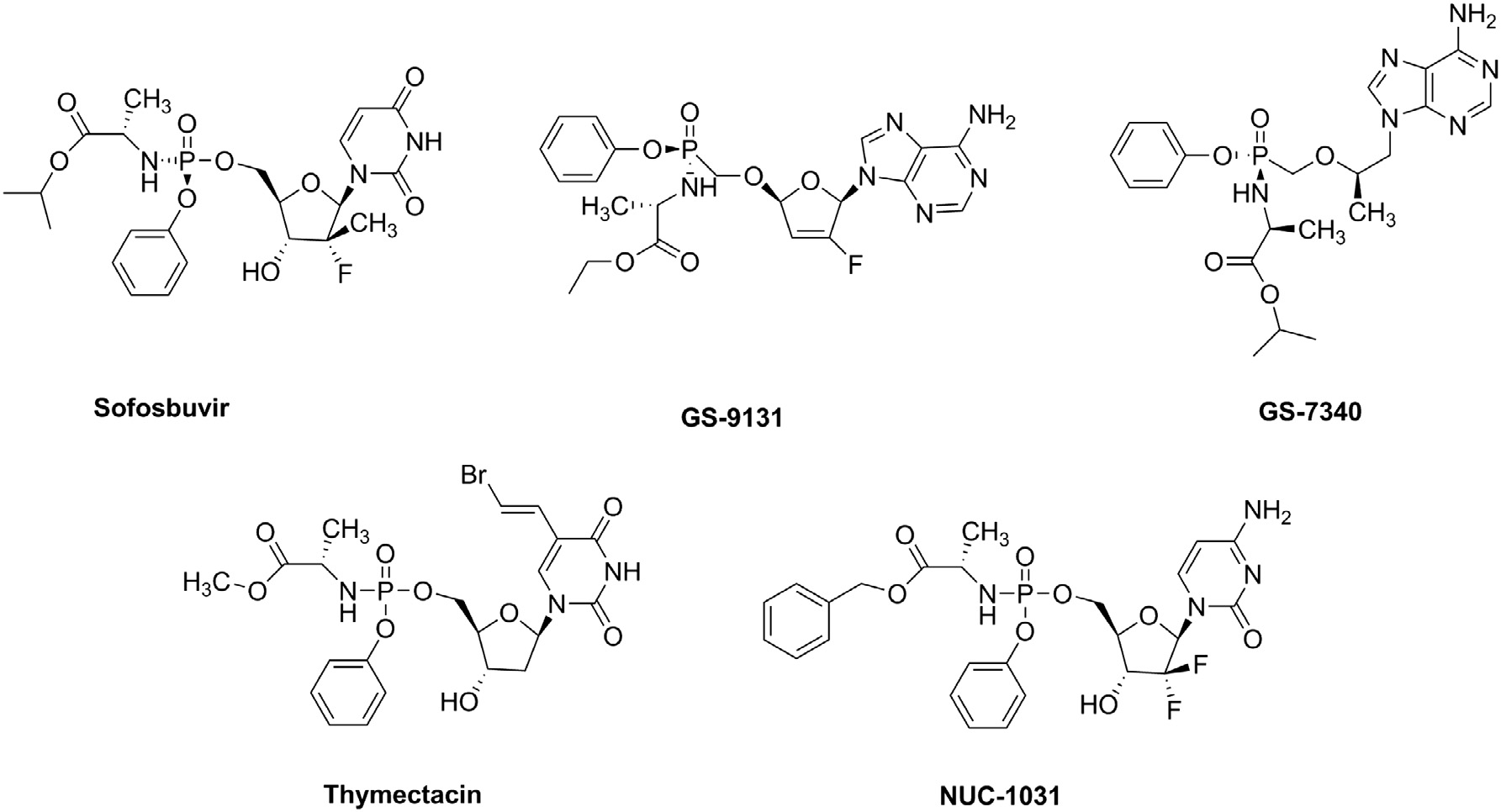
Known ProTides: SOFOSBUVIR, GS-9131, GS-7340, Thymectacin, NUC-1031.
CAS number: 233277-99-1
K-11777 is a cysteine protease inhibitor that acts as a broad-spectrum antiviral, by targeting cathepsin-mediated cell entry.
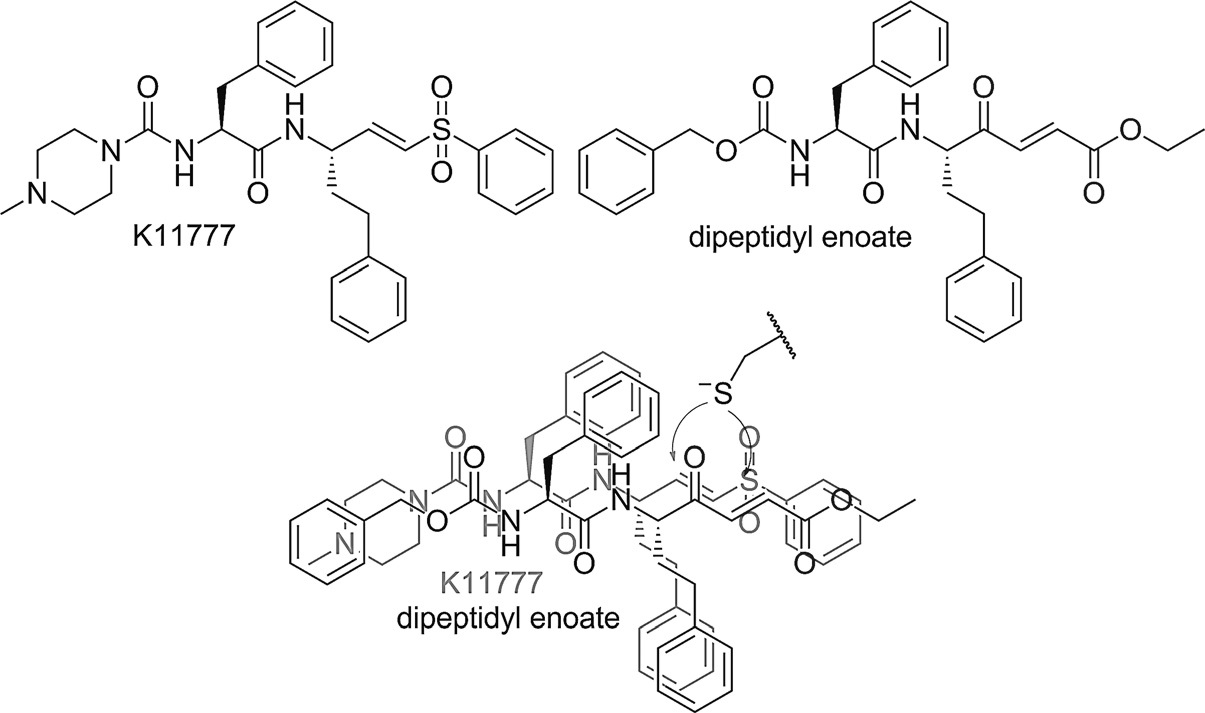
Michael acceptor inhibitors.
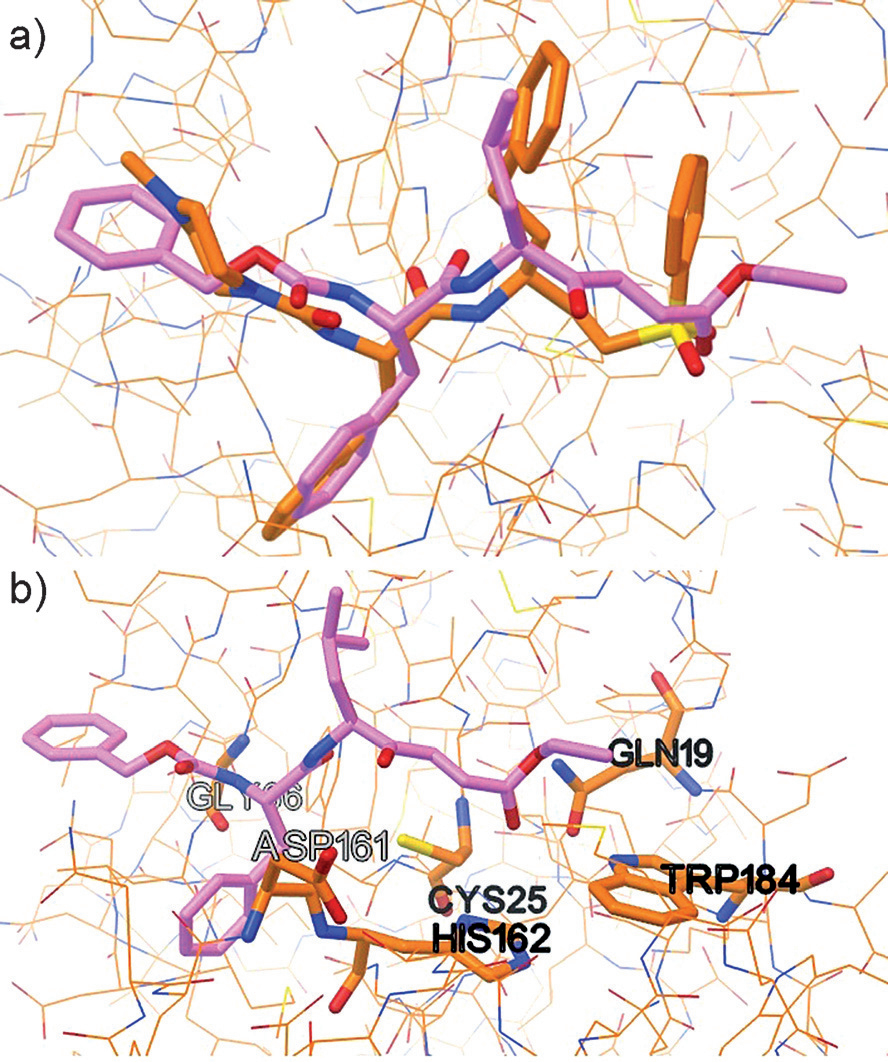
a) Docking pose of inhibitor 6 (magenta) superimposed with K11777 (orange) in complex with rhodesain (PDB ID: 2P7U). b) Proposed docking pose of inhibitor 6 (magenta) in complex with rhodesain.
CAS number: 24050-16-6
2-Methylthiazolidine is a member of thiazolidines.
![Isomeric and conformational equilibrium for 2-methylthiazolidines 8a and 8b, with selected H and [13C] NMR data; analogous oxazolidine 183a–c is shown for comparison.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4360132_08.png)
Isomeric and conformational equilibrium for 2-methylthiazolidines 8a and 8b, with selected H and [13C] NMR data; analogous oxazolidine 183a–c is shown for comparison.
CAS number: 24159-07-7
Febrifugine, a quinazolinone alkaloid that inhibits P. falciparum and has antimalarial activity, is an excellent compound that can be used to block the proliferation of malarial parasites.
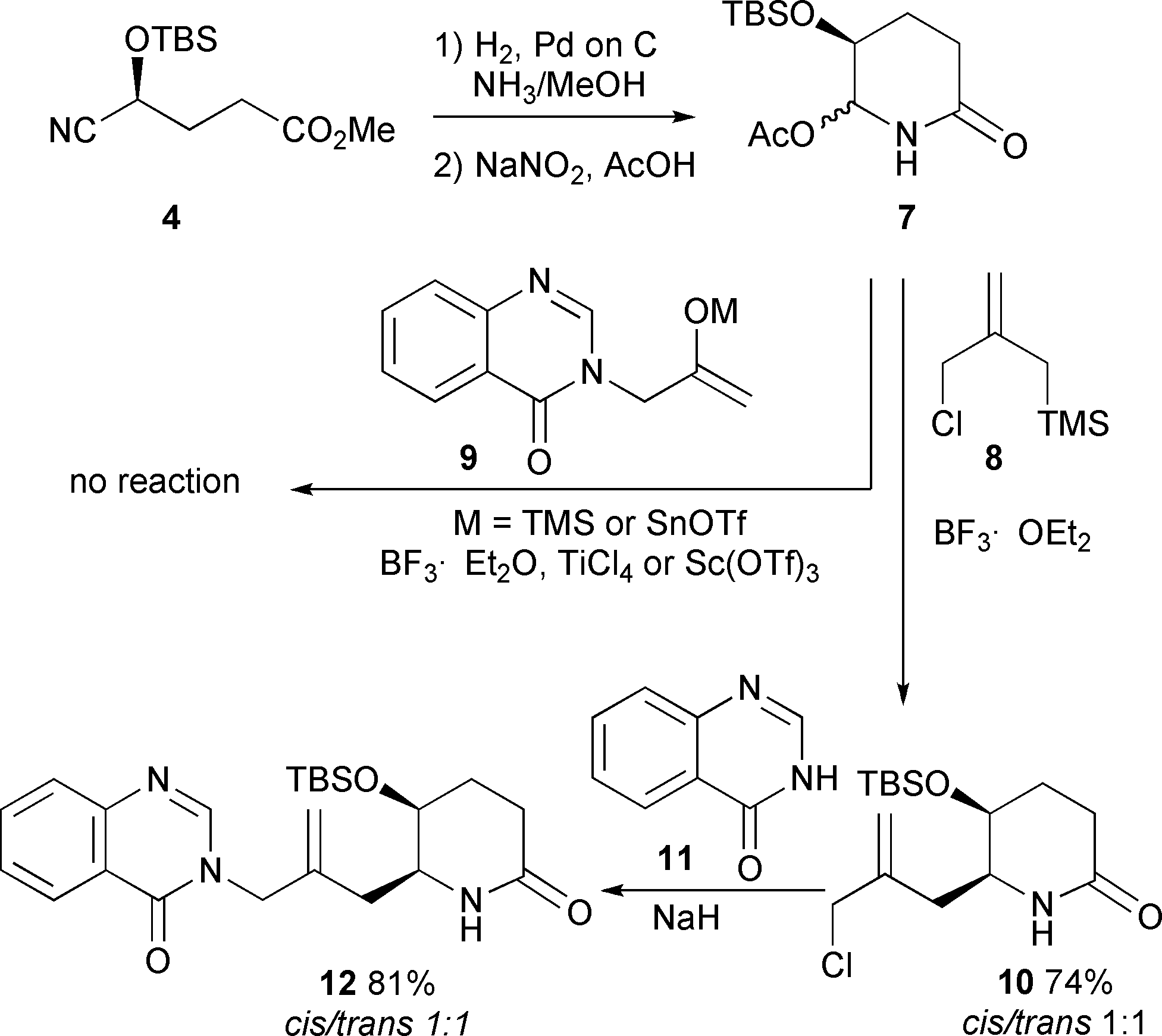
Initial approaches to febrifugine.
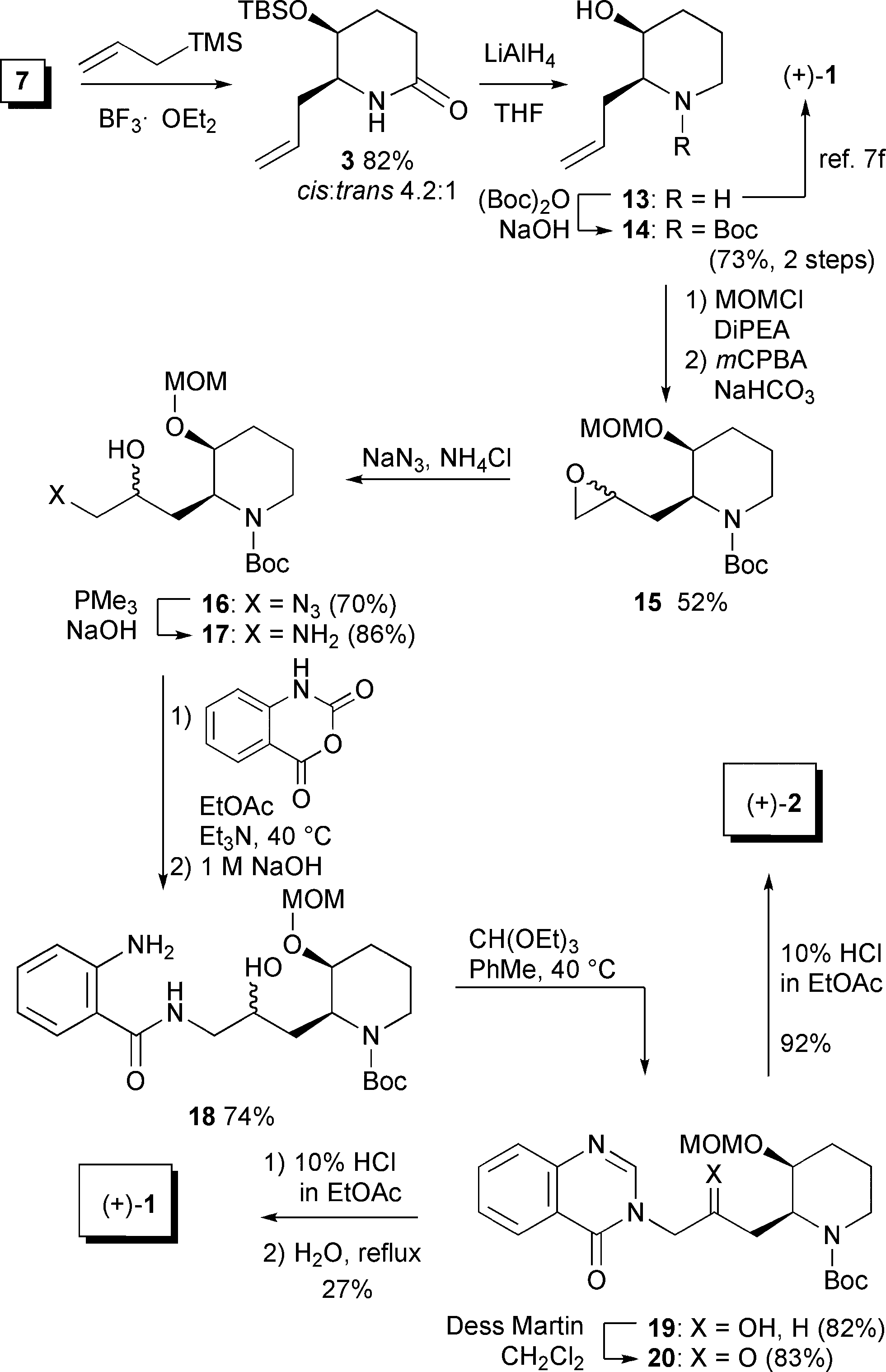
Synthesis of (+)-febrifugine.
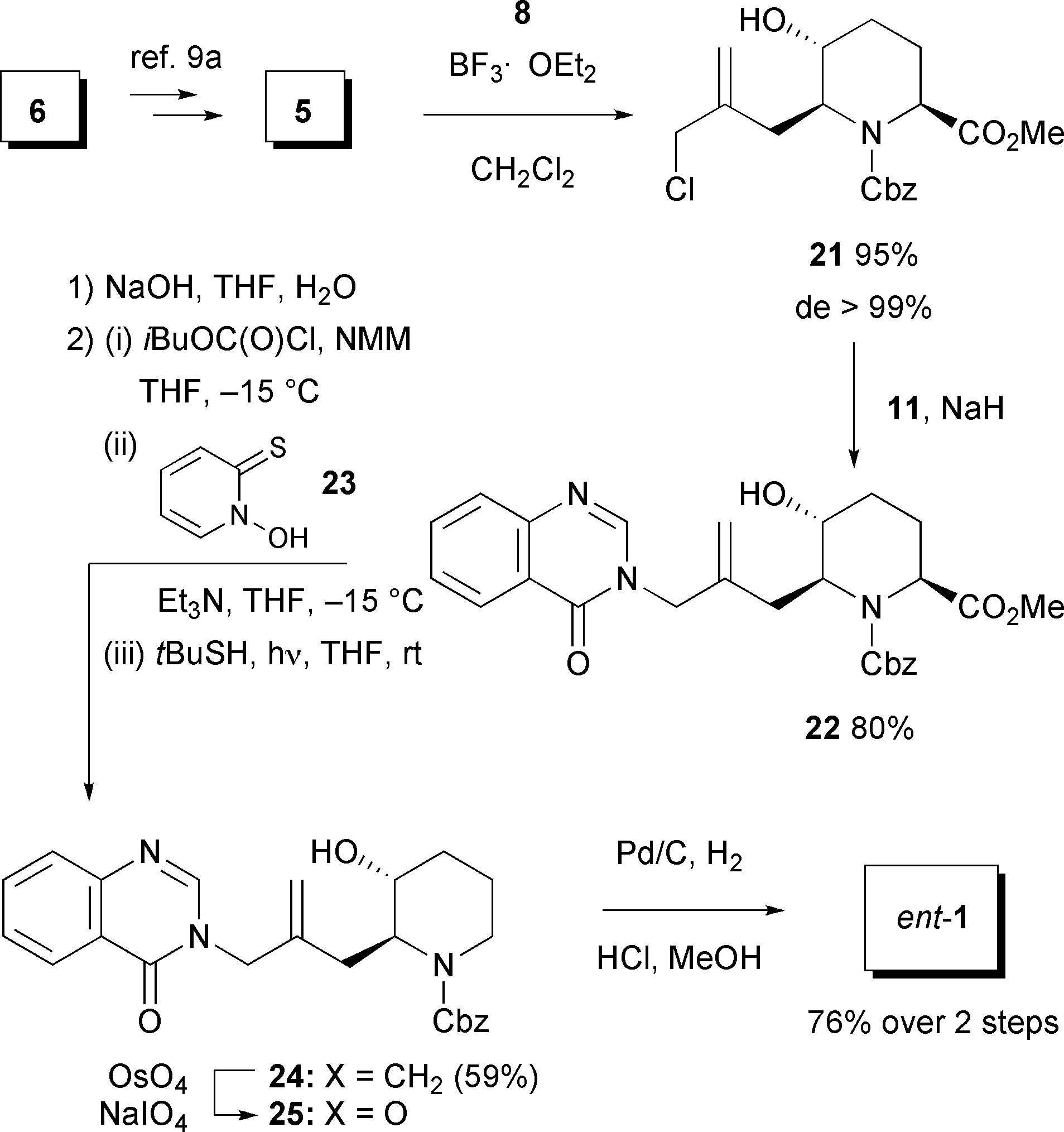
Synthesis of ent-febrifugine.
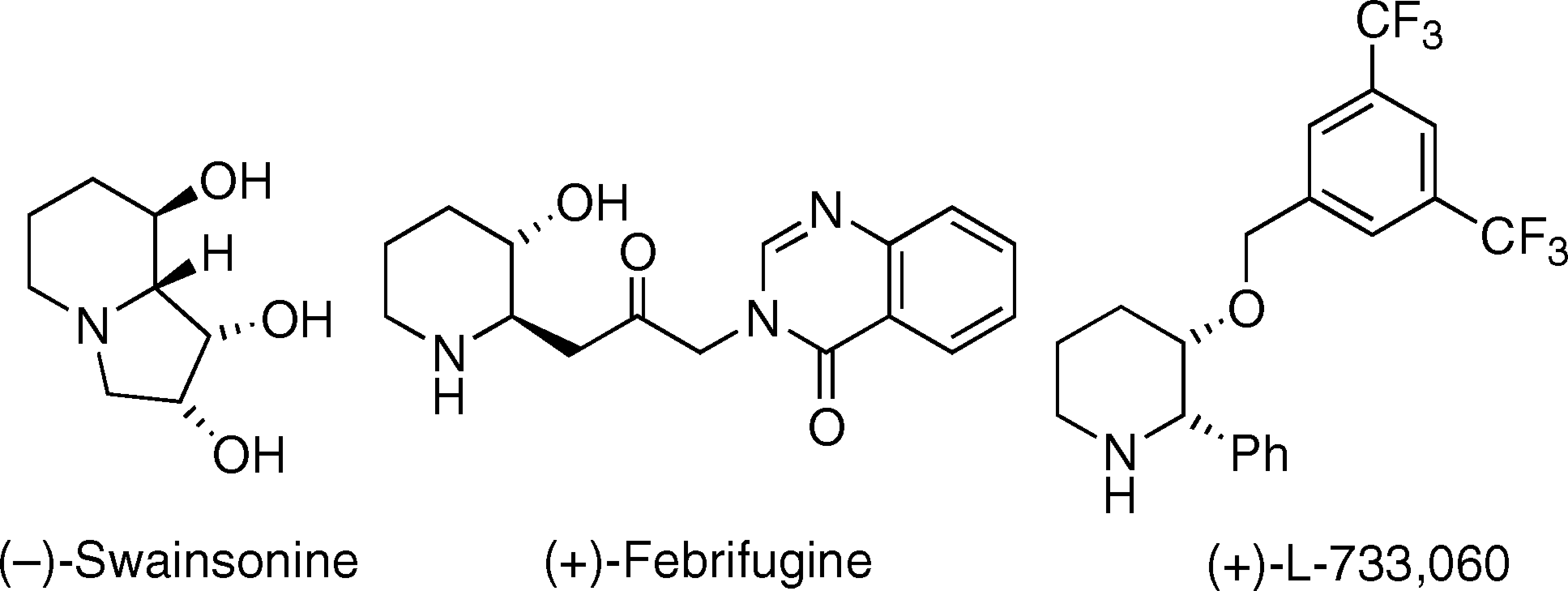
Biologically active β-hydroxy piperidines.
CAS number: 2417-82-5
Cyclopropyl radical is a highly reactive organic intermediate characterized by a three-membered cyclopropane ring bearing an unpaired electron on one of the carbon atoms.
![LED-mediated cyclopropane synthesis. [a] Using trans-b-methylstyrene. [b] Using cis-b-methylstyrene. [c] 20 equiv of styrene. [d] Violet LED used. Also 27% of malonate dimer by H NMR. 1[e] Using soluble ylide 1o.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5329828_16.png)
LED-mediated cyclopropane synthesis. [a] Using trans-b-methylstyrene. [b] Using cis-b-methylstyrene. [c] 20 equiv of styrene. [d] Violet LED used. Also 27% of malonate dimer by H NMR. 1[e] Using soluble ylide 1o.