Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 119-65-3
Isoquinoline is an ortho-fused heteroarene that is a benzopyridine in which the N atom not directly attached to the benzene ring. It is a mancude organic heterobicyclic parent, an azaarene, an ortho-fused heteroarene and a member of isoquinolines.
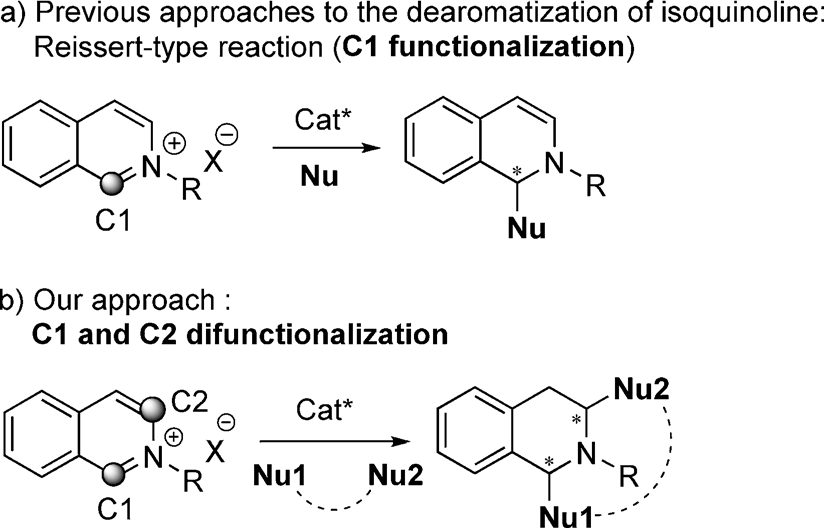
Strategies for the dearomatization of isoquinoline.
CAS number: 1190307-88-0
Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide conjugate that is used in combination with ledipasvir (under the trade name Harvoni) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. It has a role as a prodrug, an antiviral drug and a hepatitis C protease inhibitor. It is a L-alanyl ester, a phosphoramidate ester, a nucleotide conjugate, an organofluorine compound and an isopropyl ester. It is functionally related to a uridine 5'-monophosphate.
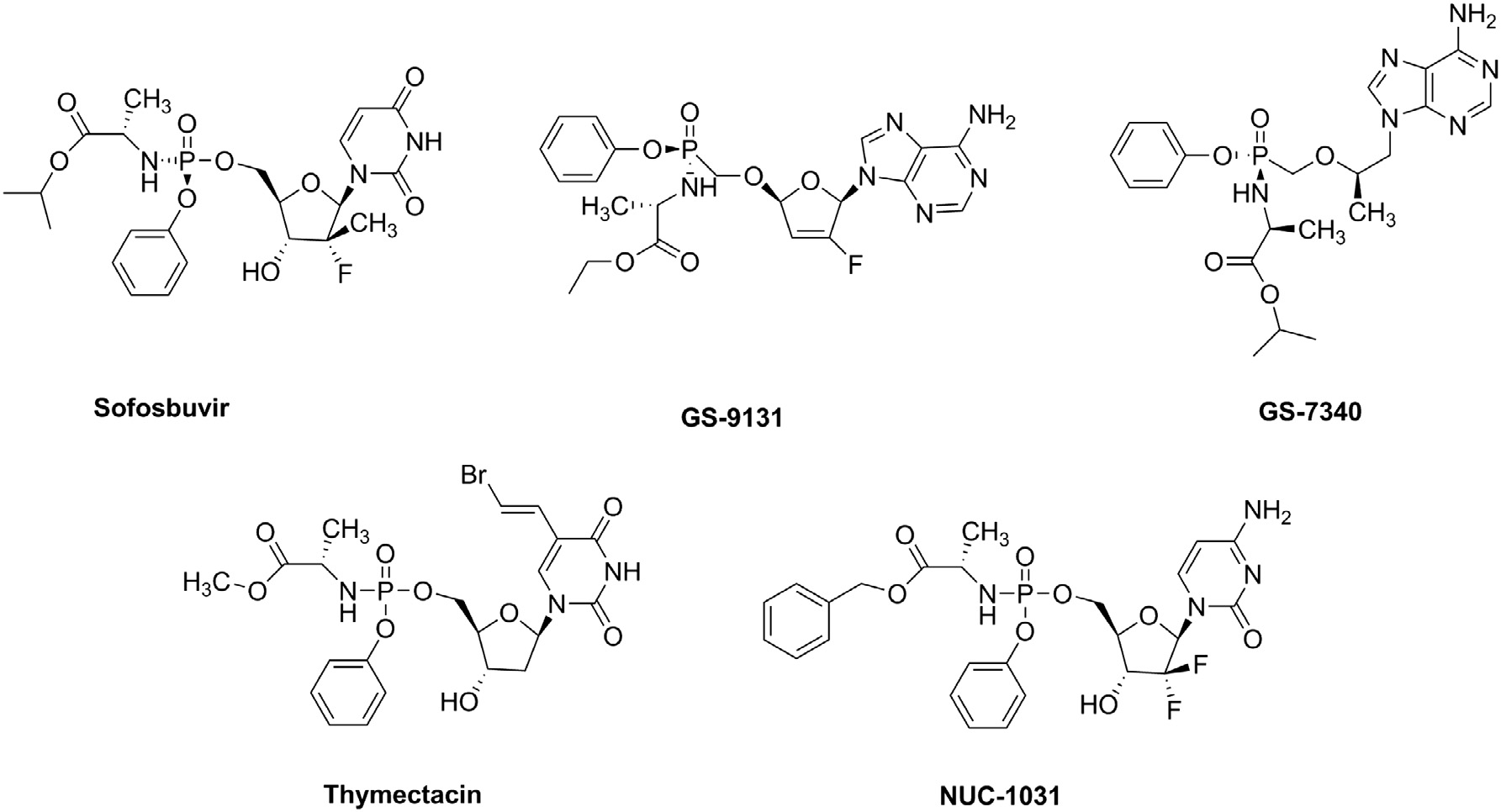
Known ProTides: SOFOSBUVIR, GS-9131, GS-7340, Thymectacin, NUC-1031.
CAS number: 1191-15-7
Diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAL-H) is an organometallic compound that has found wide use as a reducing agent.
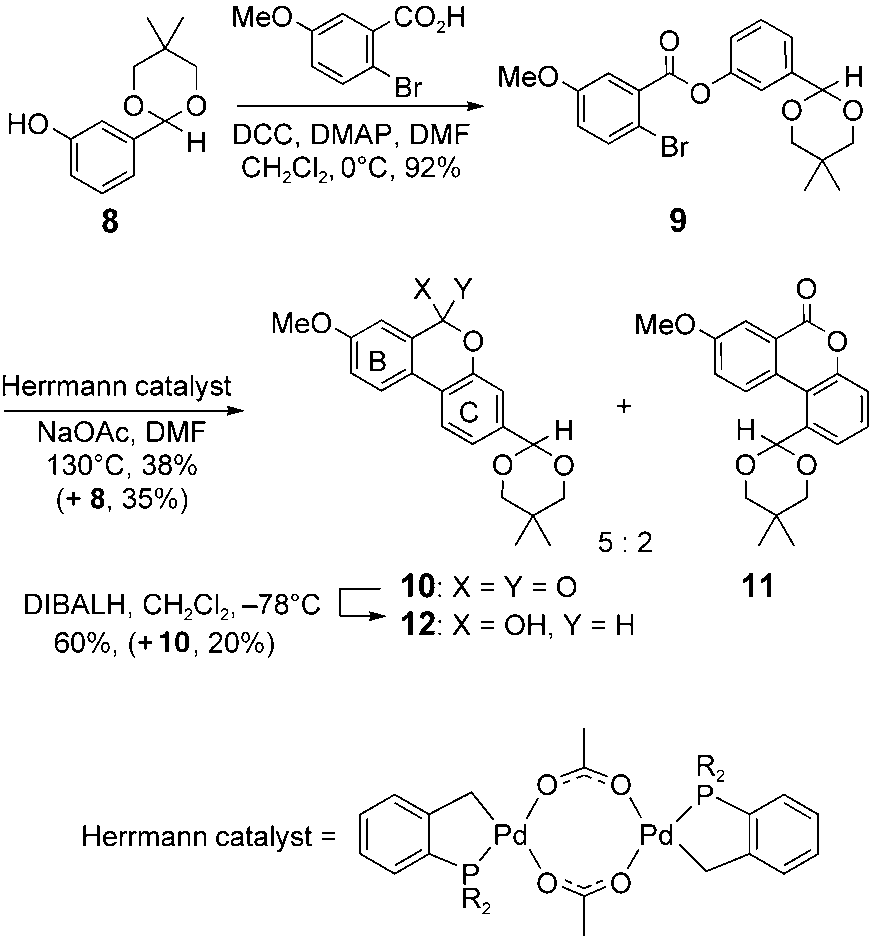
Synthesis of the BC ring system. DCC=dicyclohexylcarbo-diimide, DMAP=4-dimethylaminopyridine, DIBALH=diisobutylaluminum hydride, R=o-tolyl.
CAS number: 1191-95-3
Cyclobutanone is a four-membered cyclic ketone, meaning it's a molecule containing a ring of four carbon atoms, one of which is part of a ketone group (C=O). It's used in organic synthesis, particularly as a starting material for synthesizing other cyclobutane derivatives and in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates.
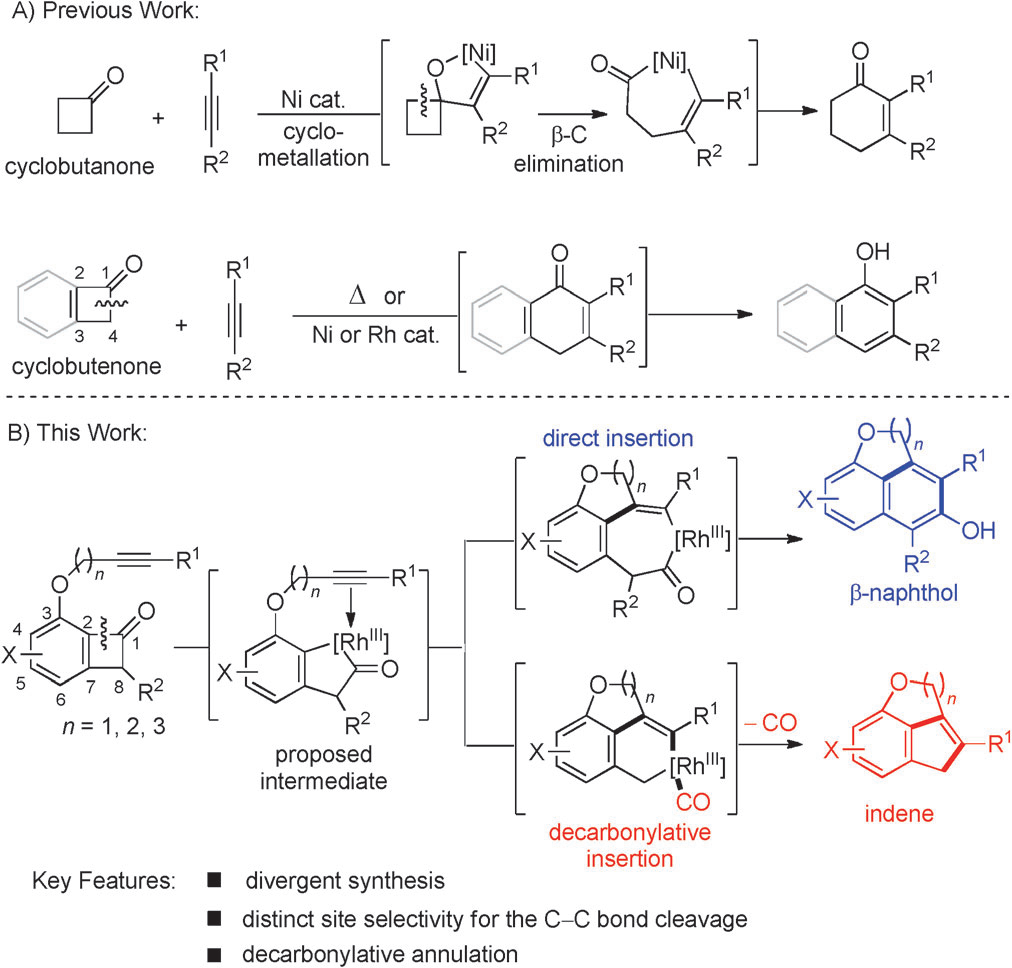
C C bond cleavage in cyclobutenones and cyclobutanones.
CAS number: 1191-99-7
2,3-Dihydrofuran is defined as a five-membered aromatic heterocycle with an enthalpy of formation of −23.52 kcal mol −1, as calculated using semi-empirical methods.
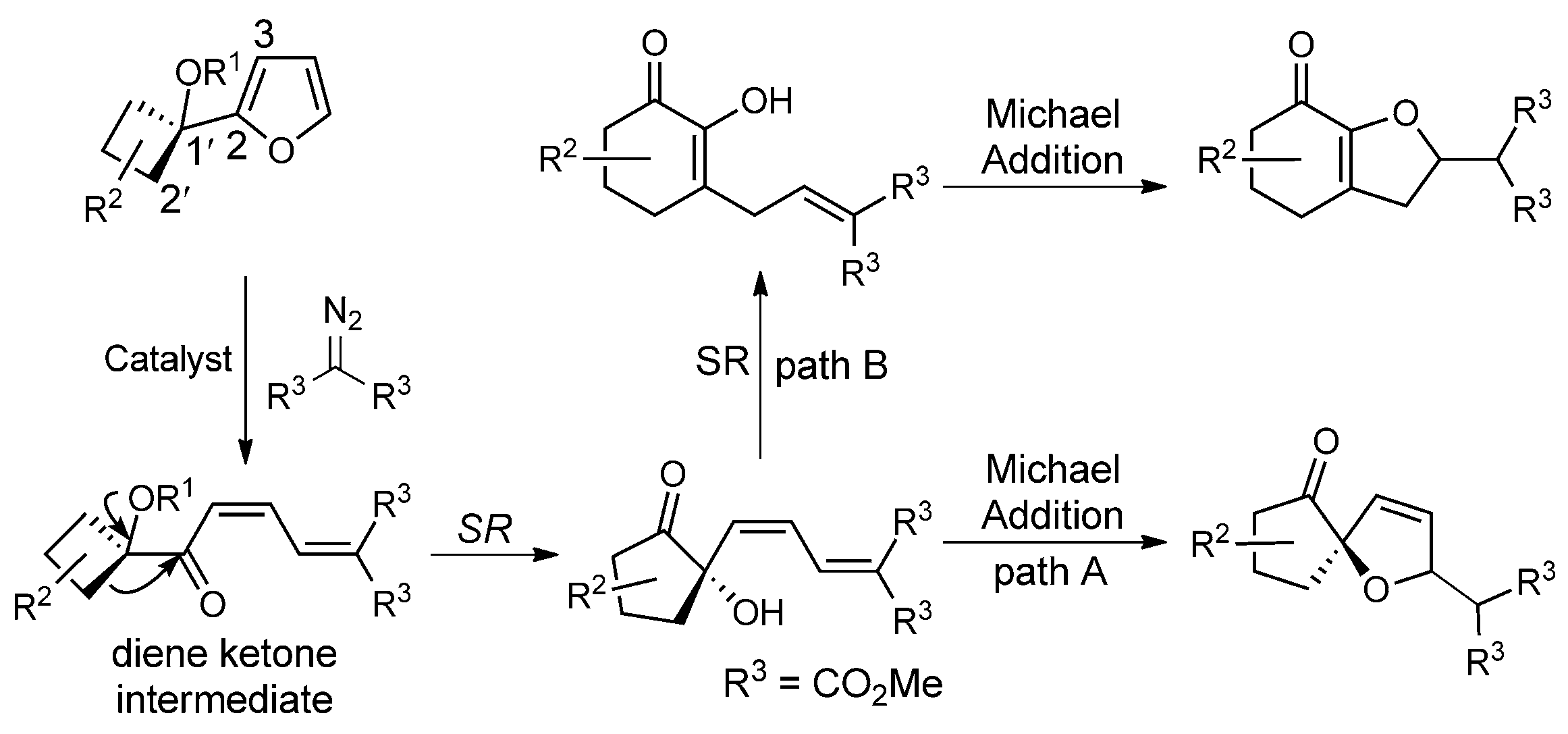
A tunable tandem reaction towards the syntheses of dihydrofuran derivatives. SR=semipinacol rearrangement.
CAS number: 1192-37-6
Methylenecyclohexane is an organic chemical compound, specifically an unsaturated hydrocarbon. It consists of a cyclohexane ring with a methylene group (CH2) attached to it. It's also known as 1-methylenecyclohexane.
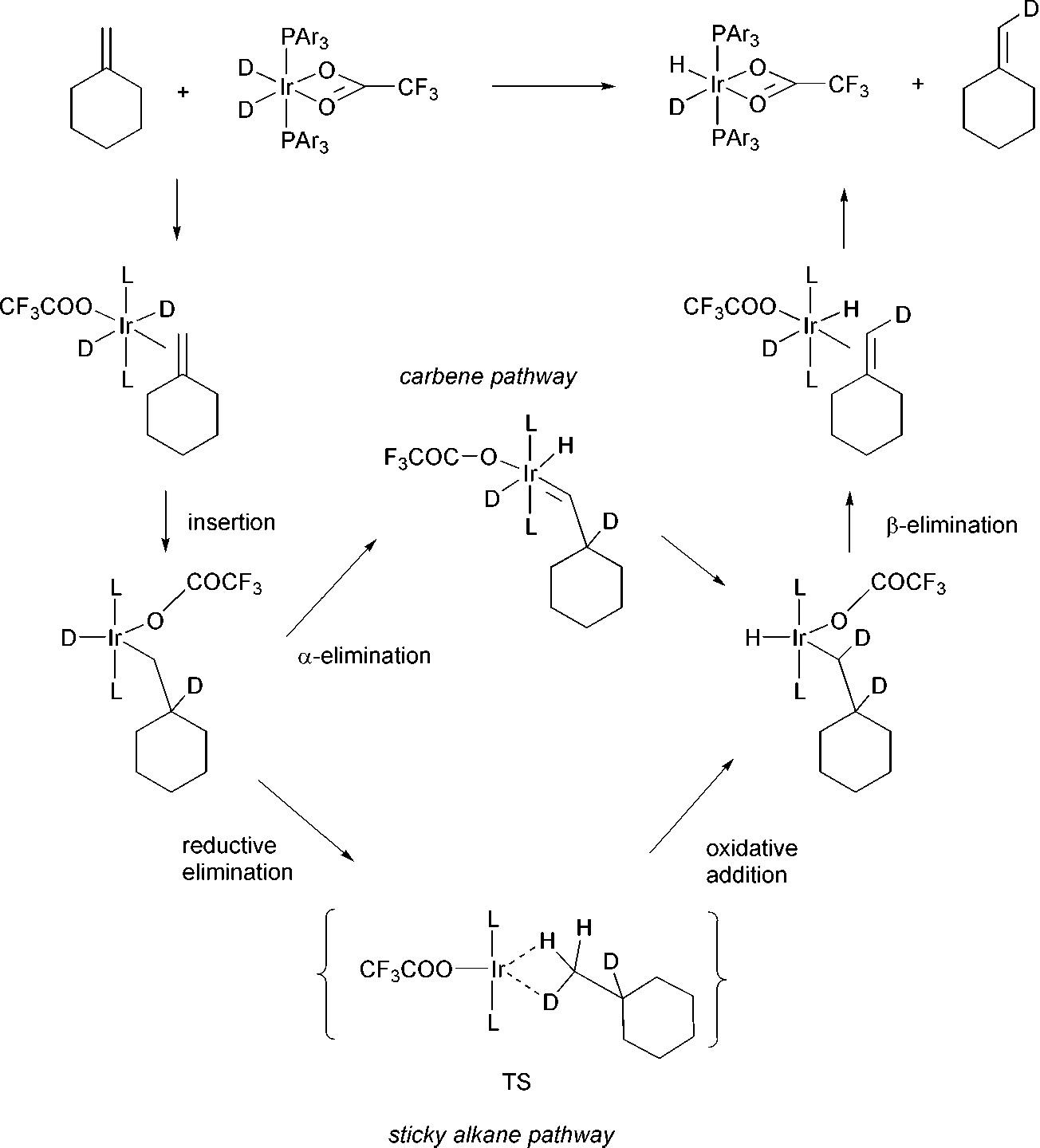
The mechanism for H/D exchange in methylenecyclohexane via the carbene and the alkane routes.
CAS number: 119422-08-1
Diethylhomospermine is a polyamine analogue with antiproliferative and potential anti-diarrheal activities. Diethylhomospermine (DEHSPM) antagonizes polyamine activity via NMDA receptor glutamine binding site, thereby modulating inotropic stasis and reducing stool volume (anti-diarrhea). However, due to the toxic effects from metabolites of DEHSP, other tetramine derivatives with less toxicity have been developed.
![metabolism of diethylnorspermine [DENSPm; DE(3,3,3)] and diethylhomospermine [DEHSPm; DE(4,4,4)].](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4915294_02.png)
metabolism of diethylnorspermine [DENSPm; DE(3,3,3)] and diethylhomospermine [DEHSPm; DE(4,4,4)].
CAS number: 119683-68-0
Ferumoxytol is an intravenously administered iron preparation indicated in the EU and the US for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is comprised of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles which are coated by a semi-synthetic carbohydrate shell in an isotonic, neutral pH solution that may be administered at relatively high dose by rapid intravenous injection.
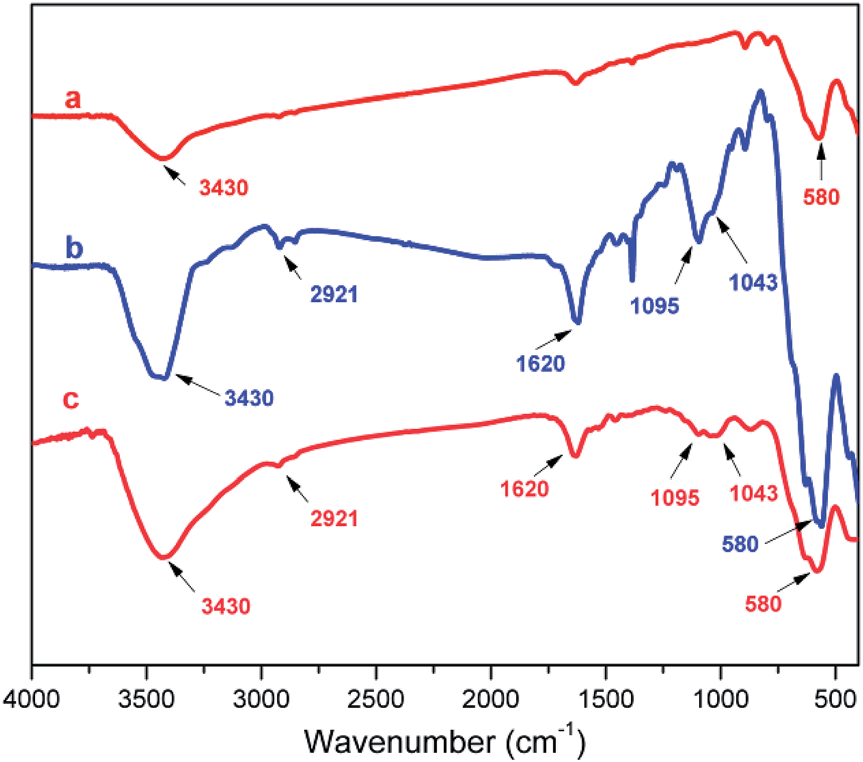
FT-IR spectra of Fe3O4 (a), primitively prepared LAIL@MNP (b), and the LAIL@MNP sample after the fifth recovery (c).
CAS number: 1199-02-6
2-Phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-in-5-one is a chemical compound that contains a phenyl group (C6H5) attached to a 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring. Specifically, it's a 1,3,4-oxadiazole with a phenyl substituent at the 2-position and a carbonyl group (C=O) at the 5-position.
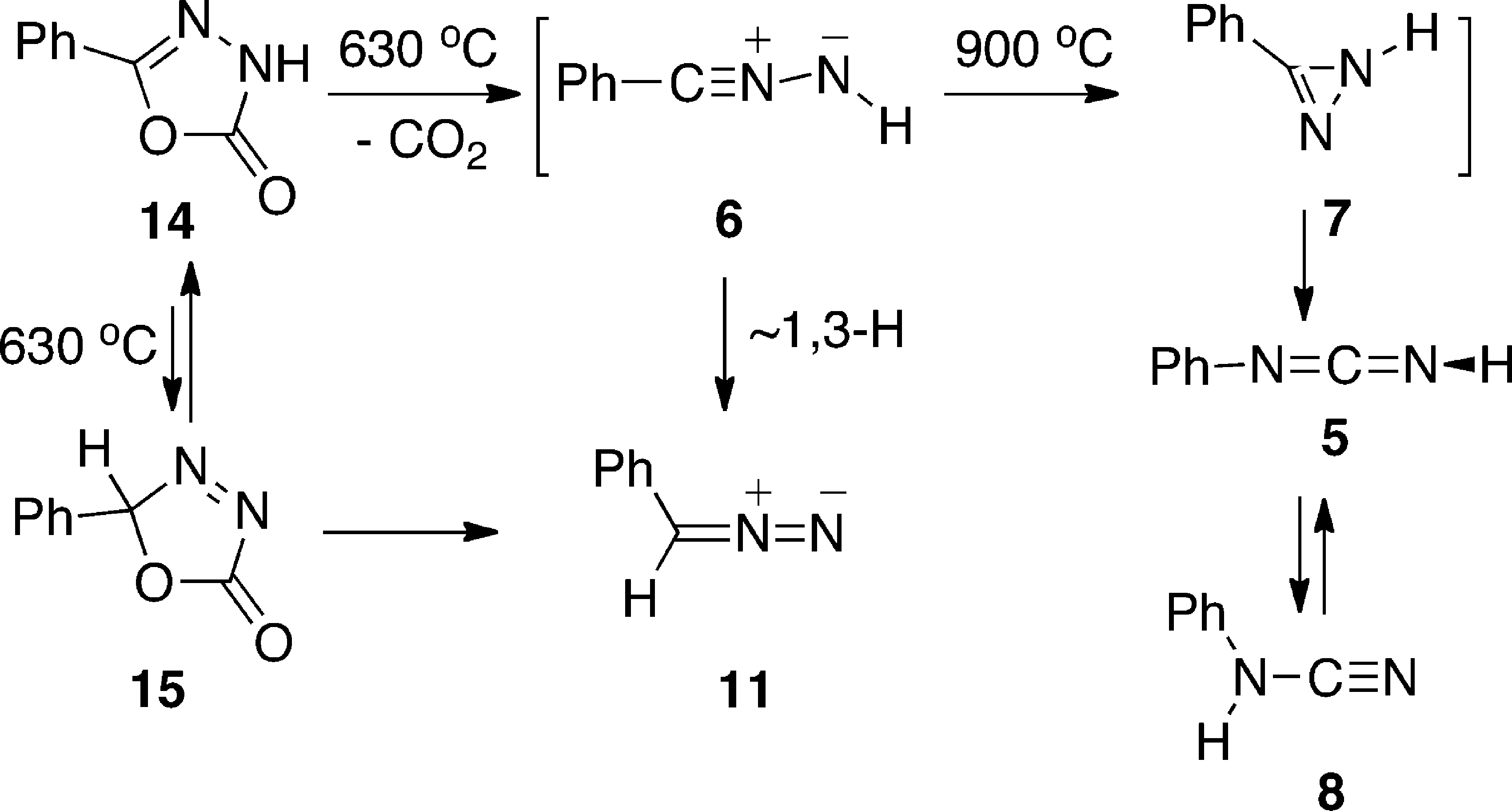
Thermolysis of 5-Phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one 14
CAS number: 120-62-7
A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl group (S=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. It's essentially a sulfur atom with a double-bonded oxygen and two organic groups (R and R') attached. Sulfoxides are often derived from sulfides (R-S-R') through oxidation.
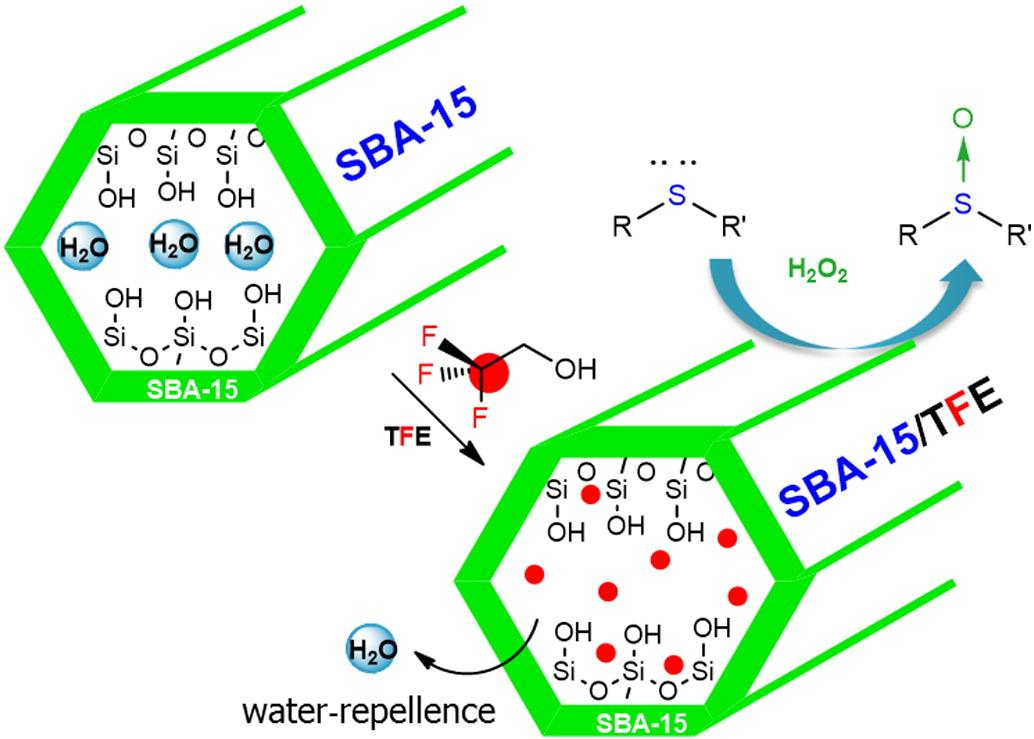
TFA/SBA-15 for green oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides.
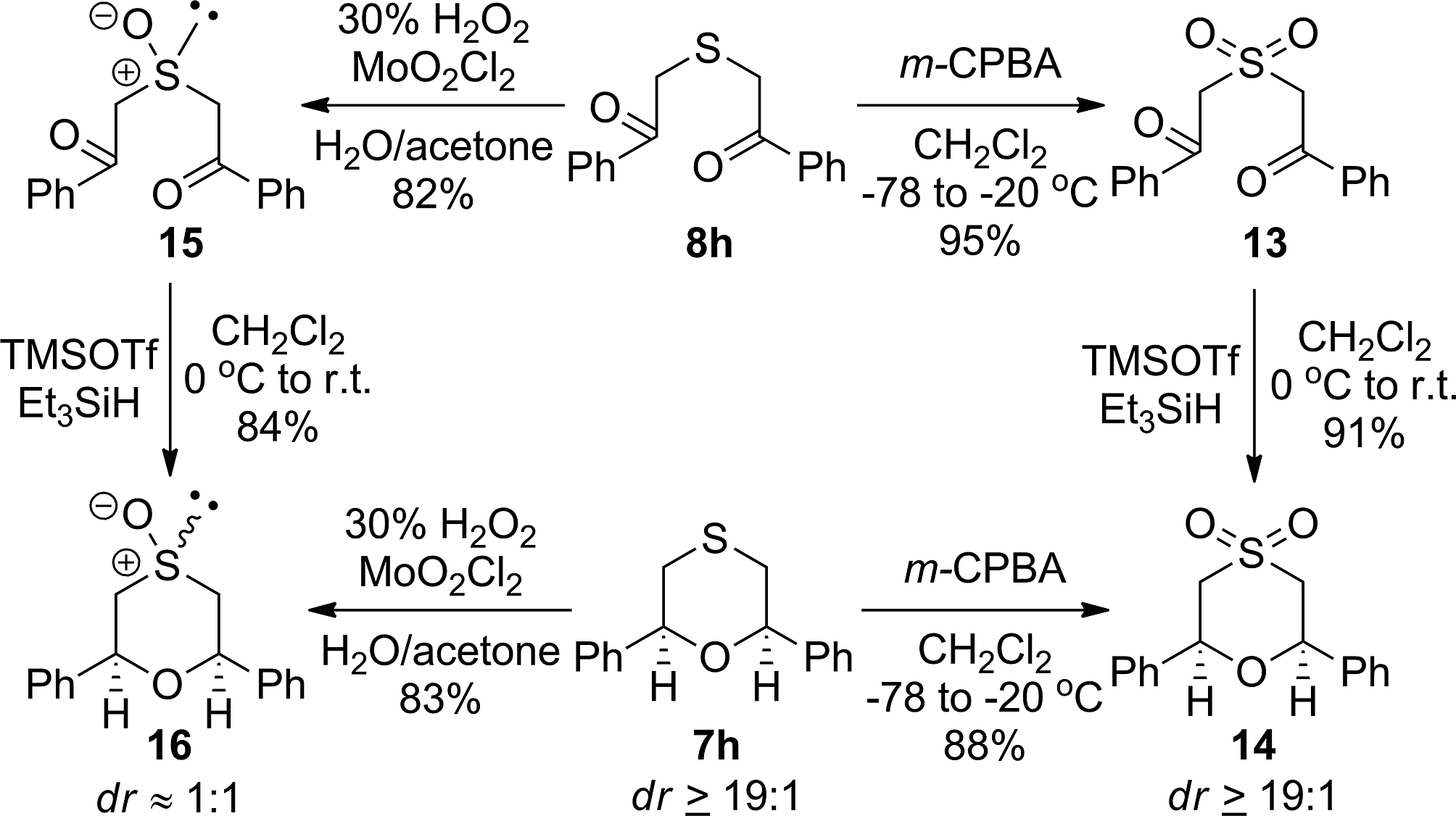
Reductive etherification reaction for the synthesis of sulfone 14 and sulfoxide 16.