Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 127931-15-1
R-(-)-Naftopidil is the active enantiomer of the drug naftopidil, an α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist (α1-blocker) that primarily treats lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by relaxing the muscles around the bladder exit and prostate gland. It is known for its selectivity towards the α1D-adrenergic receptor subtype, which differs from other α1-blockers like tamsulosin and silodosin, potentially leading to a lower incidence of side effects such as ejaculatory disorders and intraoperative floppy iris syndrome.
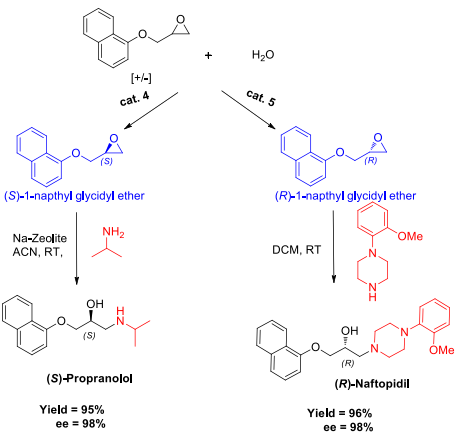
Synthesis of chiral drugs (S)-Propranolol and (R)-Naftopidil.
CAS number: 128-08-5
N-bromosuccinimide is a five-membered cyclic dicarboximide compound having a bromo substituent on the nitrogen atom. It has a role as a reagent.
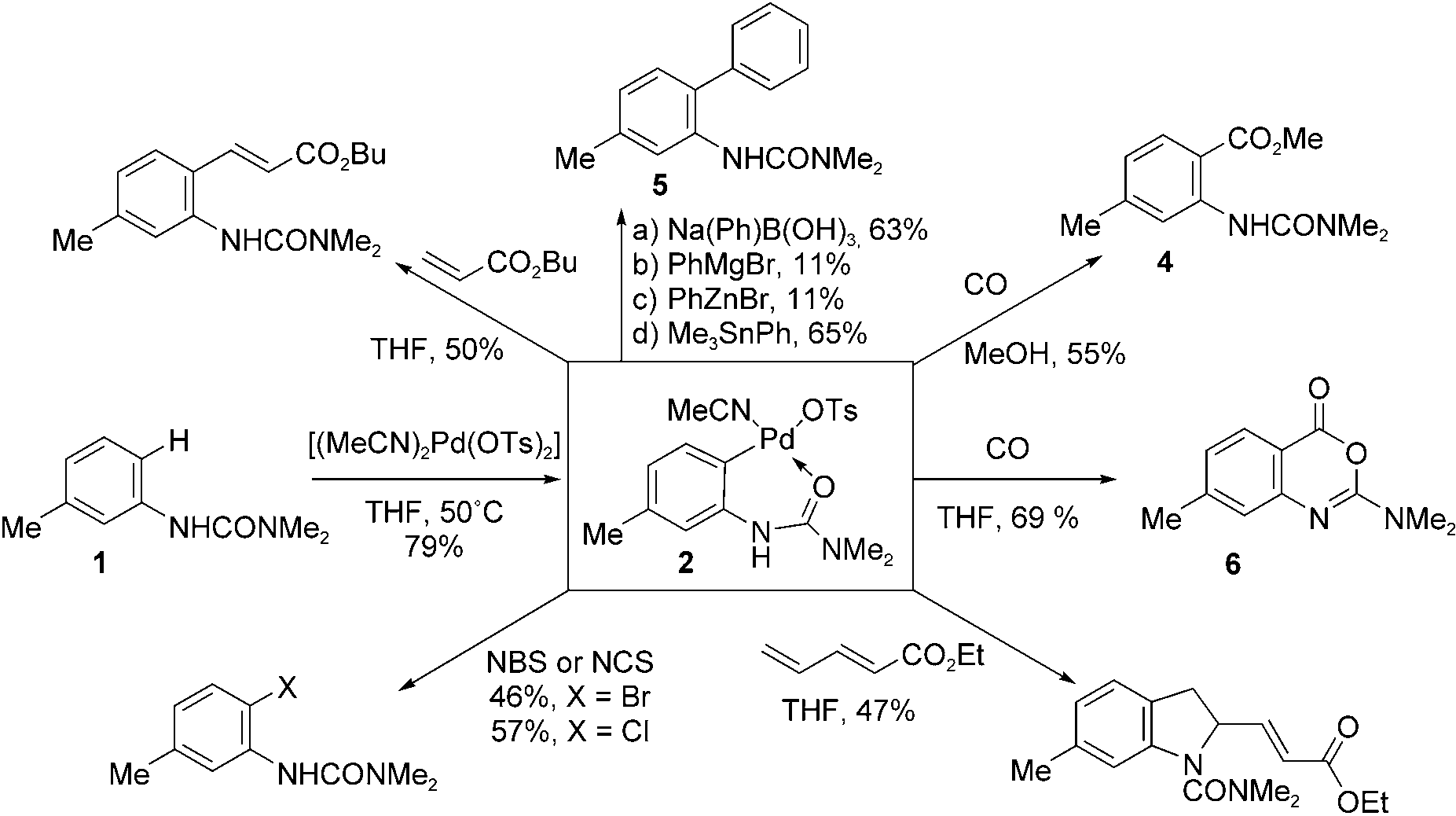
Formation and reaction of PdII complex 2. NBS = N-bromosuccinimide, NCS = N-chlorosuccinimide.
![Synthesis of aminyl diradicals 1 and 2. a) NBS in chloroform, NaHCO3, Na2SO4, -40℃ for 1 h, then 08C for 2 h, 35%. b) 4-tert-butylphenylboronic acid or 4-tert-undecylphenylboronate, [Pd(PPh3)4], Na2CO3, benzene/EtOH/water, 908C (5: 62% yield, 6: 43% yield). c) nBuLi (2.4 equiv), THF/hexane, ca. -30℃ for 1 h, then solvent change to THF or 2-MeTHF, and I2 (1.06 equiv) at -90℃ or titration with I2 at -90 to -115℃ monitored by EPR spectroscopy. NBS=N-bromosuccinimide.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3912354_05.png)
Synthesis of aminyl diradicals 1 and 2. a) NBS in chloroform, NaHCO3, Na2SO4, -40℃ for 1 h, then 08C for 2 h, 35%. b) 4-tert-butylphenylboronic acid or 4-tert-undecylphenylboronate, [Pd(PPh3)4], Na2CO3, benzene/EtOH/water, 908C (5: 62% yield, 6: 43% yield). c) nBuLi (2.4 equiv), THF/hexane, ca. -30℃ for 1 h, then solvent change to THF or 2-MeTHF, and I2 (1.06 equiv) at -90℃ or titration with I2 at -90 to -115℃ monitored by EPR spectroscopy. NBS=N-bromosuccinimide.
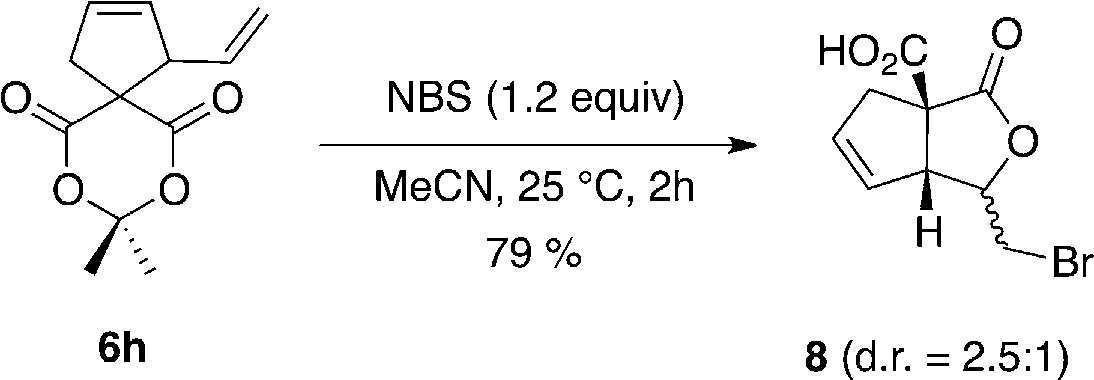
Bromolactonization of compound 6h. NBS=N-bromosuccinimide.
CAS number: 128-09-6
Chlorosuccinimide is used as a chlorinating agent, disinfectant for swimming pools, and bactericide.

Formation and reaction of PdII complex 2. NBS = N-bromosuccinimide, NCS = N-chlorosuccinimide.
CAS number: 128-95-0
Disperse Violet 1 is an organic dye, specifically a disperse dye, primarily used in the textile industry to color synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic. It's also used in hair dye formulations and, in some cases, in cosmetics. It's a violet-colored powder with a melting point of 266.9 - 267.4 °C.
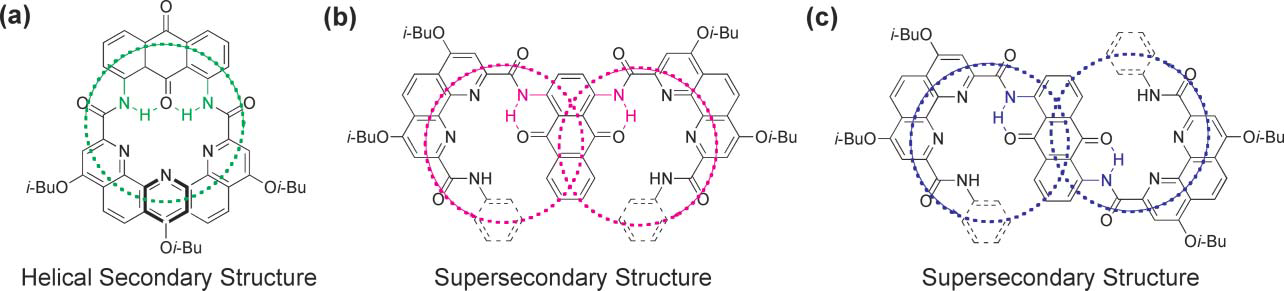
Schematic representation of the projection of the two helical oligo(phenanthroline dicarboxamide) strands segments in the plane of the 1,8-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (a), 1,4-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (b) and 1,5-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (c).
CAS number: 129-42-0
1,8-Diamino-9,10-anthracenedione is an organic compound also known as 1,8-diaminoanthraquinone.

Schematic representation of the projection of the two helical oligo(phenanthroline dicarboxamide) strands segments in the plane of the 1,8-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (a), 1,4-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (b) and 1,5-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (c).
CAS number: 129-44-2
1,5-Diaminoanthraquinone (DAAQ) is an organic compound belonging to the anthraquinone family, characterized by the presence of two amino groups (-NH2) at positions 1 and 5 of the anthraquinone structure. It's a yellow-red to dark red crystalline powder and is used as a dye and in the synthesis of various materials.

Schematic representation of the projection of the two helical oligo(phenanthroline dicarboxamide) strands segments in the plane of the 1,8-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (a), 1,4-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (b) and 1,5-diaminoanthraquinone spacer (c).
CAS number: 130-95-0
Quinine is a cinchona alkaloid that is cinchonidine in which the hydrogen at the 6-position of the quinoline ring is substituted by methoxy. It has a role as an antimalarial, a muscle relaxant and a non-narcotic analgesic. It is a conjugate base of a quinine(1+). It derives from a hydride of an (8S)-cinchonan.
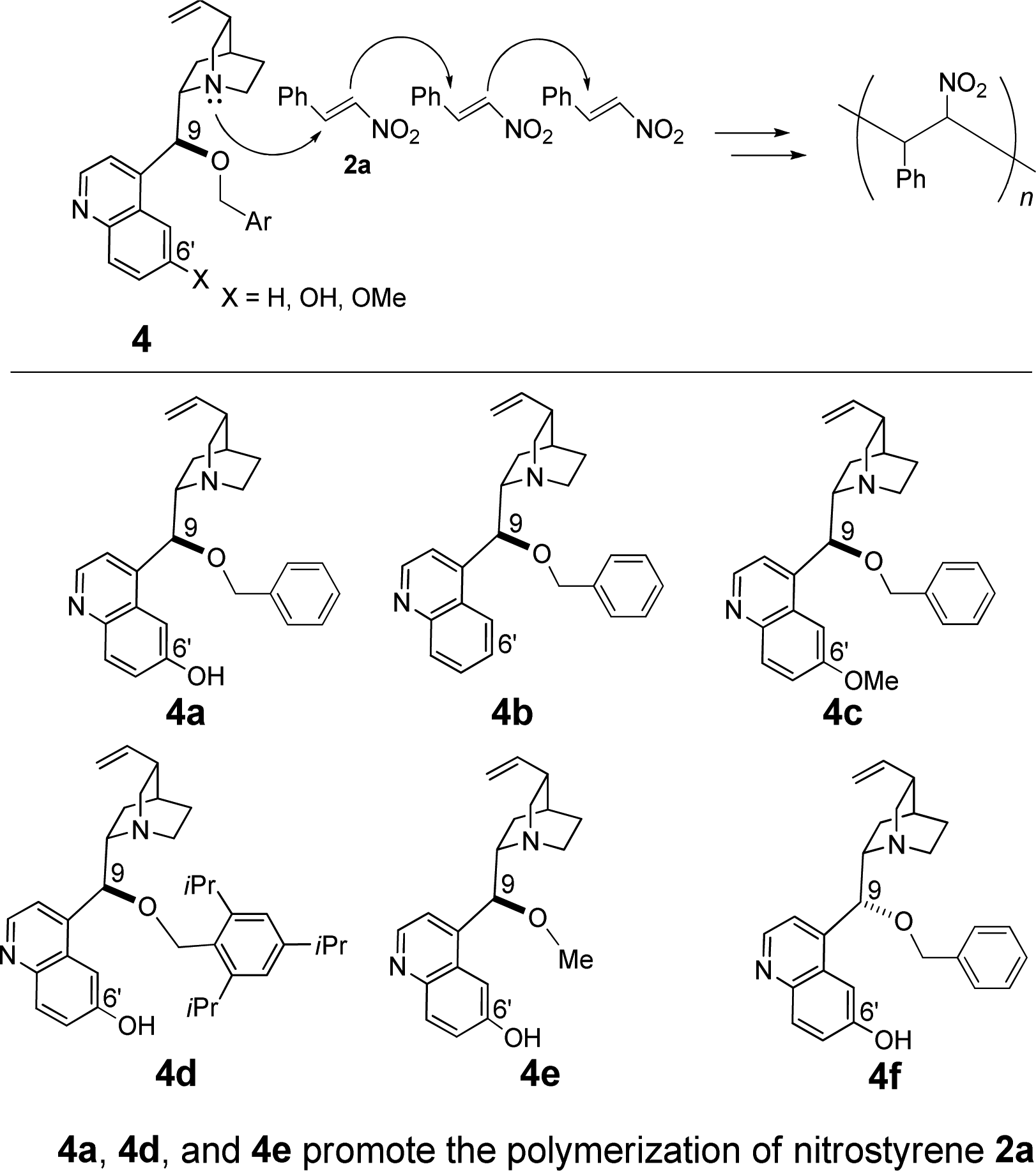
Quinine Derivative-Promoted Polymerization of Nitrostyrene
CAS number: 1300031-49-5
I-BET151 is a member of the class of imidazoquinolines that is 1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-2-one substituted by (1R)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl, 3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl, and methoxy groups at positions 1, 7, and 8, respectively. It is a pan-BET bromodomain inhibitor. It has a role as an apoptosis inducer, an antineoplastic agent and a BET bromodomain inhibitor.
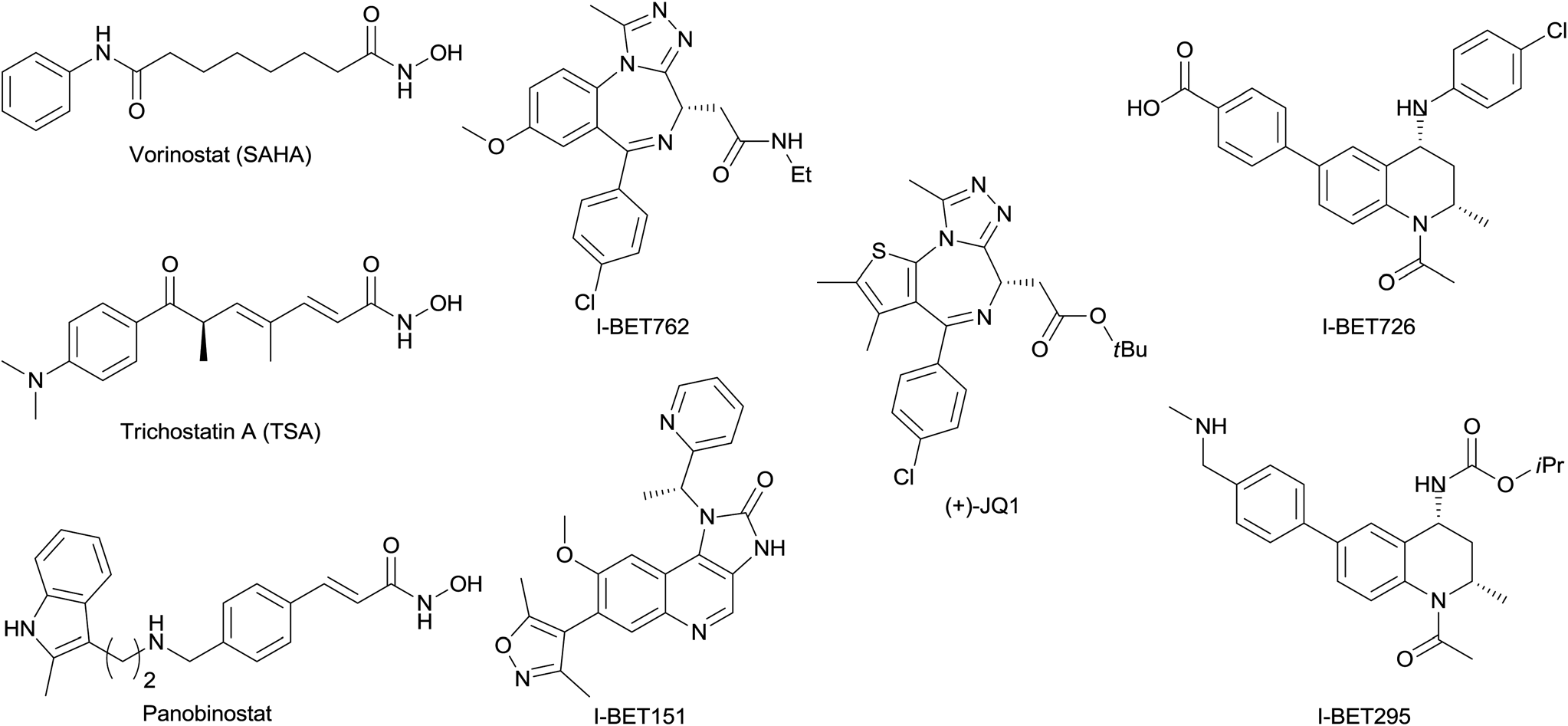
Structures of selected published BET inhibitors and selected hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitors.
CAS number: 1300031-52-0
I-BET726, also known as GSK1324726A, is a selective inhibitor of BET (Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal domain) proteins. It was identified as a novel tetrahydroquinoline-based BET inhibitor, meaning it targets and inhibits the bromodomain-containing proteins BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.

Structures of selected published BET inhibitors and selected hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitors.
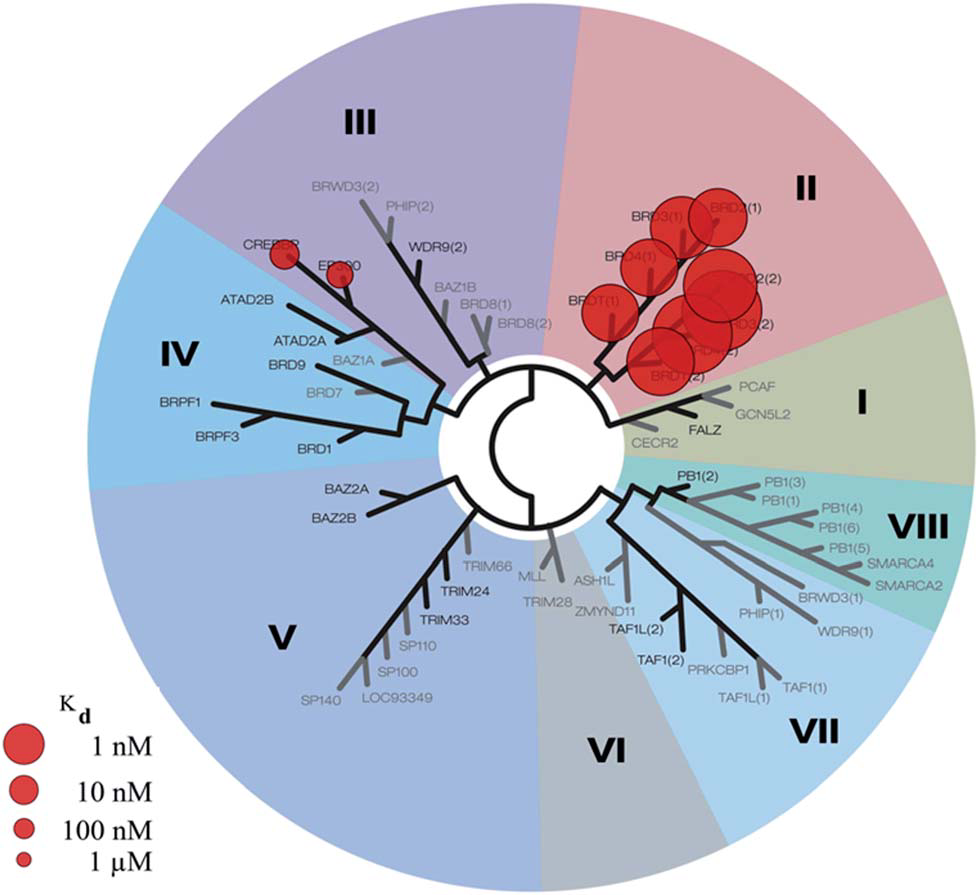
DiscoveRx BROMOscan profile for I-BET726.
CAS number: 130288-24-3
(+)Duocarmycin SA (DSA) is a highly potent antitumor antibiotic and cytotoxic agent belonging to the duocarmycin family of natural products derived from the bacterium Streptomyces. It was first isolated in 1990 from a Streptomyces strain found in Kyoto, Japan.
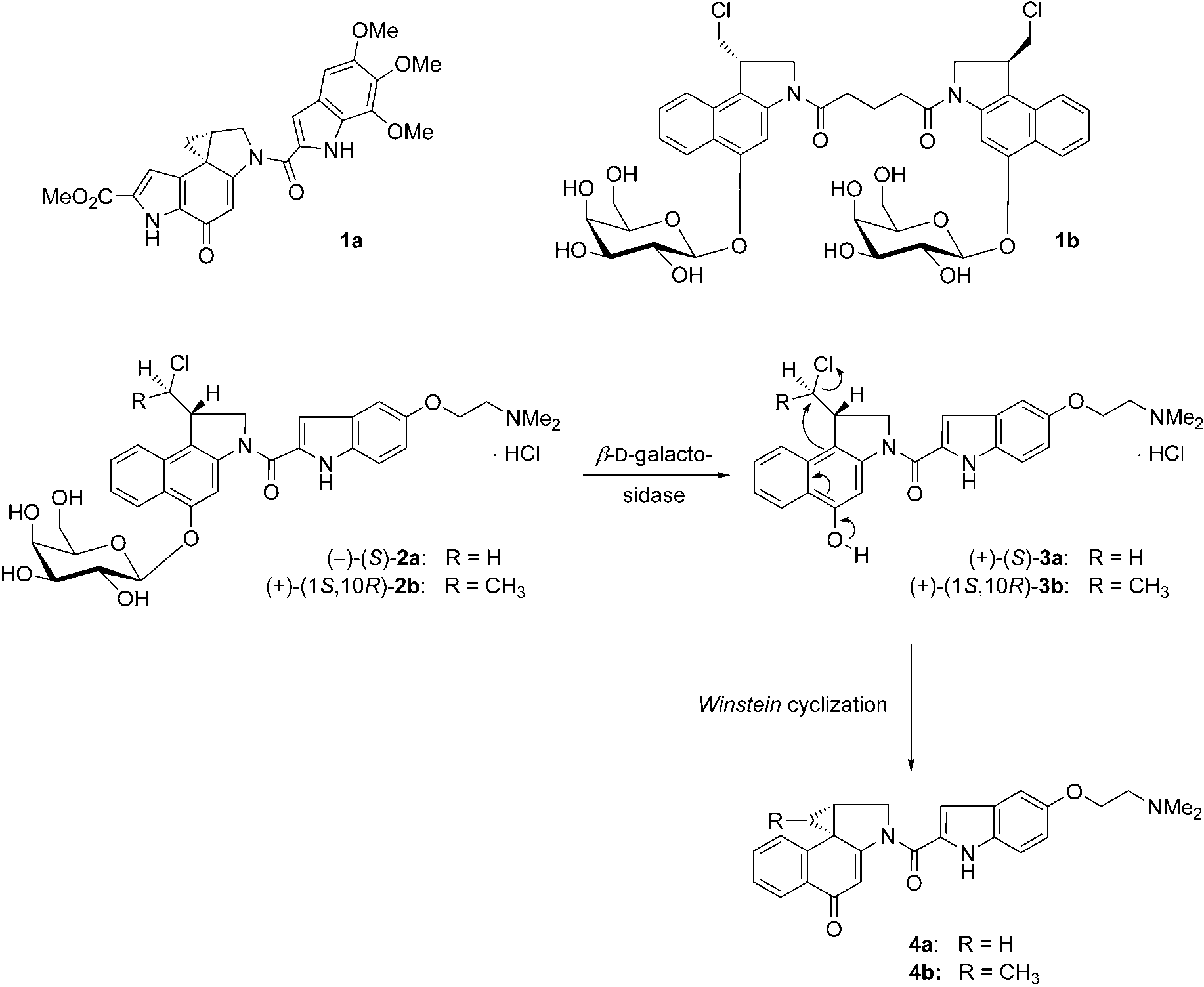
Duocarmycin SA (1a), pseudo-dimeric prodrug 1b, and prodrugs (-)-(S)-2a and (+)-(1S,10R)-2b to give the cytotoxic drugs 4a and 4b via the seco-drugs (+)-(S)-3a and (+)-(1S,10R)-3b. Cytotoxic drugs 4a and 4b share the spirocyclopropylcyclohexadienone moiety with 1a.