Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 1446756-47-3
Phosphatidyl serine (PS) is a phospholipid nutrient found in fish, green leafy vegetables, soybeans and rice, and is essential for the normal functioning of neuronal cell membranes and activates Protein kinase C (PKC) which has been shown to be involved in memory function.
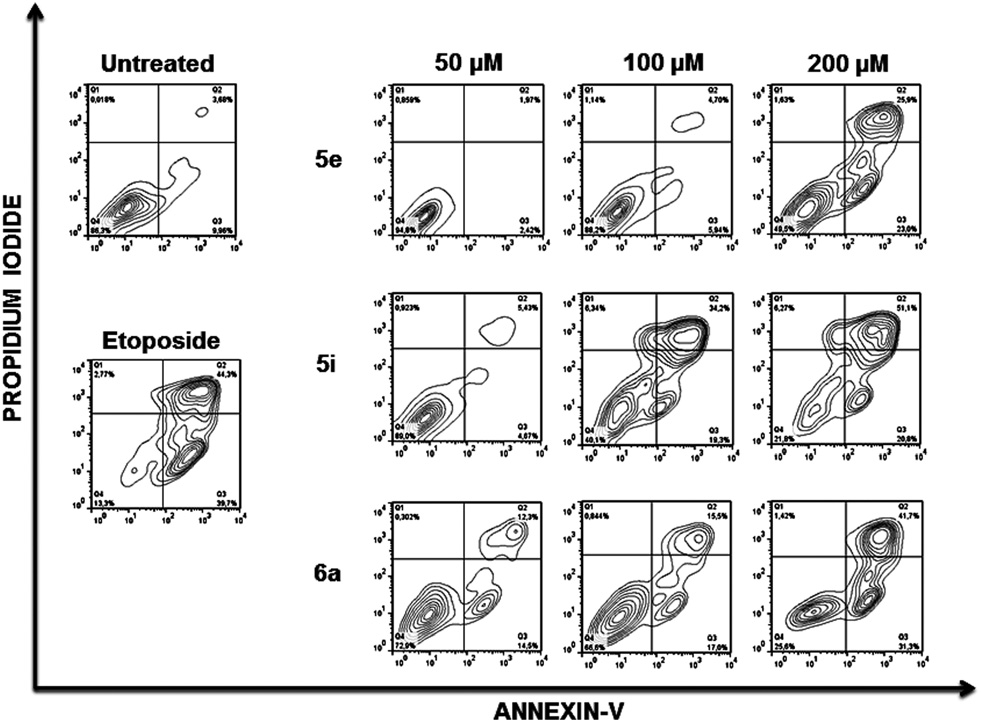
Membrane phosphatidylserine expression after treatment of Jurkat cells with compounds 5e, 5i and 6a. Jurkat cells were treated for 48 h with the indicated compounds and doses and the percentages of apoptotic cells was measured by flow cytometry after double staining with propidium iodide and Annexin-V-Fluos.
CAS number: 1450-63-1
1,1′,1′′,1′′′-(1,3-Butadiene-1,4-diylidene)tetrakis[benzene] is a complex organic compound characterized by its tetrakis-substituted benzene structure linked through a butadiene moiety.
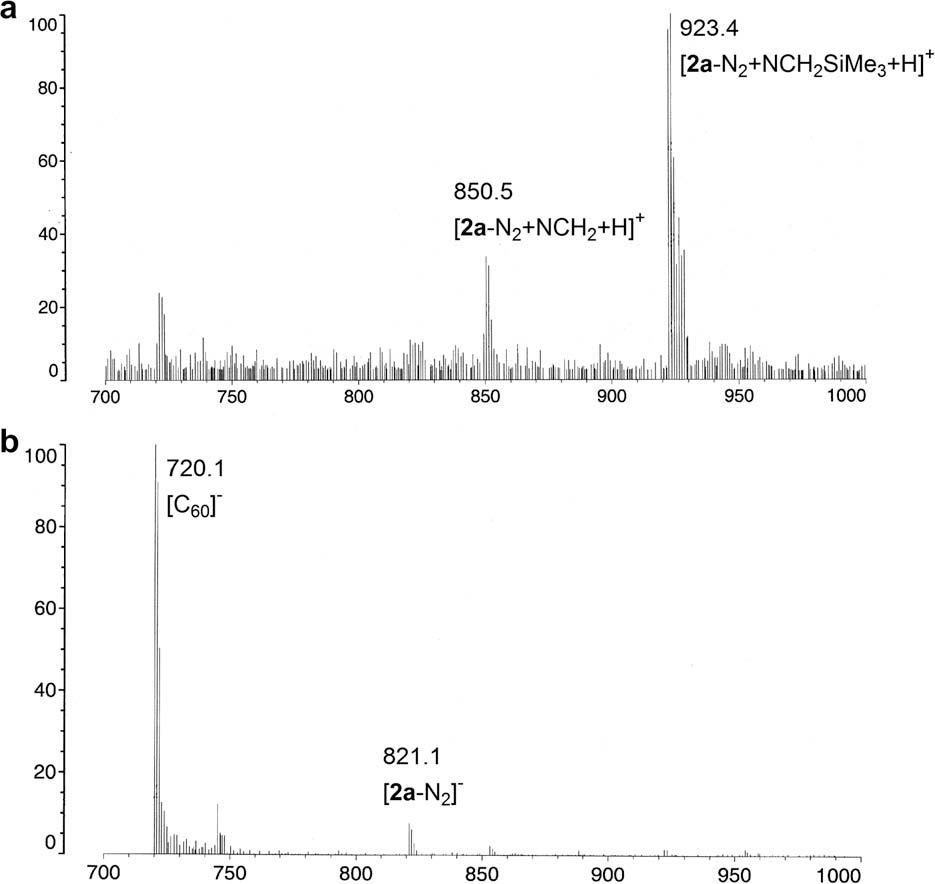
MALDI-TOF mass spectra of 2a in a 1,1,4,4-tetraphenyl-1,3-butadiene matrix; (a) positive ion reflectron mode and (b) negative ion reflectron mode.
CAS number: 14501-65-6
Clausine L belongs to the class of organic compounds known as carbazoles.
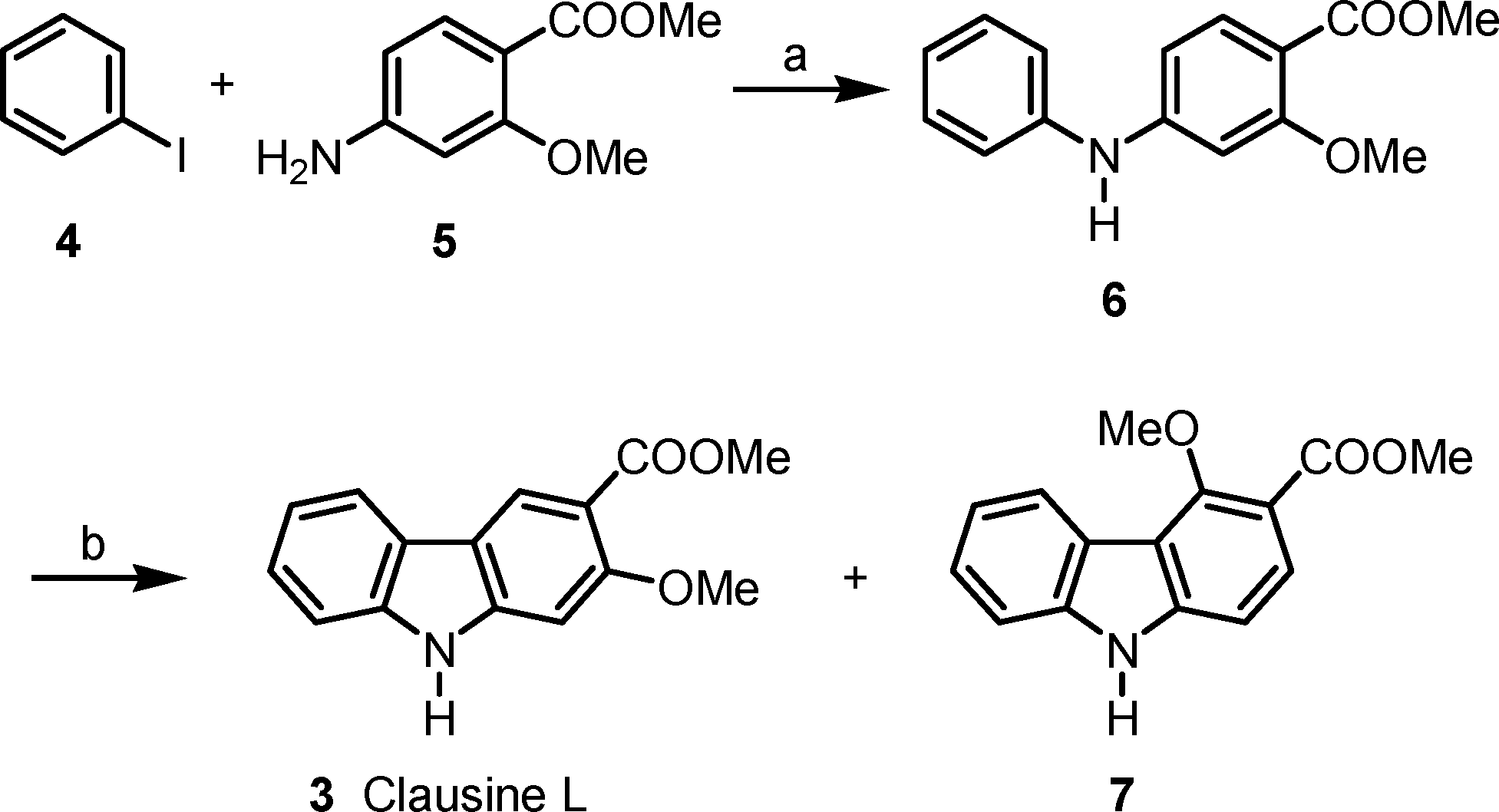
Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of clausine L (3).
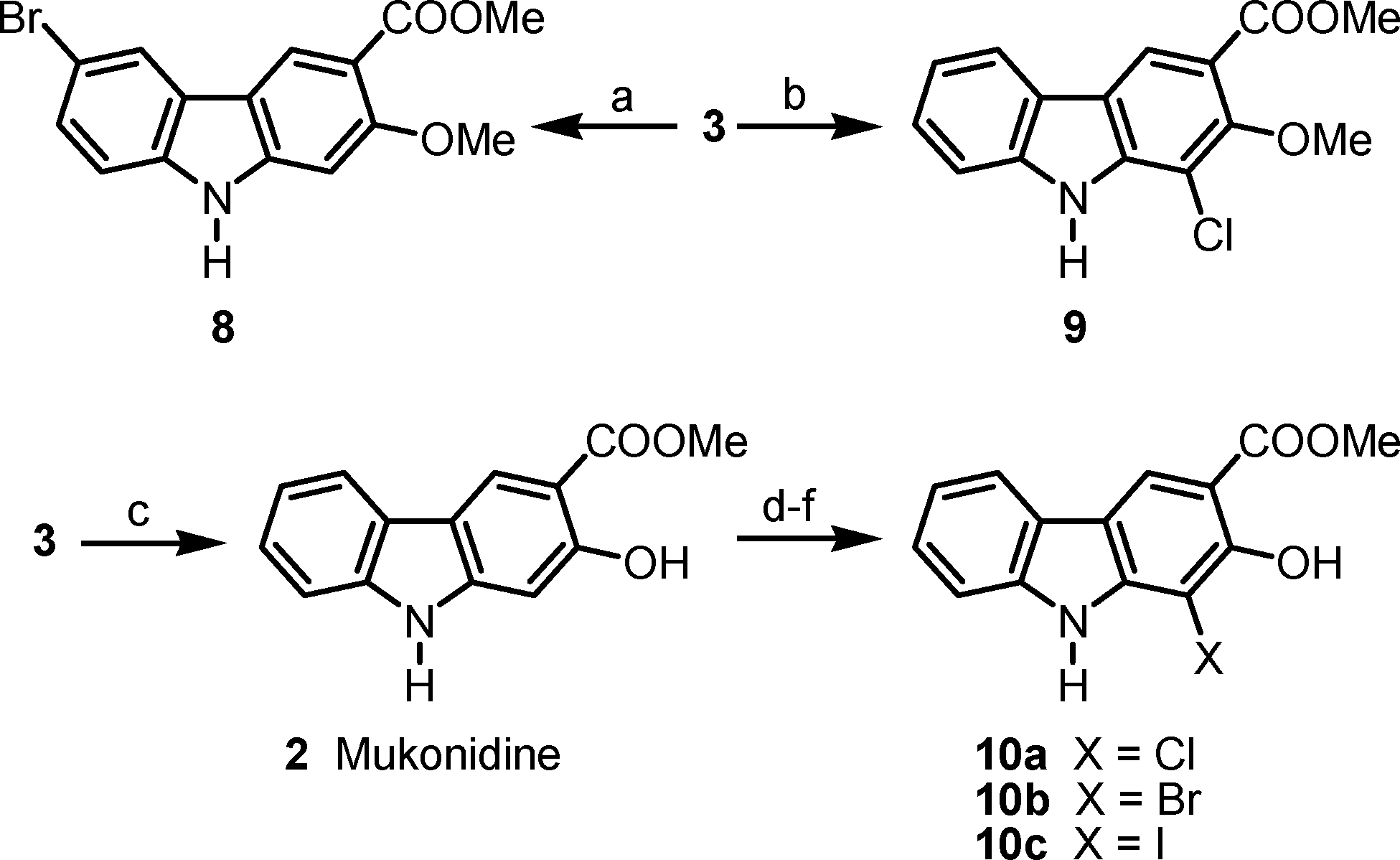
Halogenations of clausine L (3) and mukonidine (2).
CAS number: 1452-77-3
Picolinamide is a pyridinecarboxamide that is the monocarboxylic acid amide derivative of picolinic acid. It is functionally related to a picolinic acid.
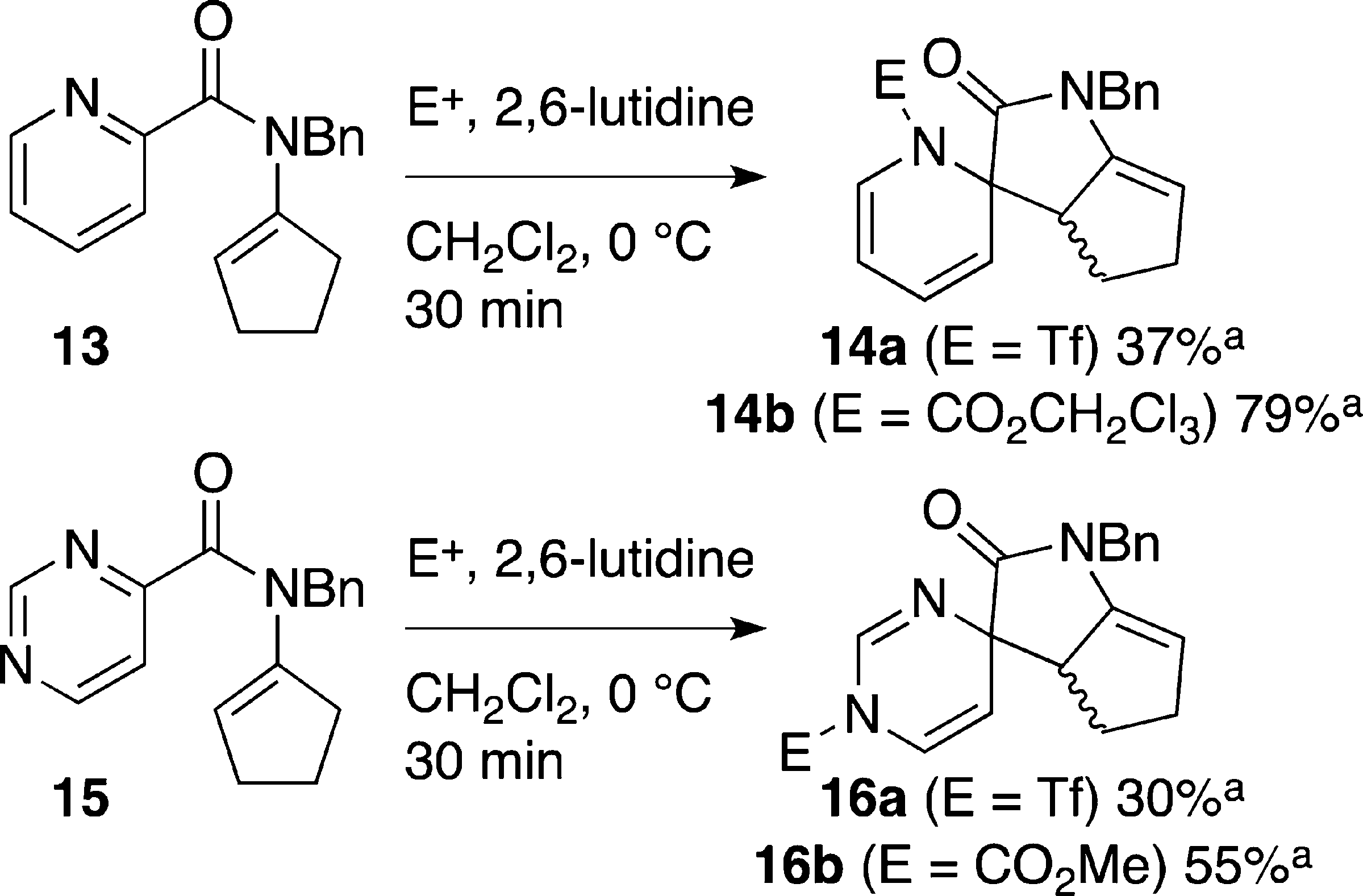
Dearomatizing Cyclization of Pyrimidinecarboxamides and Picolinamides
CAS number: 145231-45-4
Clobenpropit is an imidothiocarbamic ester that consists of isothiourea bearing S-3-(imidazol-4-yl)propyl and N-4-chlorobenzyl substituents. An extremely potent histamine H3 antagonist/inverse agonist (pA2 = 9.93). Also displays partial agonist activity at H4 receptors; induces eosinophil shape change with an EC50 of 3 nM. It has a role as a H3-receptor antagonist and a H4-receptor agonist. It is a member of imidazoles, an imidothiocarbamic ester and an organochlorine compound. It is a conjugate base of a clobenpropit(2+).
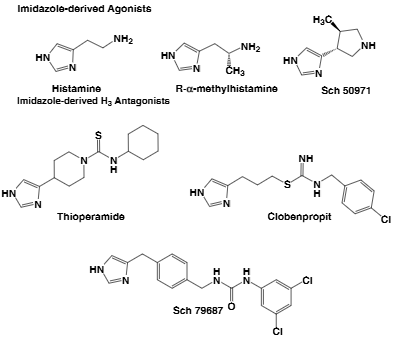
Examples of imidazole-derived agonists and antagonists:Thioperamide, clobenpropit, SCH-79687, r-alpha-methylhistamine.
CAS number: 145307-22-8
Incarvillateine is a complex monoterpene alkaloid that is a derivative of α-truxillic acid. It can be isolated from the plant genus Incarvillea.
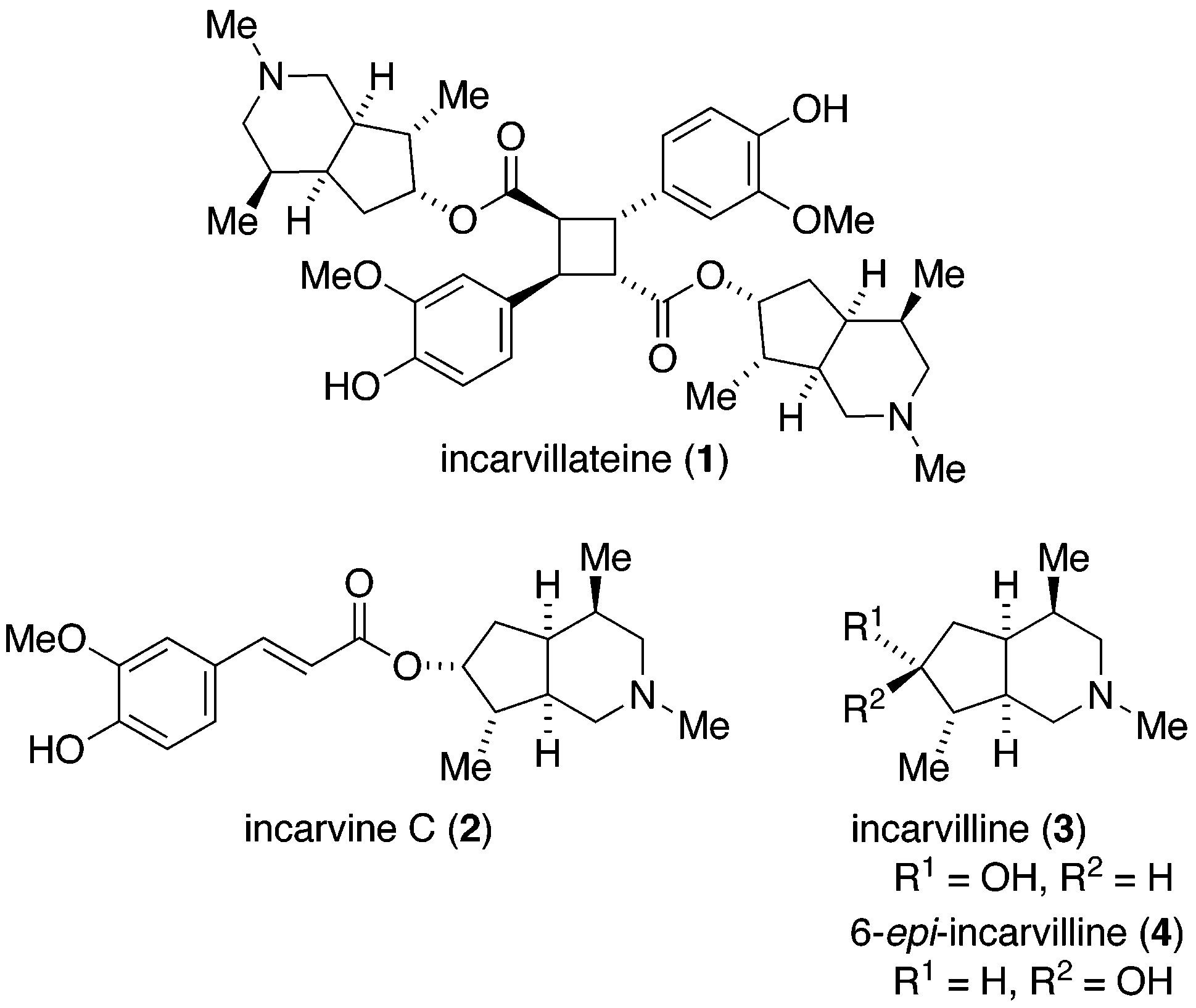
Structures of incarvillateine and related alkaloids.
CAS number: 14546-48-6
Manganese(III), often written as Mn³⁺, is a chemical species where a manganese atom has lost three electrons, resulting in a +3 charge.
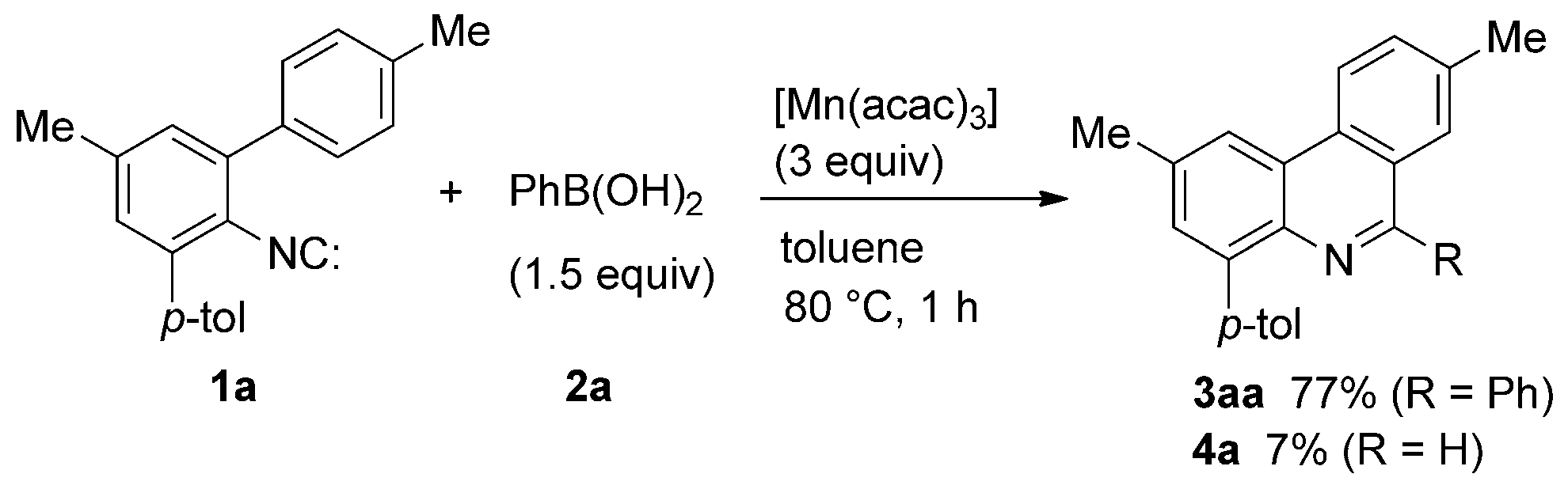
Manganese(III) mediates the cyclization of 1a and 2a.
CAS number: 145904-69-4
(+)-Myristinin A is a hydroxyflavonoid.
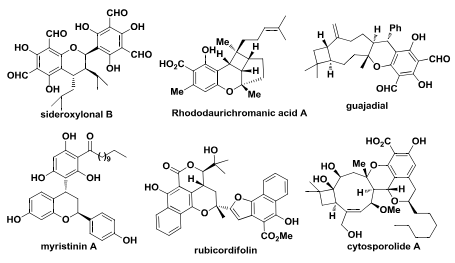
Natural products containing chromane motifs: Sideroxylonal B, Rhododaurichromanic acid A, myristinin A, Rubicordifolin, Guajadial, Cytosporolide A.
CAS number: 145964-33-6
(2'-Methoxy-1,1'-binaphthalen-2-yl)(diphenyl)phosphine is a chiral ligand, specifically known as (S)-(-)-2-Diphenylphosphino-2'-methoxy-1,1'-binaphthyl ((S)-(-)-MOP), which is frequently used in asymmetric synthesis and catalysis. It's a versatile reagent valued for its ability to facilitate enantioselective reactions.
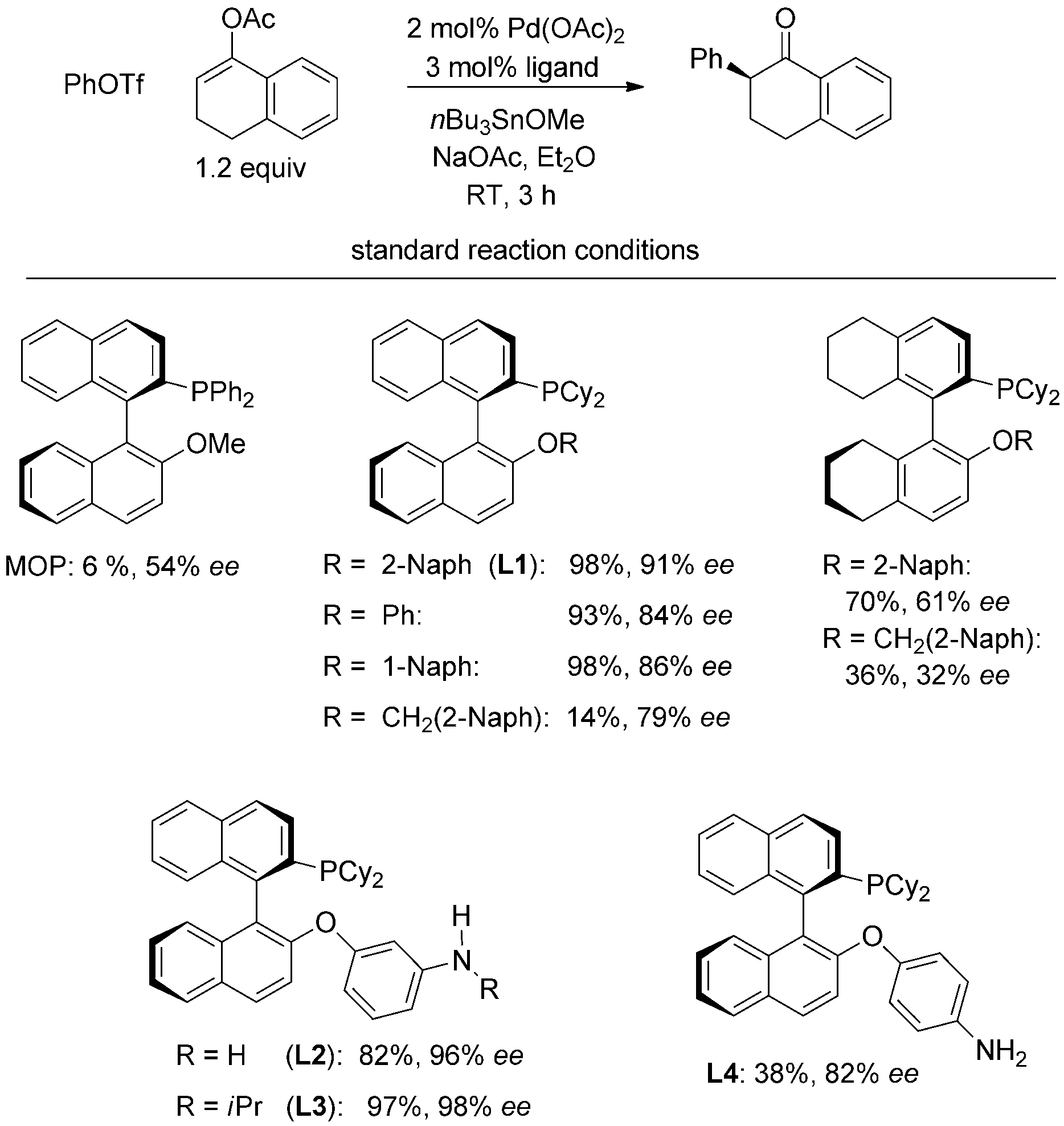
Catalyst discovery in the model arylation reaction. MOP=2-(diphenylphosphino)-2'-methoxy-1,1'-binaphthyl. Yields are those measured by GC, and the ee values were determined by HPLC analysis with a chiral stationary phase.
CAS number: 1461-15-0
Calcein is a xanthene dye. It has a role as a fluorochrome. It is functionally related to a fluoran.
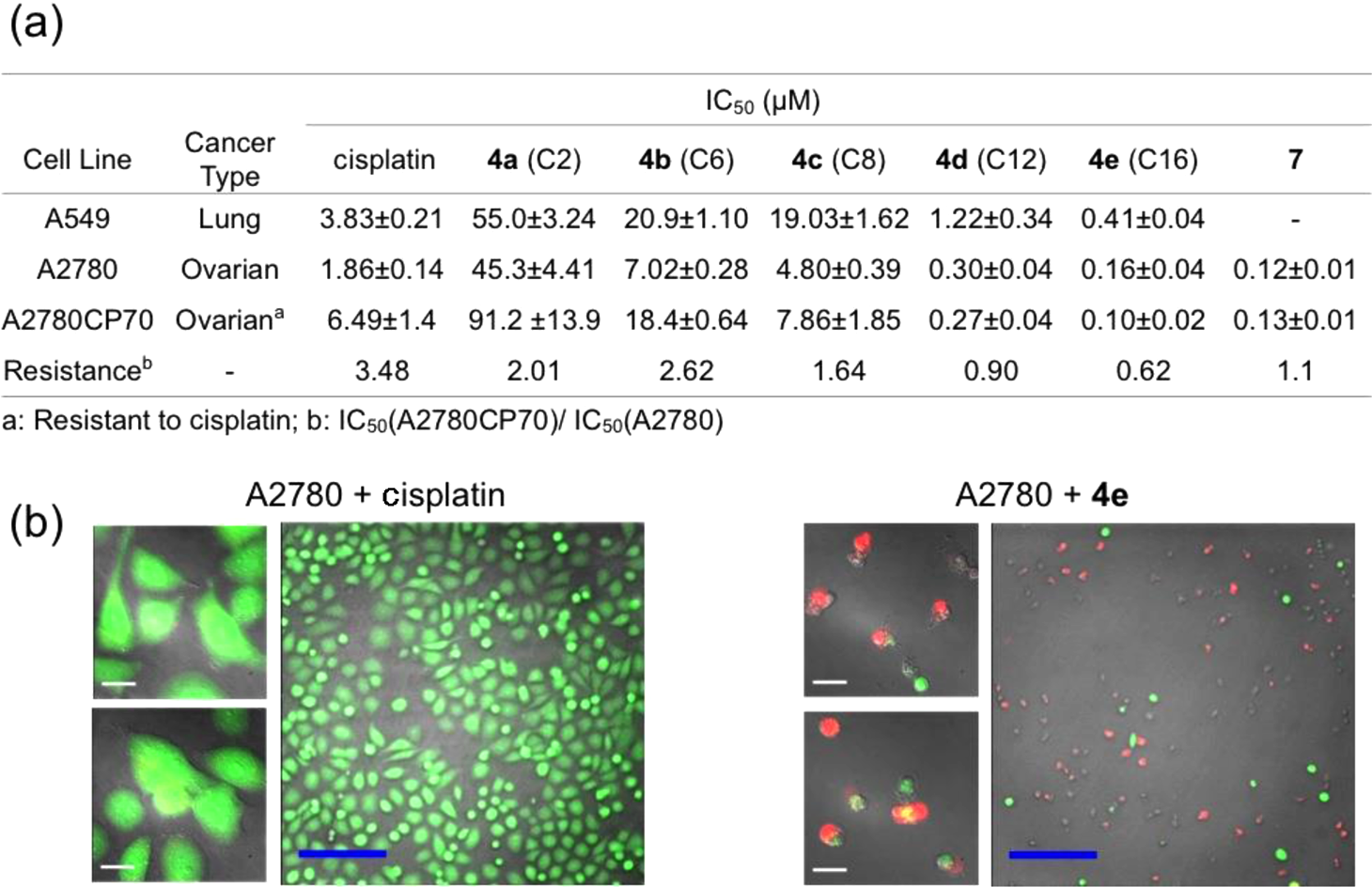
Cytotoxicity profiles of Pt(IV) prodrugs: (a) Table of IC50 values of 4a-e and 7 measured in A549, A2780, and A2780CP70 cell lines; (b) Calcein AM/ethidium homodimer-1 cell viability assay, details of which can be found in the main text and Supporting Information (white scale bar, 20 μm; blue scale bar, 200 μm).