Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 12619-70-4
A homologous group of cyclic GLUCANS consisting of alpha-1,4 bound glucose units obtained by the action of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase on starch or similar substrates. The enzyme is produced by certain species of Bacillus. Cyclodextrins form inclusion complexes with a wide variety of substances.
![Structures of cyclodextrins and cucurbit[n]urils.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/1004410_15.png)
Structures of cyclodextrins and cucurbit[n]urils.
CAS number: 12654-97-6
Triazine is a heterocyclic six-membered benzene ring containing three nitrogen atoms in the benzene ring.
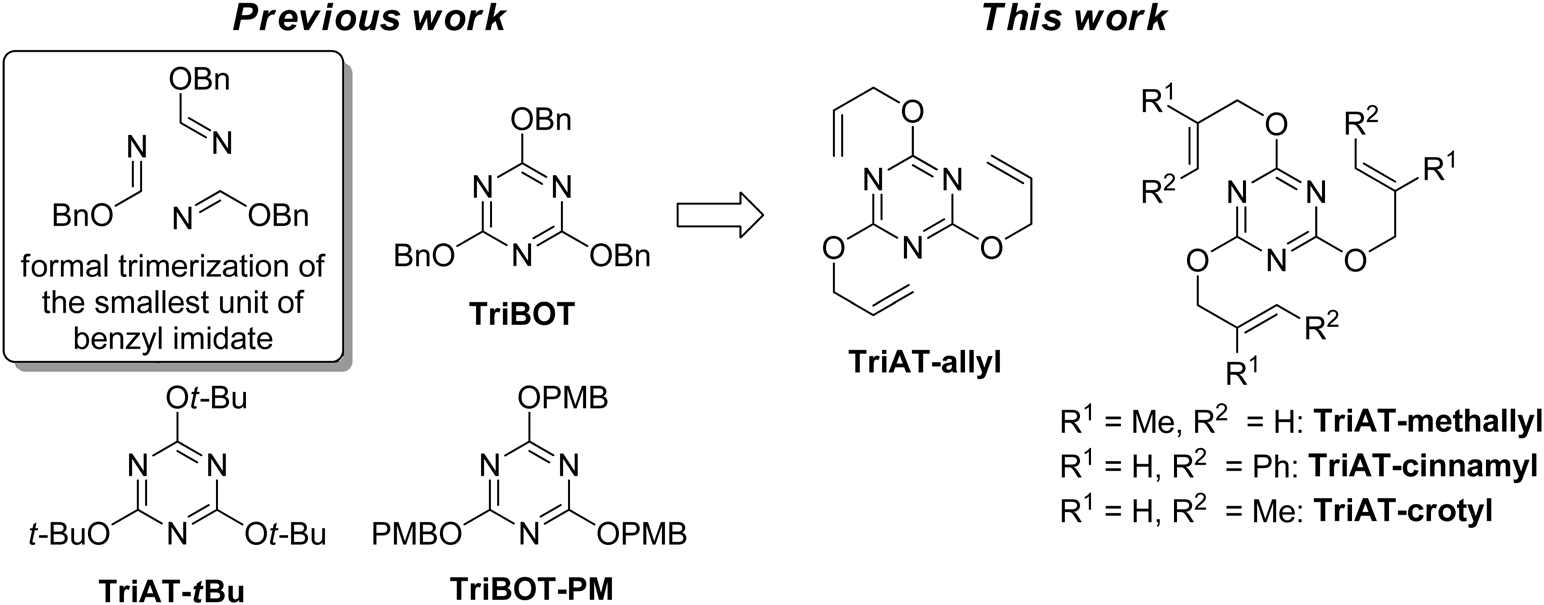
Design Concept for Triazine-Based Allylating Reagents
CAS number: 127-09-3
Sodium acetate is the trihydrate sodium salt of acetic acid with alkalinizing, diuretic and electrolyte replacement properties.
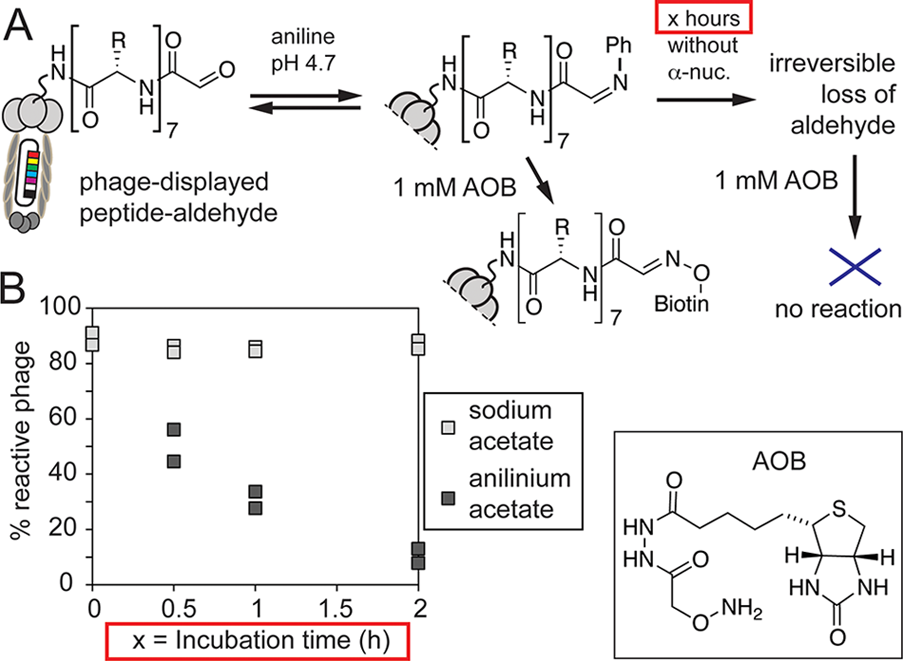
(A) Ligation of AOB to phage-displayed aldehydes is accelerated by aniline, but preincubation of phage with aniline in the absence of AOB leads to rapid loss of aldehyde and loss of reactivity toward AOB. (B) In anilinium acetate, pH 4.7, the aldehyde disappears with t1/2 ∼40 min; however, aldehydes alone are stable at the same pH in sodium acetate buffer.
CAS number: 127-27-5
(+)-Pimaric acid is a diterpenoid.
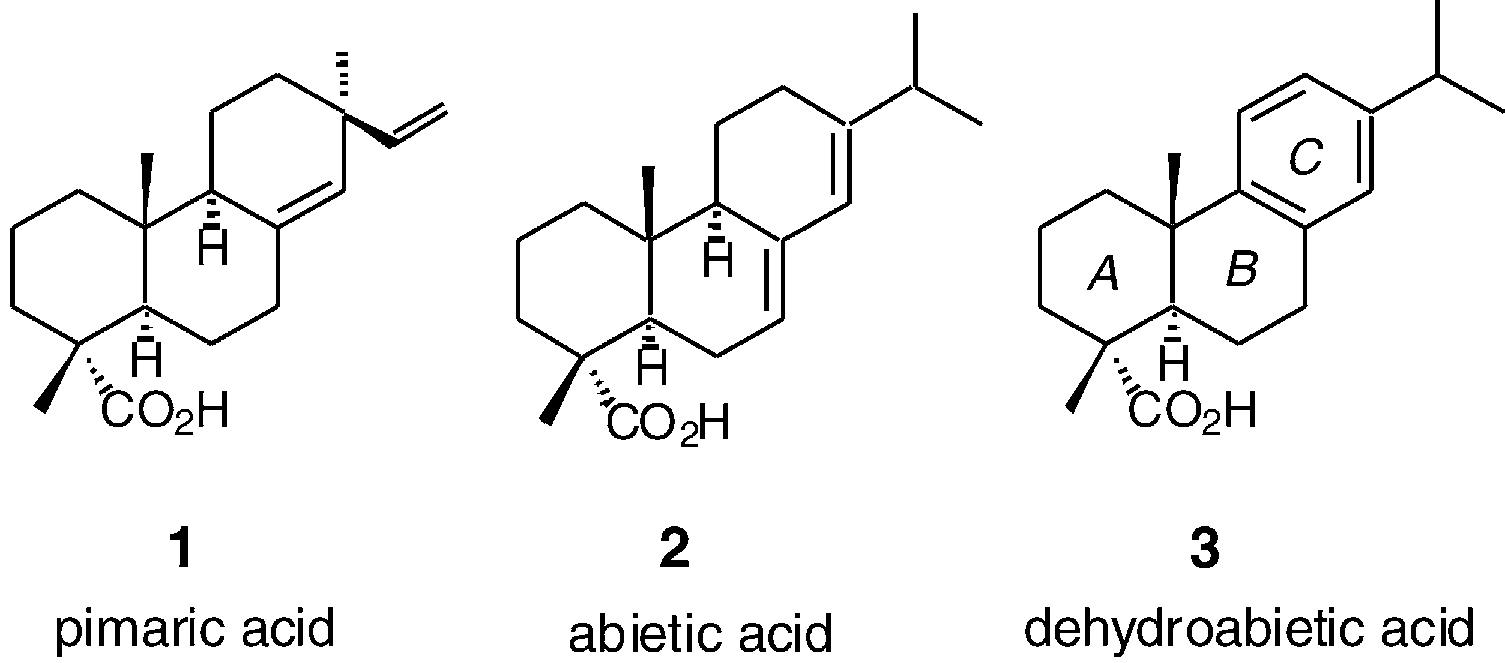
Scaffolds for BK channel modulators in this study.
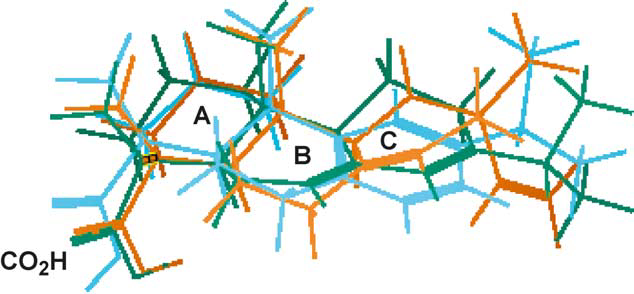
Superimposed structures of pimaric acid (1, green), abietic acid (2, brown) and dehydroabietic acid (3, blue).
CAS number: 127-65-1
Chloramine T is an organic sodium salt derivative of toluene-4-sulfonamide with a chloro substituent in place of an amino hydrogen.
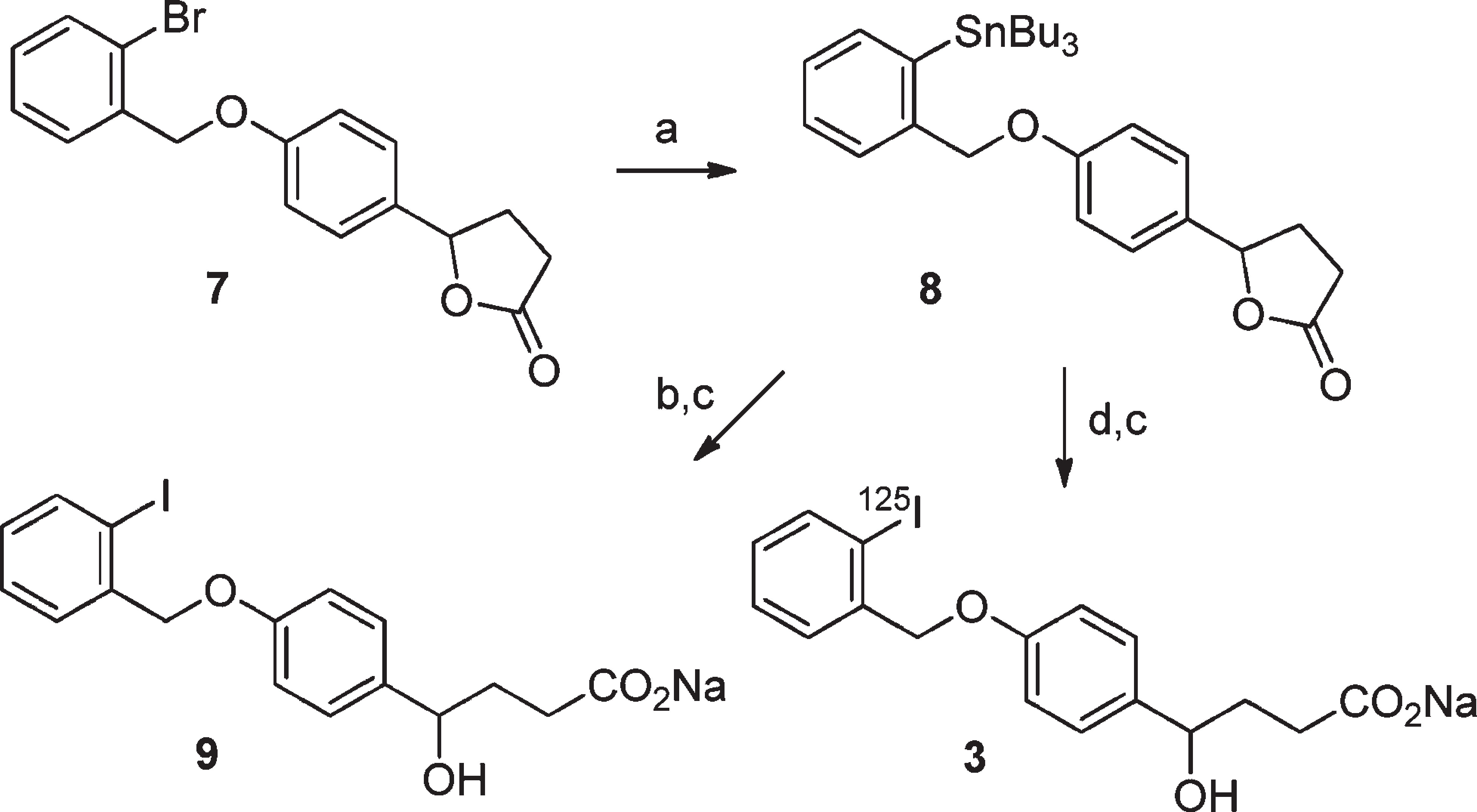
Reagents and conditions: (a) Pd(PPh3)4, (SnBu3)2, toluene, reflux, 22 h; (b) NaI, chloramine-T, 94% EtOAc, 4% DMF, 1% AcOH, 1% H2O, room temp, 30 min, Na2S3O5; (c) NaOH, 1 h; (d) 3 mCi Na125I and chloramine-T in a mixture of 94% EtOAc, 4% DMF, 1% AcOH, and 1% H2O, room temp, 30 min, Na2S3O5.
CAS number: 127-91-3
Beta-pinene is an isomer of pinene with an exocyclic double bond. It is a component of essential oils from many plants. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
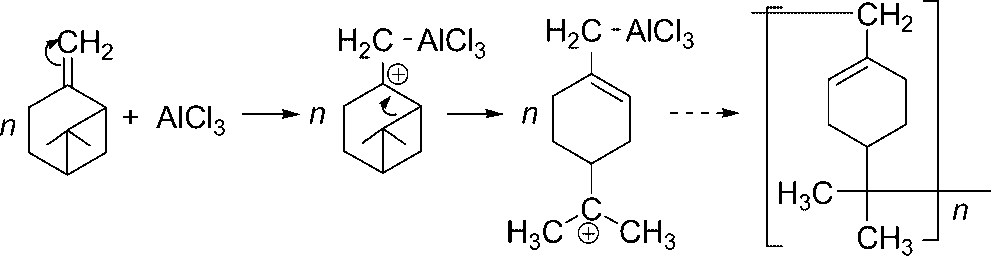
Cationic polymerisation of β-pinene.
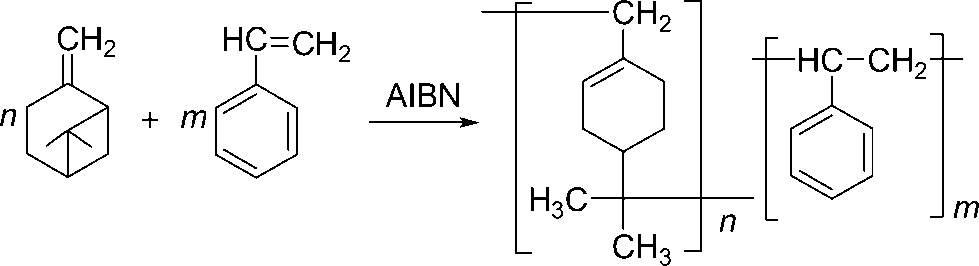
Radical copolymerisation of β-pinene with styrene.
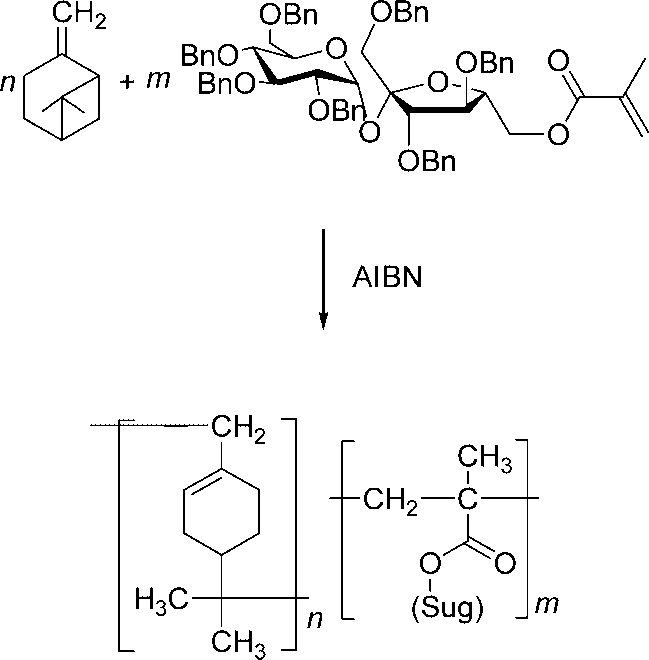
Radical copolymerisation of β-pinene with BmS.
CAS number: 1271-29-0
Titanocene is an organotitanium compound in which a titanium atom is sandwiched between two cyclopentadienyl (C₅H₅⁻) rings in a metallocene structure. It is a dark-colored, air-sensitive solid that is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as benzene or toluene. The compound is typically prepared by reacting sodium cyclopentadienide with titanium tetrachloride, producing titanocene dichloride as a precursor, which can then be reduced to titanocene itself. Titanocene’s structure and bonding are of significant interest in organometallic chemistry due to its symmetry, stability in inert atmospheres, and potential as a starting material for catalytic and polymerization processes.
![Modular titanocene synthesis via acylation reactions [24].](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/bjoc.10.169_1.png)
Modular titanocene synthesis via acylation reactions [24].
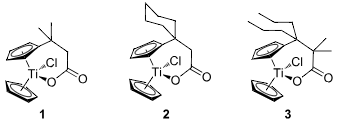
Carboxylates employed as titanocene starting materials for azide-substituted complexes.
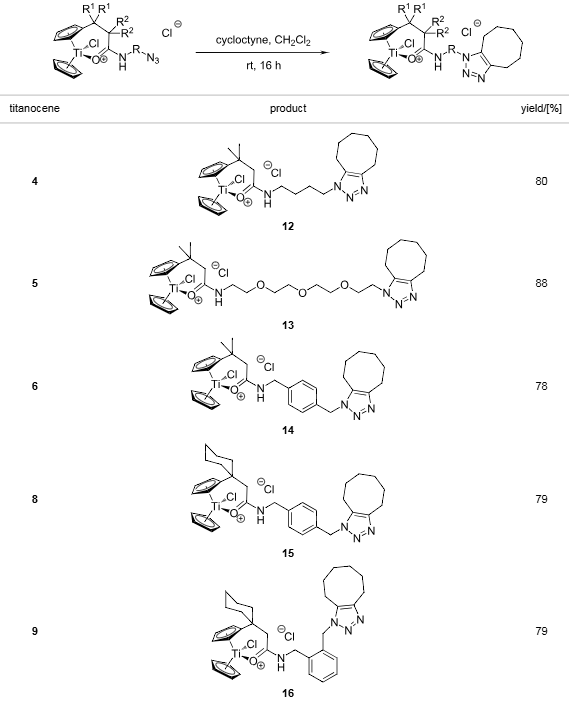
Strain-driven 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions between cyclooctyne and azide-functionalized titanocenes in CH2Cl2 (0.1 M).
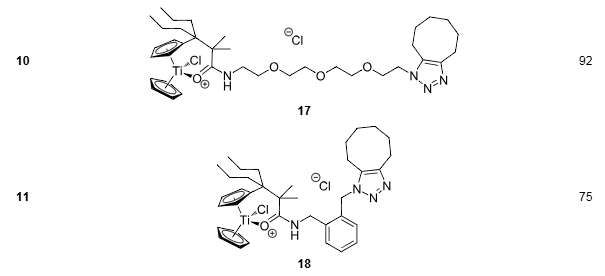
Strain-driven 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions between cyclooctyne and azide-functionalized titanocenes in CH2Cl2 (0.1 M). (continued)
CAS number: 127500-84-9
Ro-41-1049 is a small-molecule, reversible, and selective inhibitor of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), originally developed by Roche. It binds with high affinity to MAO-A in human frontal cortex (Kd ~16.5 nM) and placenta (Kd ~64.4 nM), acting as an orally active MAO-A inhibitor that has been used in biochemical research to probe MAO-A function.
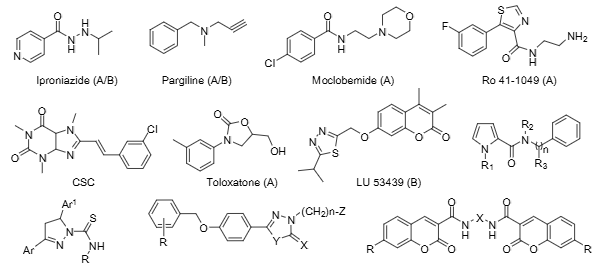
Some representative structures of MAO inhibitors used in research or clinical practice: Iproniazide, Pargiline, Moclobemide, Ro 41-1049, CSC, Toloxatone, LU-53439.
CAS number: 127682-96-6
Methylidenemolybdenum is a type of carbene ligand.
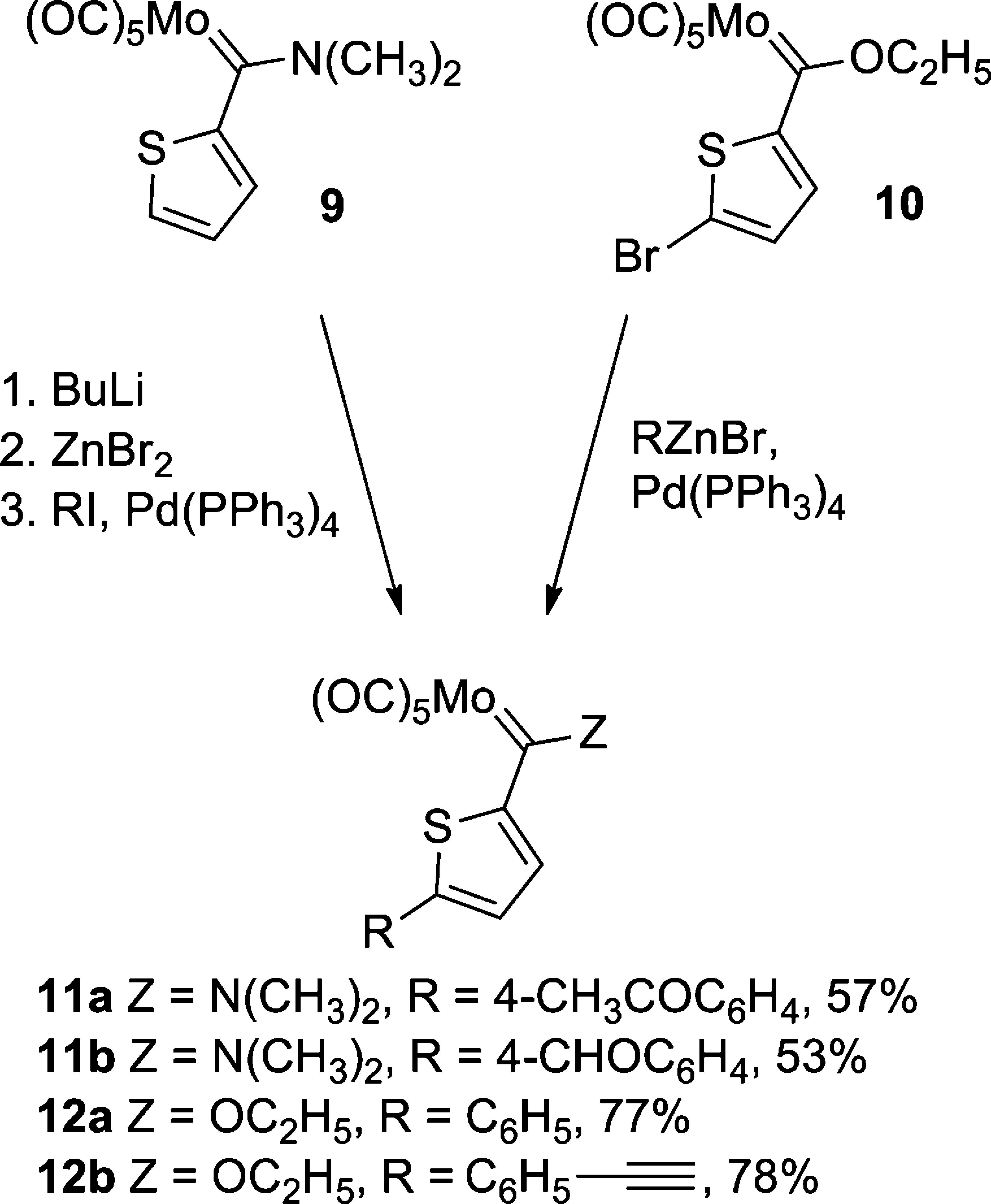
Cross-Coupling of Molybdenum Carbene Complexes
CAS number: 127882-73-9
GL-331 is a synthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin belongs to the class of semisynthetic lignans and is structurally related to etoposide and teniposide, which are well-known anticancer agents. GL-331 functions primarily as a topoisomerase II inhibitor, interfering with DNA replication and transcription in rapidly dividing cells, making it a potential chemotherapeutic agent. Preclinical studies have demonstrated its cytotoxic effects against various tumor cell lines, and it has shown promise in overcoming multidrug resistance in certain cancer models.
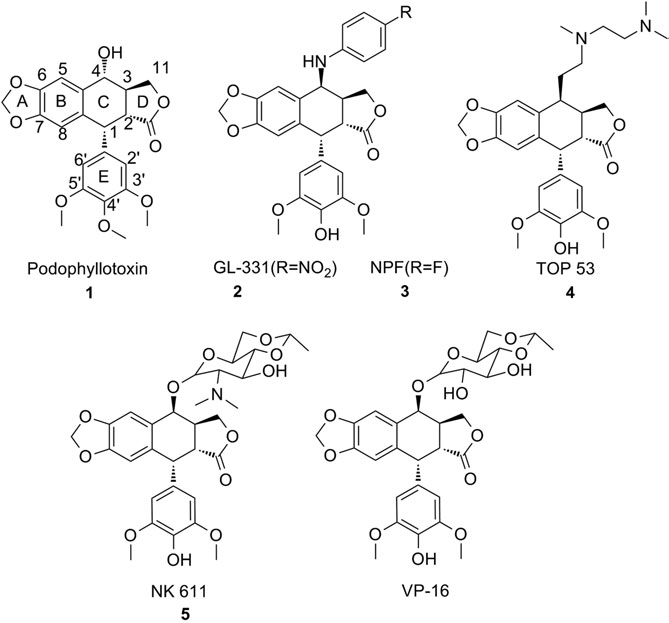
Structures of podophyllotoxin, NPF, GL331, TOP 53, NK61, and VP-16.