Doxorubicin
CAS number: 23214-92-8
Doxorubicin is a deoxy hexoside, an anthracycline, an anthracycline antibiotic, an aminoglycoside, a member of tetracenequinones, a member of p-quinones, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a doxorubicin(1+). It derives from a hydride of a tetracene.
Related images
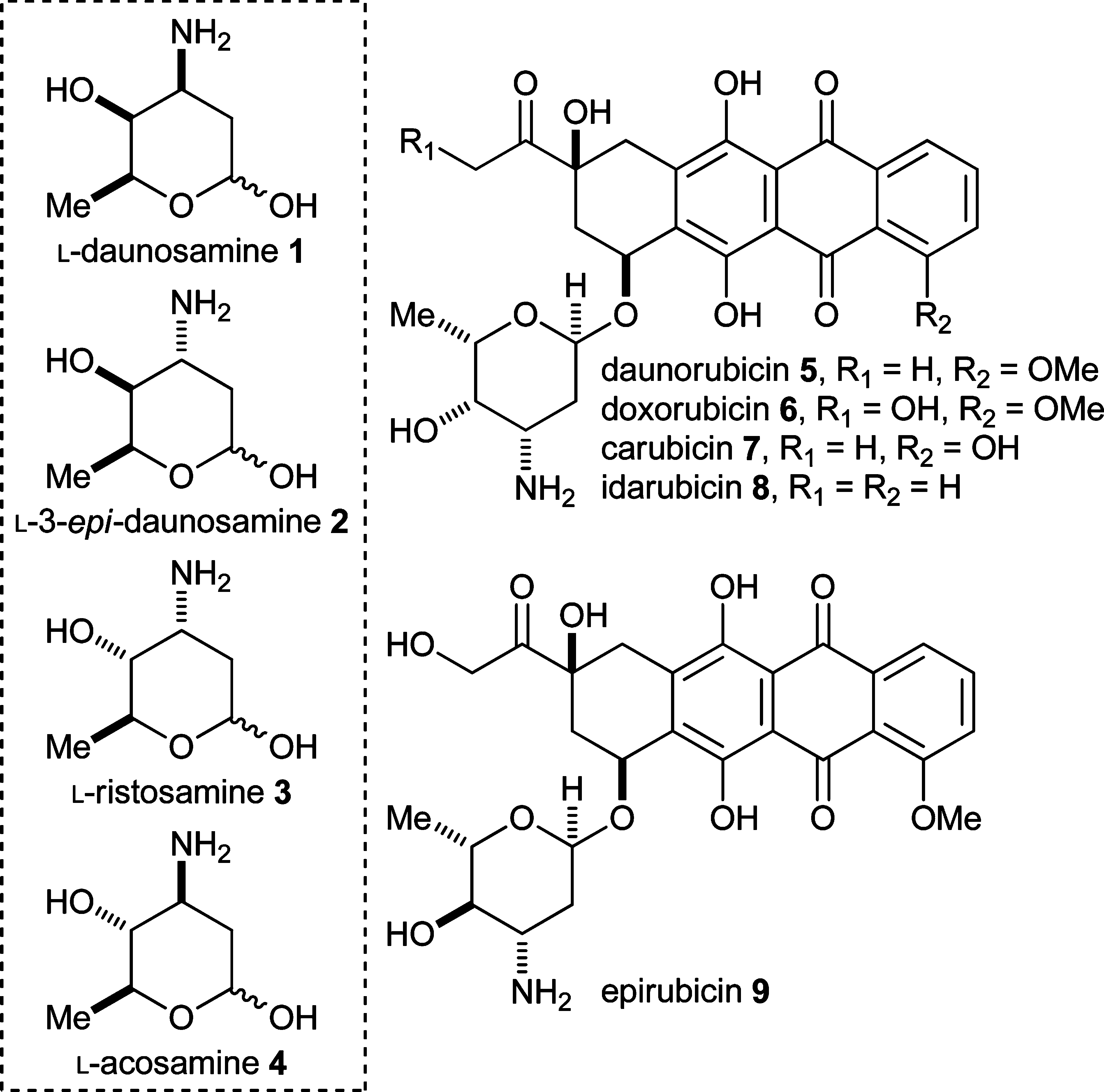
Structures of L-daunosamine 1, L-3-epi-daunosamine 2, L-ristosamine 3, L-acosamine 4, and the anthracycline antibiotics daunorubicin 5, doxorubicin 6, carubicin 7, idarubicin 8, and epirubicin 9.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Doxorubicin provides a broad-spectrum cytotoxic effect in both regimens, contributing to the overall efficacy of the treatment by targeting rapidly dividing cancer cells.
A: Doxorubicin is administered at a dose of 30 mg/m² on day one of the biweekly cycles. It is an anthracycline antibiotic that helps in achieving tumor regression and is part of the combination therapy that enhances the overall efficacy of the regimen.