Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 1118-68-9
N,N-dimethylglycine (DMG) is a naturally occurring compound being widely used as an oral supplement to improve growth and physical performance.
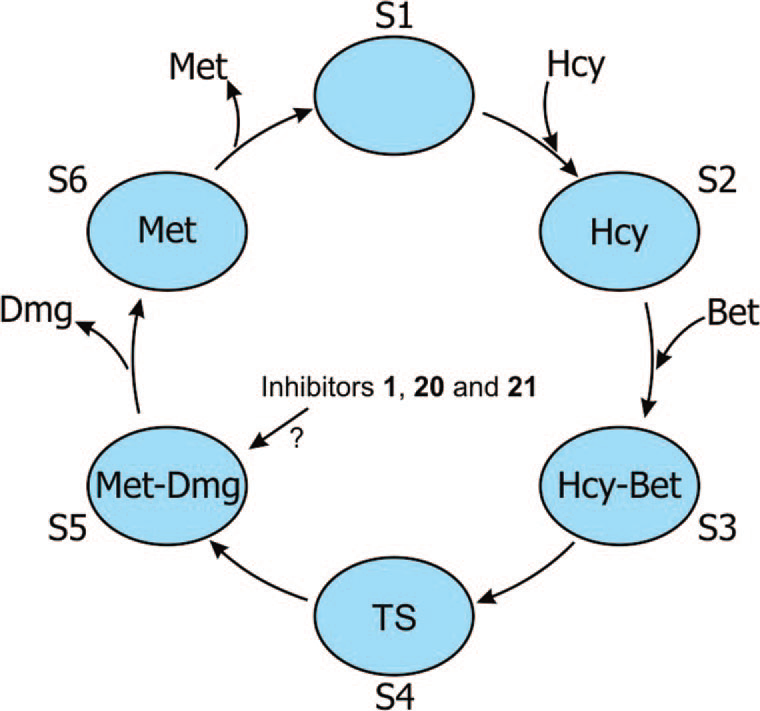
Schematic diagram showing the possible structural changes of BHMT during the binding process with substrates and products. The blue ovals (S1-S6) represent the different structural states of BMHT monomers. Hcy represents homocysteine, Bet represents betaine, Met represents methionine, Dmg represents dimethylglycine, and TS represents the assumed transition state of the substrate.
CAS number: 112-55-0
1-Dodecanethiol, also known as n-dodecyl mercaptan or lauryl mercaptan, is an alkyl thiol (a molecule containing a sulfur-hydrogen bond attached to a carbon chain) with 12 carbon atoms. It's a colorless to pale yellow oily liquid at room temperature and has a mild, skunk-like odor.

a) S 2p XPS signals for VHF 2 SAMs. b) Optical images of water droplets on surfaces of DHA 1 (left) and VHF 2 (right) SAMs, and revers- ible wettability transitions as a function of alternating thermal treatment and UV irradiation. c) Optical transmission spectra of rGO films with a series of film thicknesses. Inset, a ≈7 nm-thick rGO film transferred onto quartz for transmission measurement. d) Optical and AFM images of rGO films transferred onto bottom electrodes. The ultrathin flexible rGO film follows the topography of the electrode patterns and ensures a good contact to the SAMs at the bottom of the microholes. The texture of the film is clearly visible.
CAS number: 112-62-9
Methyl oleate is a fatty acid methyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of oleic acid with methanol. It is functionally related to an oleic acid.
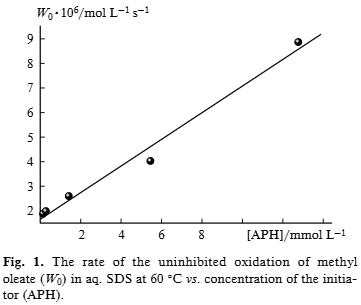
The rate of the uninhibited oxidation of methyl oleate (W0) in aq.
CAS number: 112-80-1
Oleic acid is an octadec-9-enoic acid in which the double bond at C-9 has Z (cis) stereochemistry.
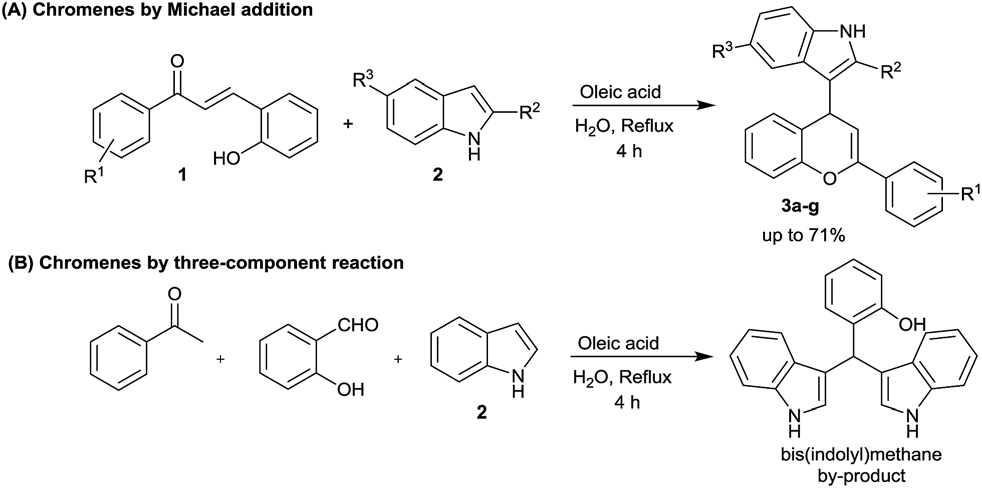
Oleic acid catalysed 4H-chromene synthesis.
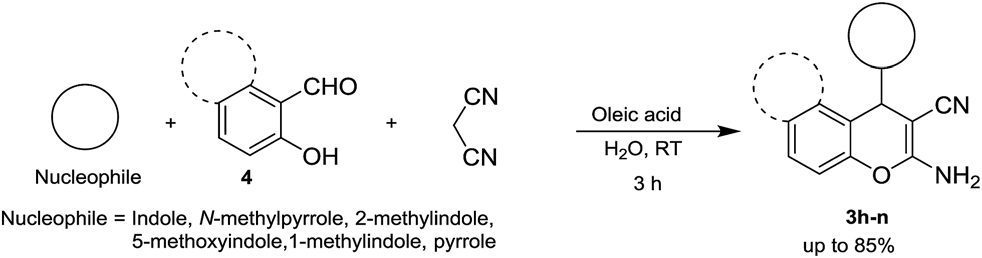
Oleic acid catalysed 4H-chromene synthesis by three-component reaction.
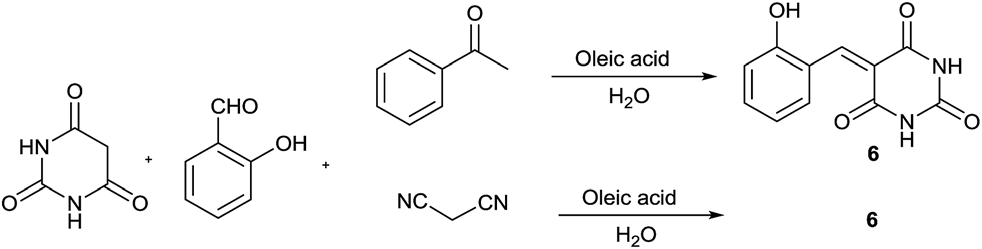
Oleic acid catalysed pyrimidine-fused heterocycles synthesis.
Oleic acid catalysed pyrimidine-fused heterocycles synthesis.
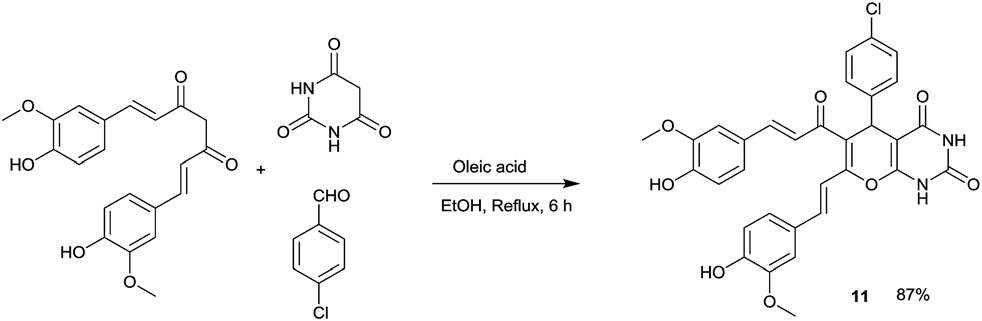
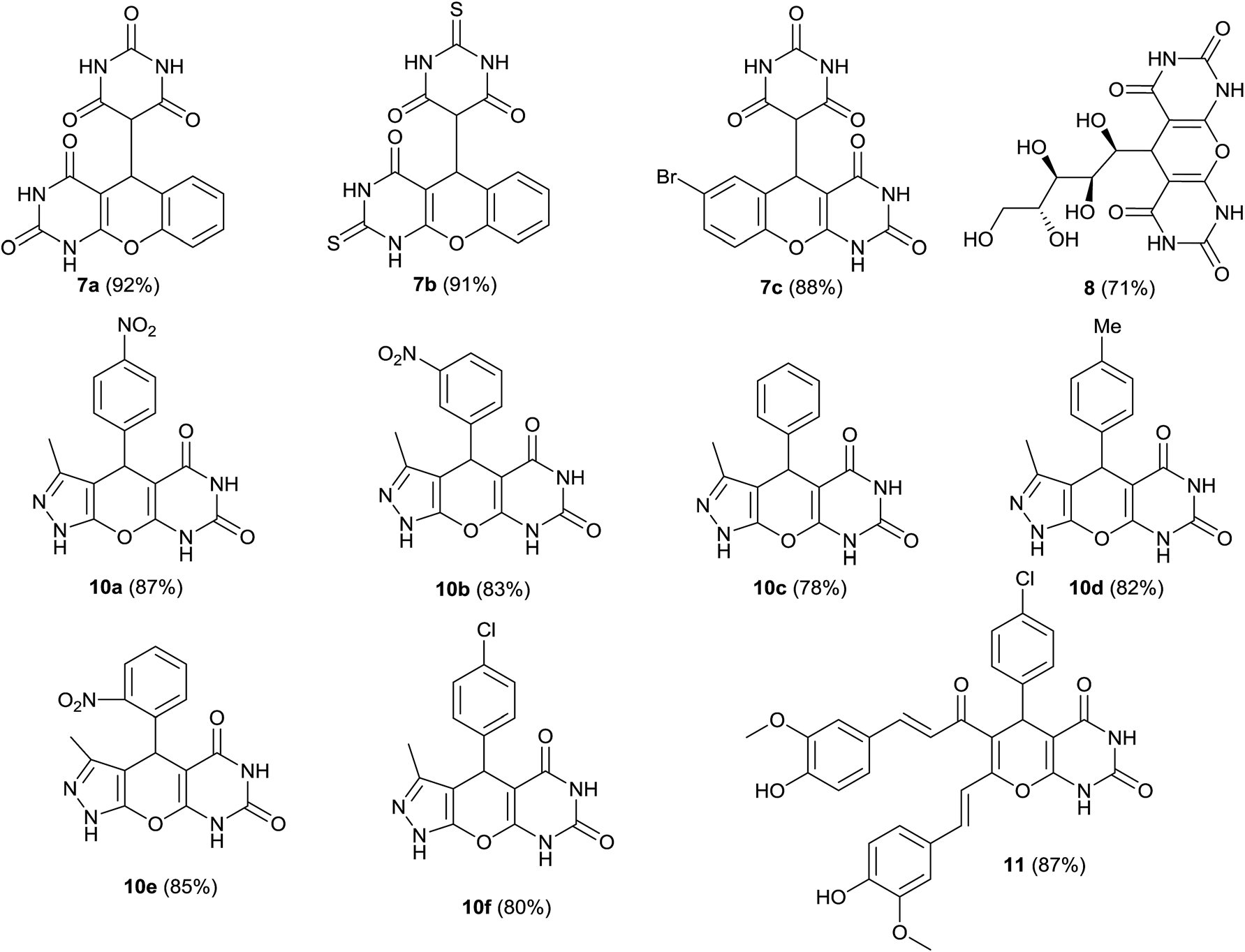
Oleic acid catalysed bioactive skeleton synthesis.
CAS number: 1120-53-2
1,3-Cyclobutadiene (C₄H₄) is a highly reactive and unstable organic compound that consists of a four-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds, specifically at the 1 and 3 positions. Due to its antiaromatic nature — having 4 π-electrons in a conjugated planar system — it experiences significant electronic instability, which leads to rapid dimerization or reaction with other species under standard conditions. The molecule exists transiently in the gas phase or at very low temperatures and has a rectangular rather than square geometry, as predicted by molecular orbital theory to relieve some of the antiaromatic strain. 1,3-Cyclobutadiene is of considerable interest in theoretical and organometallic chemistry, particularly in studies of aromaticity, bonding, and as a ligand in metal complexes where its stability can be enhanced through coordination.
![Calculated energies relative to the corresponding cyclobutadiene complex [34 + CO].](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3613301_14.png)
Calculated energies relative to the corresponding cyclobutadiene complex [34 + CO].
CAS number: 1122-58-3
4-Dimethylaminopyridine is a dialkylarylamine and a tertiary amino compound. 4-Dimethylaminopyridine has been reported in Panax ginseng with data available.
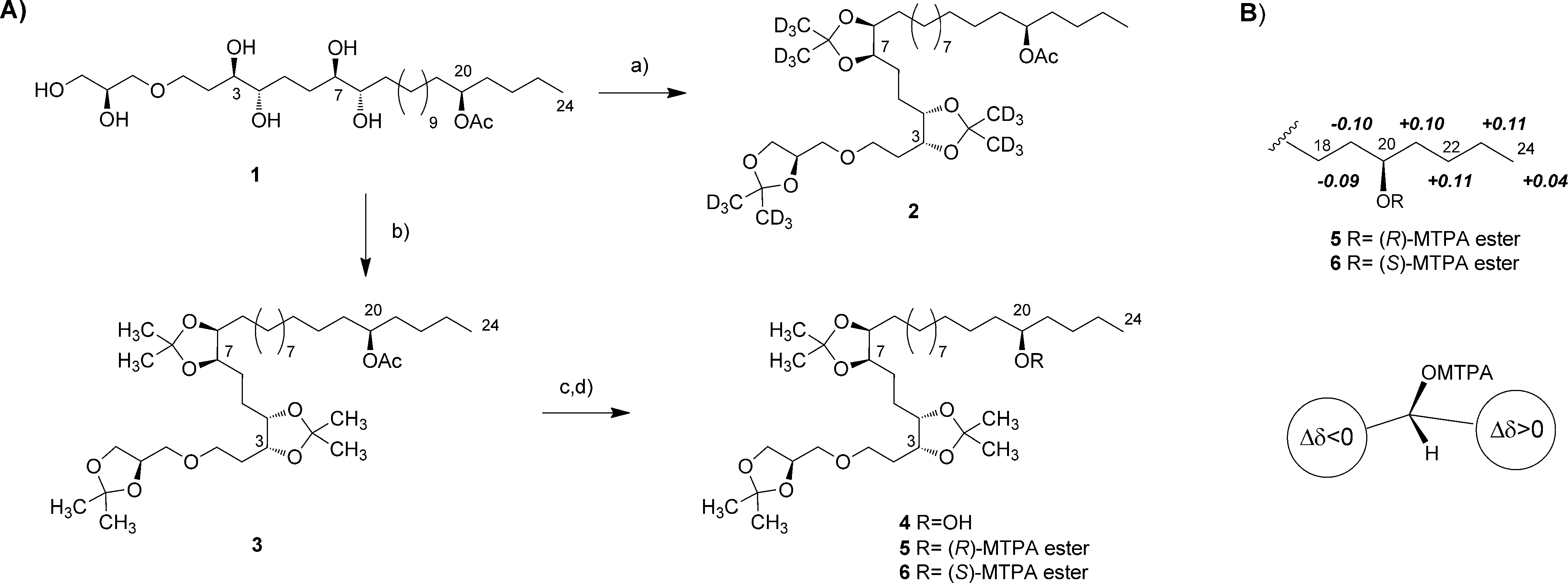
A) Synthesis of acetonide and MTPA derivatives of mycalol (1). B) Δδ (δS-δR) values (ppm) for selected protons of (R)-MTPA ester 5 and (S)-MTPA ester 6. Reagents and conditions: a) (CD3)2CO, I2, RT, 24 h; b) (CH3)2C(OCH3)2, PPTS, 758C, 6 h; c) Na2CO3, MeOH, 558C, 28 h; d) S-(-)- or R-(-)-MTPA chloride, DMAP, dry CH2Cl2, RT, overnight. Ac=acetyl, DMAP=4-dimethylaminopyridine, MTPA-Mosher’s acid; a- methoxy-a-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetic acid, PPTS-pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate
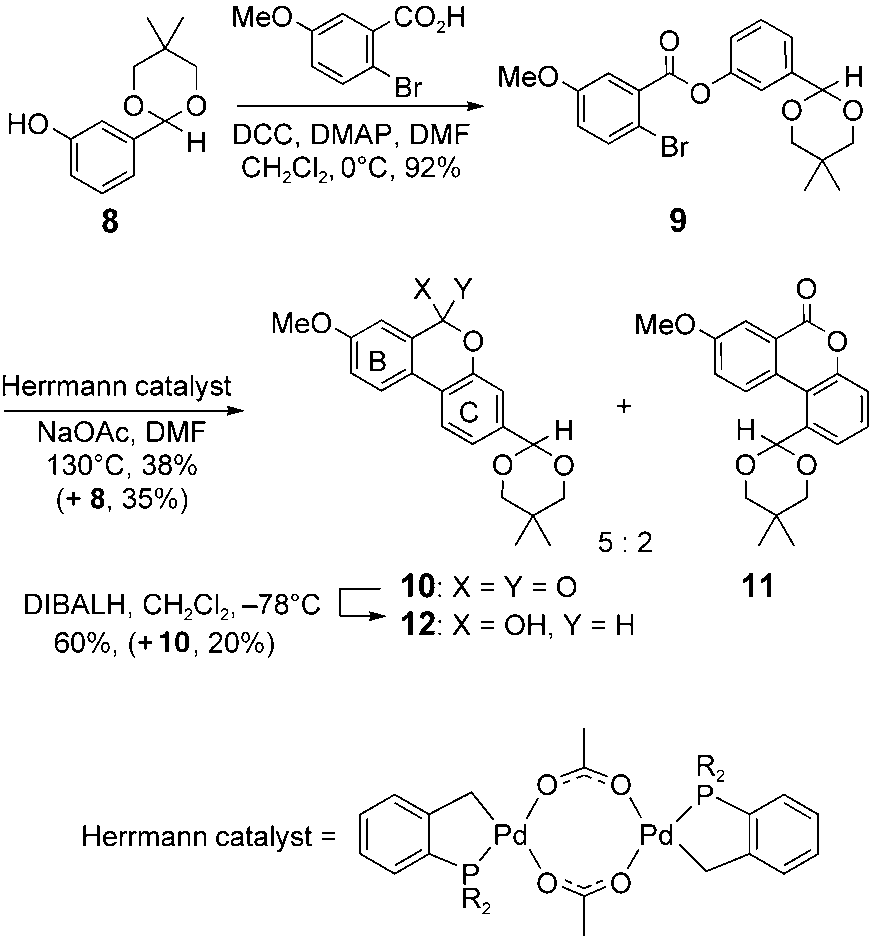
Synthesis of the BC ring system. DCC=dicyclohexylcarbo-diimide, DMAP=4-dimethylaminopyridine, DIBALH=diisobutylaluminum hydride, R=o-tolyl.

Preparation of cyclohexenol 16. DMAP=4-(dimethylamino)-pyridine, Cbz=benzyloxycarbonyl, THF=tetrahydrofuran, TBS=tert-butyldimethylsilyl, dppf=1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene.
CAS number: 113-73-5
Gramicidin S is a homodetic cyclic peptide.
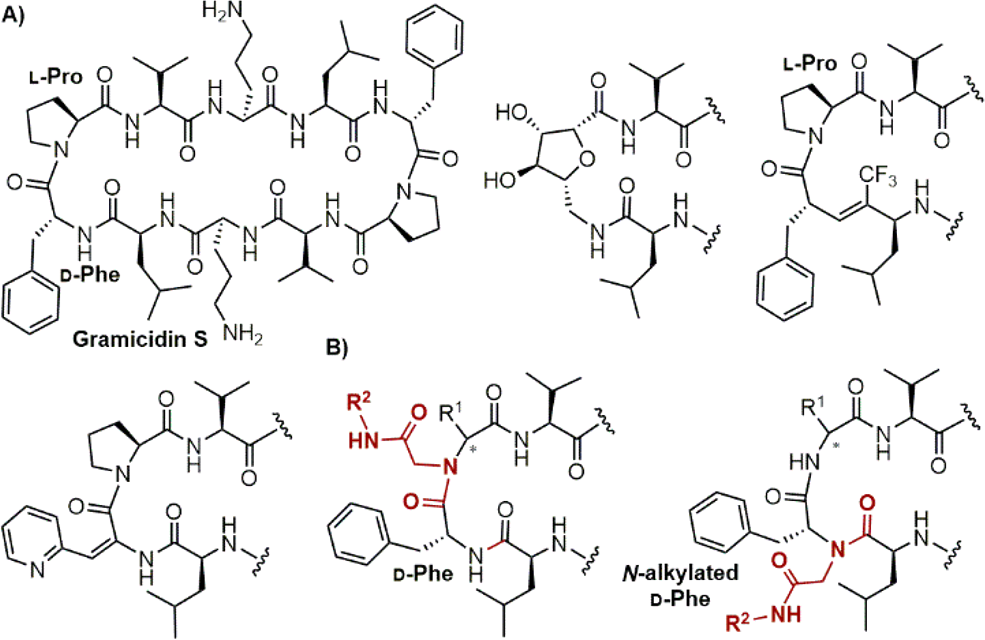
(A) Gramicidin S and some β-turn mimics used in its analogs. (B) Ugi-reaction-derived N-alkylated peptide fragments as novel β-hairpin-stabilizing templates.
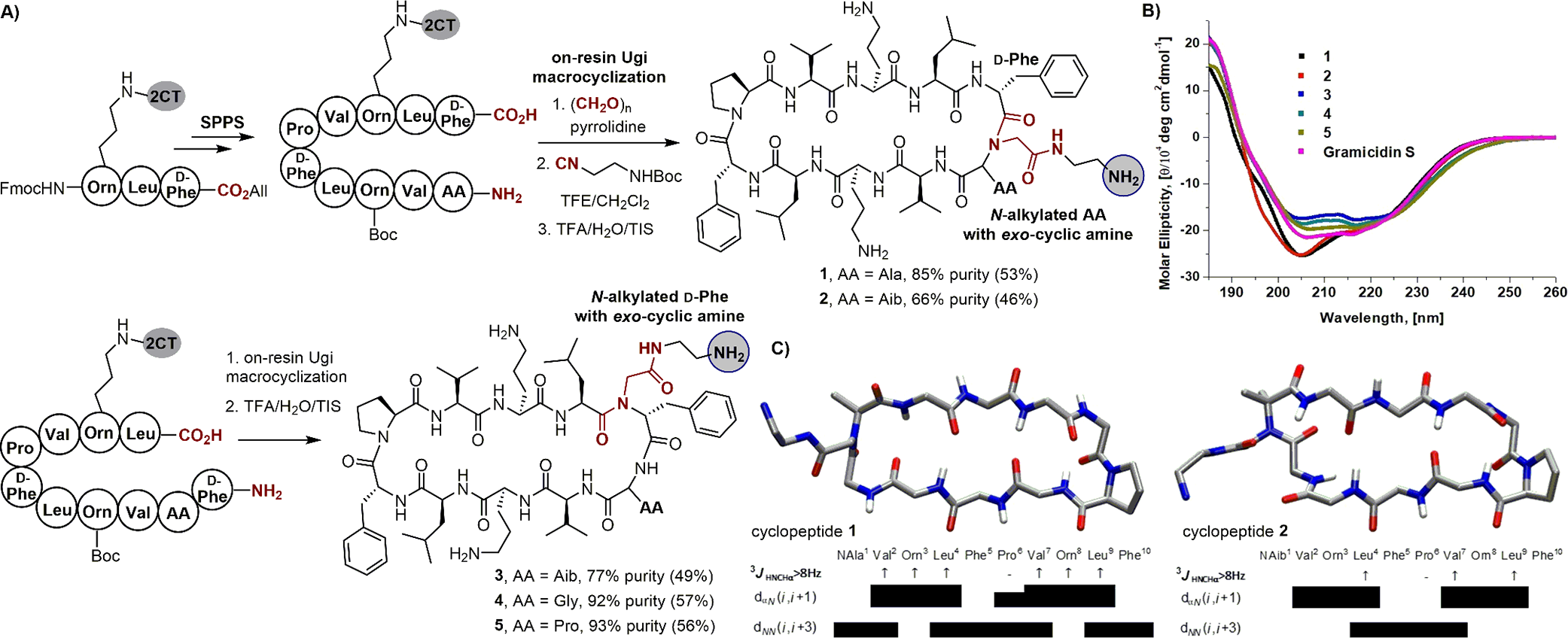
(A) Synthesis of cyclic peptide β-hairpins by on-resin Ugi macrocyclization, (B) comparison of circular dichroism spectra of bUgi-derived β-hairpins with gramicidin S, and (C) average NmR-derived structures of cyclic peptides 1 and 2
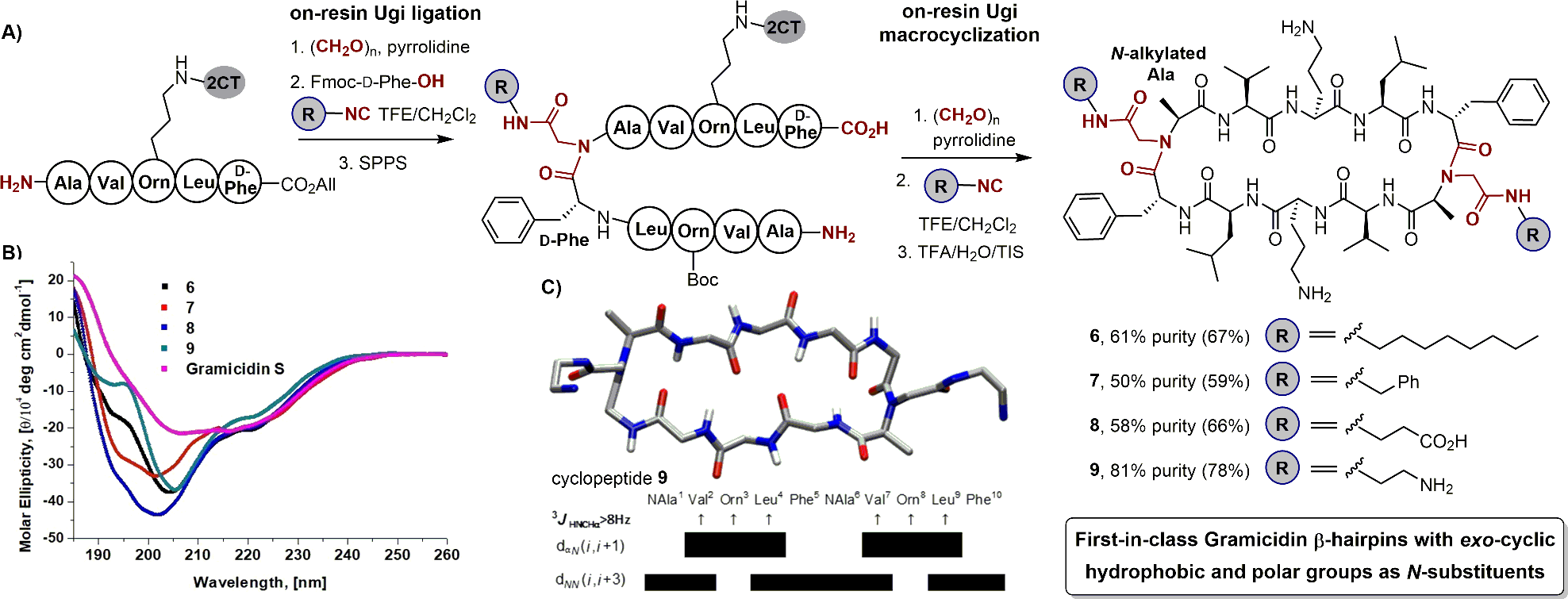
(A) Synthesis of cyclic β-hairpin structure by SPPS method involving two Ugi reactions, (B) CD spectra comparison of the double Ugi-derived β-hairpin structure and gramicidin S, and (C) average NmR-derived structure of cyclic peptide 9b
CAS number: 113411-17-9
DIF-3, or Differentiation-inducing factor 3, is a chlorinated hexaphenone compound derived from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. It's known for its role in cell differentiation and its potential as an anticancer agent. DIF-3 is structurally similar to DIF-1, another compound from the same family, and is involved in regulating various cellular processes.
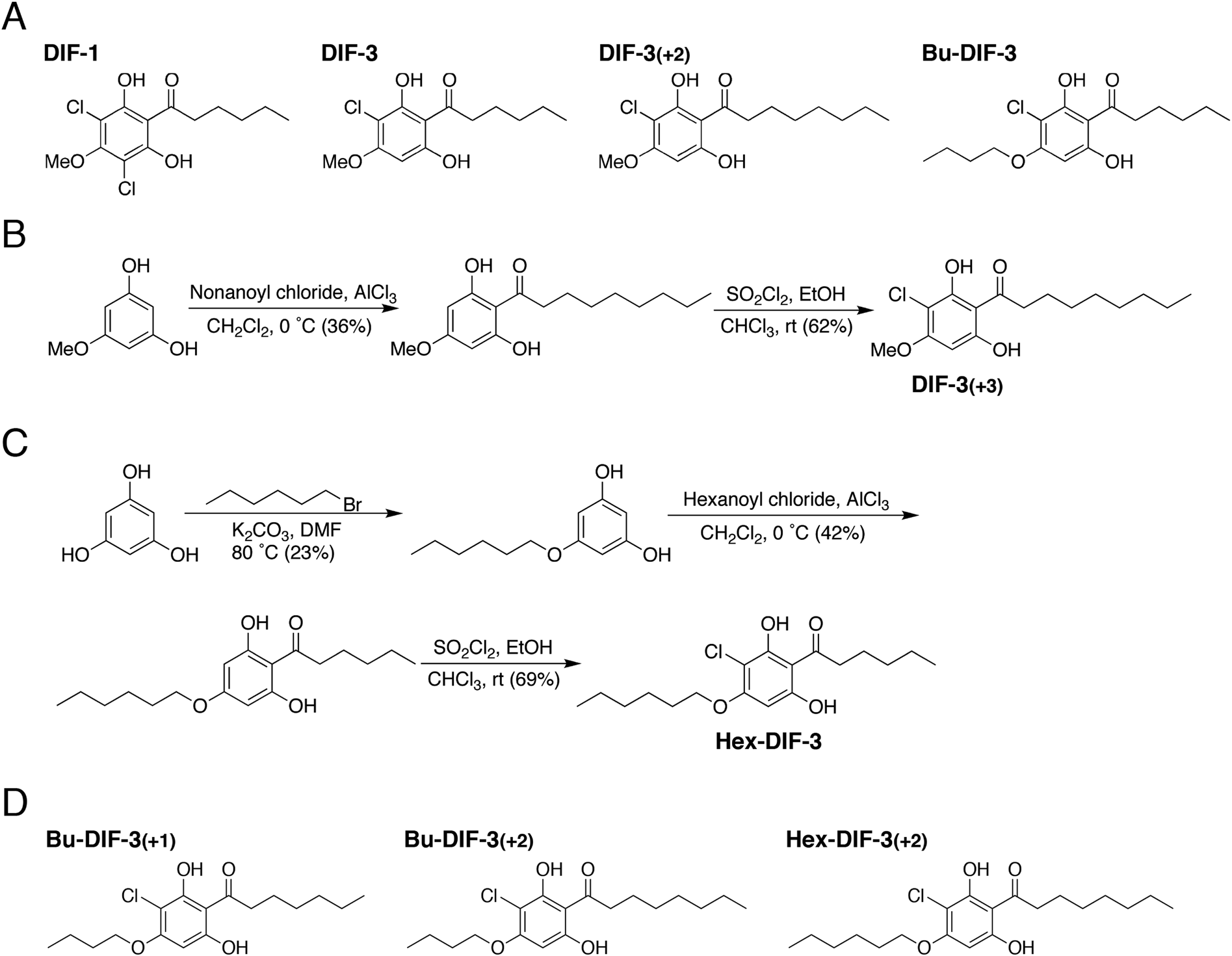
Synthetic Routs to DIF Derivatives
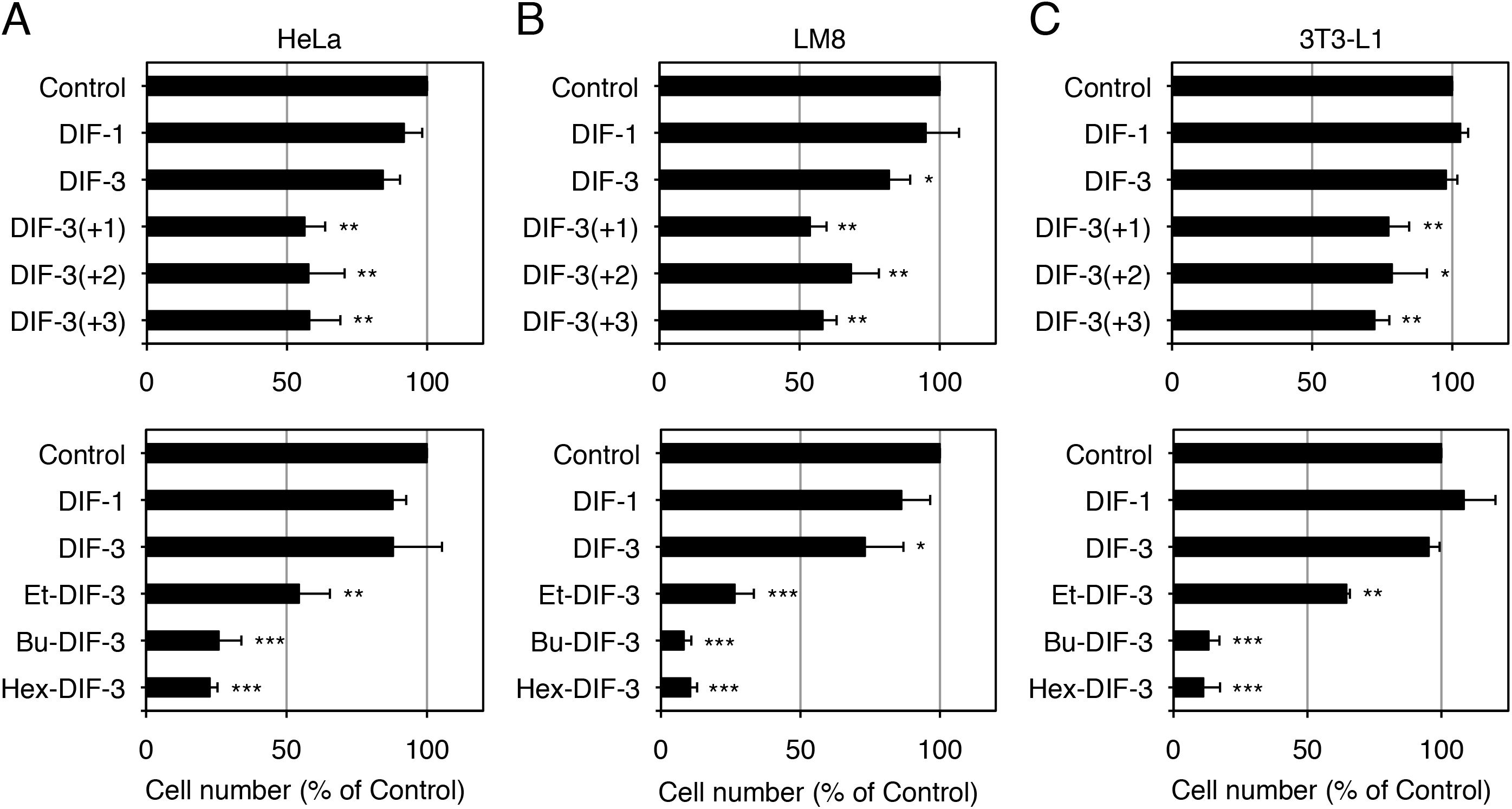
Effects of DIF Derivatives on Cell Growth in HeLa, LM8, and 3T3-L1 Cells
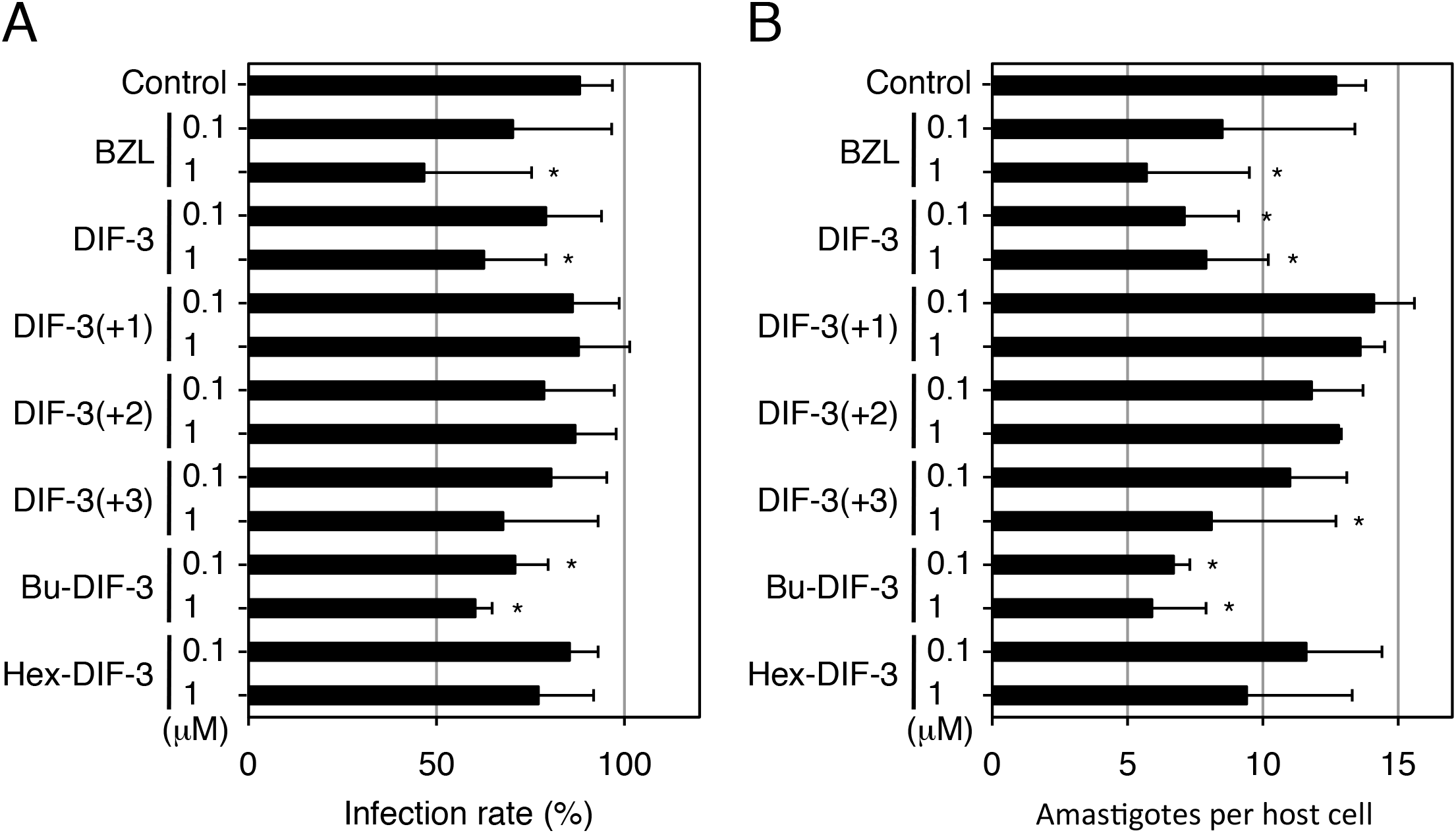
Effects of DIF Derivatives on Infection and Growth of T. cruzi
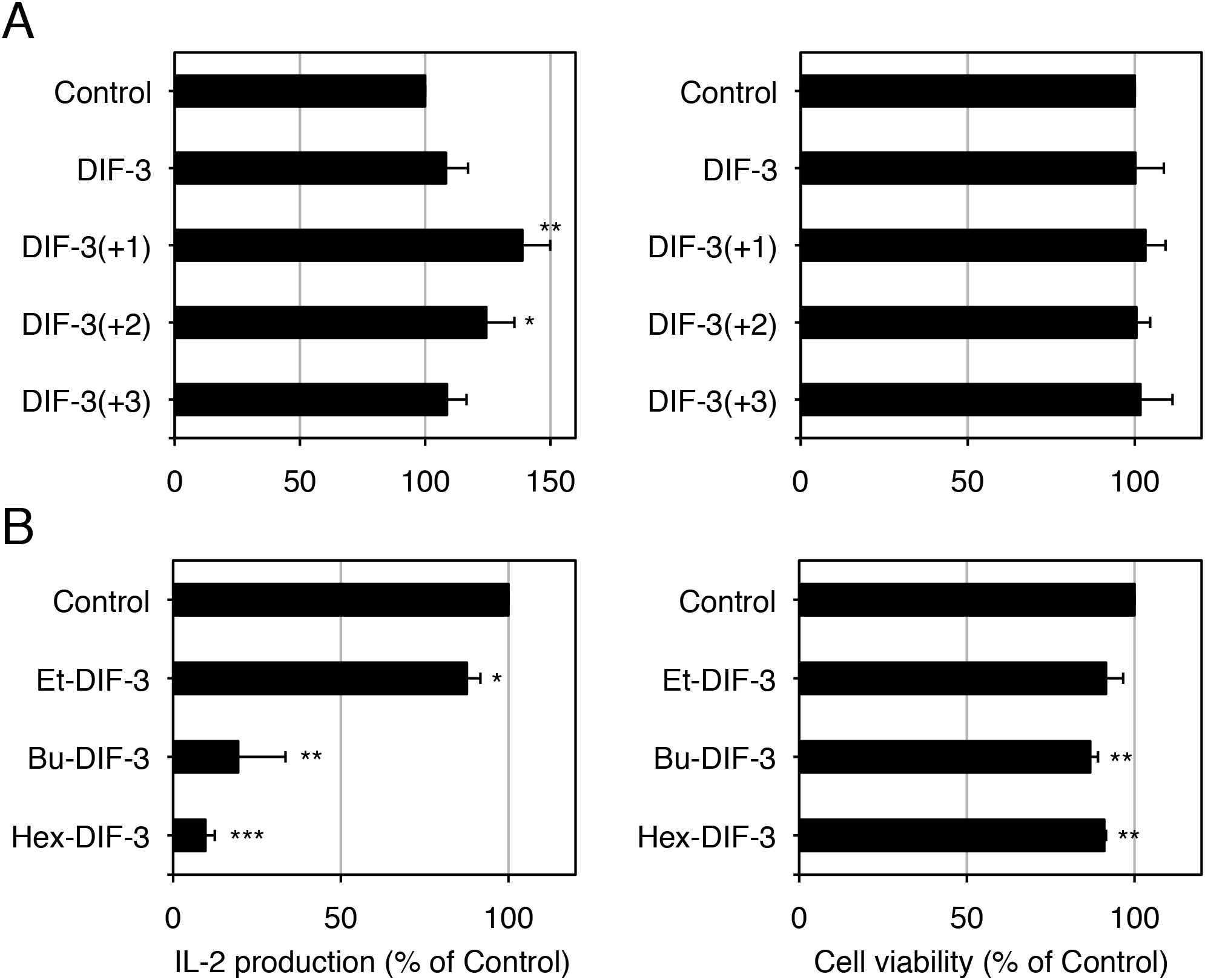
Effects of DIF Derivatives on IL-2 Production in Jurkat T Cells
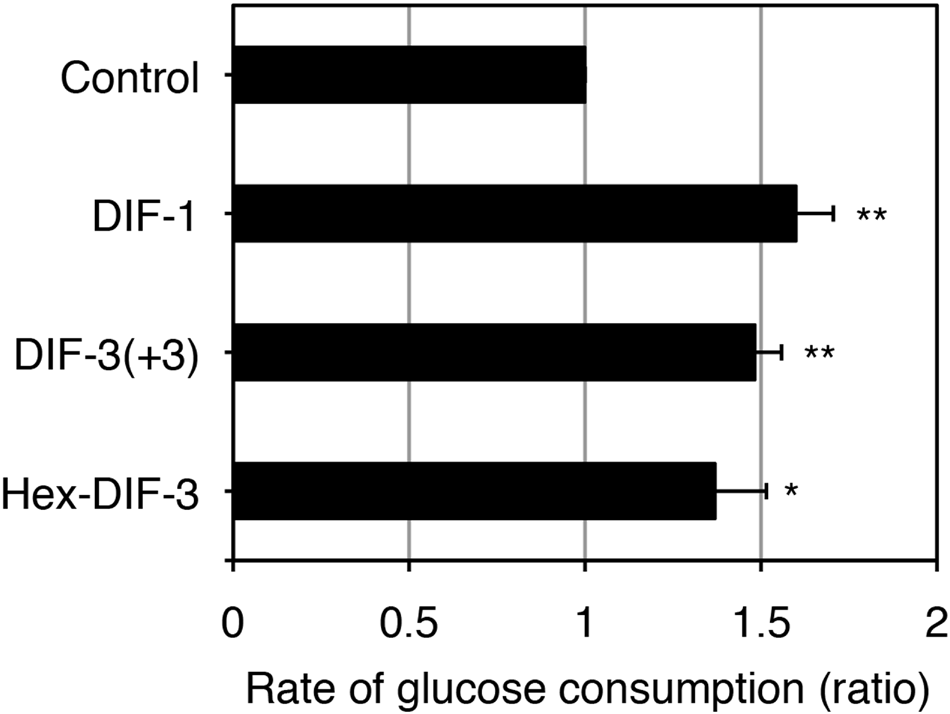
Effects of DIF Derivatives on Glucose Consumption in 3T3-L1 Cells
CAS number: 1135-24-6
Ferulic acid is a member of the class of ferulic acids that is cinnamic acid substituted by a methoxy and a hydroxy group at positions 3 and 4 of the phenyl ring. It has a role as a neuroprotective agent, a plant metabolite and an antioxidant.
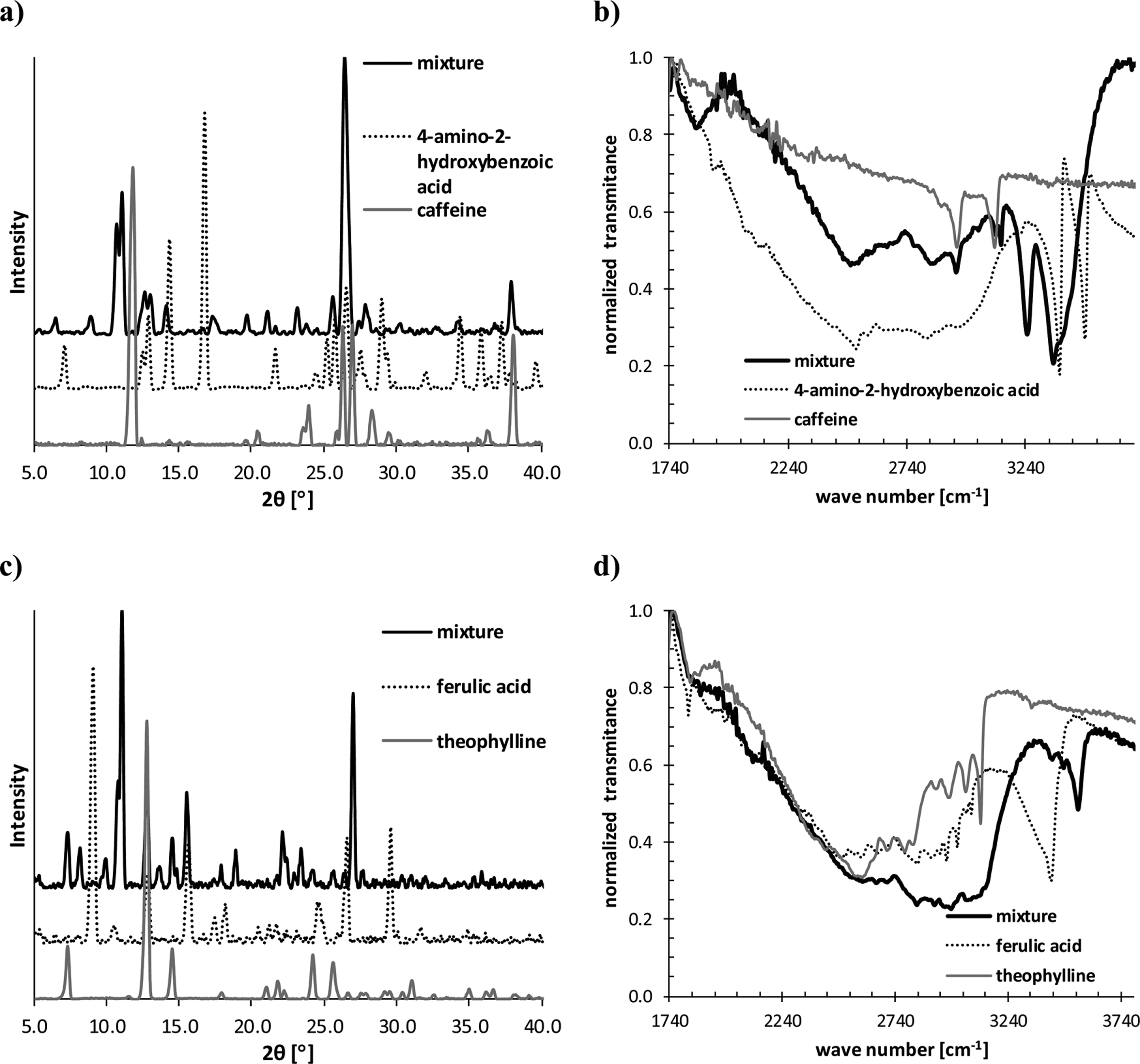
PXRD and FTIR spectra recorded for 1:1 caffeine/4-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid mixture (a, b) and 1:1 theophylline/ferulic acid mixture (c, d) obtained via liquid-assisted grinding.
CAS number: 1135695-98-5
Q-VD-OPh hydrate is an organic molecular entity. It has a role as an apoptosis inhibitor.
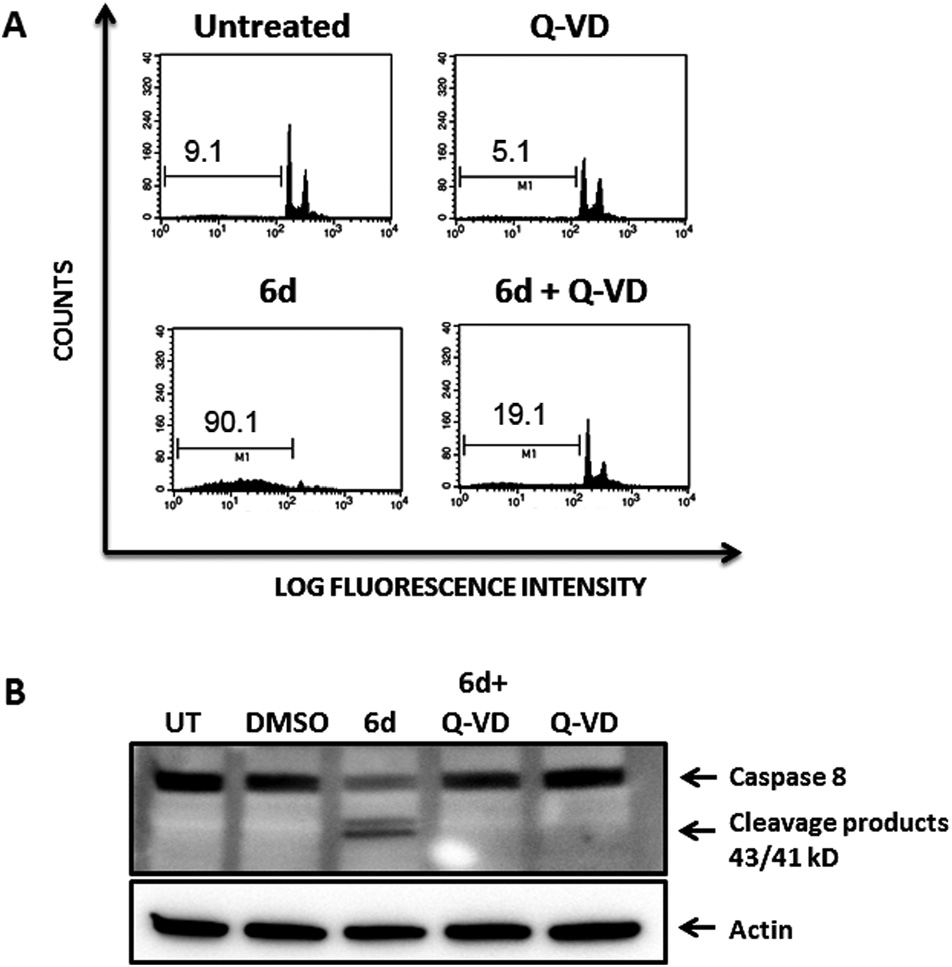
Pre-treatment of Jurkat cells with the pan-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh abrogates cell dead mediated by compound 6d.