Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 120-72-9
1H-indole is an indole and a polycyclic heteroarene. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a tautomer of a 3H-indole.
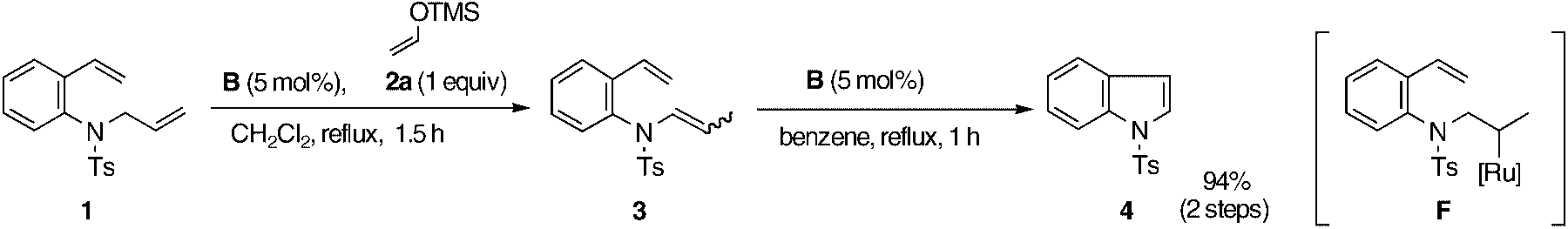
Selective isomerization of a terminal olefin: the synthesis of an indole through RCM. Ts=p-toluenesulfonyl, TMS=trimethylsilyl.
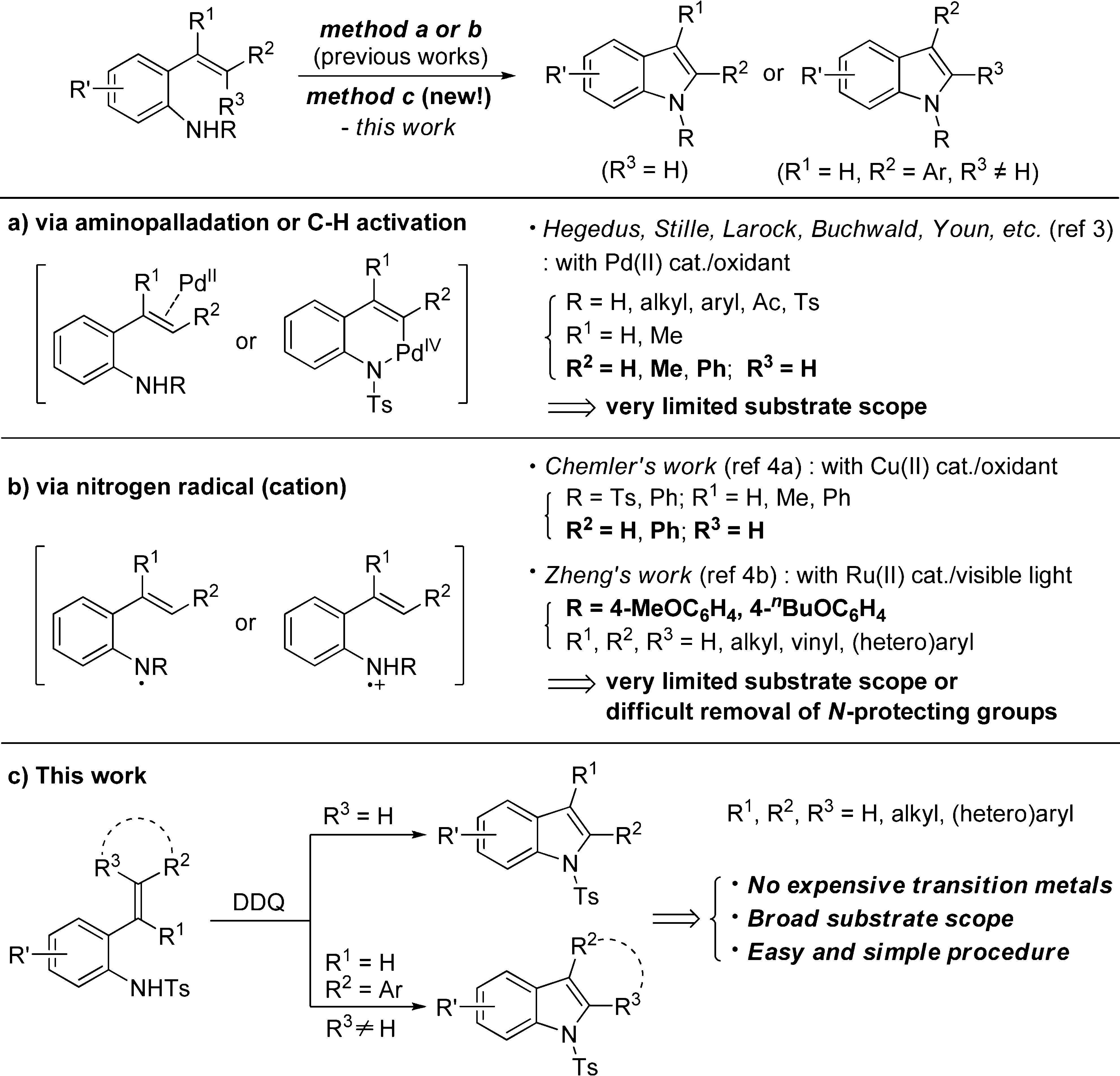
Indole Synthesis from 2-Alkenylanilines
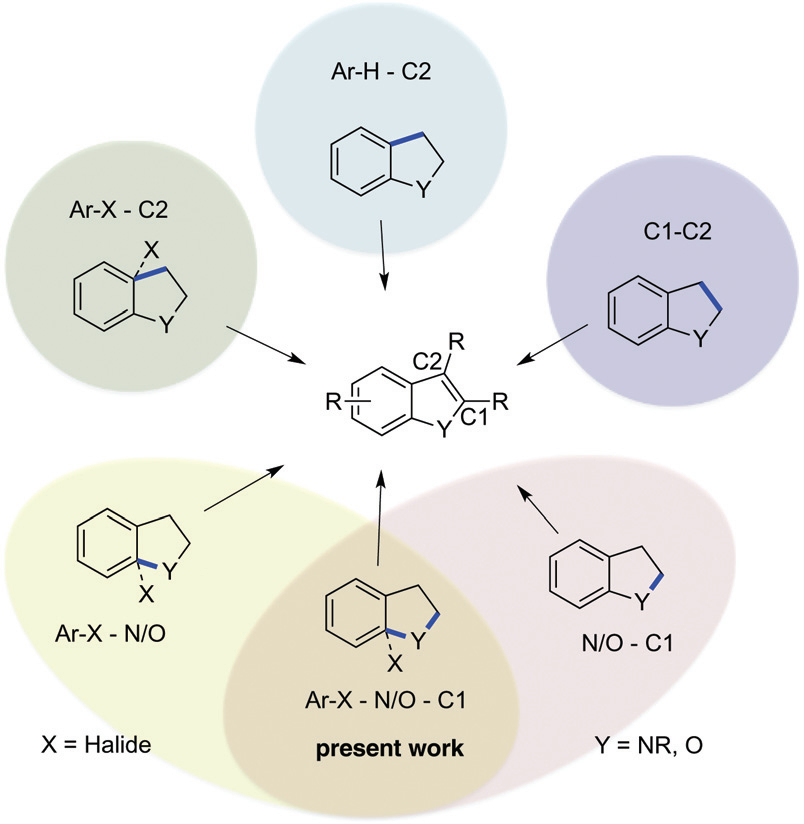
Strategies for the synthesis of indoles and benzofurans.
CAS number: 120-75-2
2-Methylbenzothiazole is an organic chemical compound which is a benzothiazole derivative, meaning it contains a benzene ring fused to a thiazole ring.
![Scalability of the CBr4-catalyzed synthesis of 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/1028122_84.png)
Scalability of the CBr4-catalyzed synthesis of 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole.
CAS number: 120-80-9
Catechol is a benzenediol comprising of a benzene core carrying two hydroxy substituents ortho to each other. It has a role as a genotoxin, an allelochemical and a plant metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a catecholate(1-).
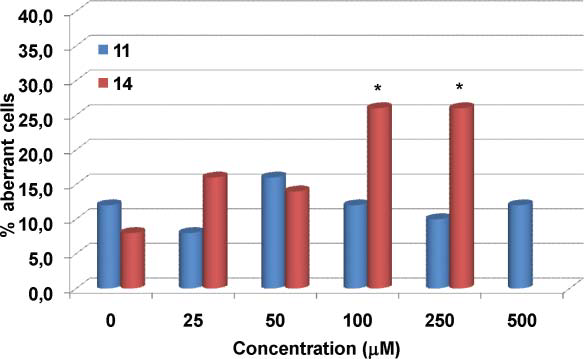
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the lignan 7-hydroxymatairesinol 11 and its catechol derivative 14 in V79 cells in vitro.
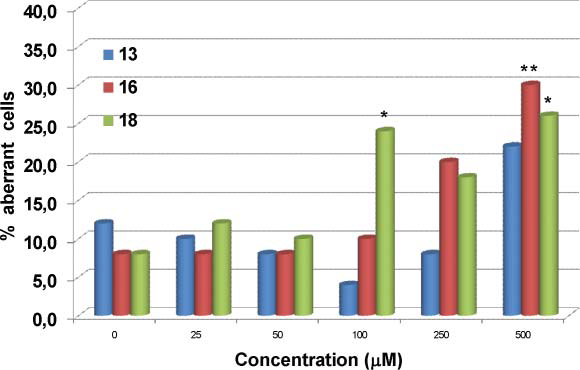
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the lignan lariciresinolo 13 and their catechol and acetylated catehcol derivatives 16 and 18 respectively in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 120-93-4
2-Imidazolidinone is a cyclic urea compound with a five-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms and a carbonyl group. It's used as a building block in synthesizing pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, and as a formaldehyde scavenger in various industries. It also has applications in detergents, dyestuffs, and electronic materials.
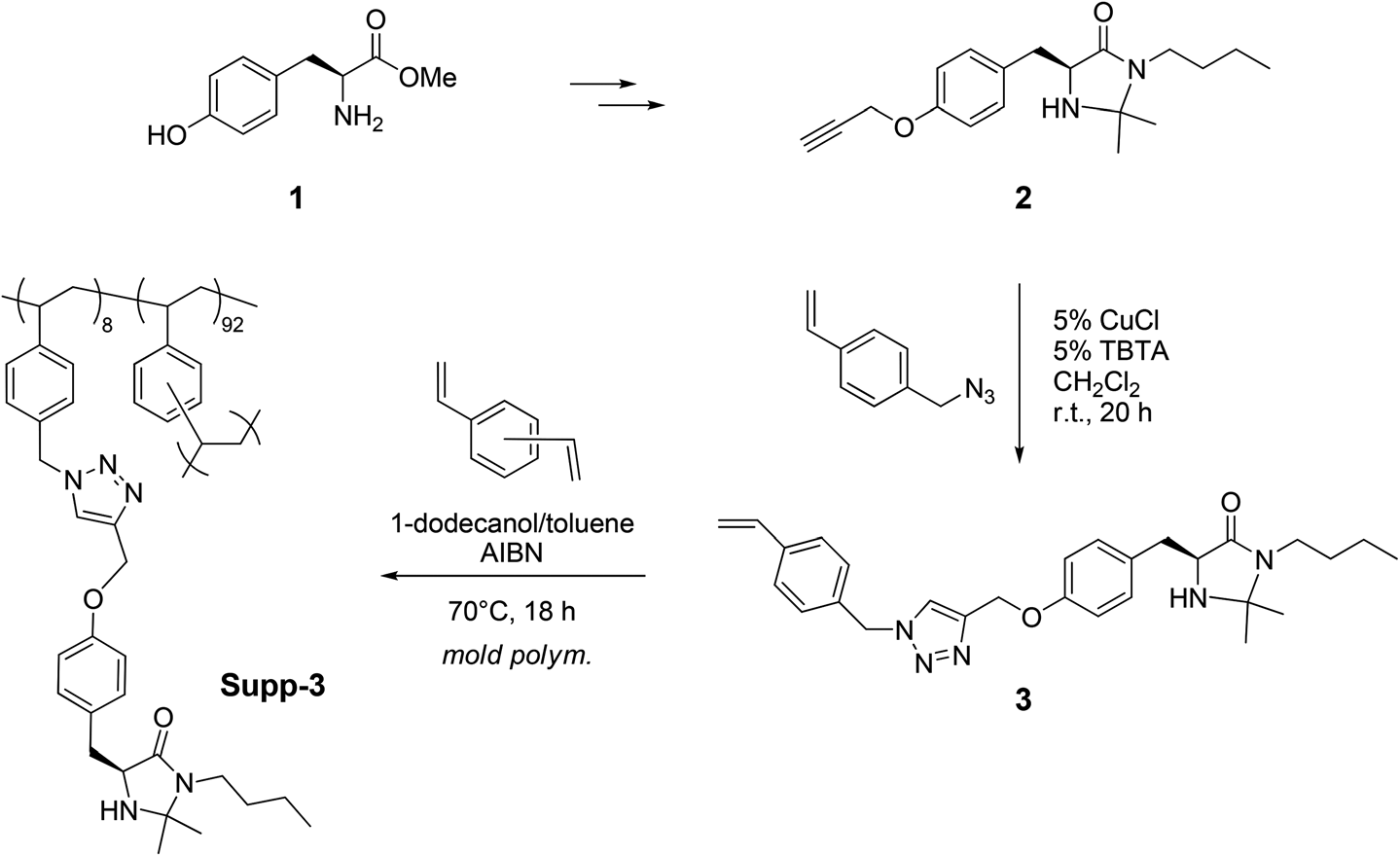
Preparation of the monolithic reactor containing the chiral imidazolidinone catalyst Supp-3.
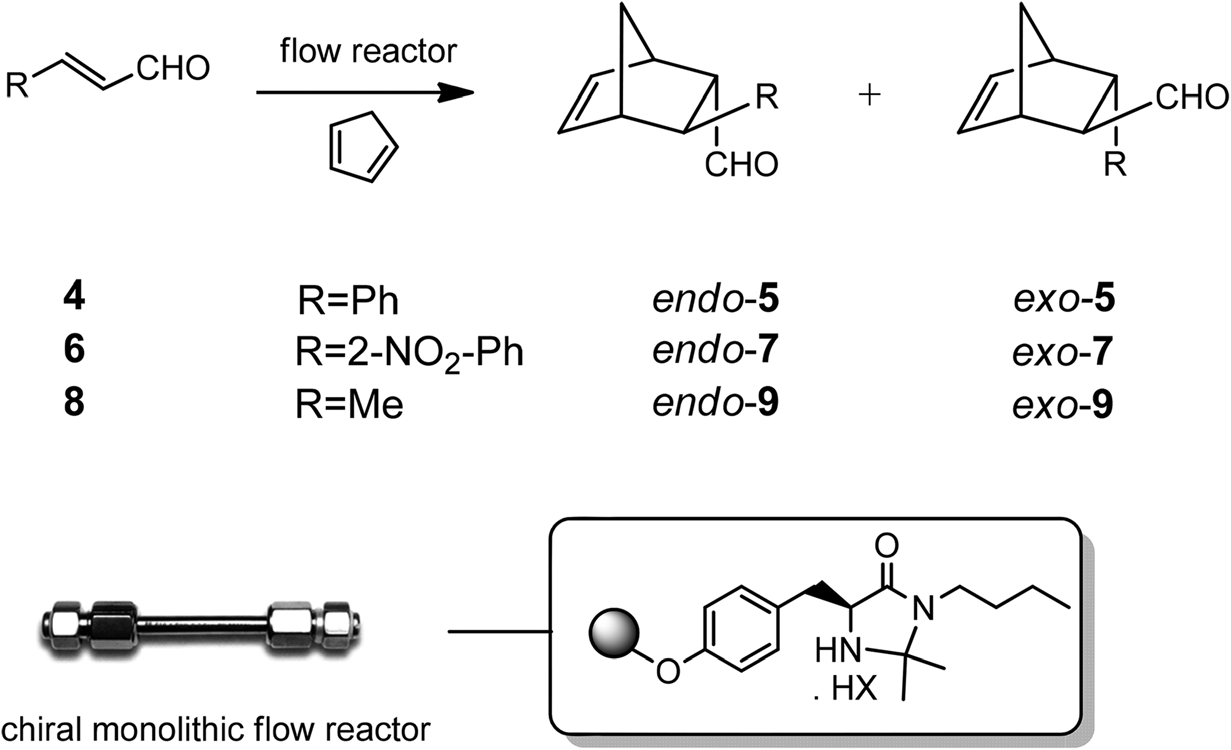
Enantioselective Diels–Alder reactions with different substrates under continuous-flow conditions catalyzed by imidazolidinone supported catalyst Supp-3.
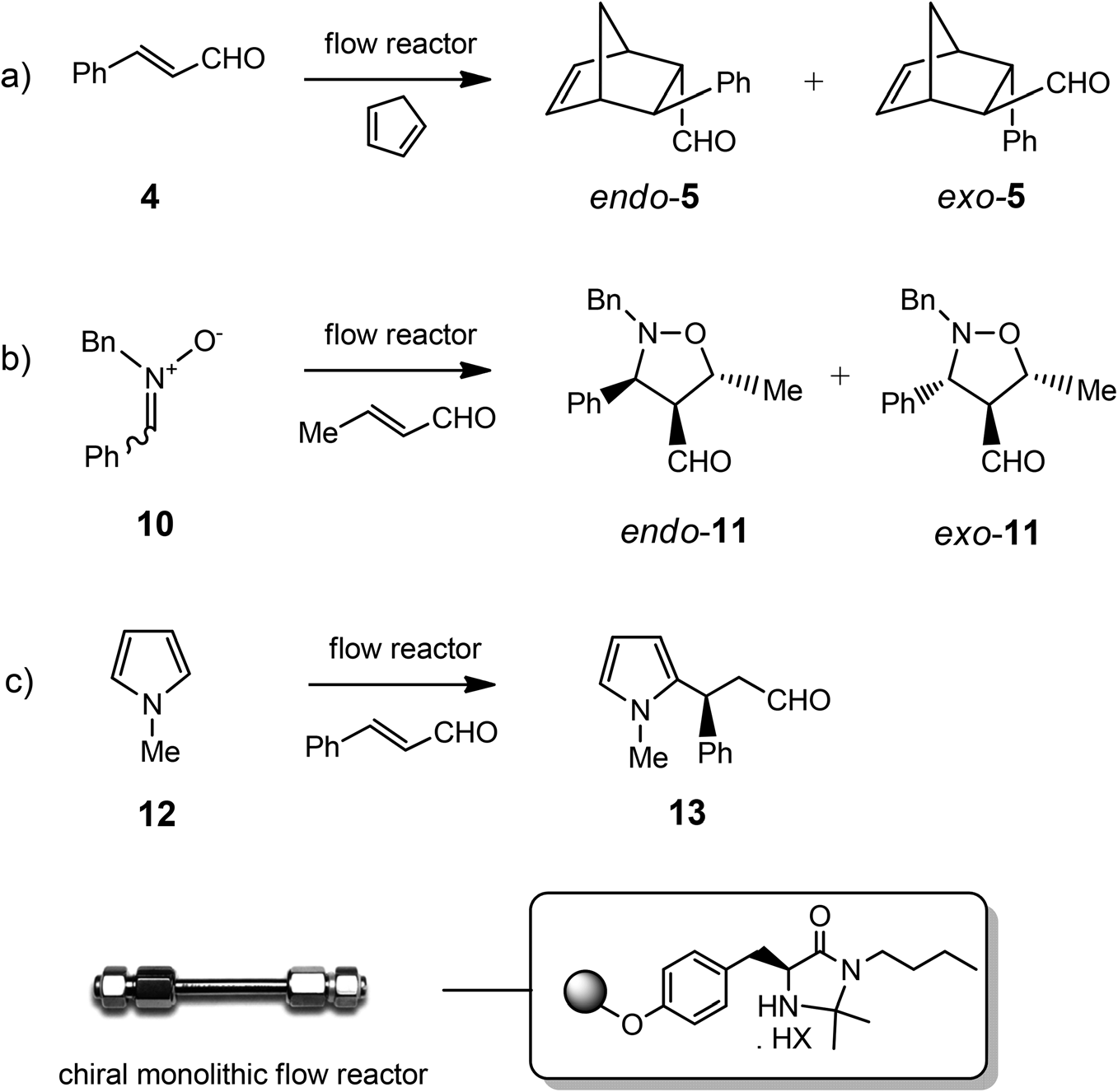
Enantioselective catalytic reactions under continuous-flow conditions with imidazolidinone supported catalyst Supp-3.
CAS number: 120014-06-4
Donepezil is a racemate comprising equimolar amounts of (R)- and (S)-donepezil. A centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, its main therapeutic use is in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease where it is used to increase cortical acetylcholine. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, a nootropic agent and an EC 3.1.1.8 (cholinesterase) inhibitor. It contains a (R)-donepezil and a (S)-donepezil. It is a conjugate base of a donepezil (1+).
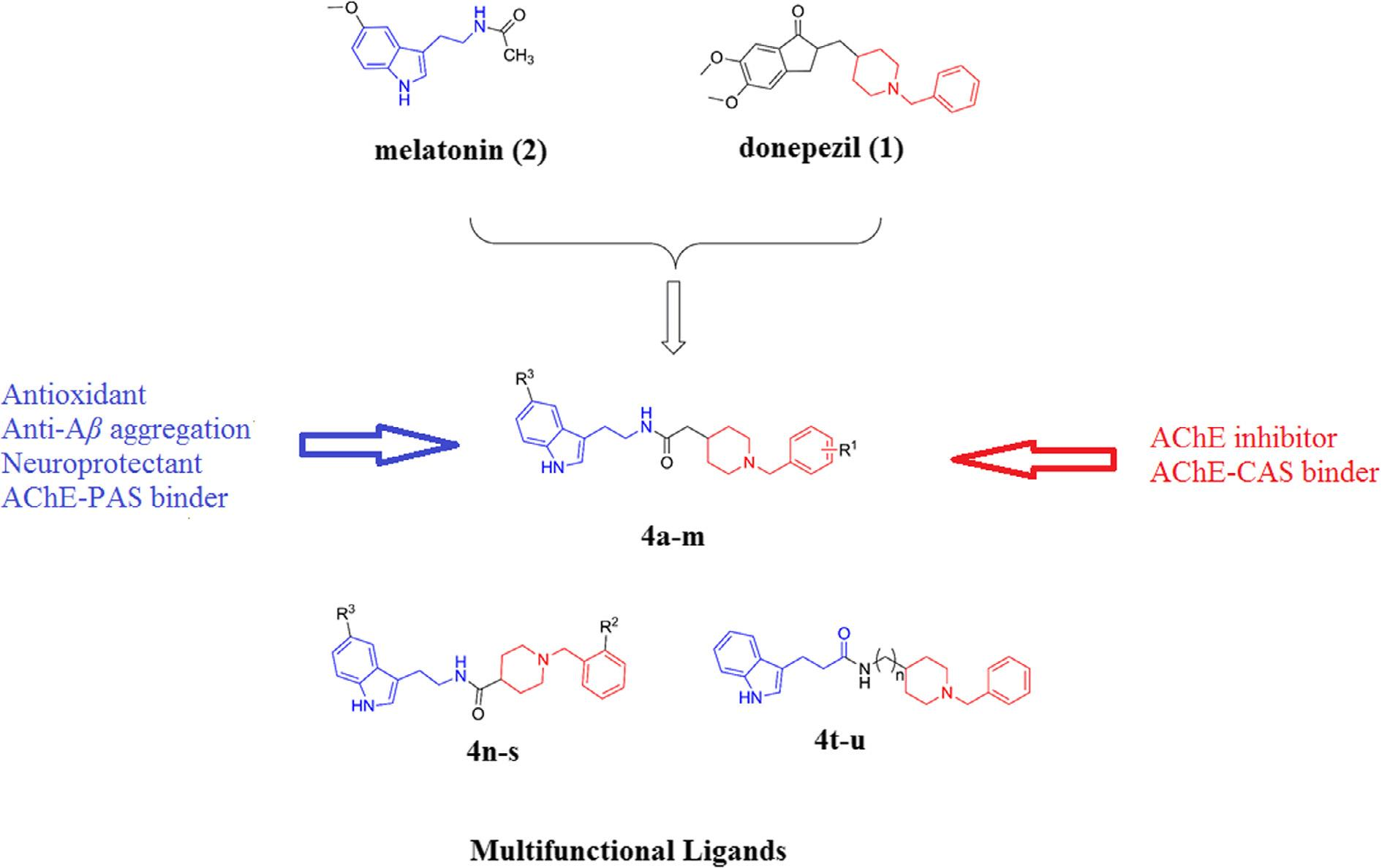
Structure of melatonin, donepezil and donepezil–melatonin hybrids.

Synthesis of donepezil–melatonin hybrids.
CAS number: 120068-37-3
Fipronil is a slow acting poison. When mixed with a bait it allows the poisoned insect time to return to the colony or haborage. In cockroaches the feces and carcass can contain sufficient residual pesticide to kill others in the same nesting site. In ants, the sharing of the bait among colony members assists in the spreading of the poison throughout the colony. With the cascading effect, the projected kill rate is about 95% in 3 days for ants and cockroaches.
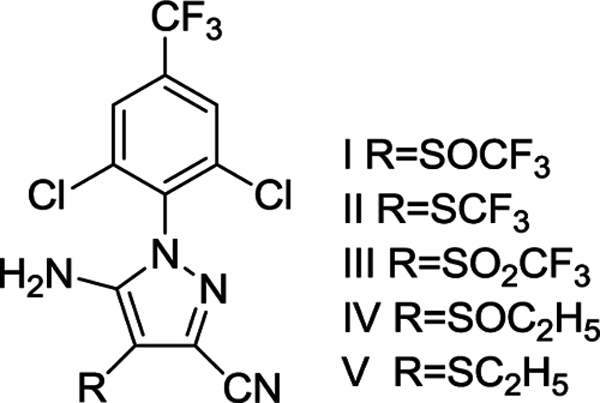
Fipronil (I) and analogs (II, III, IV, V)
CAS number: 121-33-5
Vanillin is a member of the class of benzaldehydes carrying methoxy and hydroxy substituents at positions 3 and 4 respectively. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an anti-inflammatory agent, a flavouring agent, an antioxidant and an anticonvulsant. It is a member of phenols, a monomethoxybenzene and a member of benzaldehydes.
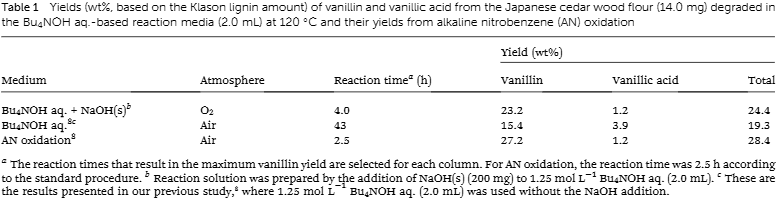
Yields (wt%, based on the Klason lignin amount) of vanillin and vanillic acid from the Japanese cedar wood flour (14.0 mg) degraded in the Bu4NOH aq.-based reaction media (2.0 mL) at 120 ℃ and their yields from alkaline nitrobenzene (AN) oxidation
CAS number: 121-34-6
Vanillic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid that is 4-hydroxybenzoic acid substituted by a methoxy group at position 3. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is a monohydroxybenzoic acid and a methoxybenzoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a vanillate.

Yields (wt%, based on the Klason lignin amount) of vanillin and vanillic acid from the Japanese cedar wood flour (14.0 mg) degraded in the Bu4NOH aq.-based reaction media (2.0 mL) at 120 ℃ and their yields from alkaline nitrobenzene (AN) oxidation
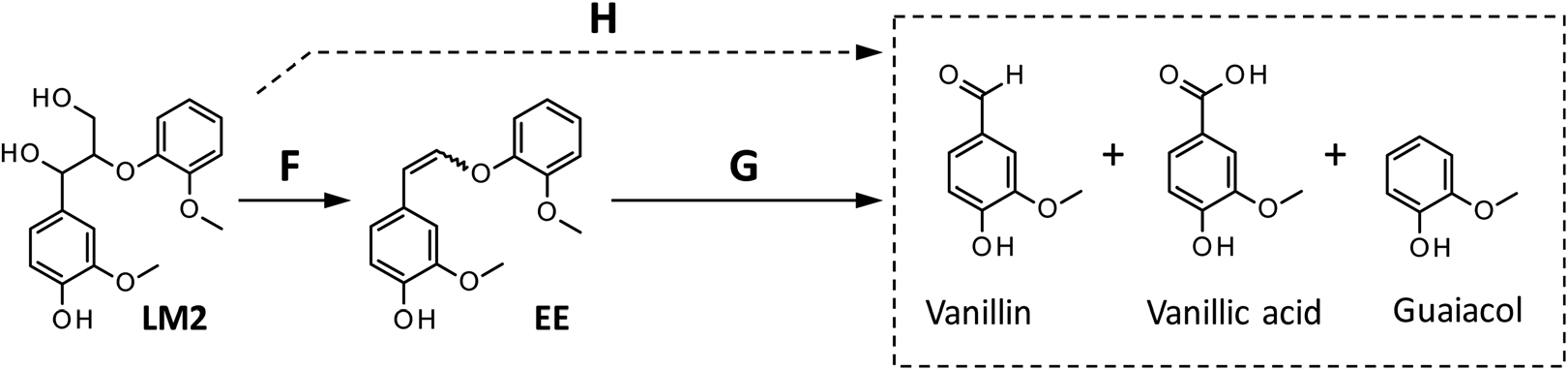
Reaction pathways from Lm2 to the products detected in this study. The formation of vanillic acid via pathway H is less significant than that via pathway G
CAS number: 121-44-8
Et3N is the chemical formula for triethylamine, a colorless, flammable liquid with a strong ammonia-like odor.
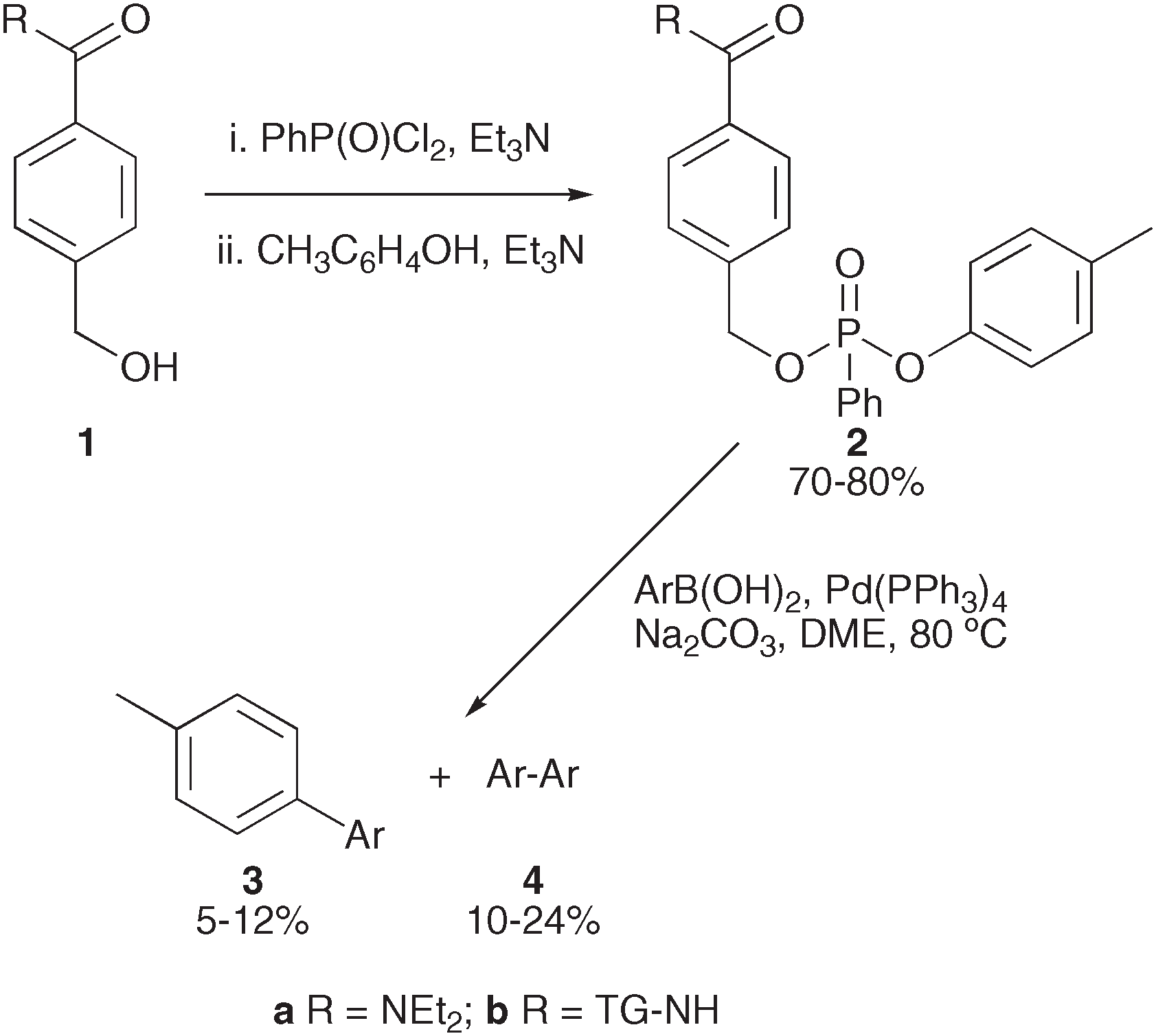
Benzyl alcohol 1a was reacted with 1.25 equivalents of phenylphosphonyl dichloride (PPDC; PhP(O)Cl2) in the presence of triethylamine (Et3N) to afford a mixture of mono- and bis-phosphates. The monosubstituted product was reacted directly with p-cresol without purification to afford the desired phenylphosphonate 2a.
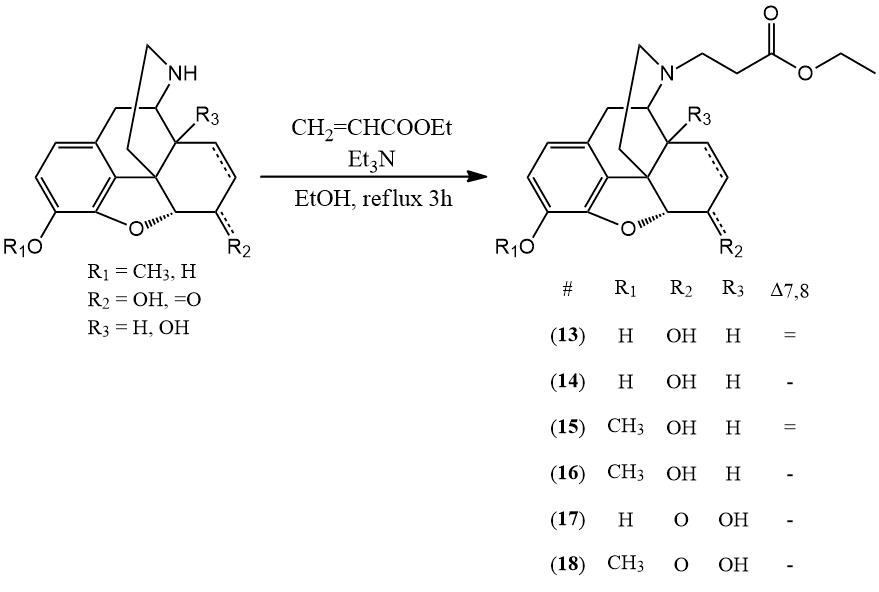
N-alkylation of nor-compounds: ethyl acrylate, triethylamine, ethanol, refl. 3 h.
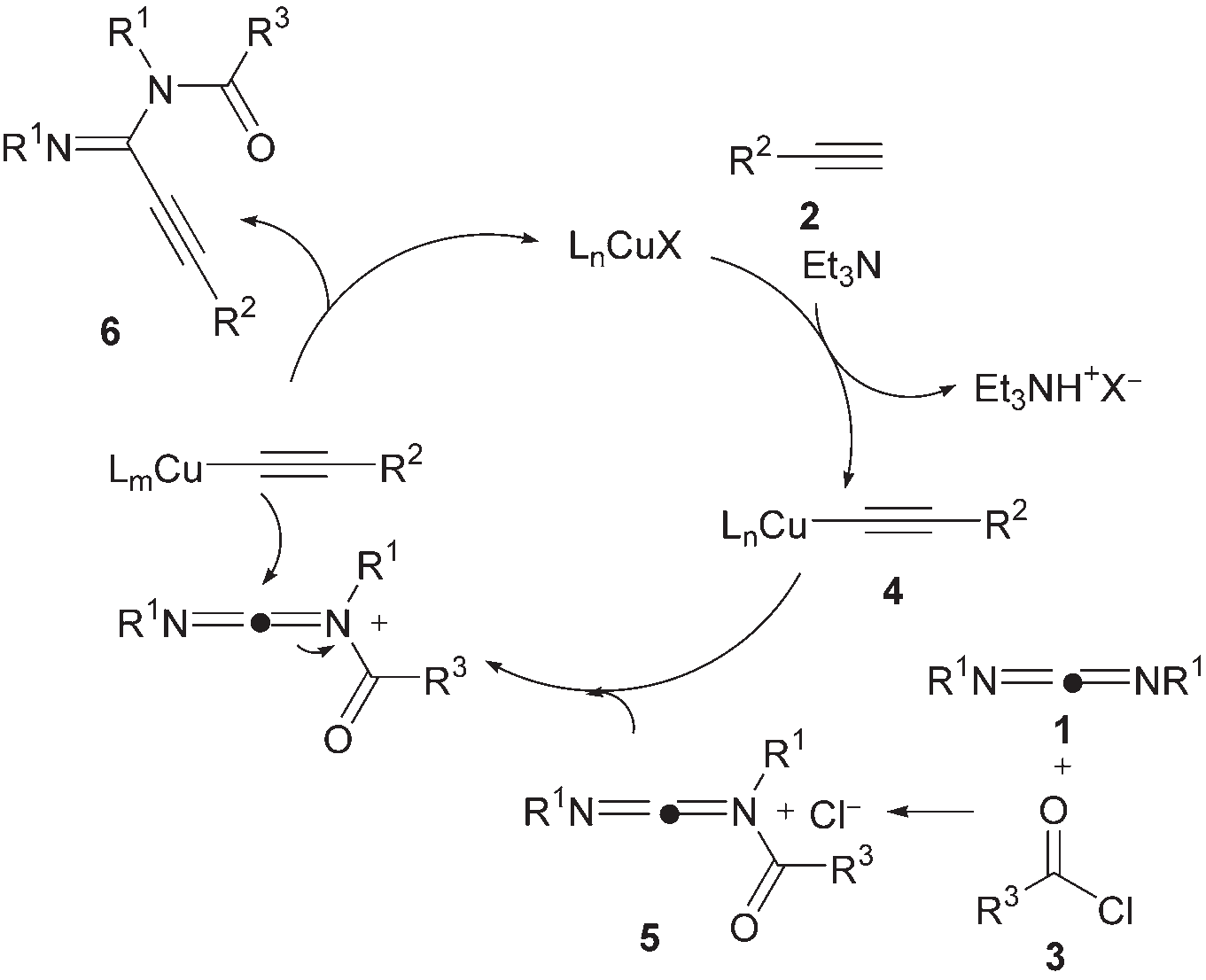
Carbodiimide 1 reacts with acyl chloride 3 to generate N-acylimide salt 5. Alkyne 2 is immediately converted to acetylide copper 4 in the presence of triethylamine, and 1 equivalent of triethylamine acid salt is released. Subsequently, 4 undergoes nucleophilic attack on 5 to obtain the target product 6, and the copper catalyst is released, completing the catalytic cycle.
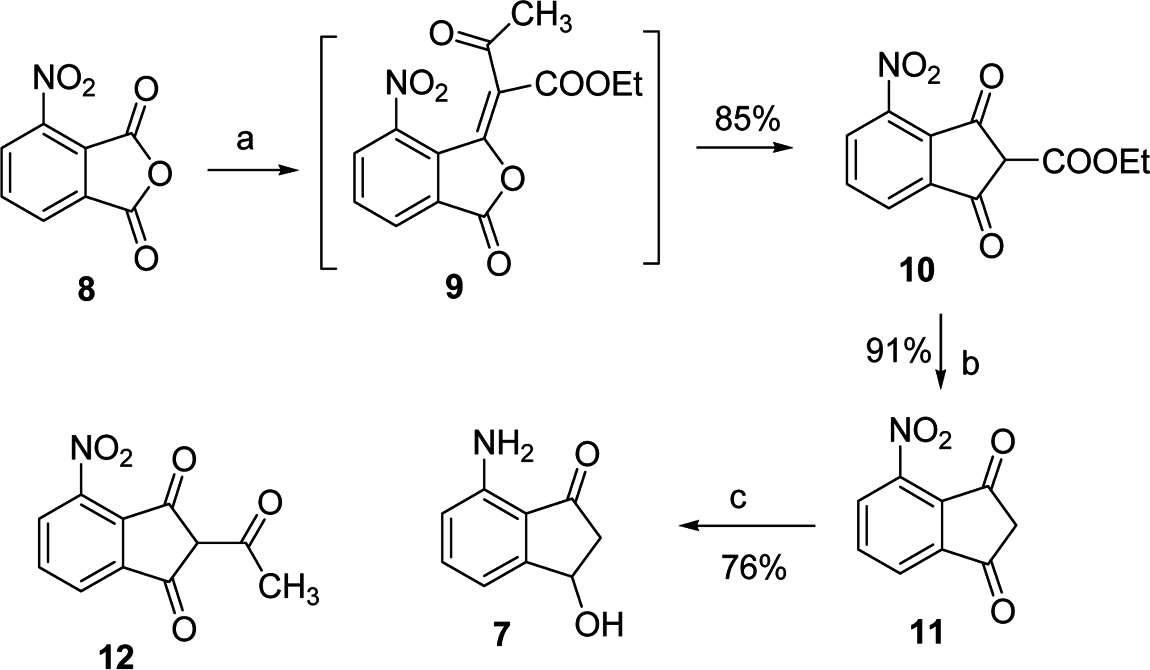
Reagents and conditions: (a) ethyl acetoacetate, acetic anhydride, triethylamine, dichloromethane, room temperature, 30 min; (b) trifluroacetic, acetonitrile, room temperature, 45 min; (c) 40 psi H2, 10% Pd=C, methanol, 24 h.
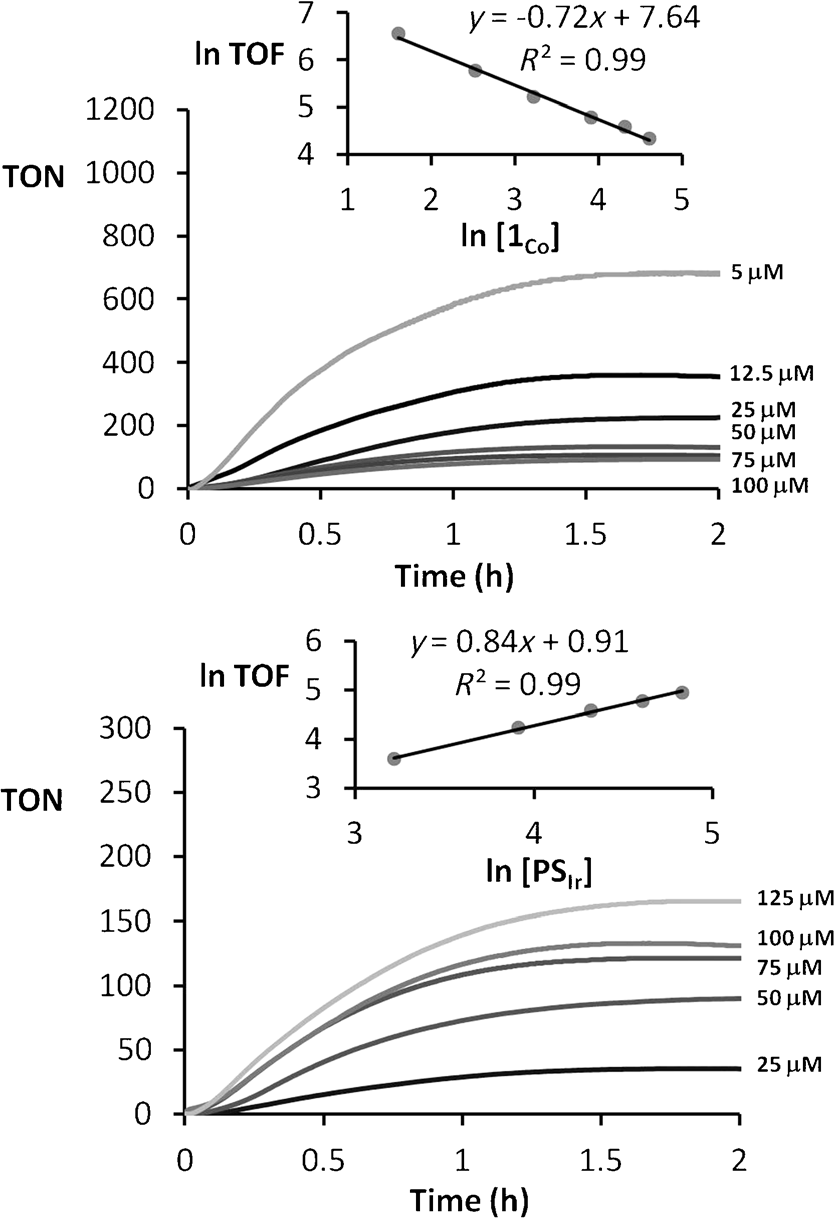
Plots of on-line pressure monitored versus time for reactions using CH3CN/H2O/Et3N (2:8:0.2) as solvent mixture under irradiation at l=447 nm.
CAS number: 121-69-7
N,N-dimethylaniline is a tertiary amine that is aniline in which the amino hydrogens are replaced by two methyl groups. It is a tertiary amine and a dimethylaniline.
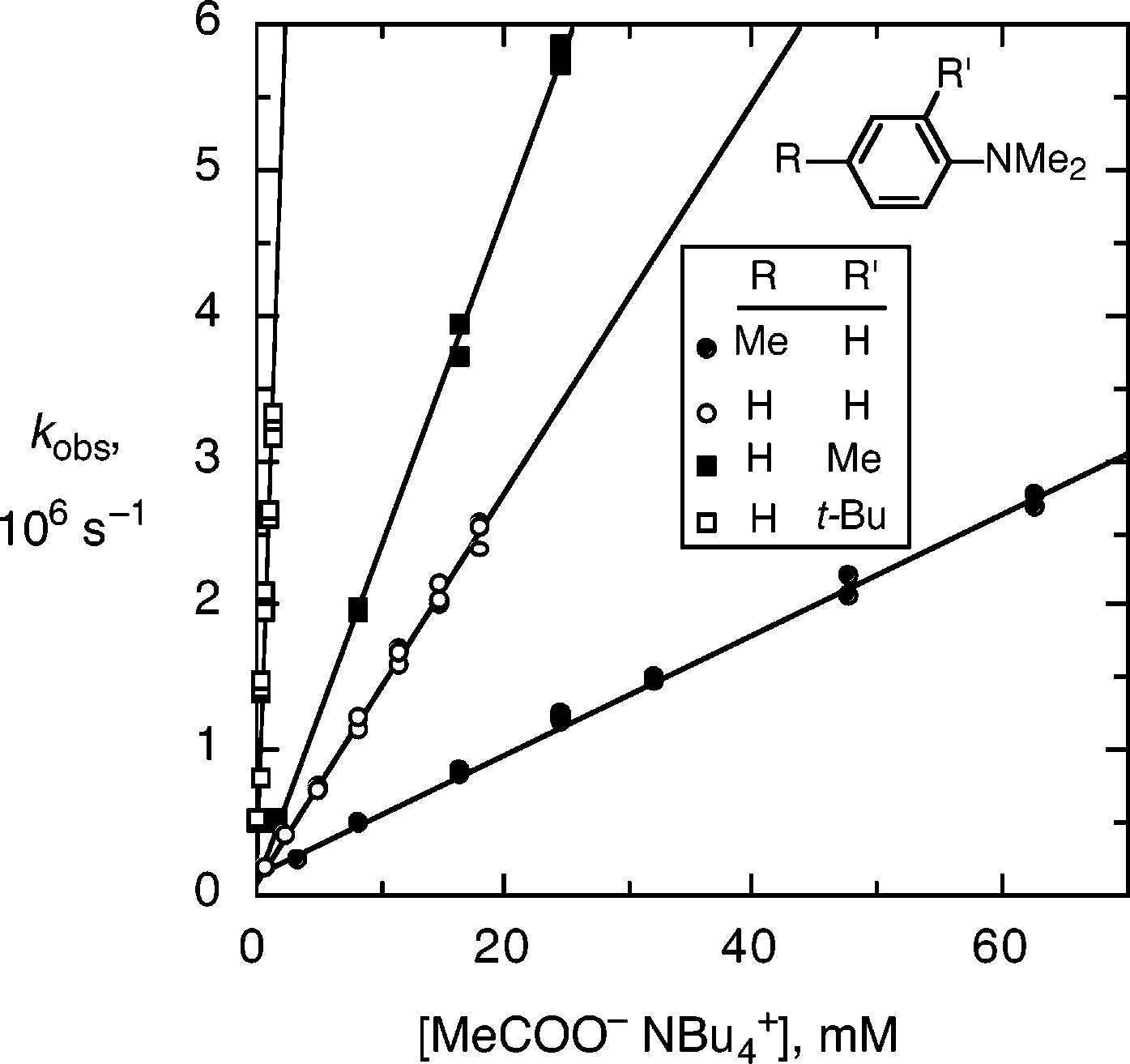
Plots of observed rate of pseudo-first-order decay, kobs, versus concentration of tetrabutylammonium acetate for deprotonation of the radical cations of (open circles) N,N-dimethylaniline, 1c, and N,N,-dimethylaniline with (filled circles) a 4-methyl substituent, 1b, (filled squares) a 2-methyl substituent, 2, and (open squares) a 2-tert-butyl substituent, 3, in acetonitrile with 0.5 m water and 0.5 m tetramethylammonium perchlorate, at room temperature.
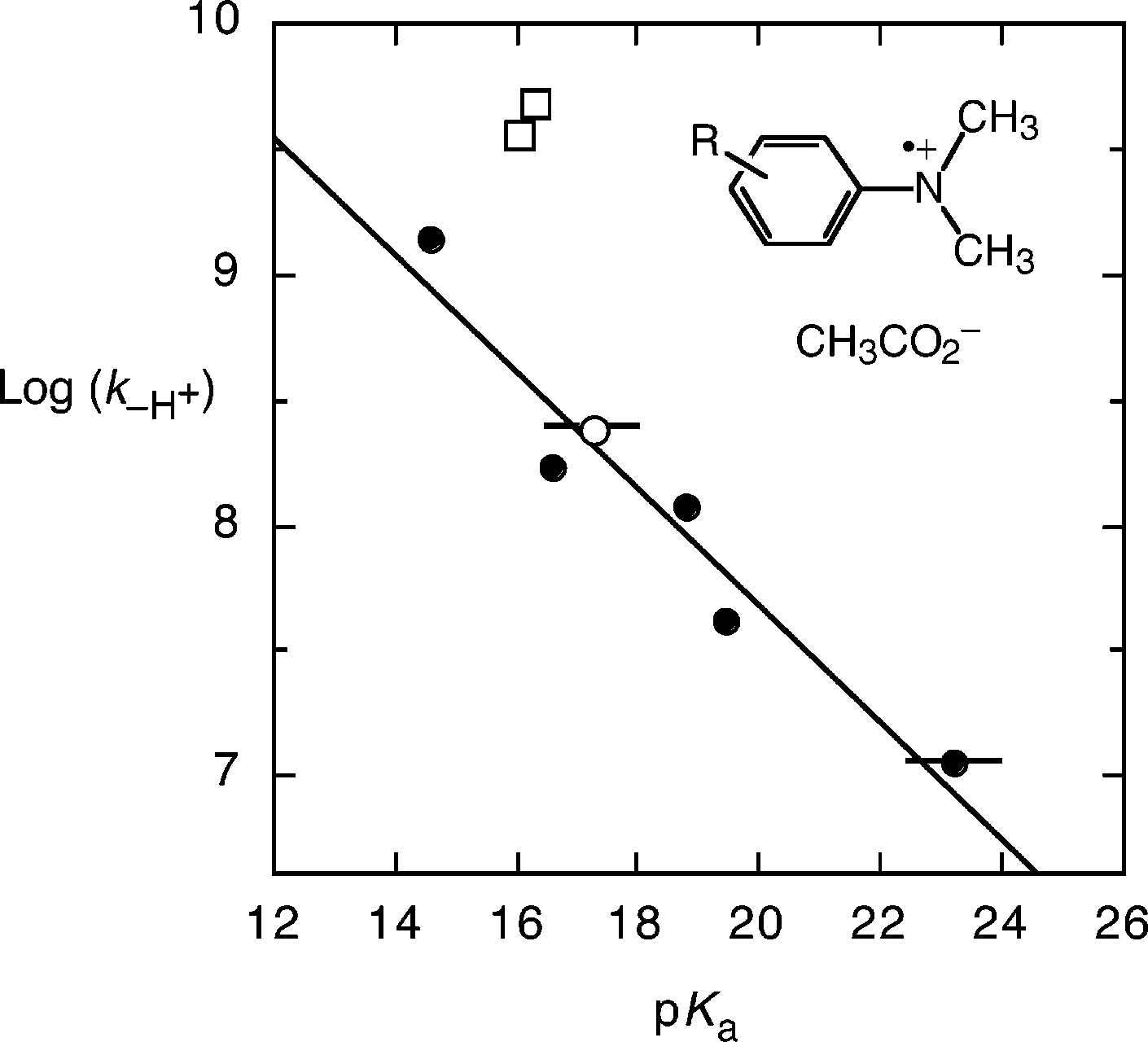
Brønsted plot of the logarithm of the bimolecular rate constant for deprotonation of the radical cations of N,N-dimethylaniline derivatives: (closed circles) 4-substituted-N,N-dimethylanilines, 1a-1e; (open circle) N,N,2-trimethylaniline, 2; (open squares) 2-tert-butyl-N,N-dimethylaniline, 3; and N,N,2,6-tetramethylaniline, 4.
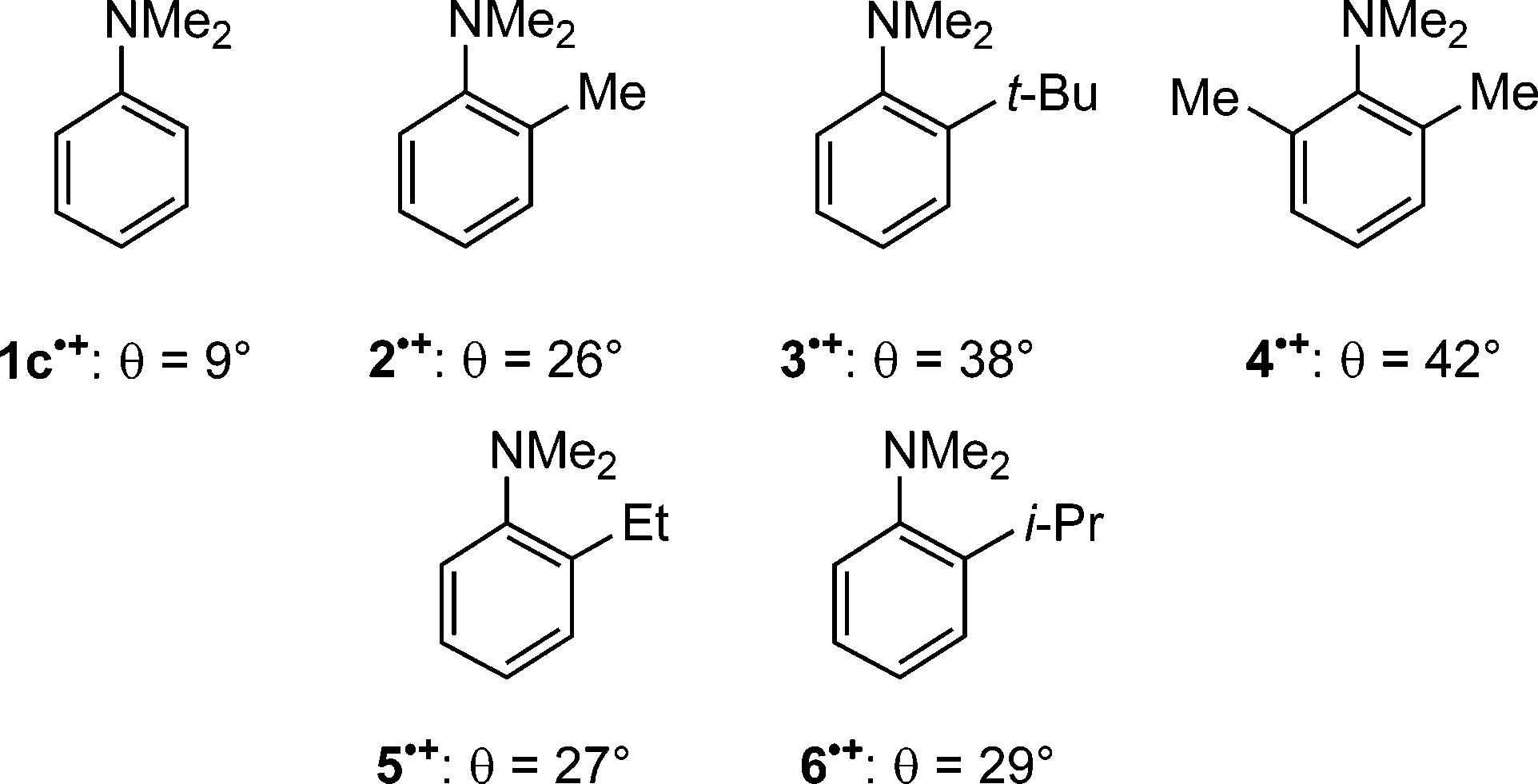
Structures of Sterically Twisted N,N-Dimethylaniline Radical Cations, and the Dihedral Angles between the Planes Containing the Aromatic Ring and the Amino Nitrogen, θ.
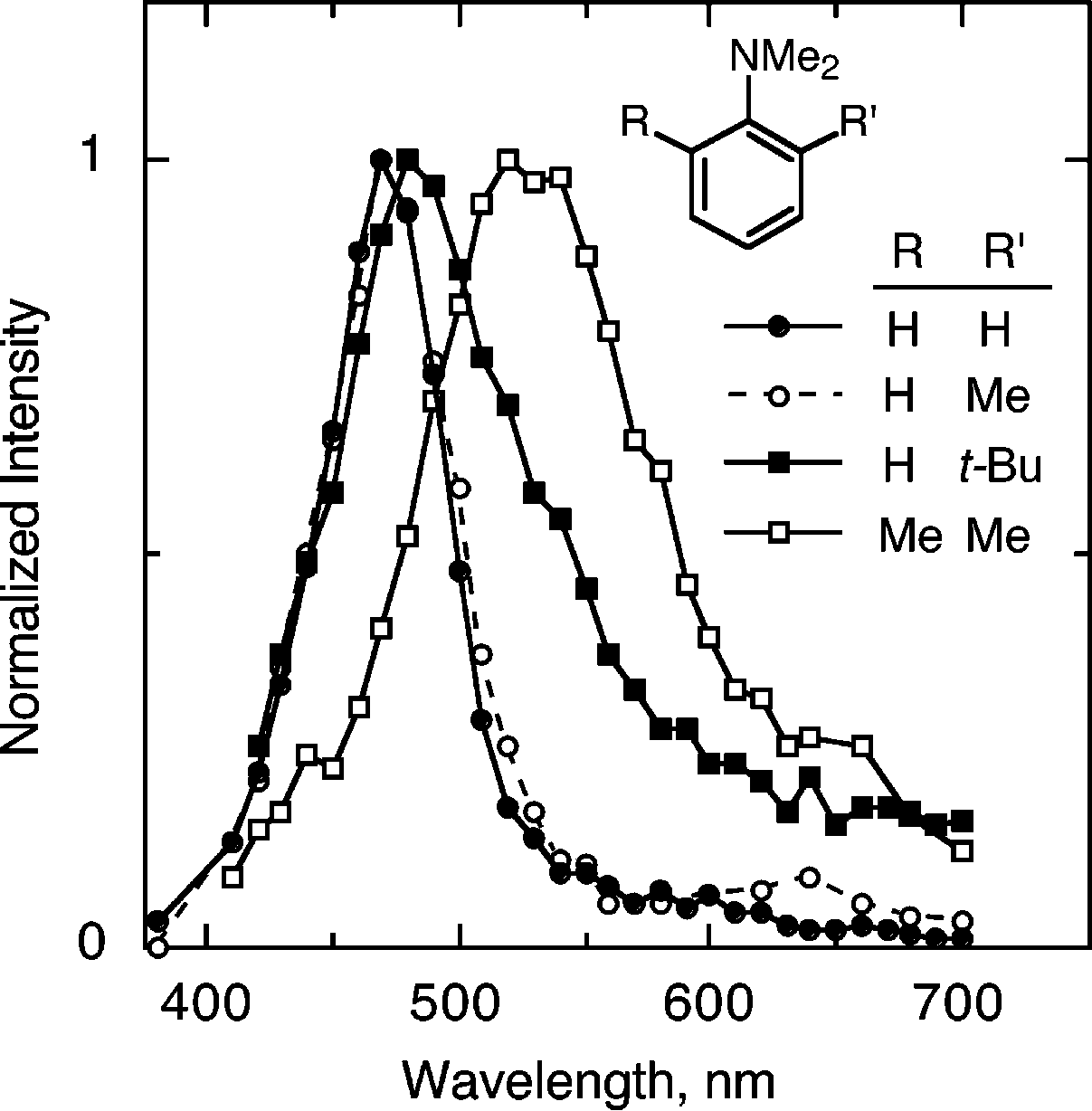
Absorption spectra of the radical cations of (closed circles) N,N-dimethylaniline, 1c, and N,N,-dimethylaniline with (open circles) a 2-methyl substituent, 2, (closed squares) a 2-tert-butyl substituent, 3, and (open squares) 2,6-dimethyl substituents, 4, in acetonitrile containing 0.5 m water and 0.5 m tetrabutylammonium perchlorate, at room temperature.
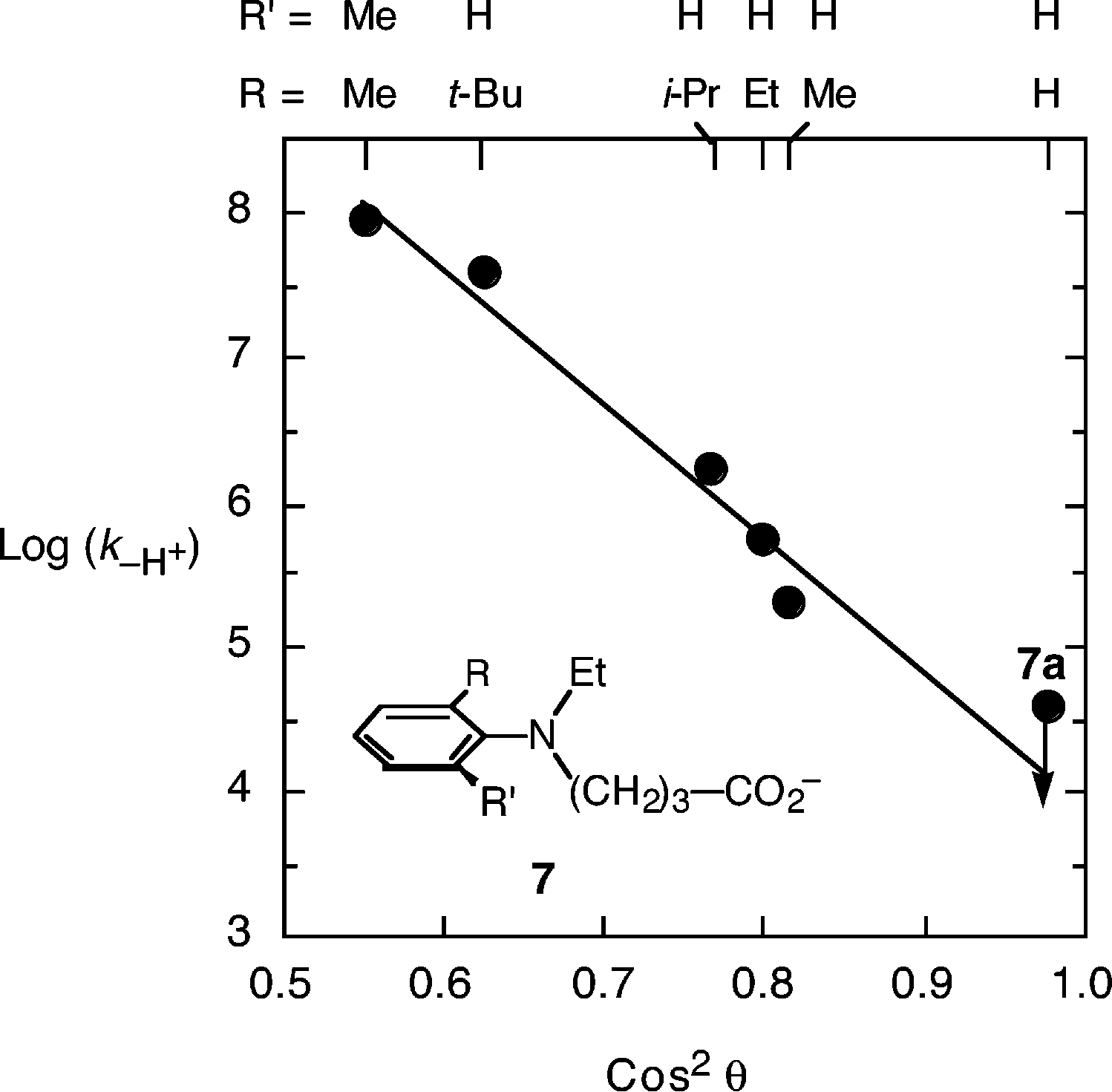
Plot of the logarithm of the rate constant for unimolecular deprotonation (log(k-H )) versus the cosine squared of the dihedral angle θ, for the simple dimethylanilines, assumed to be appropriate for the intramolecular deprotonating anilines here.