Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 124-41-4
Sodium methylate is a white amorphous powder. It reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide, a corrosive material, and methyl alcohol, a flammable liquid. The heat from this reaction may be sufficient to ignite surrounding combustible material or the sodium methylate itself if the water is present in only small amounts. It is used to process edible fats and oils, and to make other chemicals.
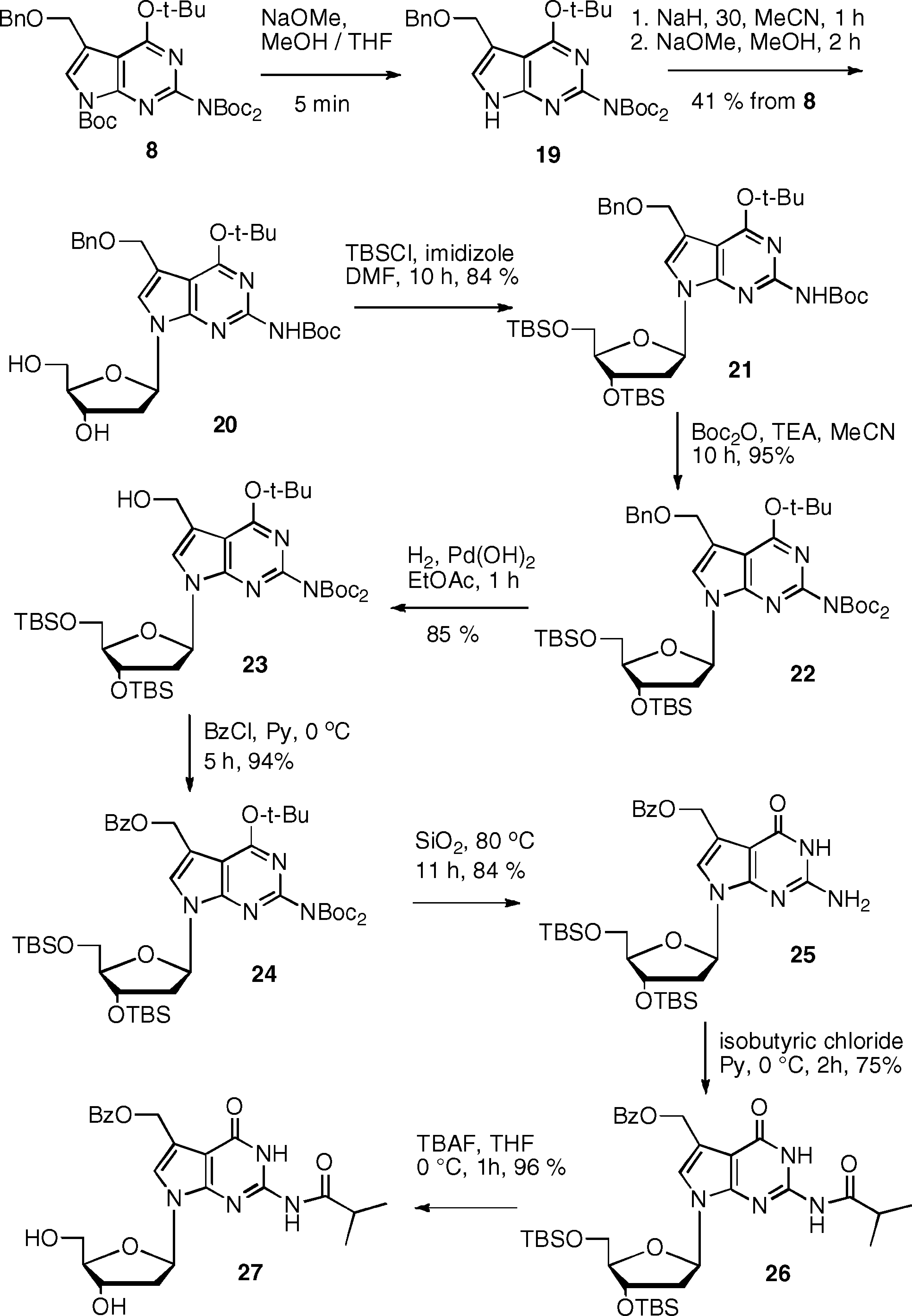
The conversion of 8 to the deoxynucleoside 27 involved its coupling to the chlorosugar after selective removal of the N7-Boc group with NaOMe (Scheme 4).
CAS number: 124505-87-9
Pentosidine is an advanced glycosylation end product and protein cross-link that results from the reaction of pentoses with proteins.
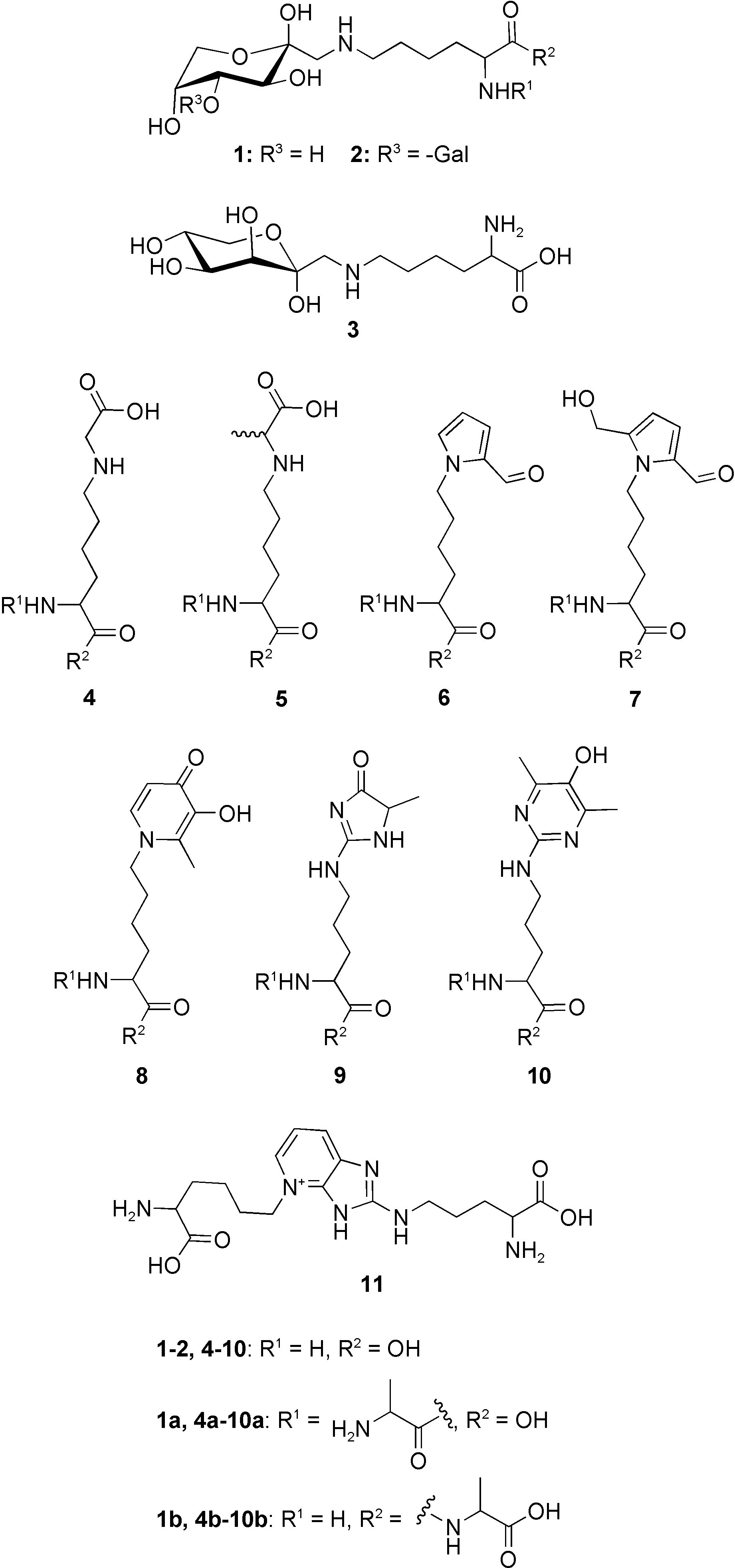
Chemical structures of the investigated Maillard reaction prod- ucts fructoselysine (1), lactuloselysine (2), tagatoselysine (3), CML (4), CEL (5), formyline (6), pyrraline (7), maltosine (8), MG-H1 (9), argpyrimidine (10), and pentosidine (11).
CAS number: 124721-15-9
Artonin A is a member of pyranoxanthones.
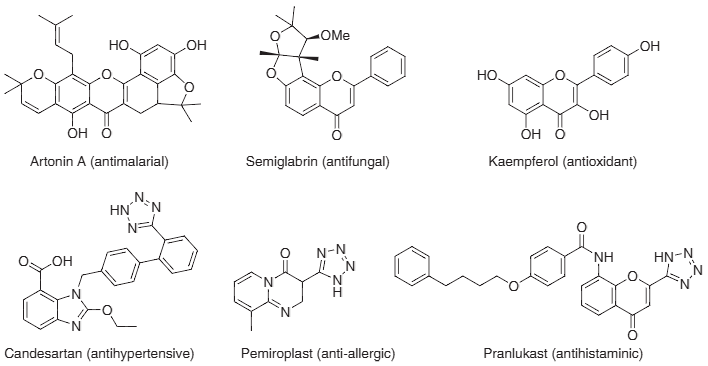
Naturally occurring flavones and pharmacologically important tetrazole drugs: Artonin A, Semiglabrin, Kaempferol, Candesartan, Pemiroplast, Pranlukast.
CAS number: 124843-18-1
Pectenotoxin 6 (PTX6) is a marine toxin, specifically a pectenotoxin, that is produced by certain dinoflagellate algae. It's a polyether macrolide and a structural analog of pectenotoxin-2 (PTX2). PTX6 is found in shellfish and has been associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP). While not inducing diarrhea in mice when administered orally, it has been shown to cause toxicity when injected intraperitoneally and when administered orally to rats.
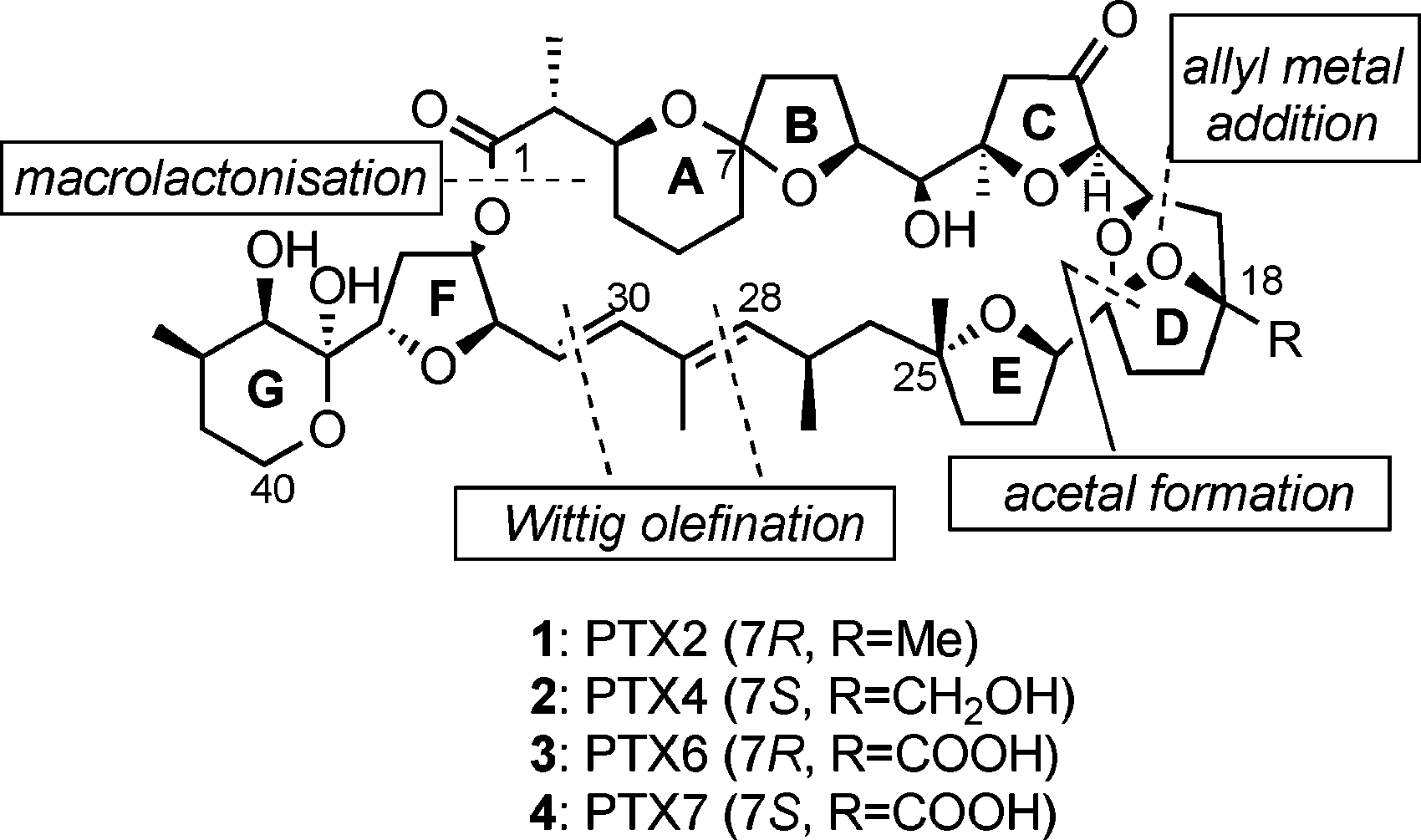
Structure of PTXs and the principal disconnections used for the synthesis of PTXs: Pectenotoxin 2, pectenotoxin 4, pectenotoxin 6, pectenotoxin 7.

Structure of PTXs and the principal disconnections used for the synthesis of PTXs: Pectenotoxin 2, pectenotoxin 4, pectenotoxin 6, pectenotoxin 7.
CAS number: 125-65-5
Pleuromutilin is a diterpenoid antibiotic derived from the fungus Clitopilus (formerly Pleurotus). It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by targeting the 50S ribosomal subunit, specifically interfering with peptide bond formation. Pleuromutilins are used to treat various bacterial infections, including community-acquired pneumonia and skin infections like impetigo.
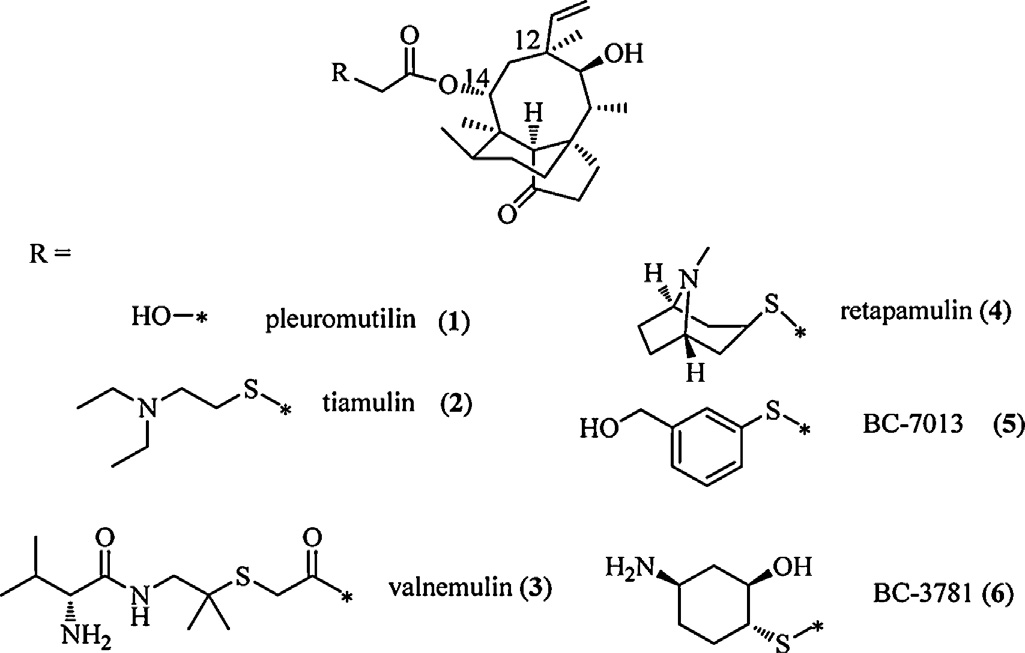
Structures of pleuromutilin and its derivatives.
CAS number: 125287-06-1
Achilleol A is a triterpenoid that is (1S)-2,2-dimethyl-4-methylidenecyclohexanol which is substituted at position 3 by a (6E,10E,14E)-2,6,10,15-tetramethylheptadeca-2,6,10,14-tetraen-17-yl group. It was the first monocyclic triterpenoid found in nature and originally isolated from Achillea odorata.
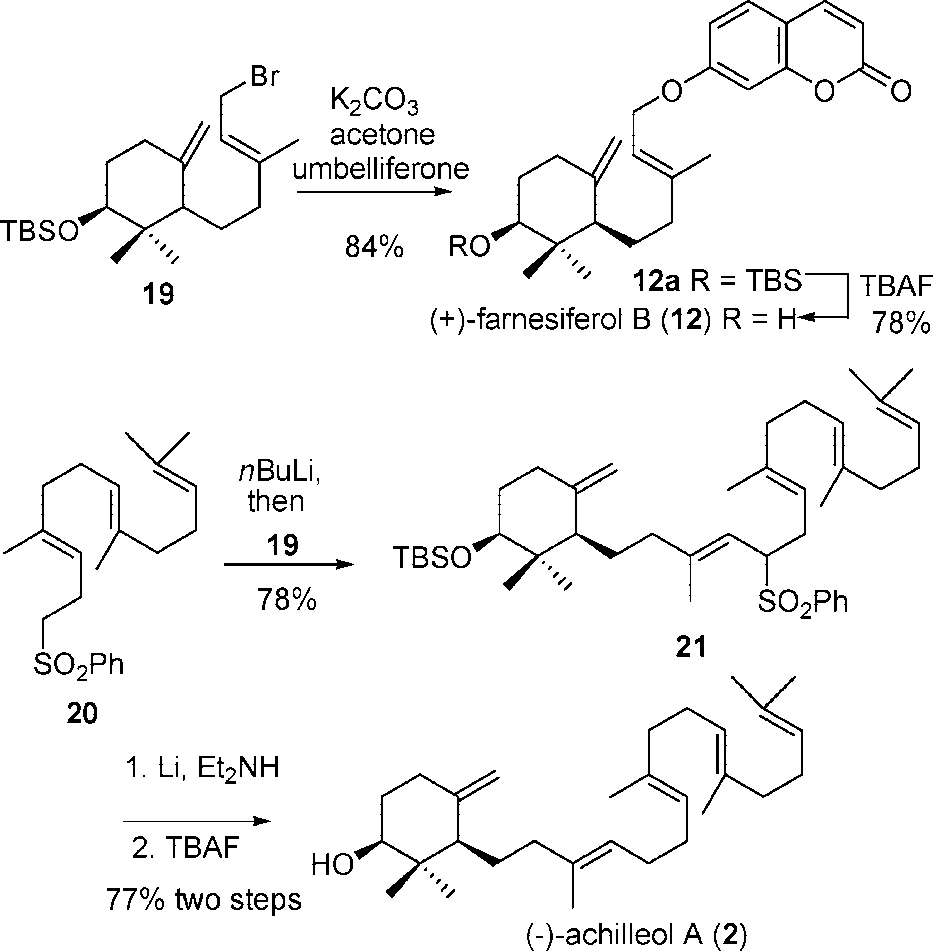
Enantioselective Synthesis of (-)-Achilleol A and (+)-Farnesiferol B
CAS number: 125343-14-8
Triterpenes are defined as a major category of secondary metabolites that consist of 30 carbon atoms arranged in six isoprene units, derived from the squalene synthesis pathway. They can be transformed into various compounds, including alcohols, aldehydes, carboxyl acids, and saponins (triterpene glycosides).
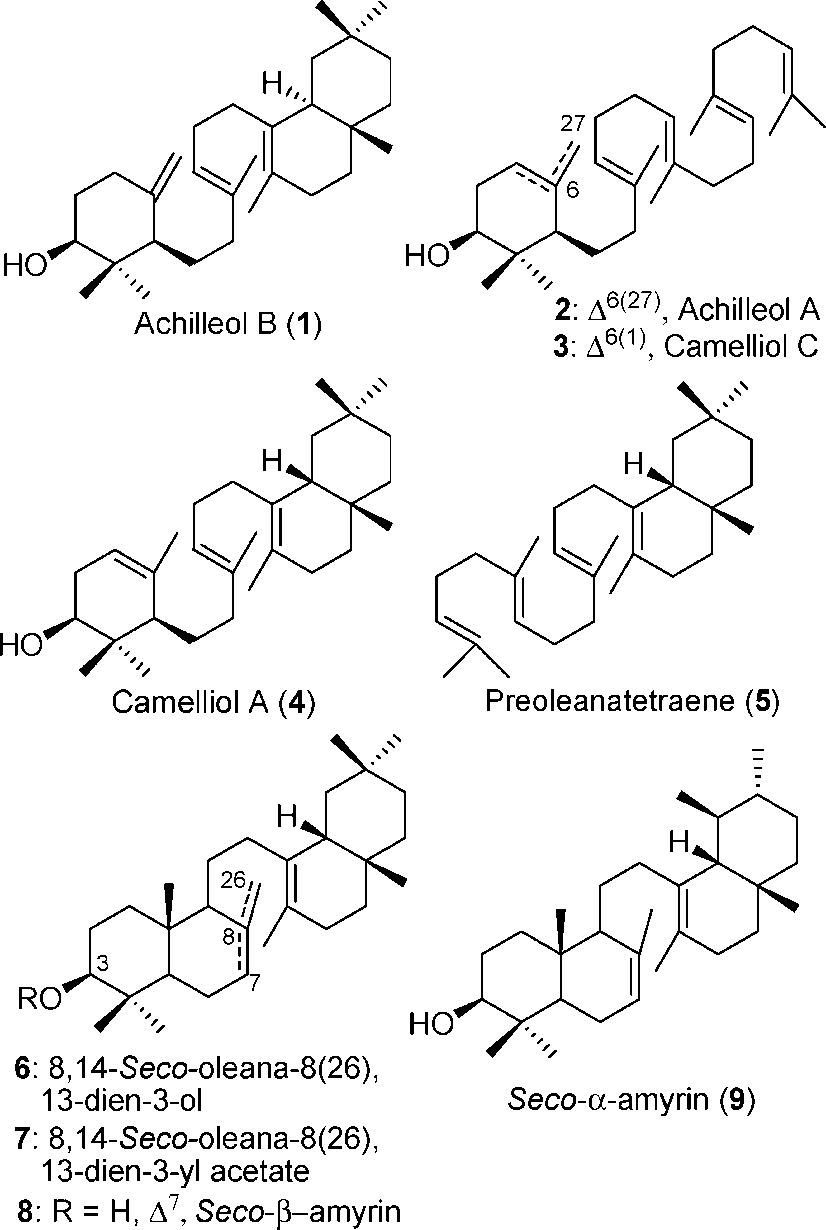
Irregular triterpenes.
CAS number: 126-81-8
Dimedone (DIM) has been introduced as a new chemical compound with anti-bacterial and anti-cancer properties.
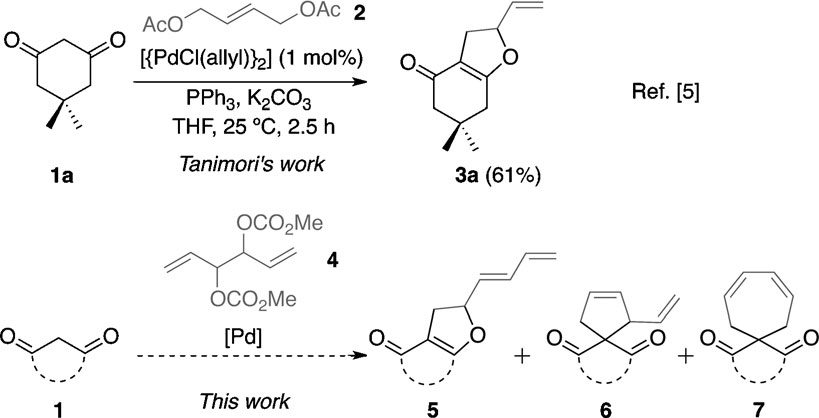
The preparation of vinyldihydrofuran 3a through a palladium-mediated bisalkylation of dimedone 1a using the symmetrical allylic diacetate 2.
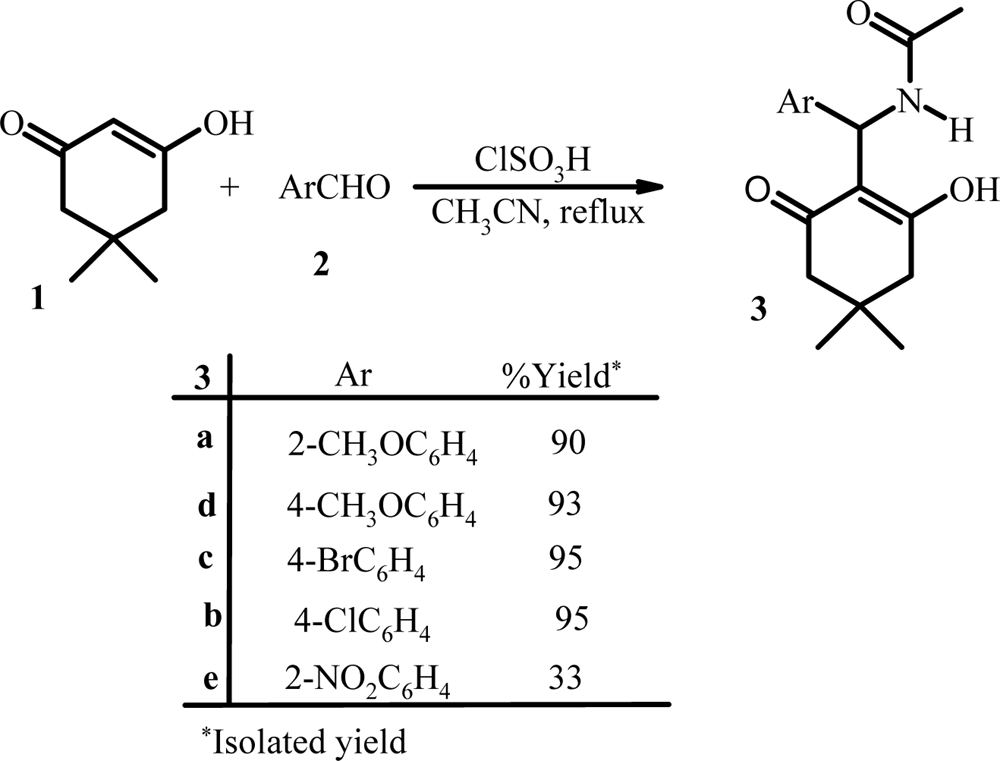
Three-component reaction of dimedon, aromatic aldehydes, and acetonitrile.
CAS number: 1260907-17-2
Molibresib is under investigation in clinical trial NCT01943851 (A Dose Escalation Study to Investigate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics (PK), Pharmacodynamics (PD) and Clinical Activity of GSK525762 in Subjects With Relapsed, Refractory Hematologic Malignancies).
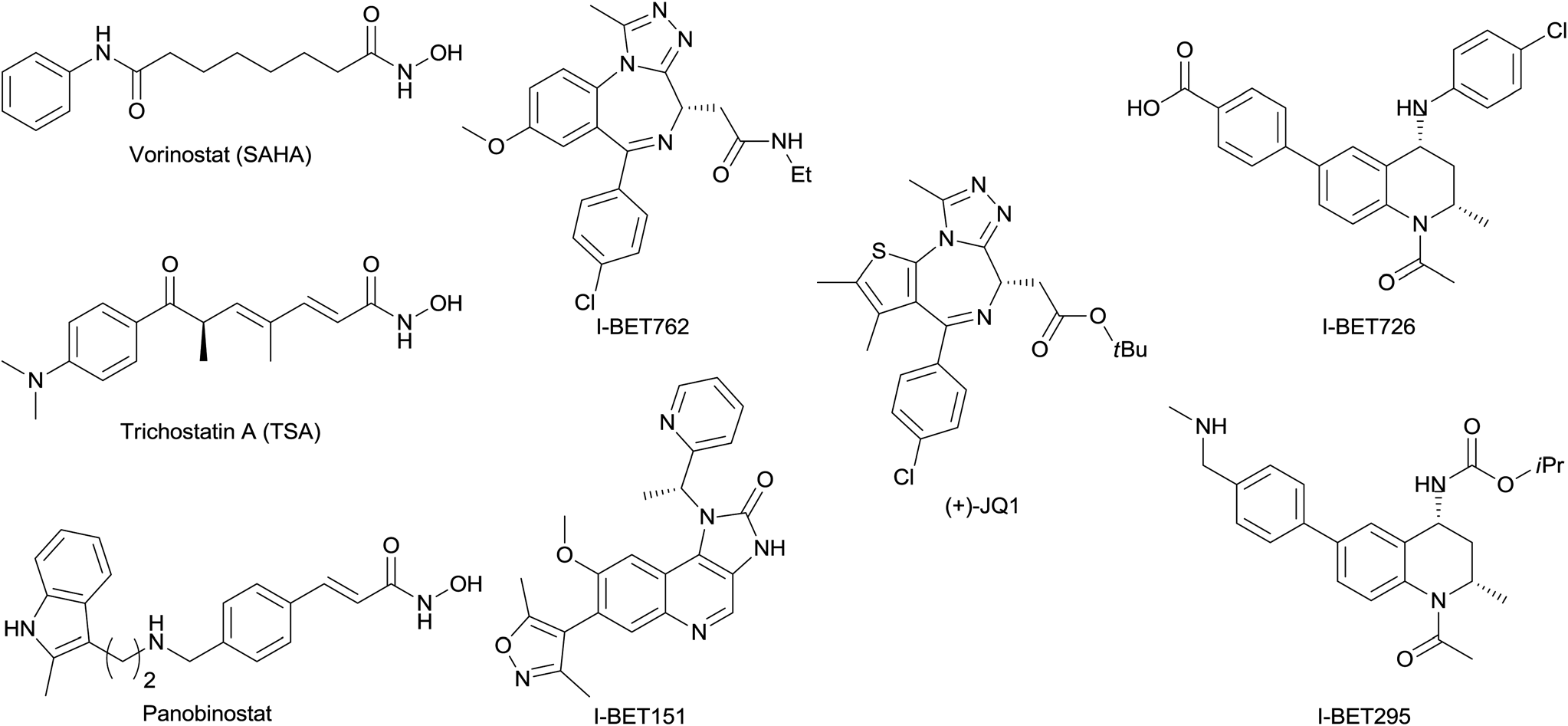
Structures of selected published BET inhibitors and selected hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitors.
CAS number: 1261171-52-1
mGluR5 modulator 1 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5). This means it enhances the effects of the neurotransmitter glutamate at the mGluR5 receptor. It's primarily being researched for its potential in treating schizophrenia and cognitive impairments.
![Autoradiography on horizontal rat brain slices, indicating heterogeneous distribution of activity with highest uptake in mGluR5-rich regions. The first and second rows represent application of 1 and 10 nM [18F]-16, respectively, and the first and second column represent baseline and blocking conditions, respectively.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5367115_16.png)
Autoradiography on horizontal rat brain slices, indicating heterogeneous distribution of activity with highest uptake in mGluR5-rich regions. The first and second rows represent application of 1 and 10 nM [18F]-16, respectively, and the first and second column represent baseline and blocking conditions, respectively.