Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 123-77-3
Azodicarbonamide appears as a yellow to orange powder. Insoluble in water and common solvents. Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide. Nontoxic. It is a chemical substance approved for use as a whitening agent in cereal flour and as a dough conditioner in bread baking.
![Synthesis of Azodicarboxamide [2]Rotaxanes 3 and 4 and Their Corresponding Hydrazodicarboxamide [2]Rotaxanes [2H]-3 and [2H]-4](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5381702_03.png)
Synthesis of Azodicarboxamide [2]Rotaxanes 3 and 4 and Their Corresponding Hydrazodicarboxamide [2]Rotaxanes [2H]-3 and [2H]-4
![1H NMR spectra (400 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K) of (a) azodicarboxamide thread 2, (b) azodicarboxamide rotaxane 4, (c) hydrazodicar-boxamide thread [2H]-2, and (d) hydrazodicarboxamide rotaxane [2H]-4.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5381702_04.png)
1H NMR spectra (400 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K) of (a) azodicarboxamide thread 2, (b) azodicarboxamide rotaxane 4, (c) hydrazodicar-boxamide thread [2H]-2, and (d) hydrazodicarboxamide rotaxane [2H]-4.
![Synthesis of Bistable Molecular Shuttles Based on Azodicarboxamide Binding Sites 7 and 8 and Their Corresponding 1,2-Hydrazodicarboxamides [2H]-7 and [2H]-8](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5381702_08.png)
Synthesis of Bistable Molecular Shuttles Based on Azodicarboxamide Binding Sites 7 and 8 and Their Corresponding 1,2-Hydrazodicarboxamides [2H]-7 and [2H]-8
CAS number: 123-78-4
Sphingosine is a sphing-4-enine in which the double bond is trans. It has a role as a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a sphingosine(1+). It is an enantiomer of a L-erythro-sphingosine.
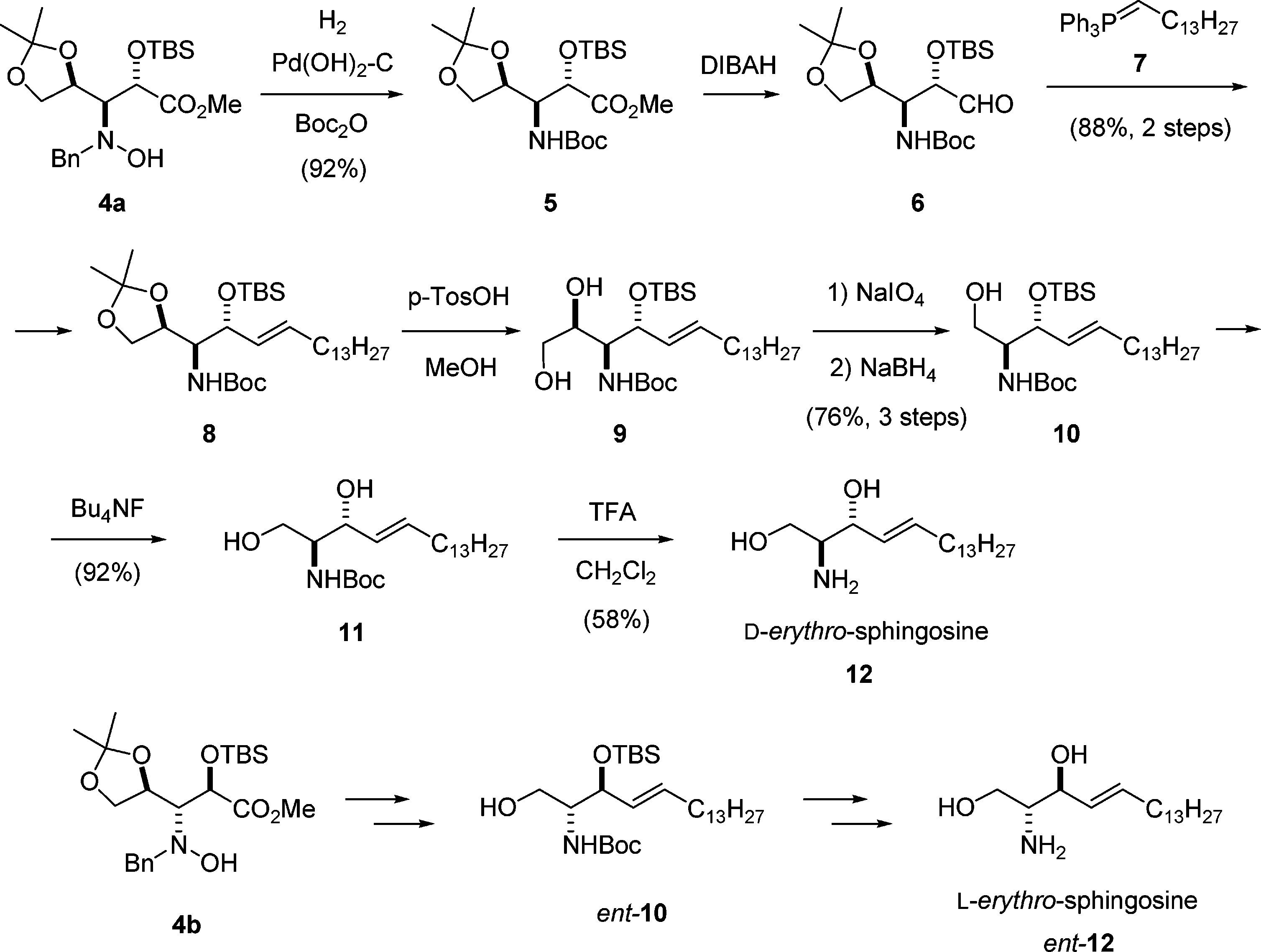
Synthesis of Sphingosines
CAS number: 123-90-0
Thiomorpholine, HN(CH2)4S, is a heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen and sulfur. It can be considered a thio analog of morpholine.
Analysis of the thiomorpholine binding site can serve as a template for the design of novel bioactive MCR scaffolds, the thiomorpholines reported herein.
CAS number: 123-91-1
1,4-Dioxane is a likely human carcinogen and has been found in groundwater at sites throughout the United States. 1,4-Dioxane is a clear liquid that easily dissolves in water. It is used primarily as a solvent in the manufacture of chemicals and as a laboratory reagent.
![O-Arylation of 3-phenylpropanol (1a) and phenol (1ab) by triarylsulfonium triflates in the presence of CsOH.[a] [a] Reaction conditions: 1a or 1ab (0.2 mmol), 2 (0.3 mmol), CsOH (0.3 mmol), 1,4-dioxane (2 mL), 508C, N2, 24 h. Isolated yield. [b] Toluene (2 mL) as solvent and at 808C. [c] 808C. [d] 0.4 mmol scale (1ab).](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/1296374_13.png)
O-Arylation of 3-phenylpropanol (1a) and phenol (1ab) by triarylsulfonium triflates in the presence of CsOH.[a] [a] Reaction conditions: 1a or 1ab (0.2 mmol), 2 (0.3 mmol), CsOH (0.3 mmol), 1,4-dioxane (2 mL), 508C, N2, 24 h. Isolated yield. [b] Toluene (2 mL) as solvent and at 808C. [c] 808C. [d] 0.4 mmol scale (1ab).
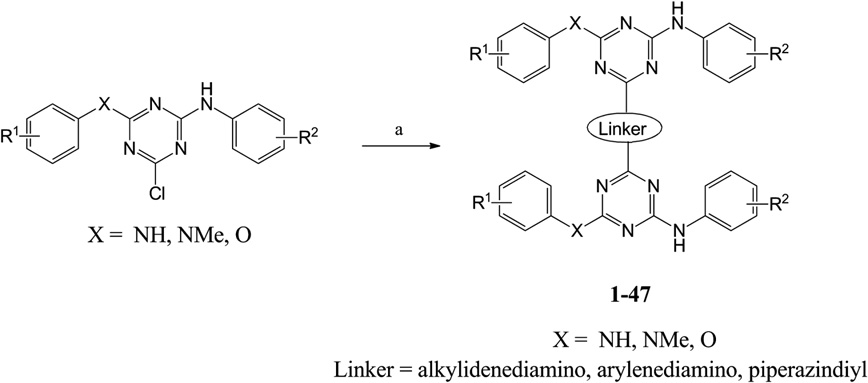
Synthesis of triazine dimers 1–47. Reagents and conditions: (a) diaminoalkanes/diaminobenzene/piperazine, DIPEA, dry dioxane, 110 °C.
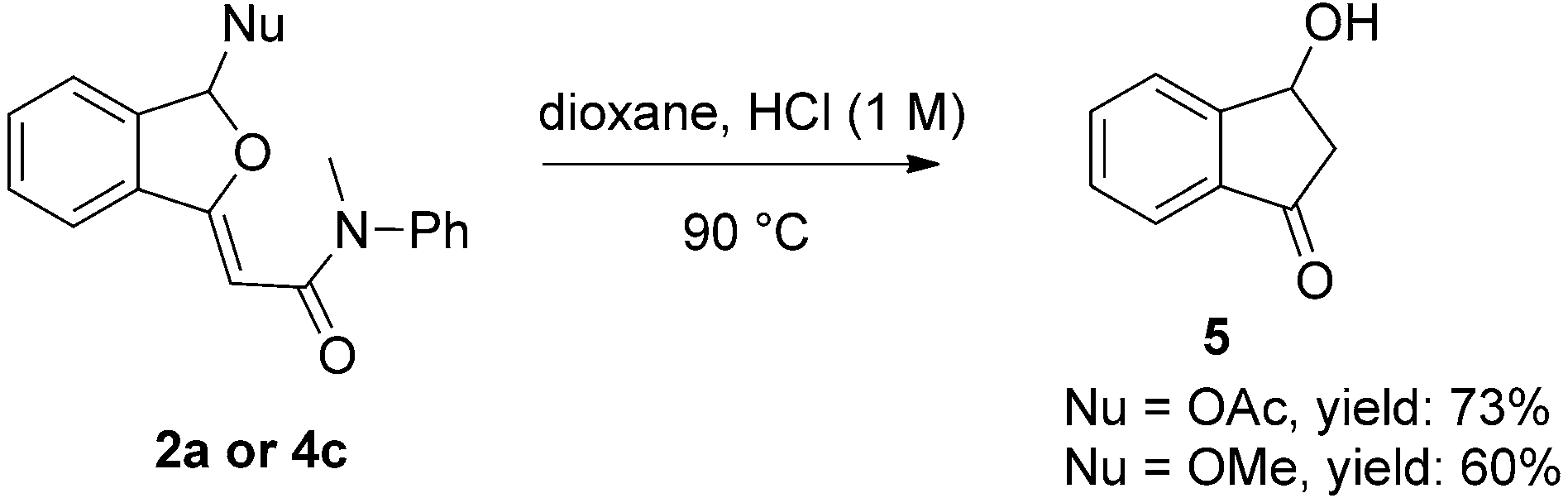
Further transformations of the products.
CAS number: 123123-32-0
Bullatacin is a polyketide. It has a role as a metabolite.
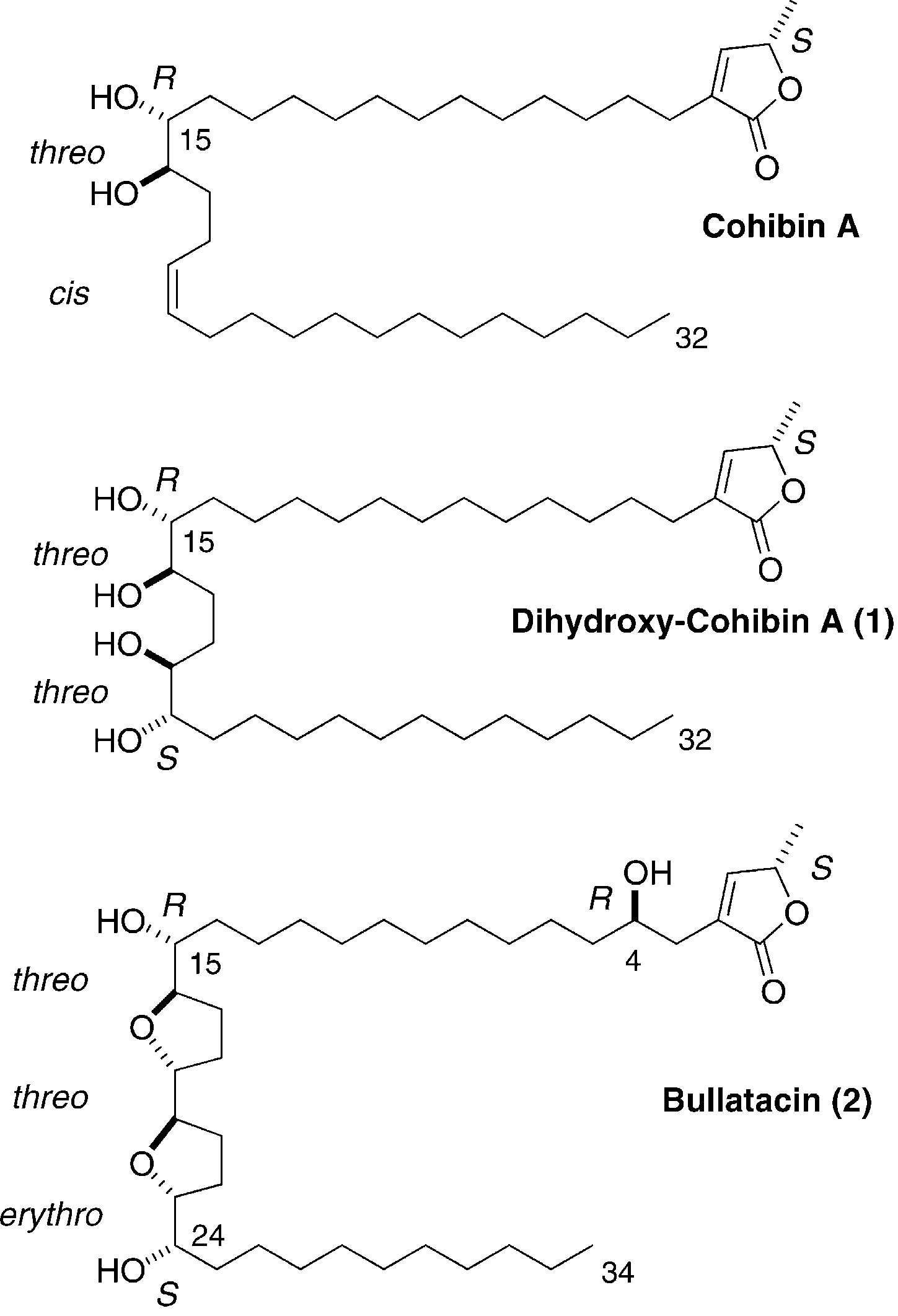
Structure of cohibin A, synthetic dihydroxy-cohibin A (1) and bullatacin (2).
CAS number: 123324-71-0
4-tert-Butylphenylboronic acid, also known as 4-tert-butylbenzeneboronic acid, is a biochemical reagent and a cross-coupling building block.
![Synthesis of aminyl diradicals 1 and 2. a) NBS in chloroform, NaHCO3, Na2SO4, -40℃ for 1 h, then 08C for 2 h, 35%. b) 4-tert-butylphenylboronic acid or 4-tert-undecylphenylboronate, [Pd(PPh3)4], Na2CO3, benzene/EtOH/water, 908C (5: 62% yield, 6: 43% yield). c) nBuLi (2.4 equiv), THF/hexane, ca. -30℃ for 1 h, then solvent change to THF or 2-MeTHF, and I2 (1.06 equiv) at -90℃ or titration with I2 at -90 to -115℃ monitored by EPR spectroscopy. NBS=N-bromosuccinimide.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3912354_05.png)
Synthesis of aminyl diradicals 1 and 2. a) NBS in chloroform, NaHCO3, Na2SO4, -40℃ for 1 h, then 08C for 2 h, 35%. b) 4-tert-butylphenylboronic acid or 4-tert-undecylphenylboronate, [Pd(PPh3)4], Na2CO3, benzene/EtOH/water, 908C (5: 62% yield, 6: 43% yield). c) nBuLi (2.4 equiv), THF/hexane, ca. -30℃ for 1 h, then solvent change to THF or 2-MeTHF, and I2 (1.06 equiv) at -90℃ or titration with I2 at -90 to -115℃ monitored by EPR spectroscopy. NBS=N-bromosuccinimide.
CAS number: 123441-03-2
Rivastigmine is a parasympathomimetic or cholinergic agent for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor that inhibits both butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase.
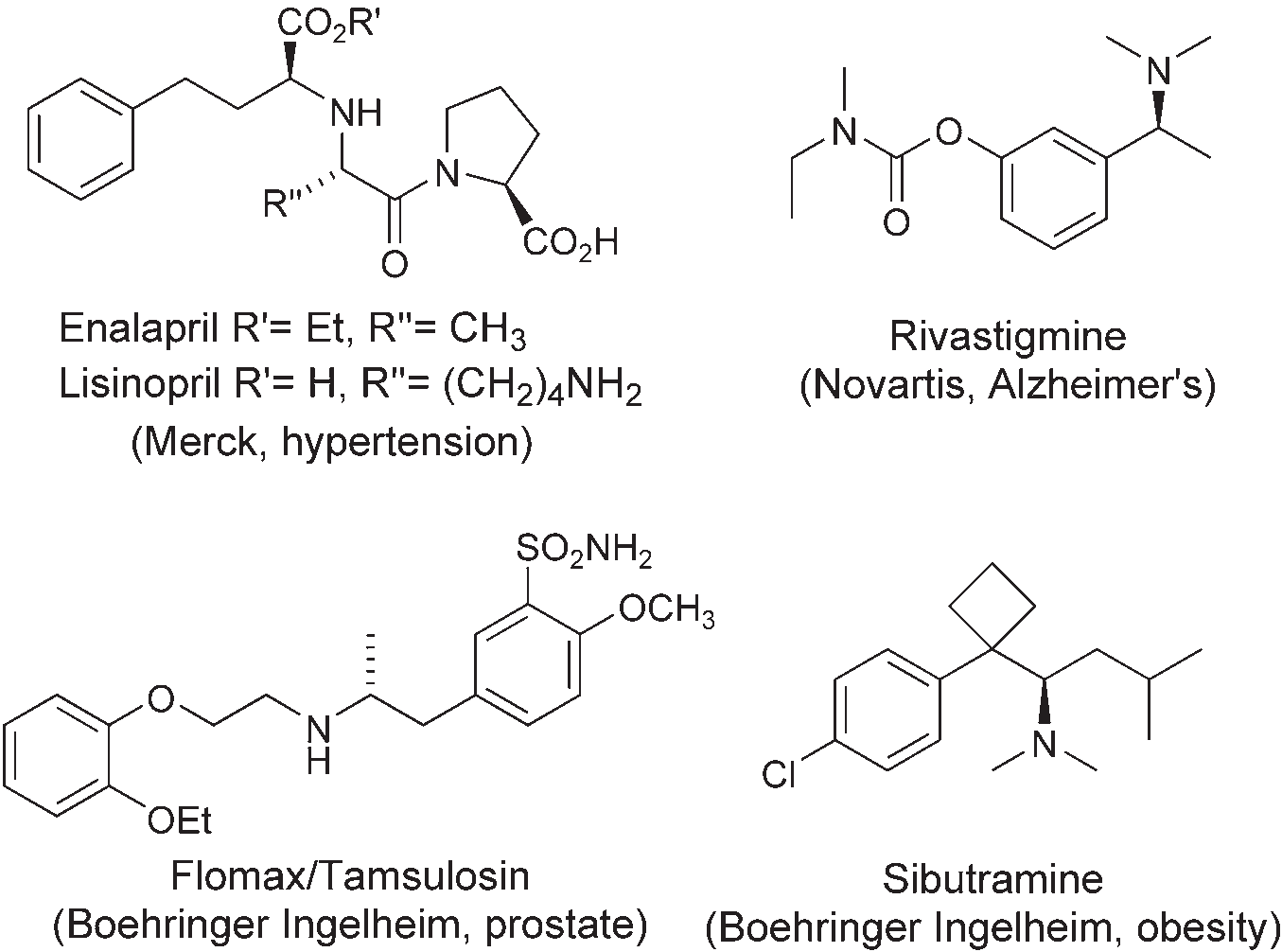
Pharmaceutical drugs containing a-chiral amine stereocenters: enalapril, lisinopril, rivastigmine, Flomax, TAMSULOSIN, sibutramine.
CAS number: 1239-45-8
Ethidium bromide is the organic bromide salt of ethidium. It has a role as a trypanocidal drug, a geroprotector and an intercalator. It contains an ethidium.
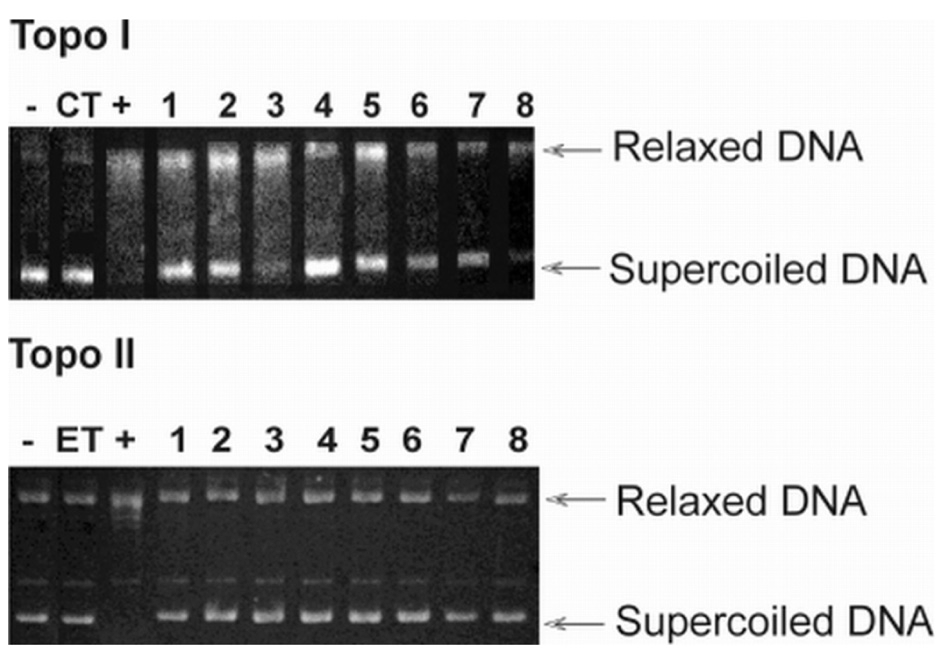
Inhibition of topoisomerase by compounds 1-8. Native pBR322 plasmid DNA (-lane) was incubated with 4 units of topoisomerase I (Topo I) and II (Topo II) without (+lane), with control (CT-camptothecin or ET-etoposide), or with drug (lanes 1-8). DNA was analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide and photographed under UV light.
CAS number: 124-07-2
Octanoic acid is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid that is heptane in which one of the hydrogens of a terminal methyl group has been replaced by a carboxy group. Octanoic acid is also known as caprylic acid. It has a role as an antibacterial agent, a human metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid and a medium-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of an octanoate.
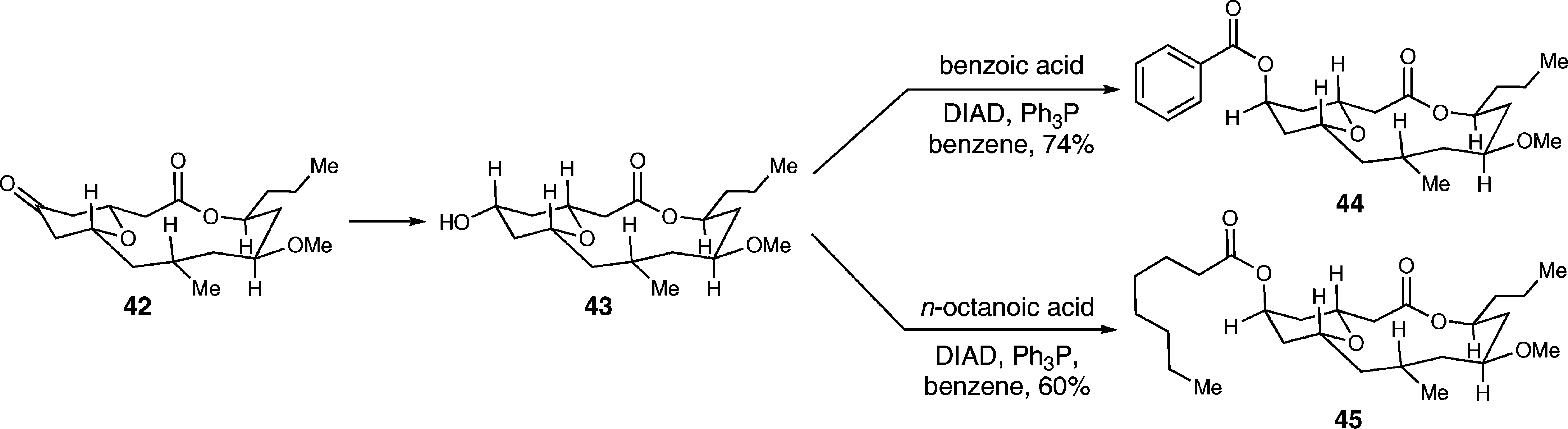
Synthesis of Neopeltolide Analogs
CAS number: 124-40-3
Dimethylamine, aqueous solution appears as a solution of a gas in water. Odor ranging from a fishlike to ammonia-like depending on vapor concentration. Corrosive to skin and eyes. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion.
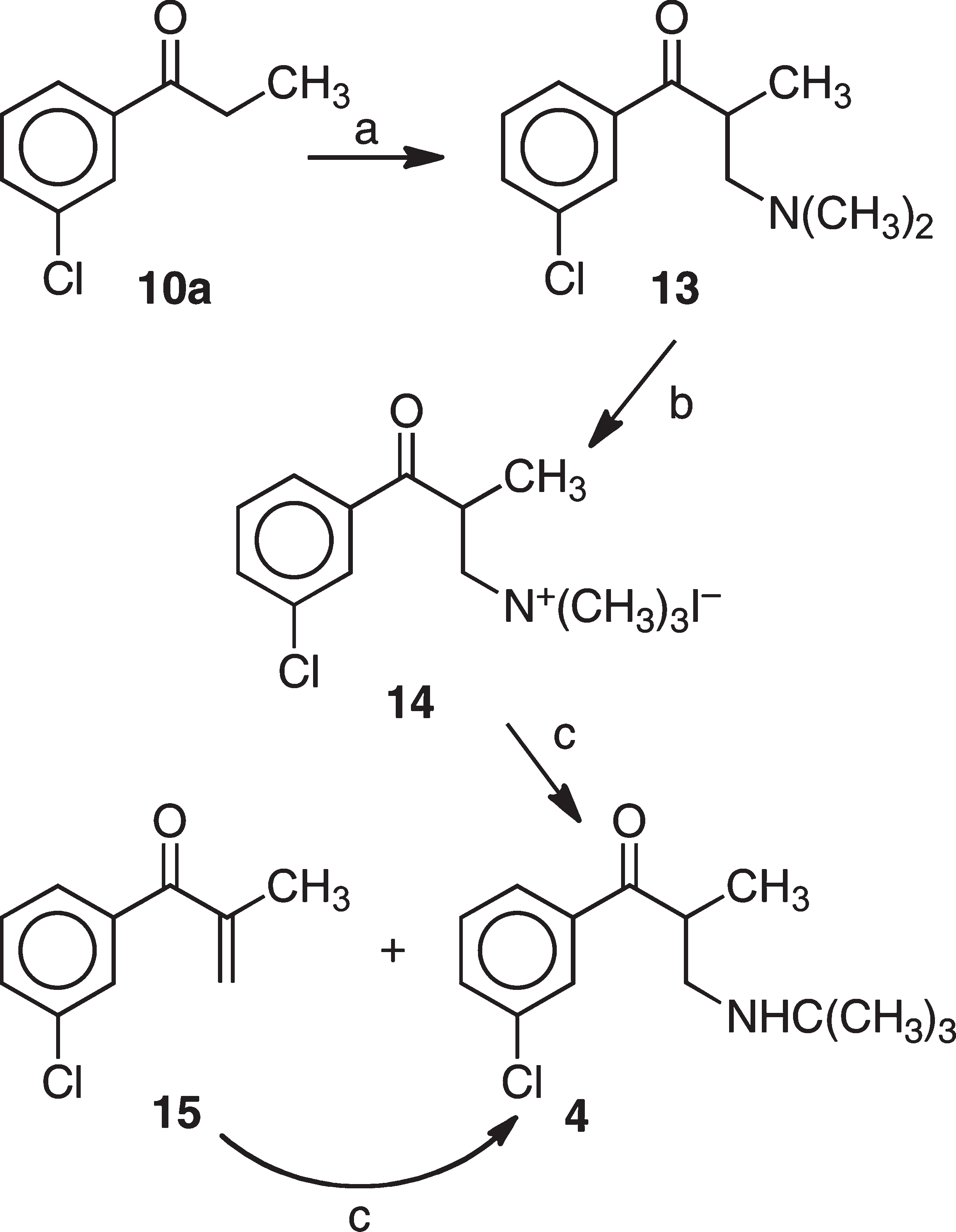
Scheme 3 shows the procedure used for the synthesis of 4. Subjection of 3'-chloropropiophenone (10a) to Mannich reaction conditions with aqueous formaldehyde and dimethylamine gave 13. The methiodide 14 was obtained by alkylation of 13 with iodomethane. Treatment of 14 with tert-butylamine gave first a mixture of 15 and the desired 4. Subjection of the mixture to excess tert-butylamine provided the desired target compound.