Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 110-87-2
Dihydro-2h-pyran appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ethereal odor. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air.
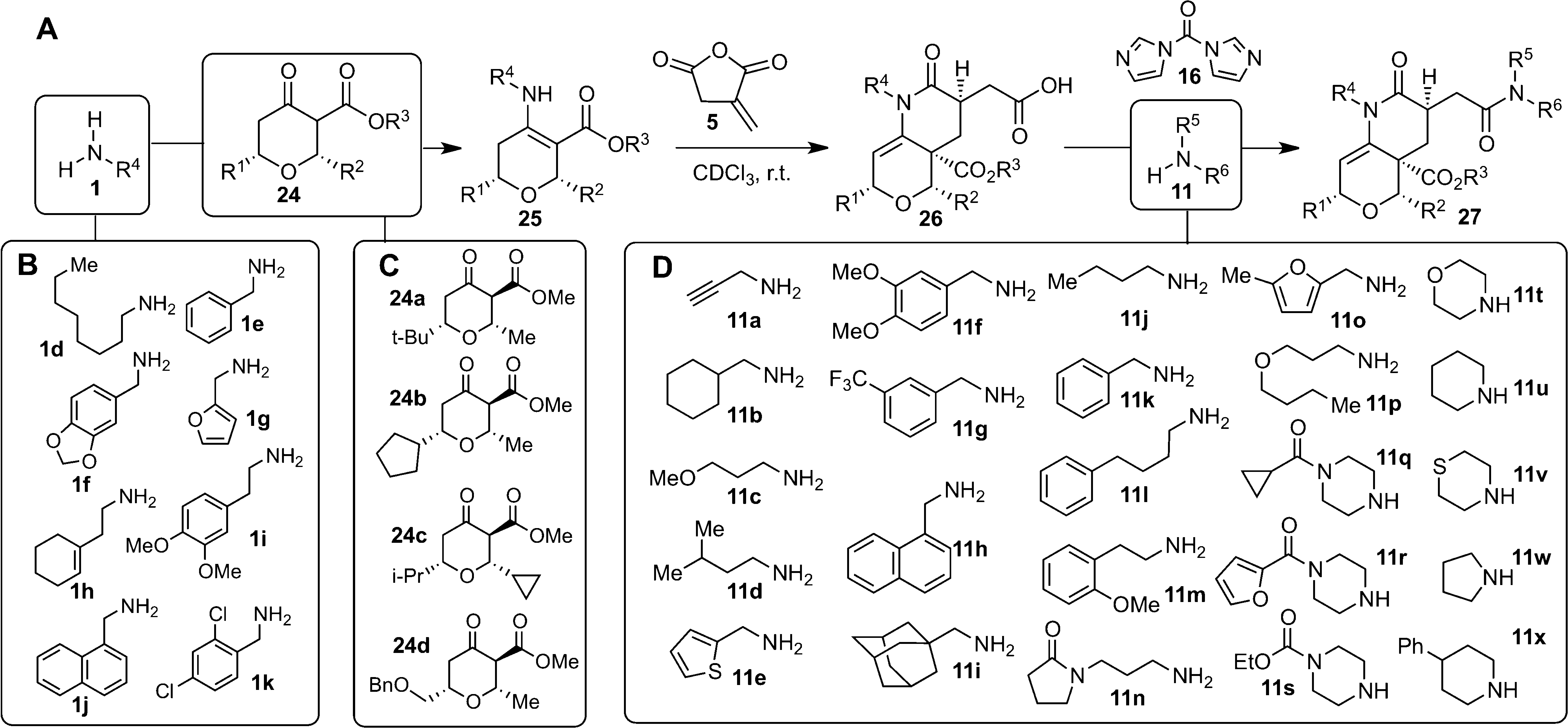
Synthesis of a 768-membered library of 2-piperidinones fused to dihydropyrans.
CAS number: 110-89-4
Piperidine is an azacycloalkane that is cyclohexane in which one of the carbons is replaced by a nitrogen.
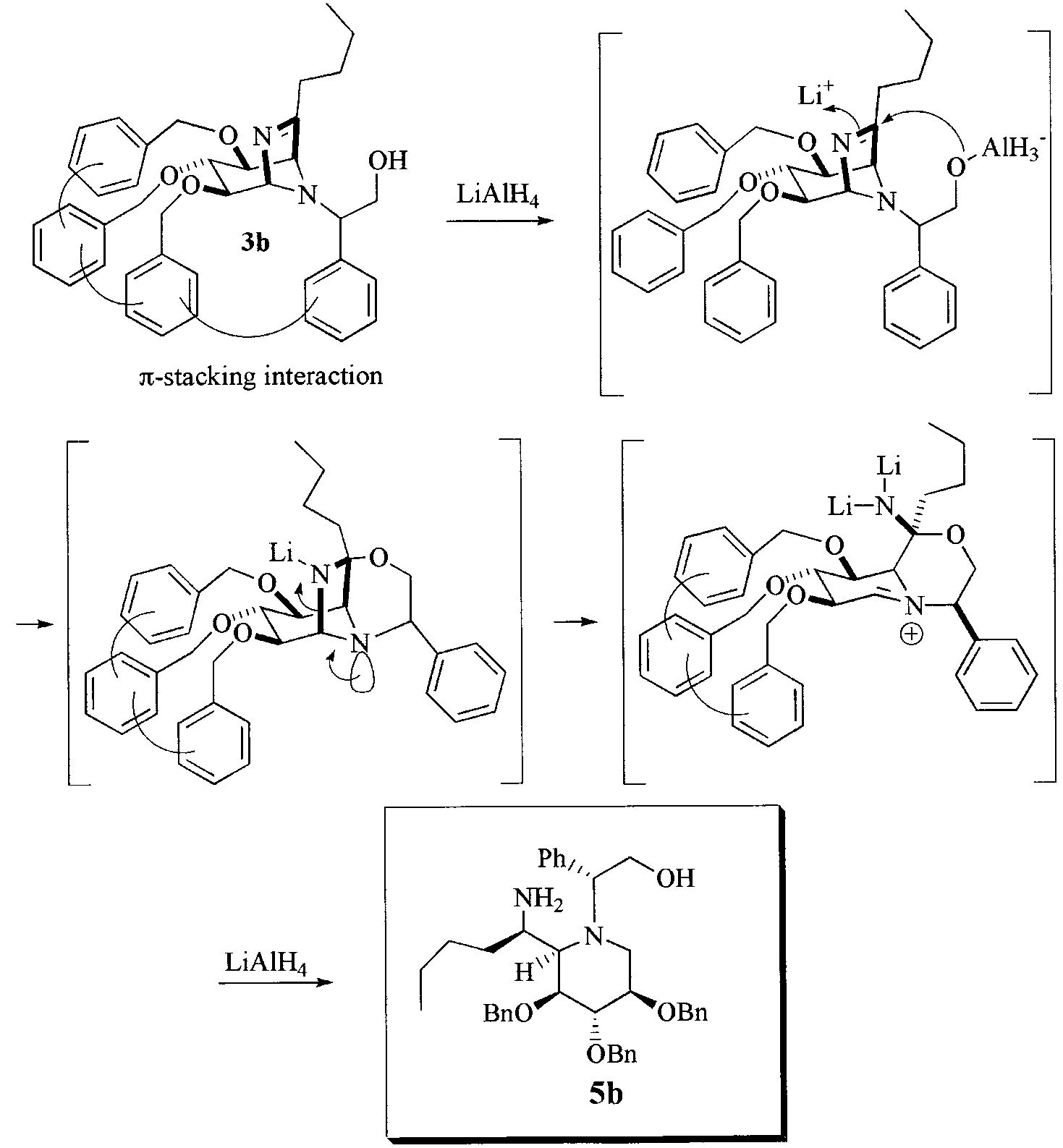
π-Stacking interaction favoring the piperidine system.
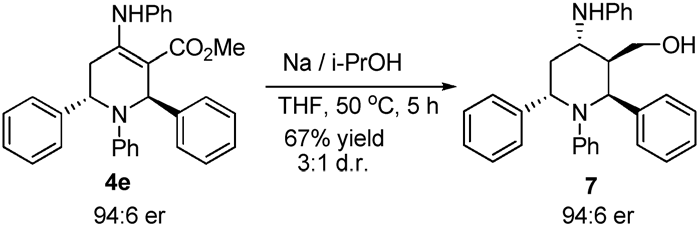
Synthesis of chiral piperidine.
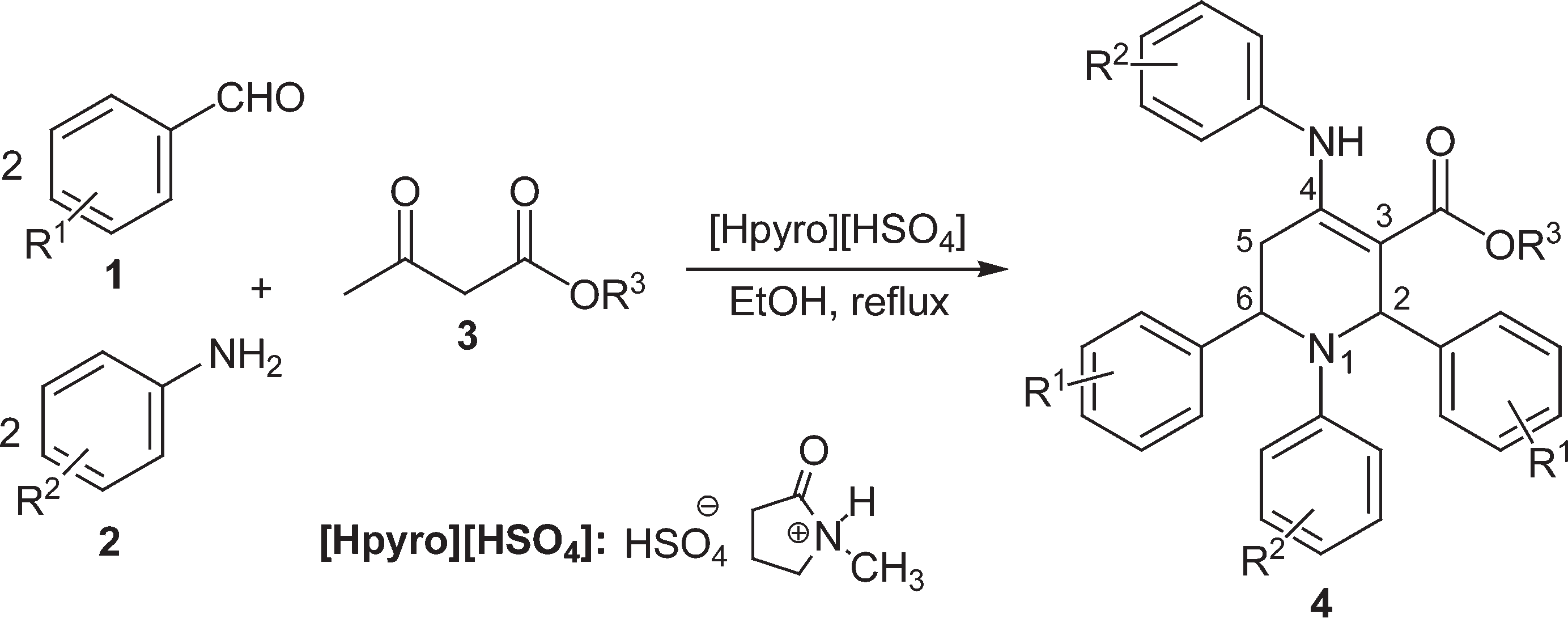
Synthesis of highly functionalised piperidine 4.
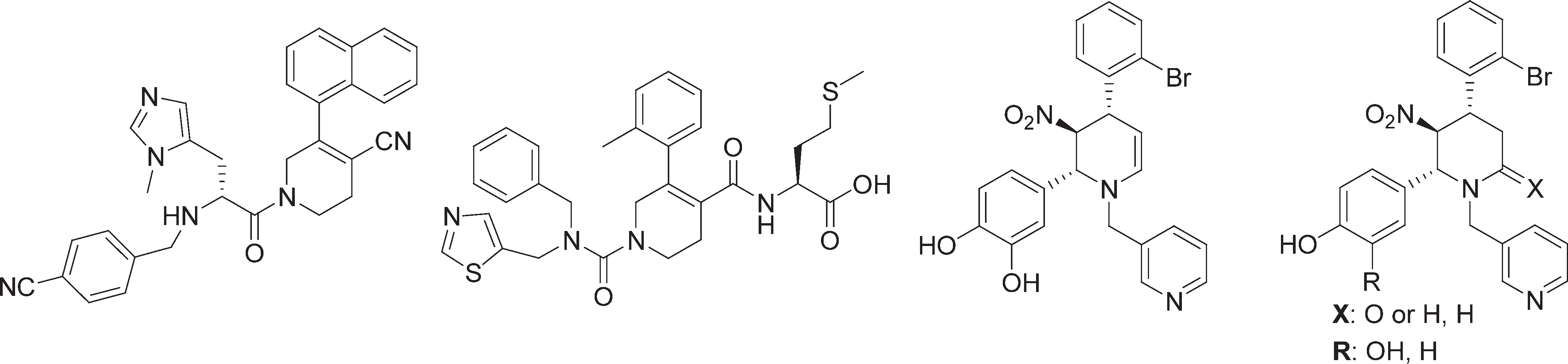
Farnesyltransferase active compounds containing piperidine framework.
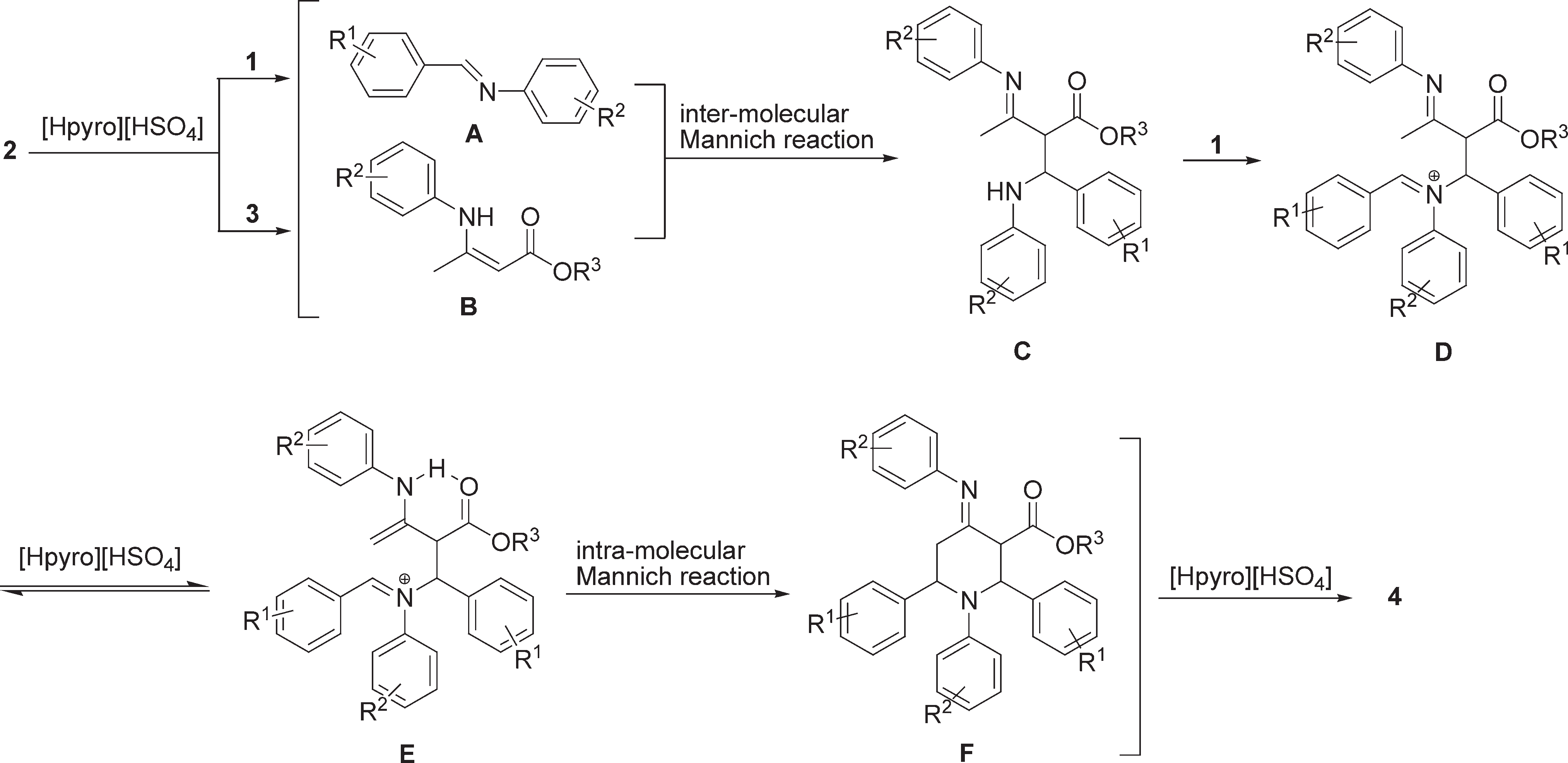
Proposed reaction mechanism for synthesis of highly functionalised piperidines 4.
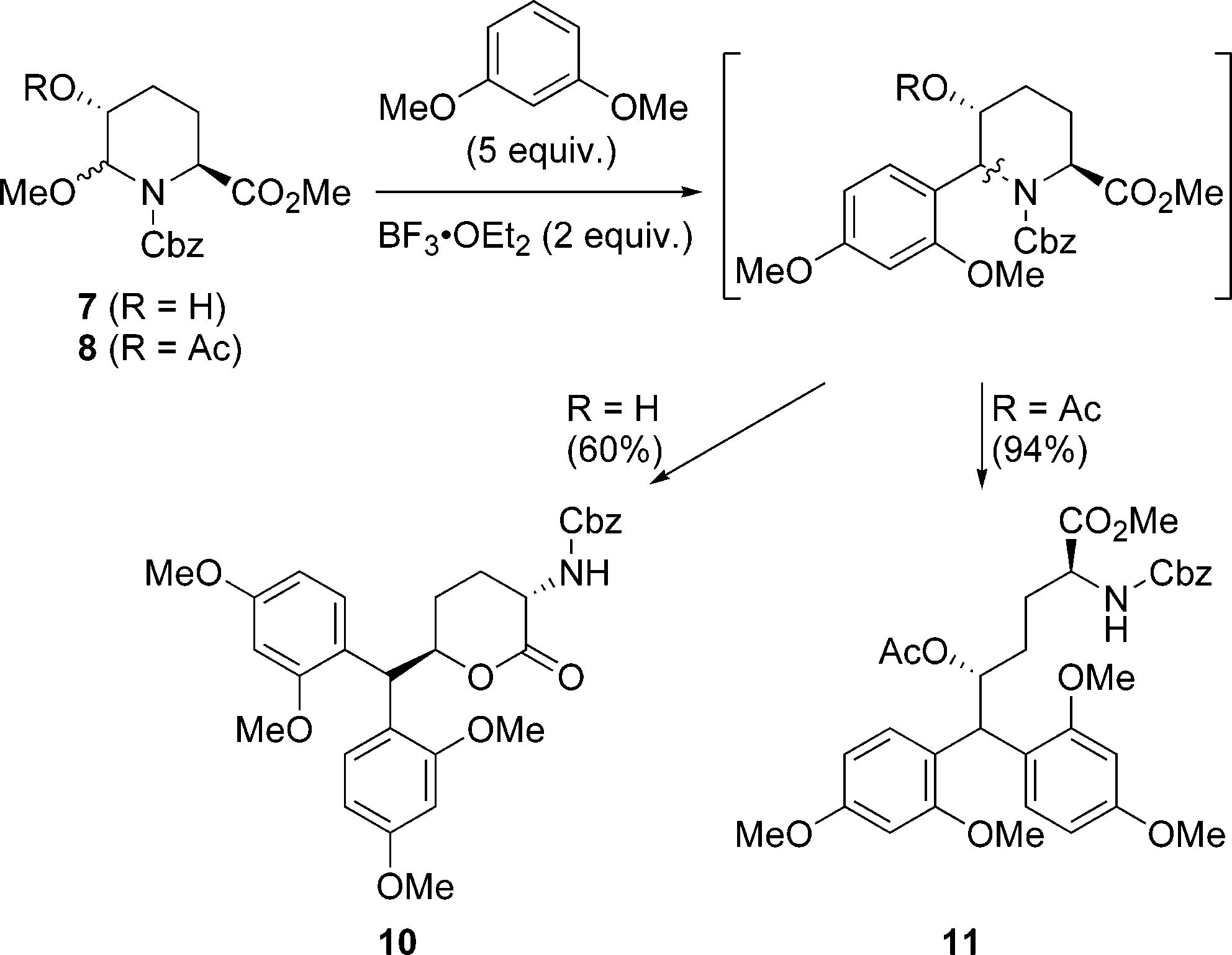
Unexpected Opening of the Piperidine Ring
CAS number: 110-91-8
Morpholine is an organic heteromonocyclic compound whose six-membered ring contains four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom and one oxygen atom that lies opposite to each other; the parent compound of the morpholine family. It is a saturated organic heteromonocyclic parent and a member of morpholines. It is a conjugate base of a morpholinium.
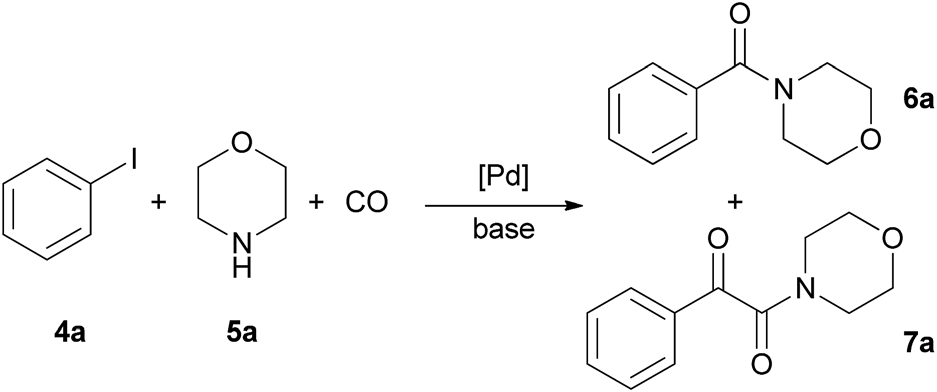
Aminocarbonylation of iodobenzene with morpholine.
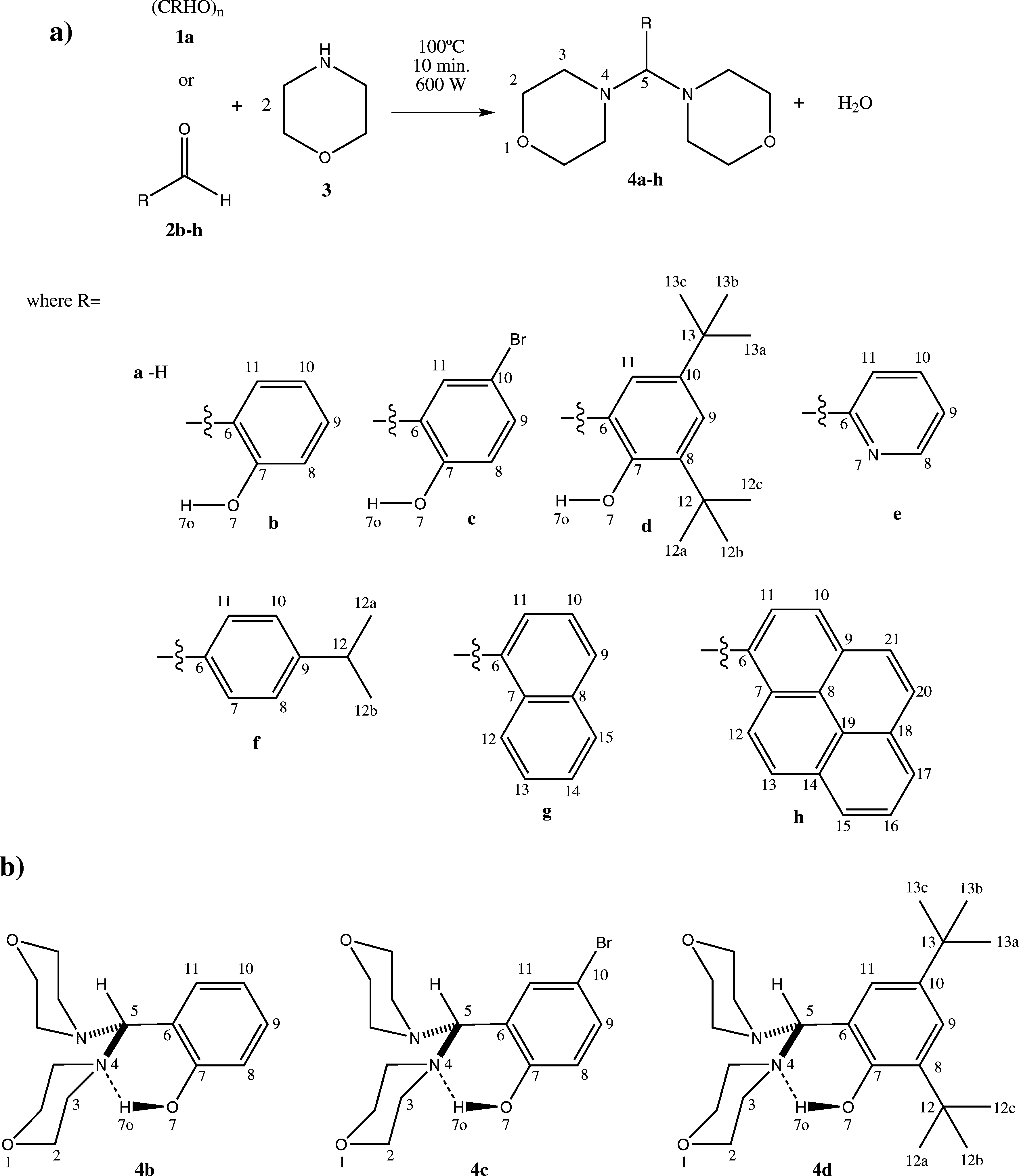
(a) Solvent-free microwave-assisted reaction of aldehydes (1a, 2b-h) with morpholine (3) to give compounds 4a-h. (b) Hydrogen bonds exist in compounds 4b, 4c, and 4d.
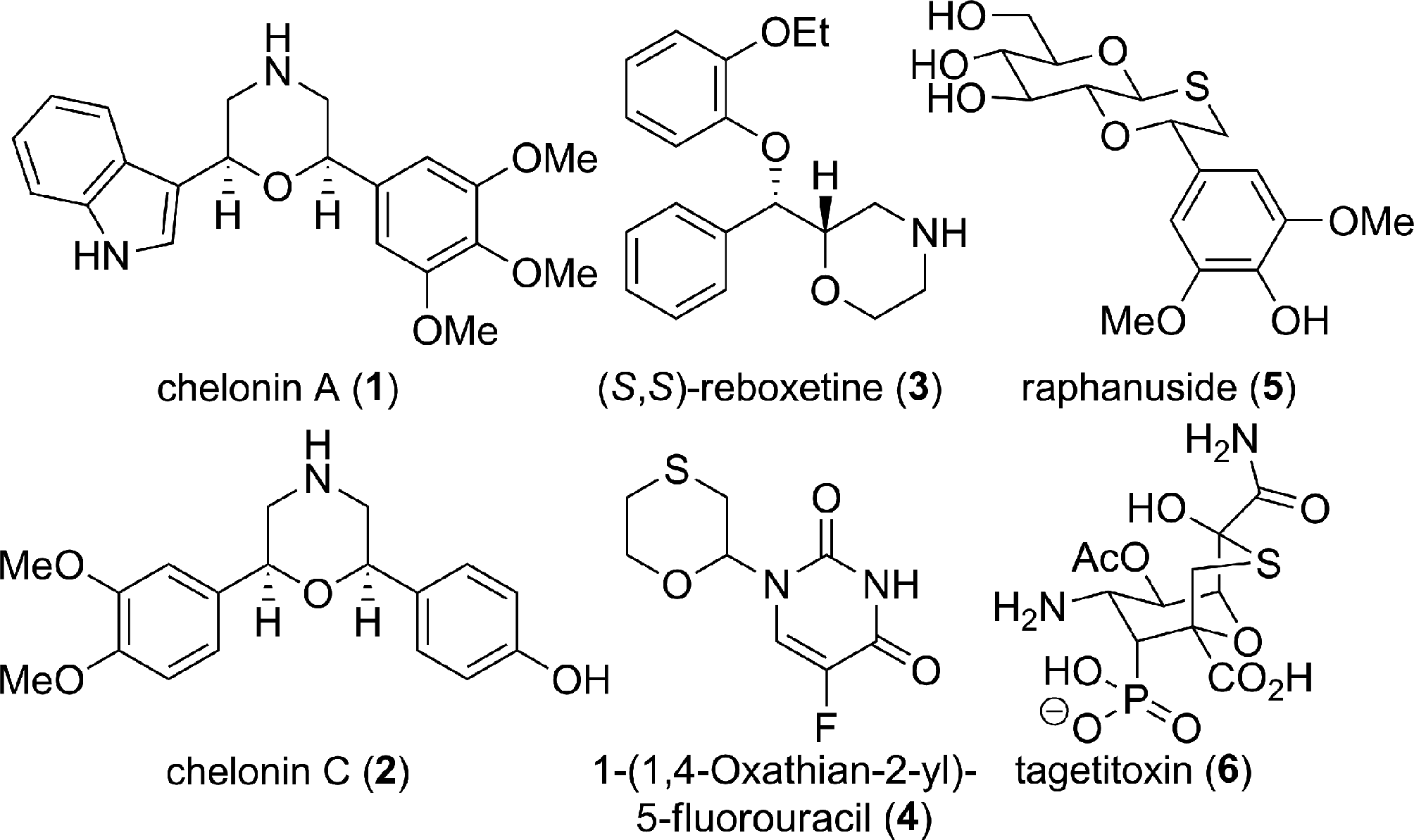
Morpholines and 1,4-oxathiane ring bearing natural products and bioactive molecules.
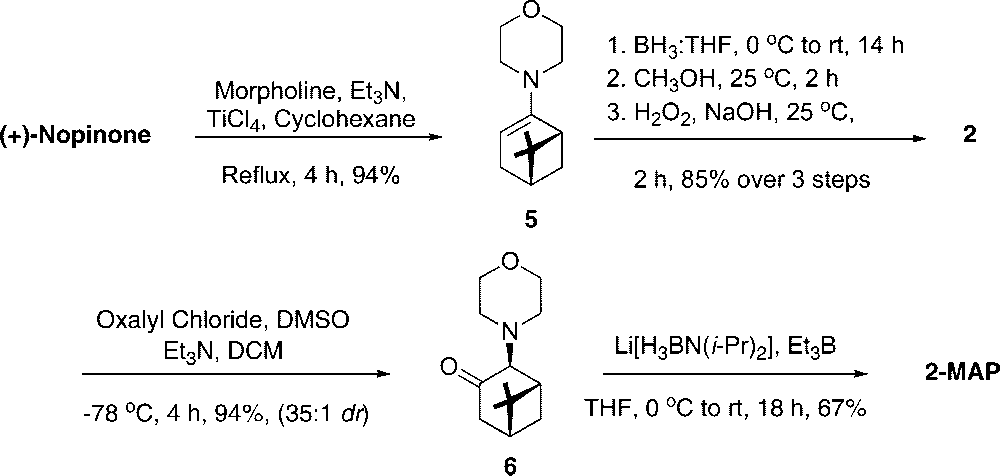
Synthesis of Chiral Auxiliary 2-MAP
CAS number: 110652-72-7
Porothramycin B is an antibiotic belonging to the pyrrolobenzodiazepine family. It's a crystalline methyl ether form of the antibiotic porothramycin. It exhibits antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. It was originally isolated from a strain of Streptomyces albus.
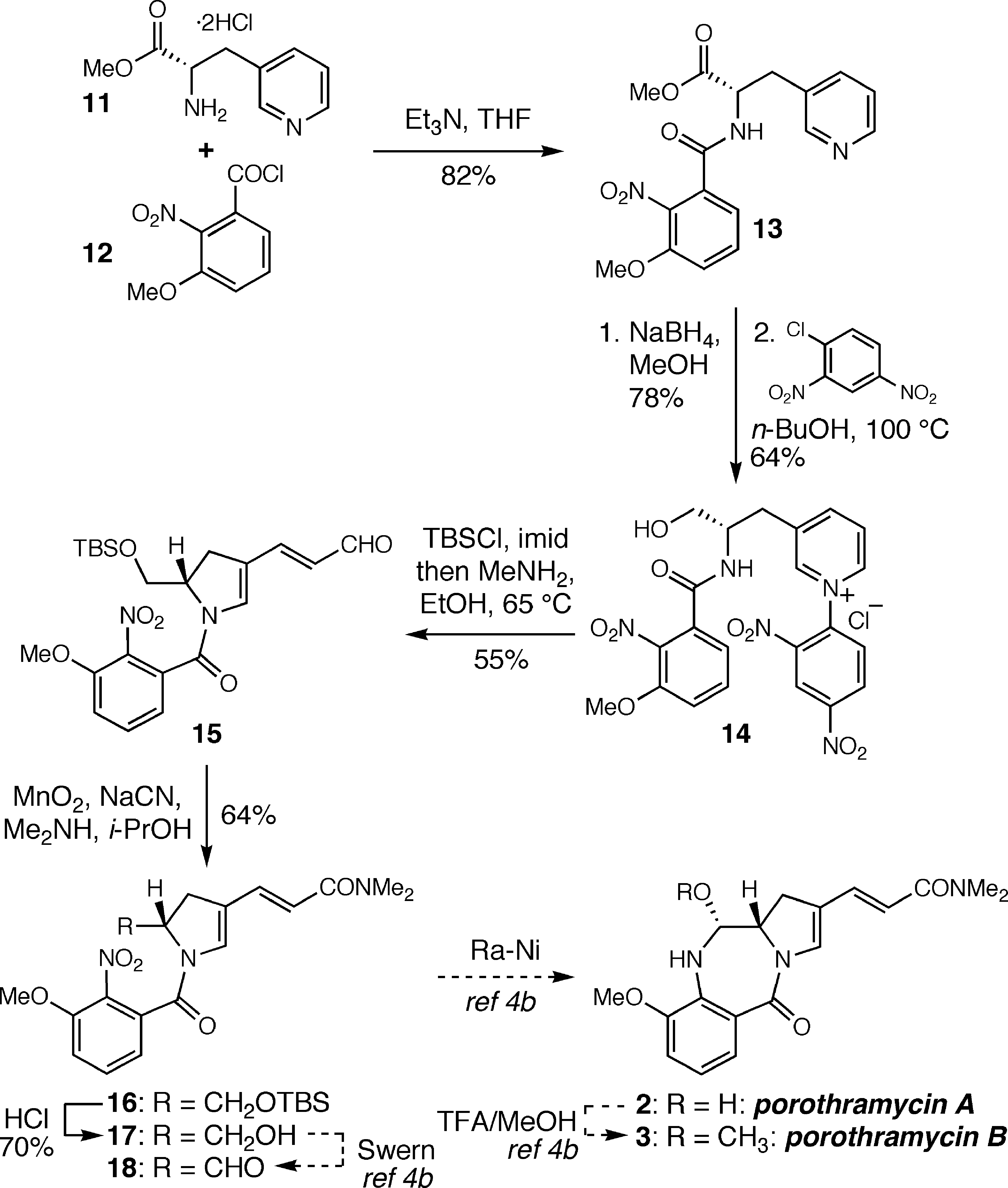
Formal Syntheses of Porothramycins A and B
CAS number: 110652-73-8
Porothramycin A is a type of pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) antibiotic, specifically a monomeric PBD. It is a natural product produced by actinomycetes, a group of bacteria known for producing various bioactive compounds.
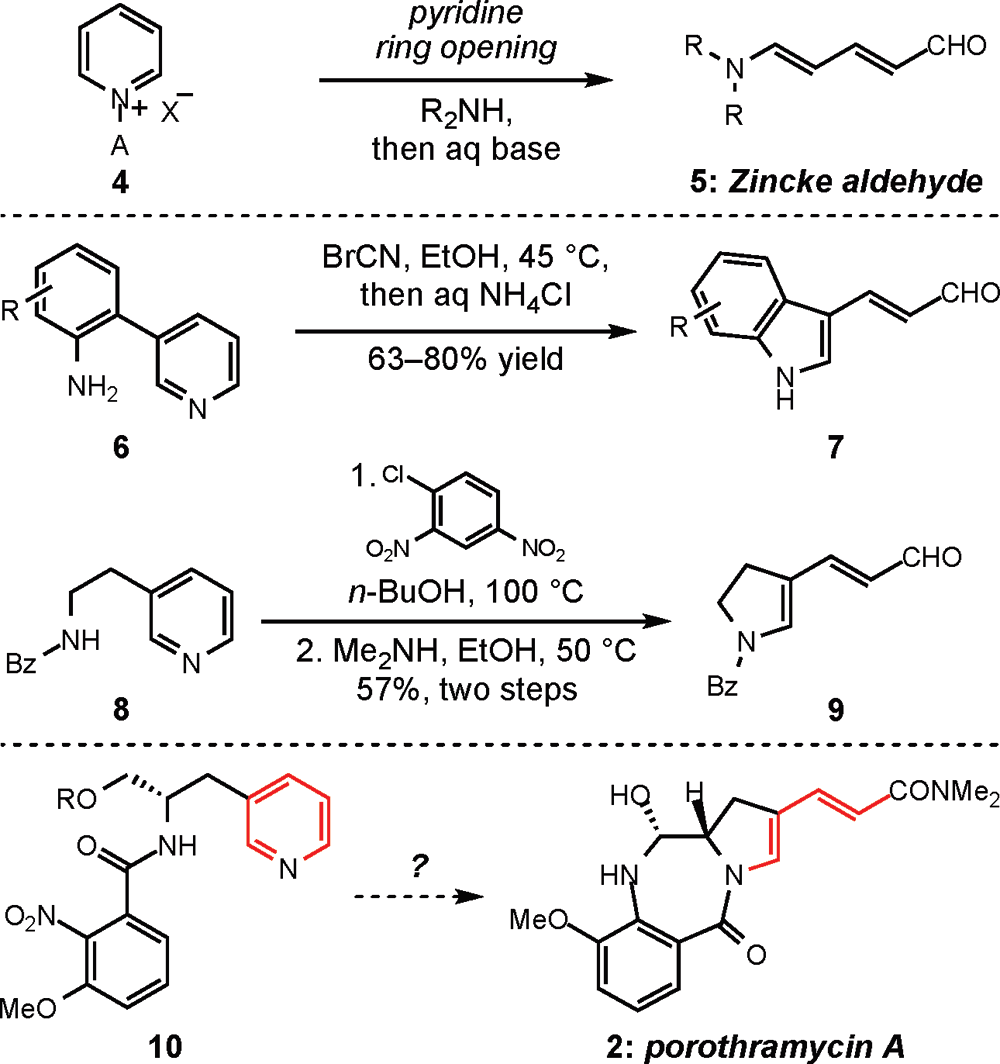
Pyridinium ring-openings to form acyclic Zincke aldehydes, indoles, and dihydropyrroles relevant to the porothramycins. A ) activating group.

Formal Syntheses of Porothramycins A and B
CAS number: 1109-15-5
Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane, also known as TPFPB, is a highly fluorinated, boron-based Lewis acid that is known for its strong electrophilic properties and thermal stability. It's a versatile reagent used in various chemical reactions, particularly in catalysis and materials science.
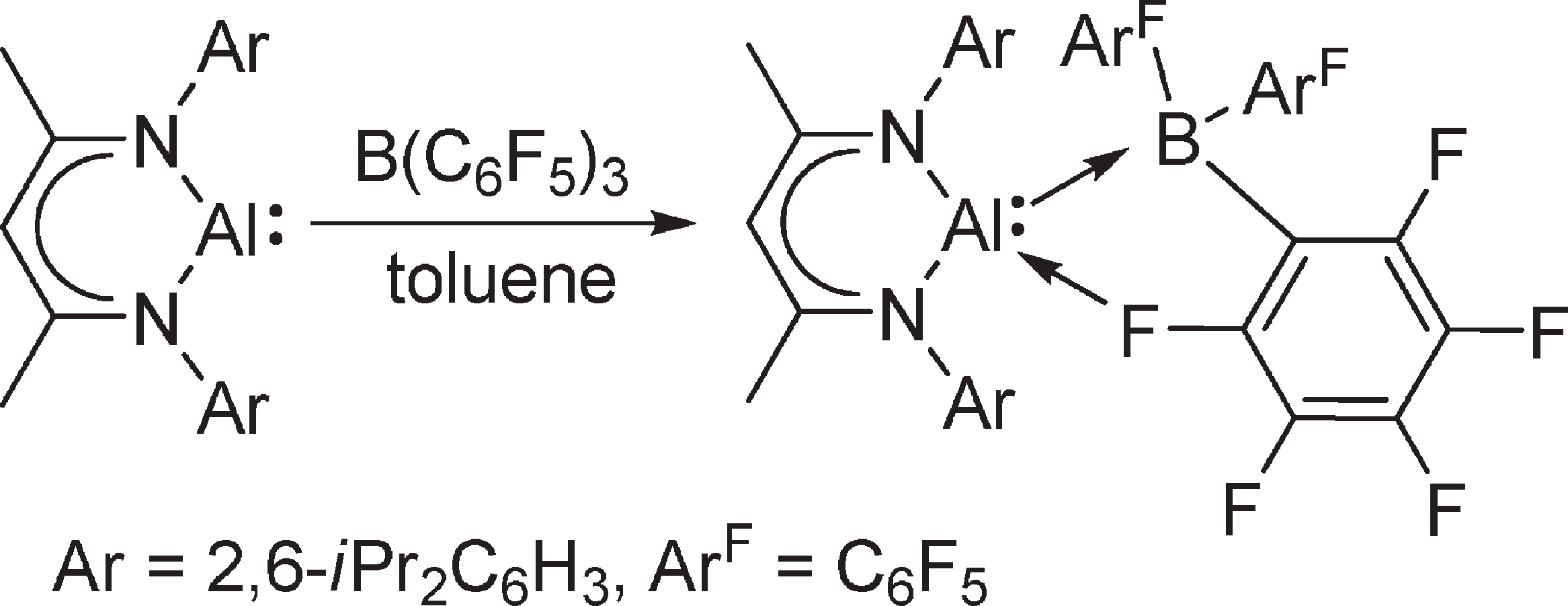
Reaction of LAl with B(C6F5)3
CAS number: 111-30-8
Glutaraldehyde is a colorless, oily liquid with a sharp, pungent odor. Glutaraldehyde is used for industrial, laboratory, agricultural, medical, and some household purposes, primarily for disinfecting and sterilization of surfaces and equipment. For example, it is used in oil and gas recovery operations and pipelines, waste water treatment, x-ray processing, embalming fluid, leather tanning, paper industry, in fogging and cleaning of poultry houses, and as a chemical intermediate in the production of various materials.
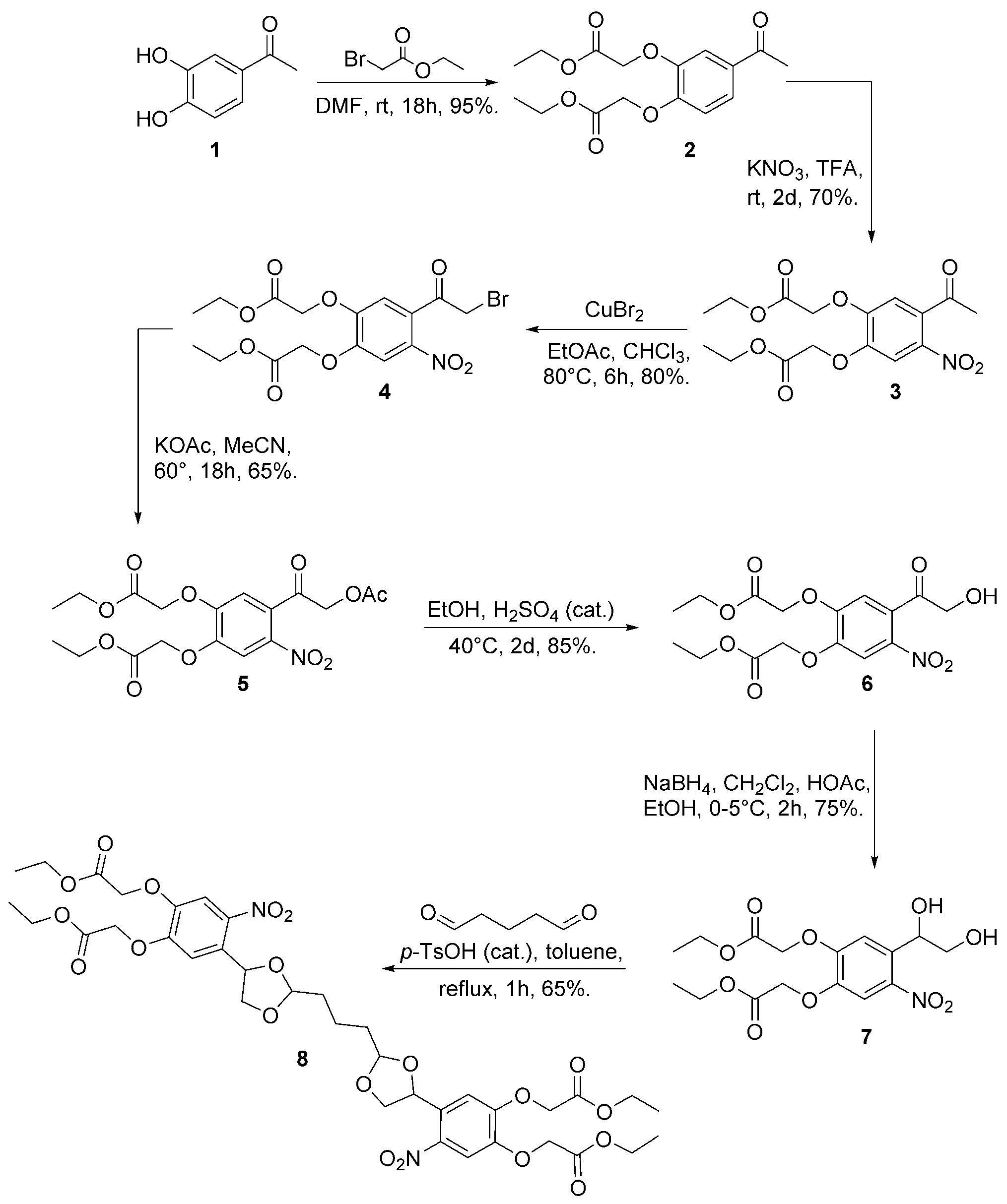
Synthesis of caged glutaraldehyde 8. p-TsOH=para-toluene-sulfonic acid, TFA=trifluoroacetic acid.
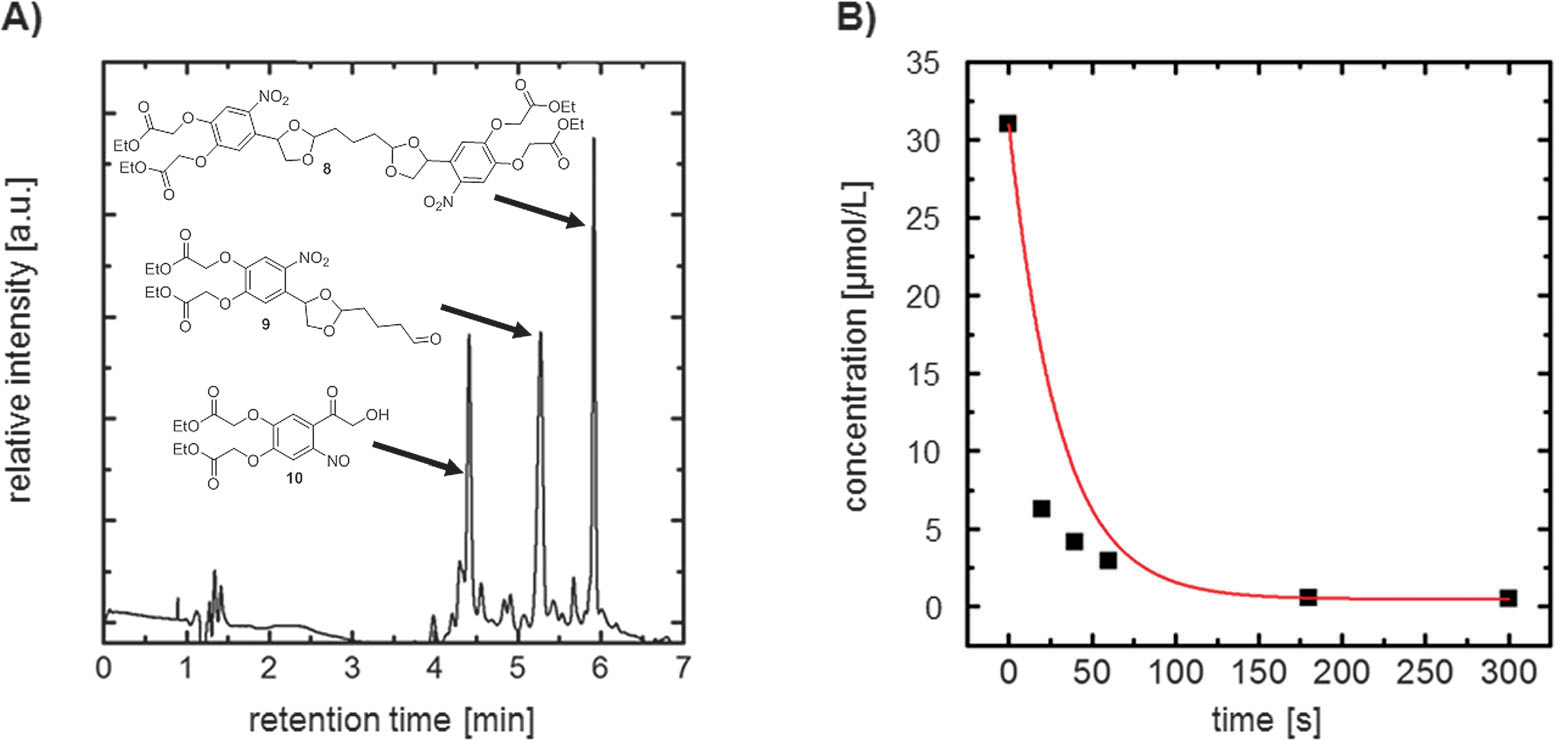
A) UPLC-MS elugram for the photolysis of caged glutaraldehyde 8 after irradiation at l=300 nm for 20 s. B) Decrease in the concentration of caged-GA 8 during photolysis.
CAS number: 111-46-6
Diethylene glycol appears as a colorless liquid. Denser than water. Contact may slightly irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be slightly toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
![Scheme 5 outlines the synthesis of 1a analogue 6. Treatment of 20 with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide in refluxing diethylene glycol (DEG) afforded 21. Compound 21 was cyclized to 22 using polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Subjection of 22 to acetamidobenzenesulfonyl azide (ABSA) in acetonitrile containing 1,4-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) yielded the diazo compound 23. Treatment of 23 with tert-butylamine in dry toluene in the presence of ruthenium acetate provided 6.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/5213099_08.png)
Scheme 5 outlines the synthesis of 1a analogue 6. Treatment of 20 with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide in refluxing diethylene glycol (DEG) afforded 21. Compound 21 was cyclized to 22 using polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Subjection of 22 to acetamidobenzenesulfonyl azide (ABSA) in acetonitrile containing 1,4-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) yielded the diazo compound 23. Treatment of 23 with tert-butylamine in dry toluene in the presence of ruthenium acetate provided 6.
CAS number: 111-49-9
An azacycloalkane that is cycloheptane in which one of the carbon atoms is replaced by a nitrogen atom.
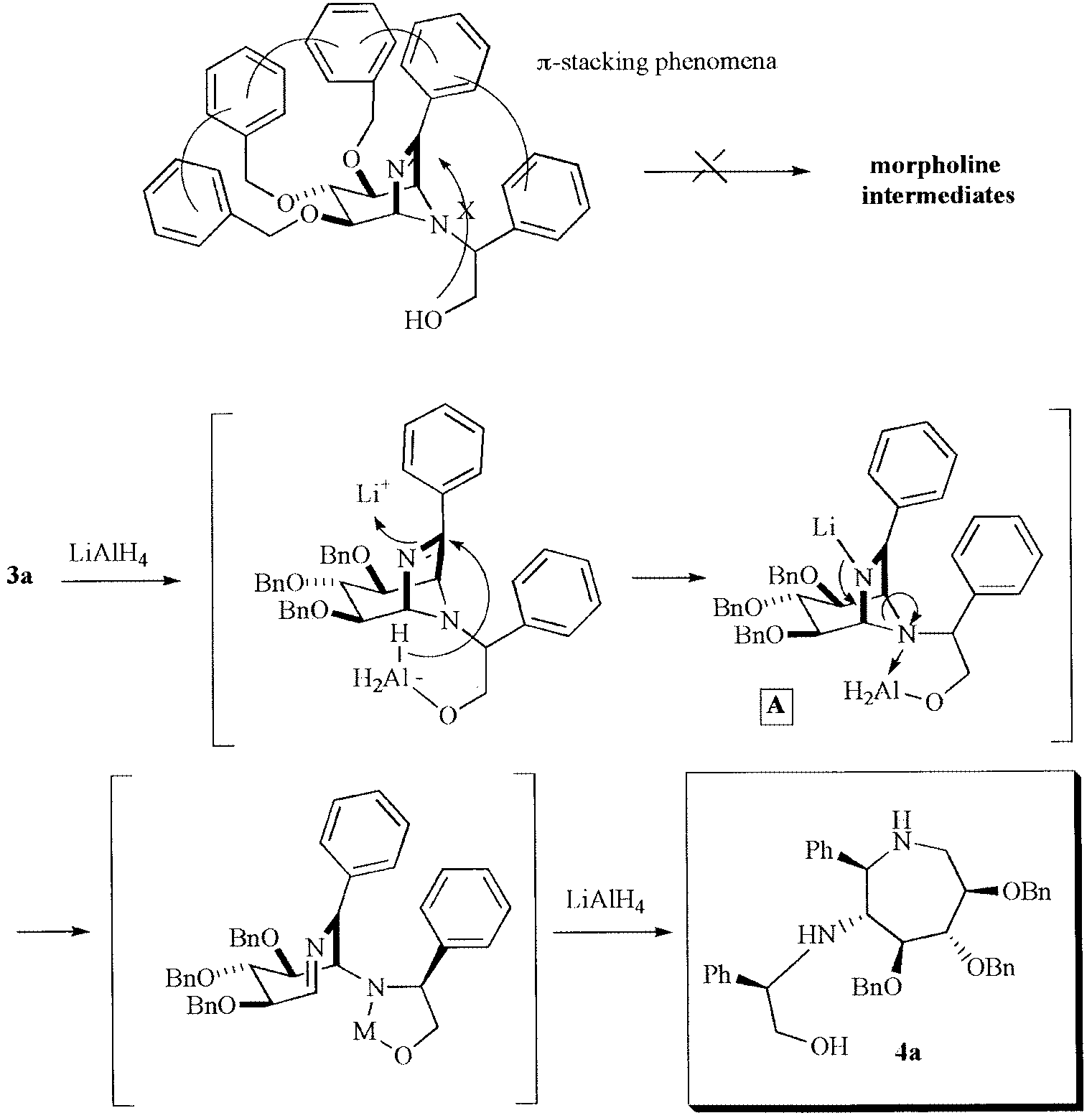
π-Stacking interaction favoring the azepane system.
CAS number: 111-65-9
Octane is a gasoline additive that is needed for the proper functioning of modern engines.
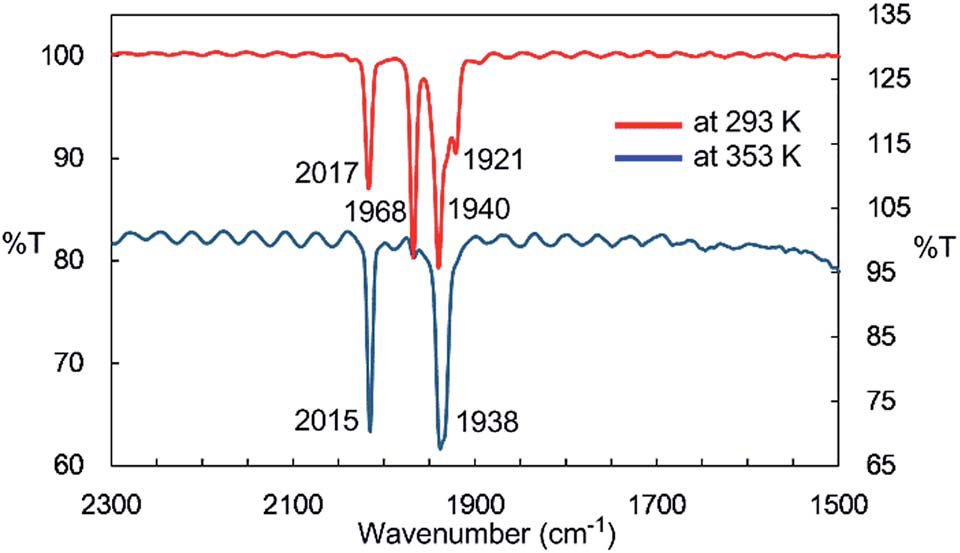
IR spectra of the n-octane solution of 2 at 293 K and 353 K.
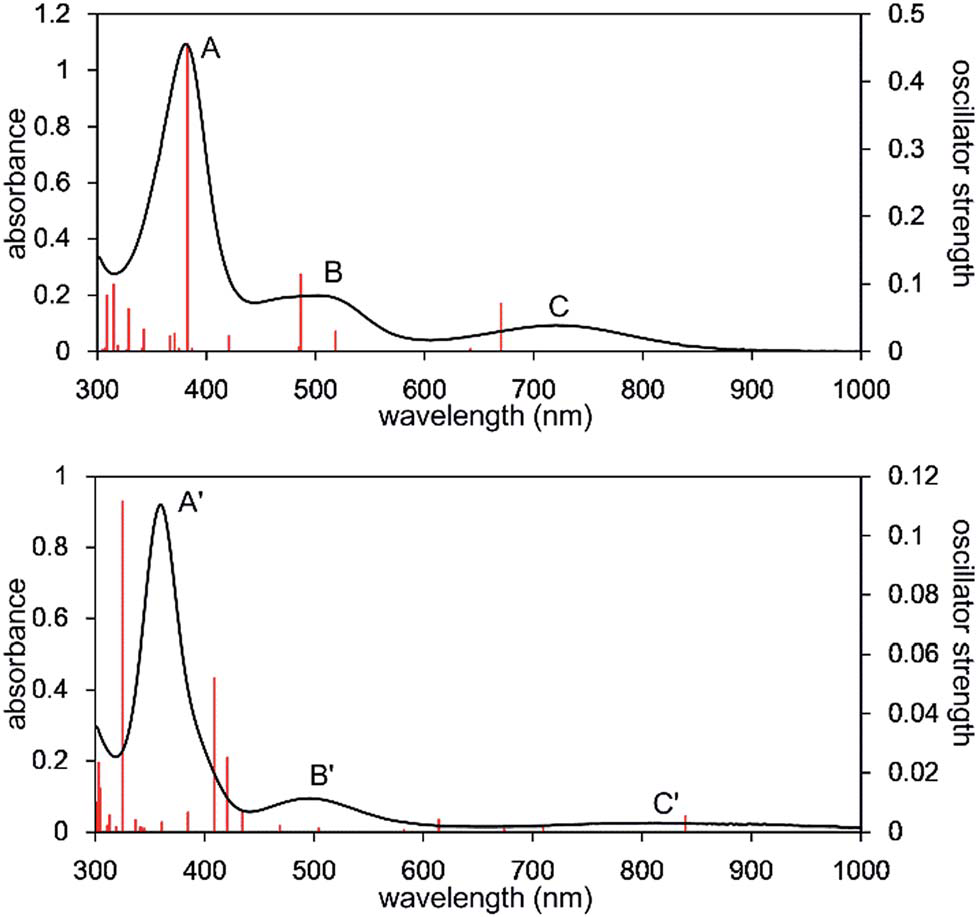
UV-Vis-NIR spectra of the n-octane solution of 2 measured at 293 K (upper) and 353 K (lower). Solid red bars indicate the calculated transition of the 2opt (upper) and 3opt (lower).