Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 133248-01-8
Dehydran 240, produced by BASF, is a modified polyalkylene glycol used as a foam-inhibiting wetting agent in emulsion paints and as a defoamer in textile printing and glue applications.
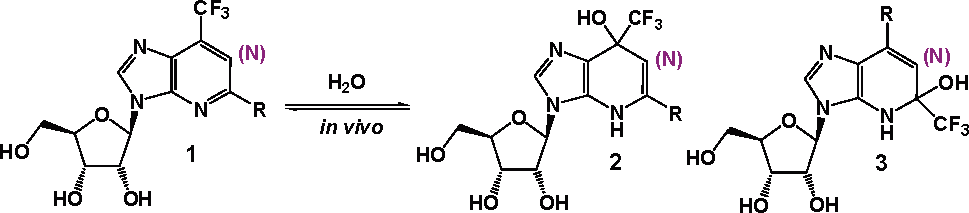
Concept: 2- and 6-trifluoromethyl-containing purines and 1-deazapurines as inhibitors of adenosine deaminase (ADA).
CAS number: 133398-13-7
Tuberculostearic acid, (R)- consists of an 18-carbon chain with a methyl branch at the 10th carbon and a chiral center, existing specifically in the (R)-enantiomeric form.
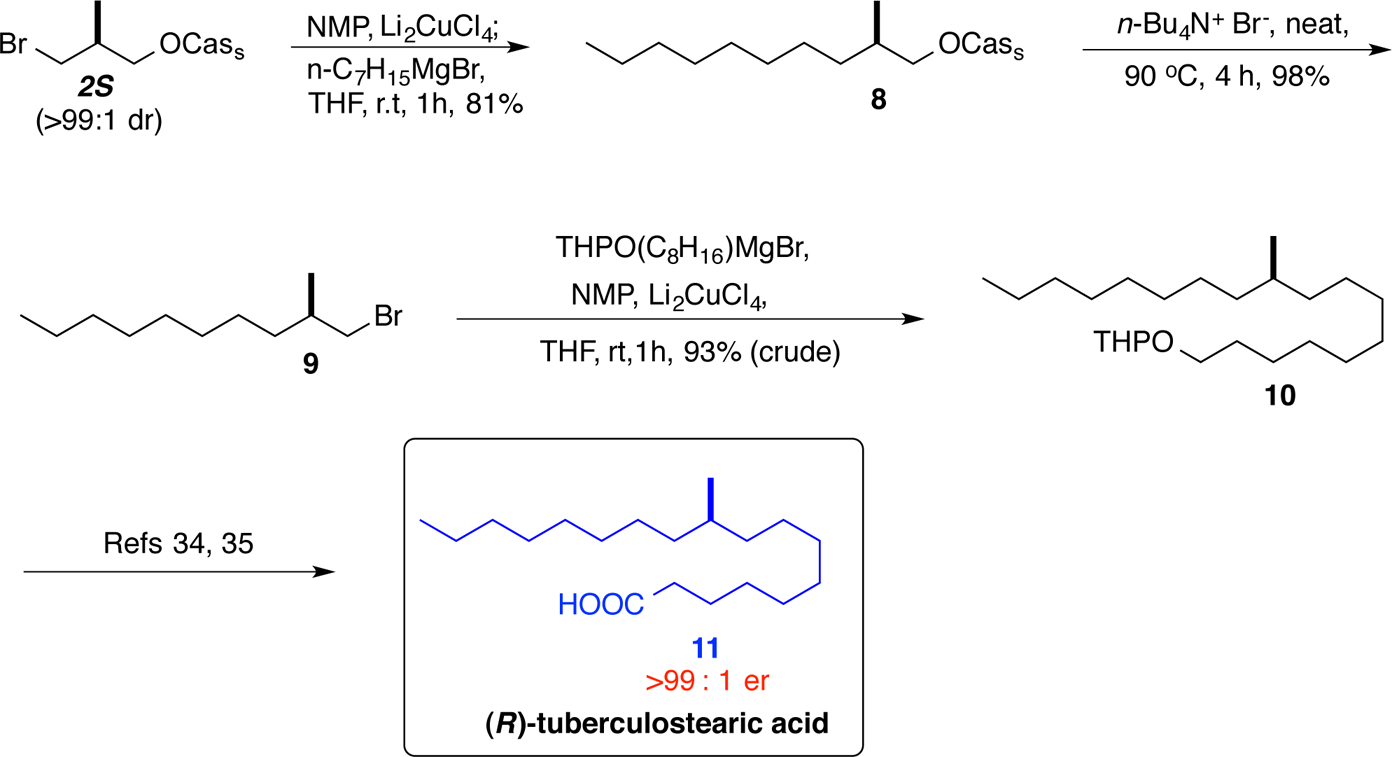
Formal Synthesis of (R)-Tuberculostearic Acid (11)
CAS number: 1334-78-7
Methylbenzaldehyde, also known as benzaldehyde, methyl-, refers to a group of aromatic aldehydes derived from benzaldehyde in which one or more hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring are substituted with a methyl group.
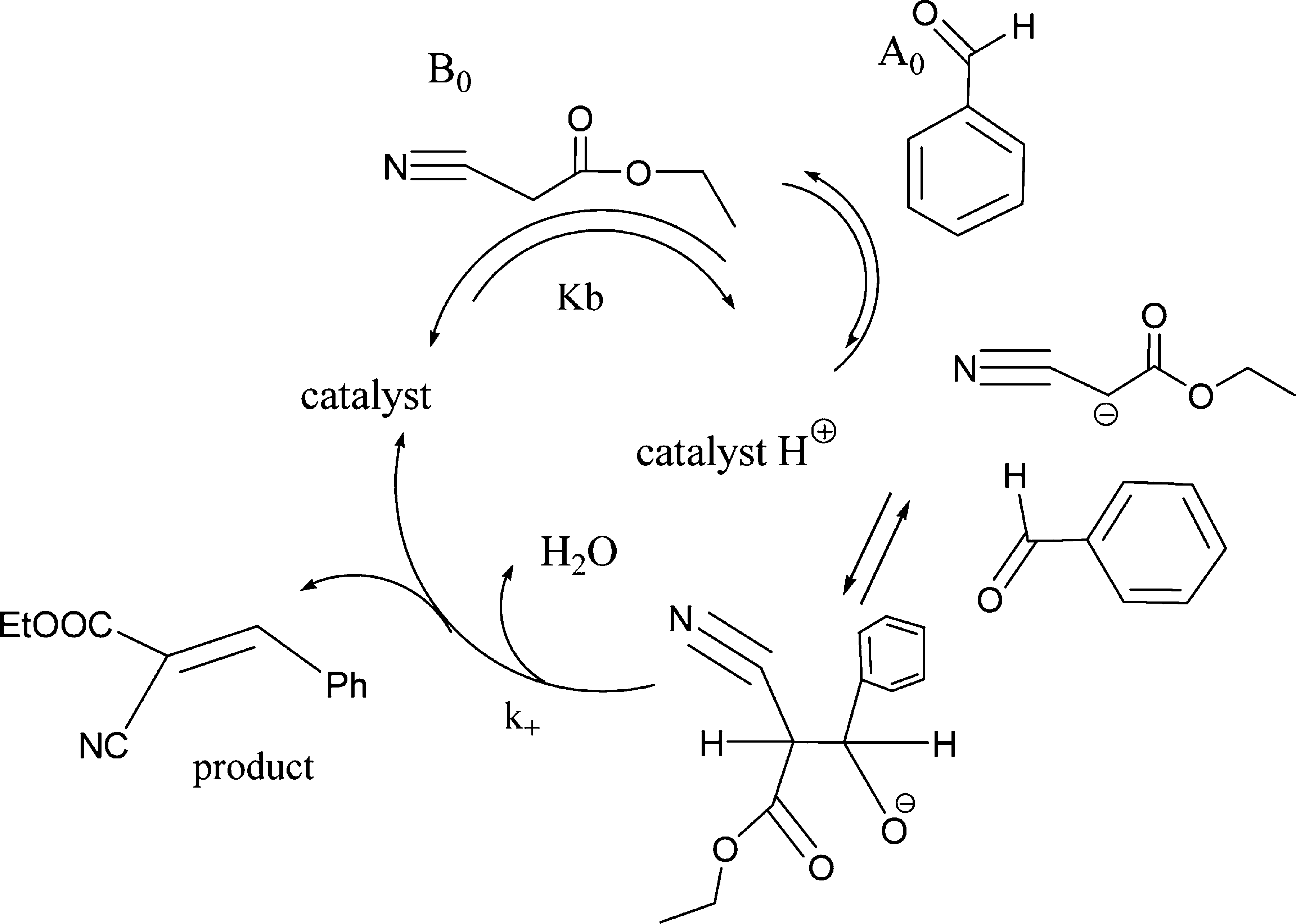
Proposed Kinetic Mechanism DNA/RNA-Salts Appears To Progress via the Shown Catalytic Cycle
CAS number: 13341-72-5
Menthalactone is a bicyclic organic compound featuring a fused furanone and cyclohexane structure. It belongs to the class of lactones, characterized by an ester group incorporated into a ring system. The molecule contains two methyl groups at the 3- and 6-positions and a partially hydrogenated benzofuran core.
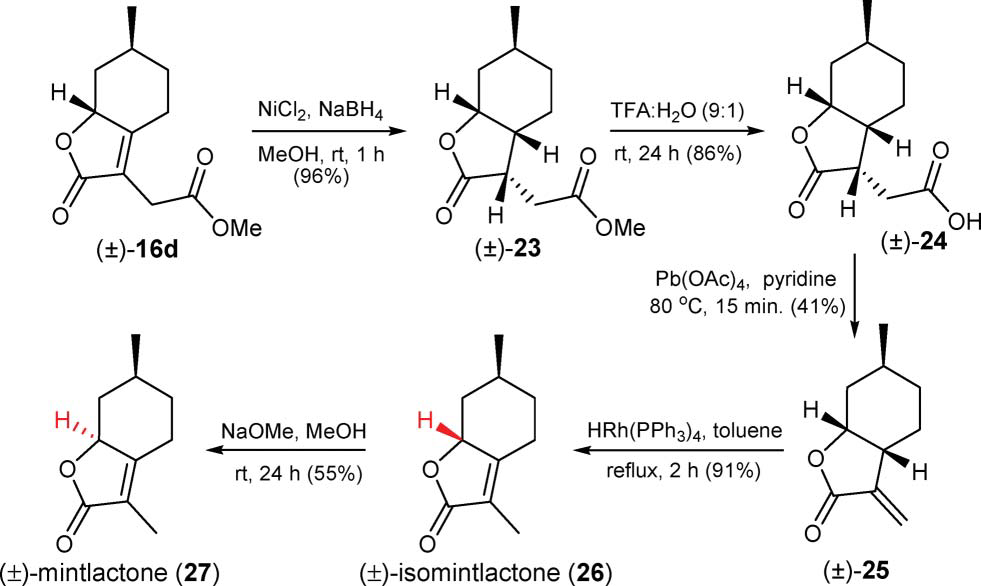
Synthesis of ( )-mintlactone and ( )-isomintlactone.
CAS number: 133413-70-4
PF1022A is a cyclooctadepsipeptide.
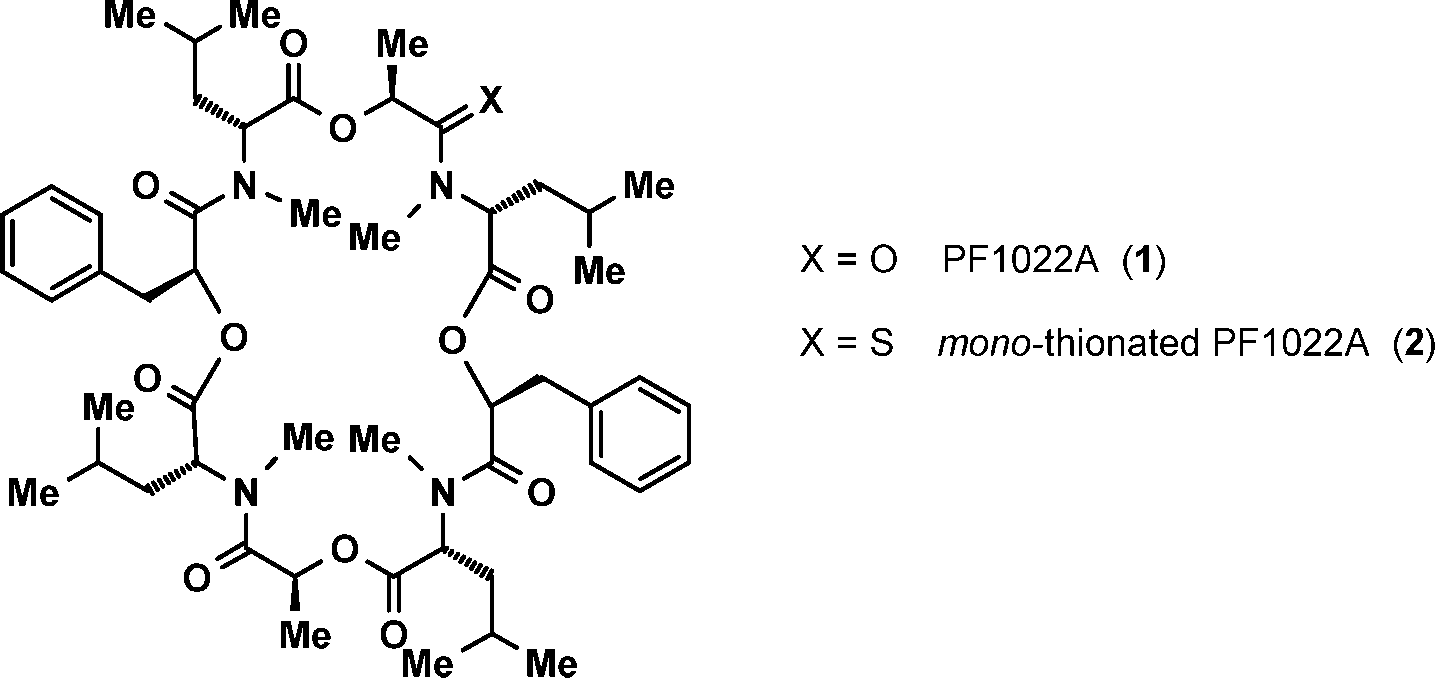
Structures of PF1022A (1) and the mono-thionated PF1022A (2).
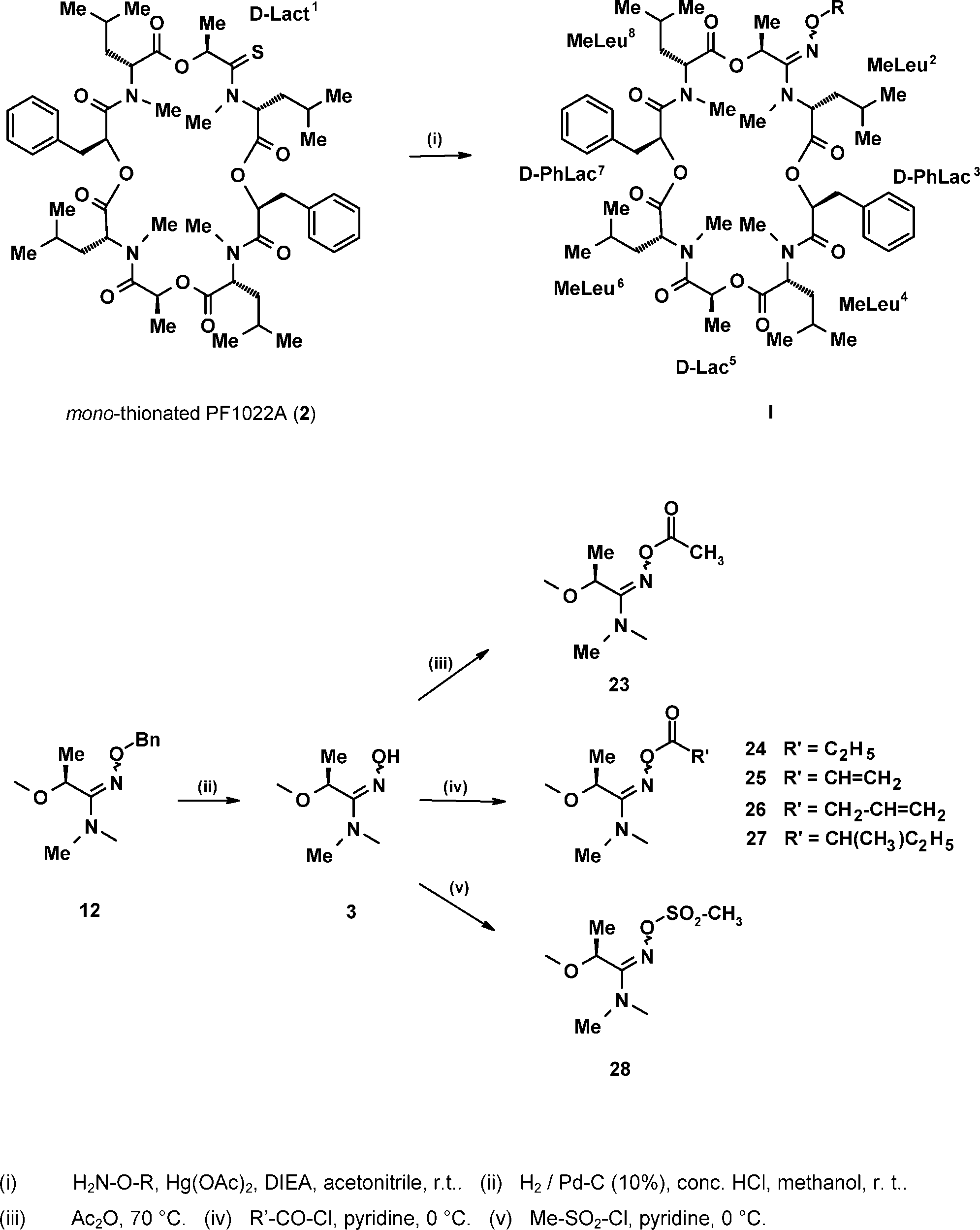
Synthetic routes to the novel N-methylated amidoxime analogues of PF1022A (I).
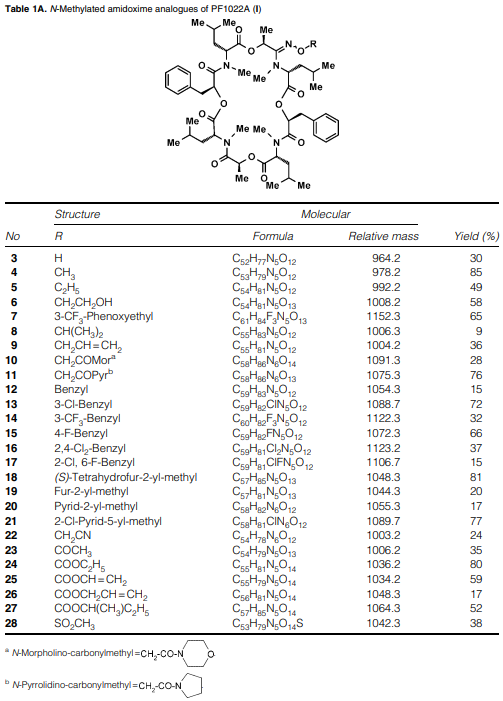
N-Methylated amidoxime analogues of PF1022A (I)
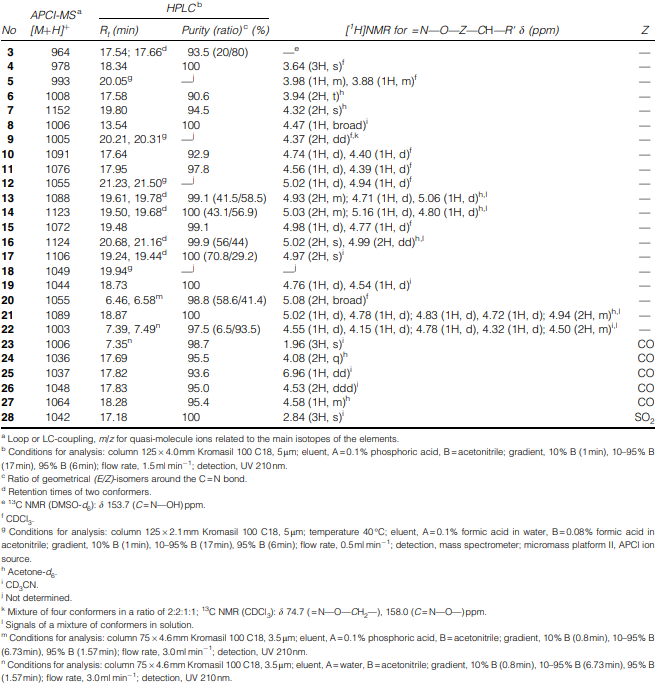
Analytical and spectroscopic data of the N-methylated amidoxime analogues of PF1022A (I)
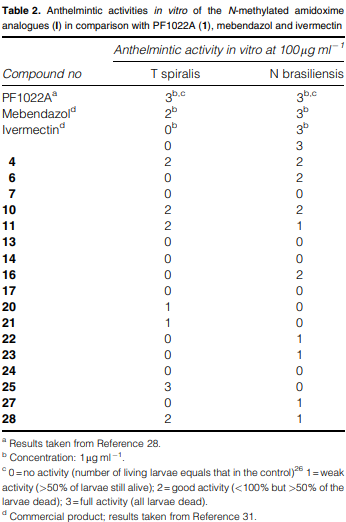
Anthelmintic activities in vitro of the N-methylated amidoxime analogues (I) in comparison with PF1022A (1), mebendazol and ivermectin
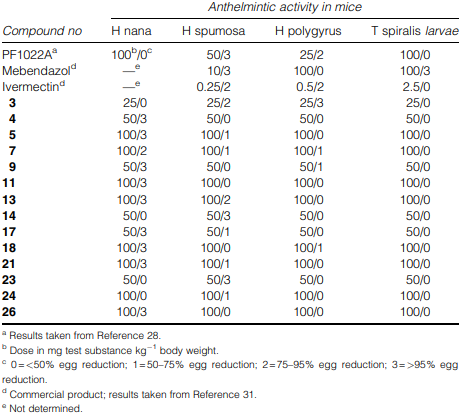
Anthelmintic activities of the N-methylated amidoxime analogues (I) in comparison with PF1022A (1), mebendazol and ivermectin
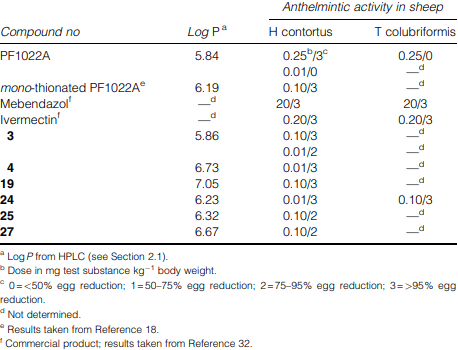
Anthelmintic activities and lipophilicities of the N-methylated amidoxime analogues (I) in comparison with PF1022A (1), mono-thionated PF1022A (2), mebendazol and ivermectin
CAS number: 134-81-6
Benzil is an alpha-diketone that is ethane-1,2-dione substituted by phenyl groups at positions 1 and 2 respectively. It is an alpha-diketone and an aromatic ketone.
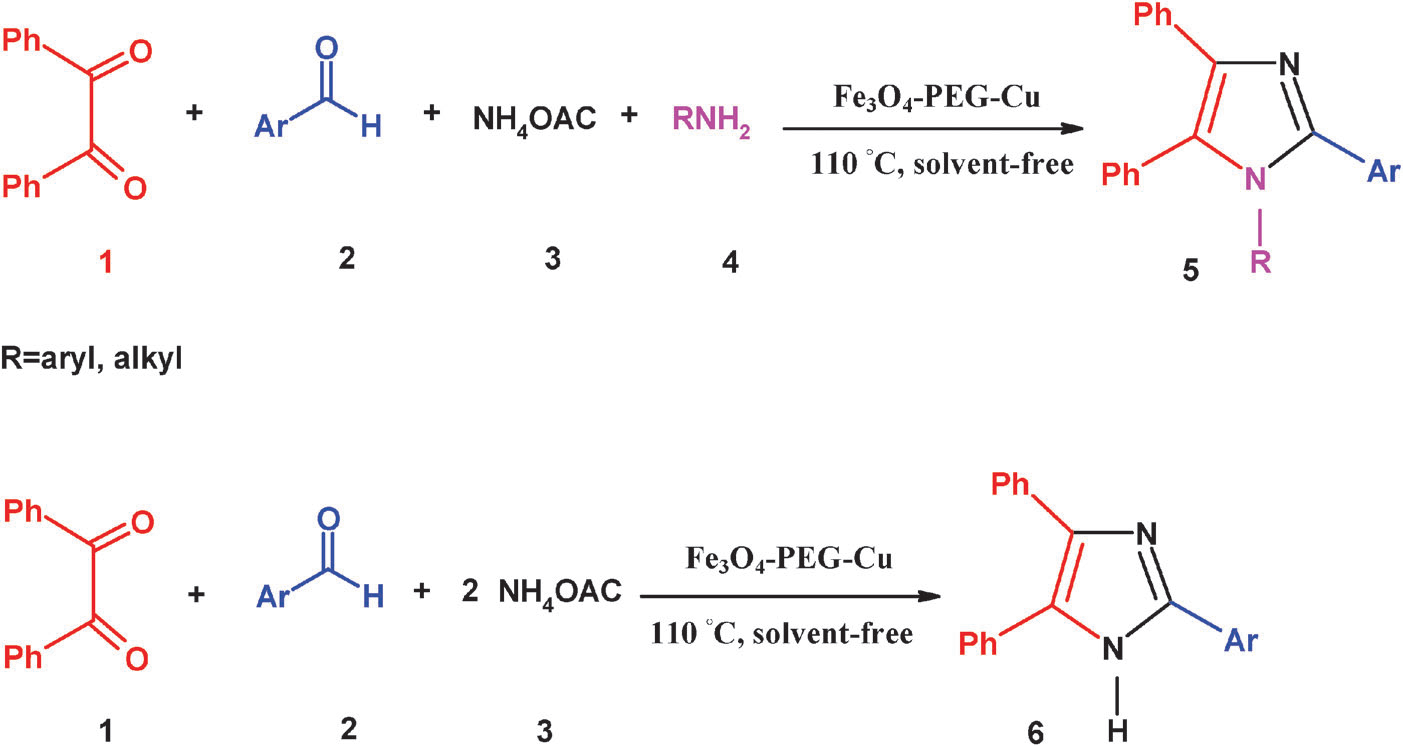
Synthesis of 1,2,4,5-tetrasubstituted/2,4,5-trisubstituted imidazoles by a multi-component reaction of benzil, aldehydes, NH4OAc, and amine by the Fe3O4–PEG–Cu catalyst under solvent-free conditions.
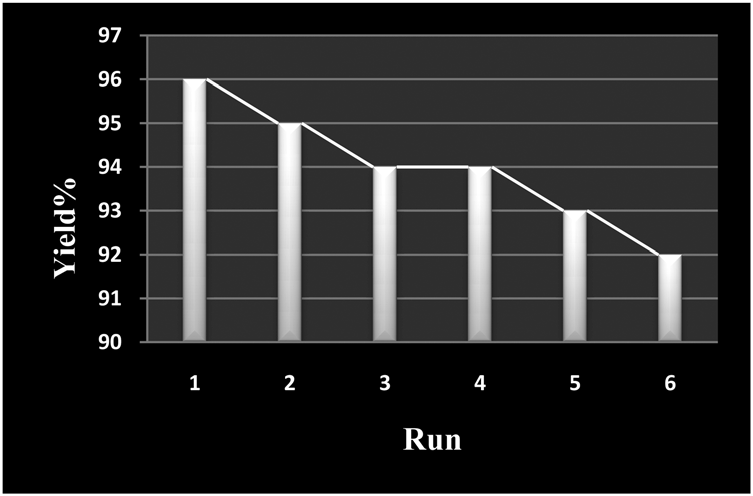
Condensation of benzil, benzaldehyde, ammonium acetate and n-Pr amine using recycled catalysts.
CAS number: 13400-26-5
3-Hydroxychromone (3HC) is a molecule known for its unique fluorescence properties due to a process called excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT). This process results in two distinct fluorescence bands, making it useful as a molecular probe and sensor.
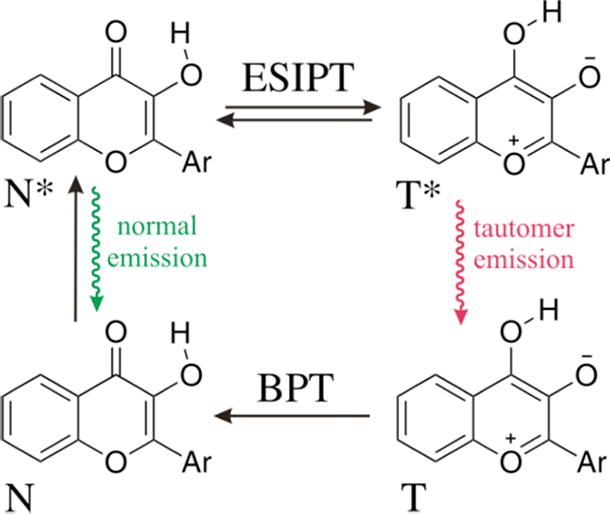
ESIPT reaction in 3-hydroxychromone. BPT stands for back proton transfer, and N* and T* represent the normal and tautomeric emitting forms, respectively.
CAS number: 134029-41-7
Manzacidin A is a bromopyrrole alkaloid, a type of natural product found in marine sponges. It is characterized by its unique structure featuring a bromopyrrole carboxylic acid linked to a tetrahydropyrimidine ring, which includes a nitrogen-containing quaternary carbon stereocenter.
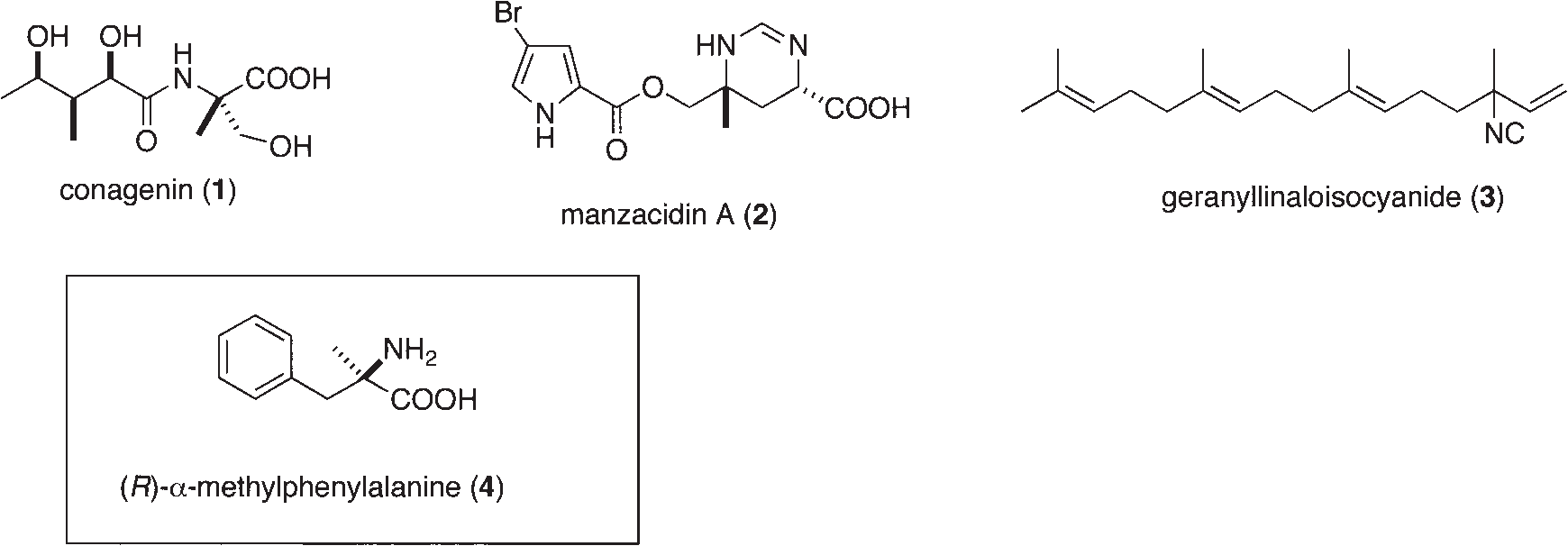
Representative Natural Products and α-Alkyl Amino Acid Containing Quaternary Stereocenter with Nitrogen Substituent: Conagenin, manzacidin A, geranyllinaloisocyanide, alpha-methyl-D-phenylalanine
CAS number: 134308-13-7
Tolcapone is benzophenone substituted on one of the phenyl rings at C-3 and C-4 by hydroxy groups and at C-5 by a nitro group, and on the other phenyl ring by a methyl group at C-4. It is an inhibitor of catechol O-methyltransferase. It has a role as an EC 2.1.1.6 (catechol O-methyltransferase) inhibitor and an antiparkinson drug. It is a member of benzophenones, a member of 2-nitrophenols and a member of catechols.
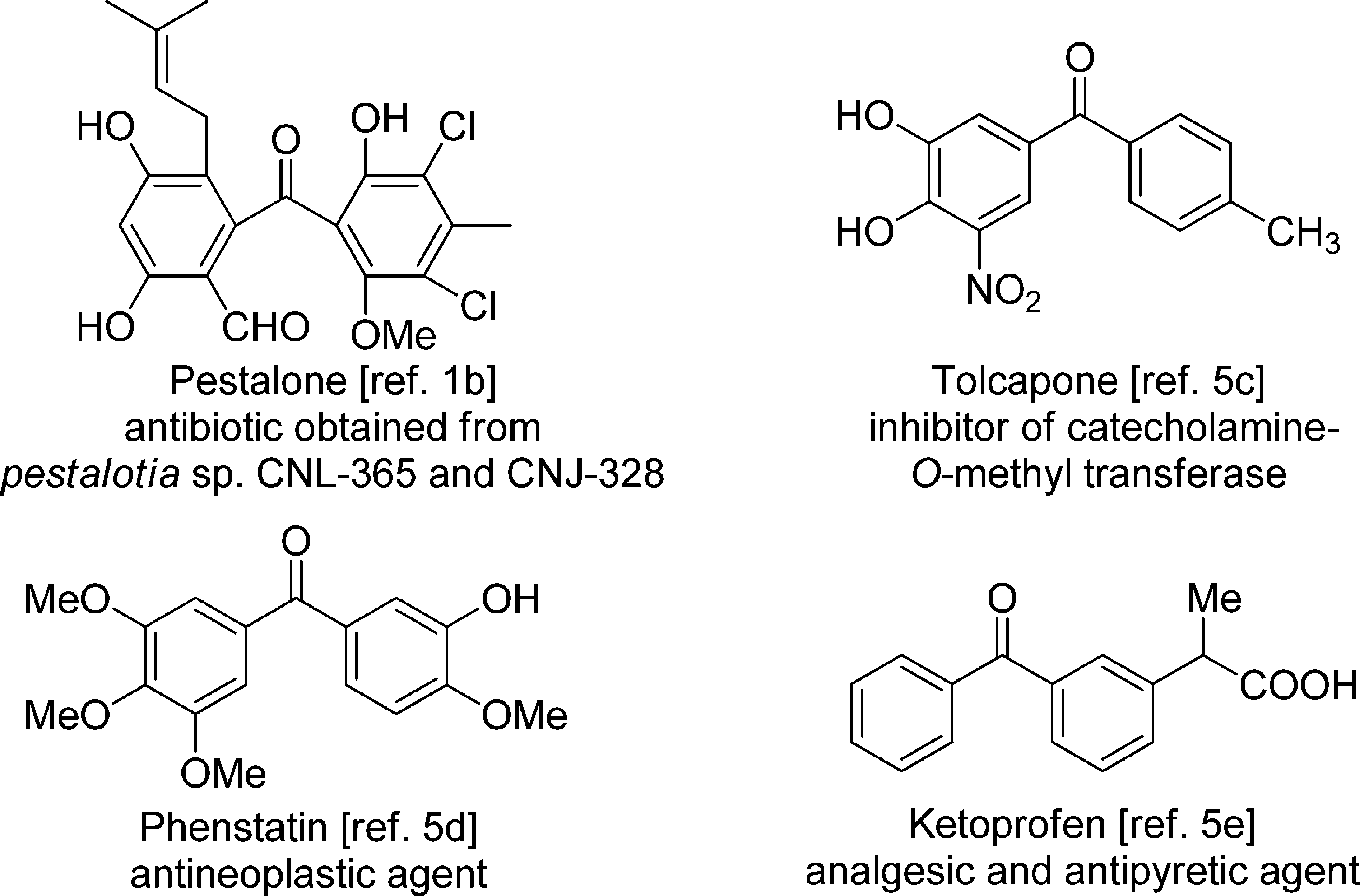
Bioactive Compounds with the Diarylmethanone Motif: Pestalone, Tolcapone, Phenstatin, Ketoprofen
CAS number: 134381-30-9
Conagenin (CNG) is a microbial metabolite, originally isolated from Streptomyces roseosporus, known for its immunomodulatory and potential antitumor properties. It acts as a T cell proliferation accelerator and may have applications in cancer chemotherapy.

Representative Natural Products and α-Alkyl Amino Acid Containing Quaternary Stereocenter with Nitrogen Substituent: Conagenin, manzacidin A, geranyllinaloisocyanide, alpha-methyl-D-phenylalanine