Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 141-78-6
Ethyl acetate is the acetate ester formed between acetic acid and ethanol. It is a widely used solvent, especially for paints, varnishes, lacquers, cleaning mixtures, and perfumes.
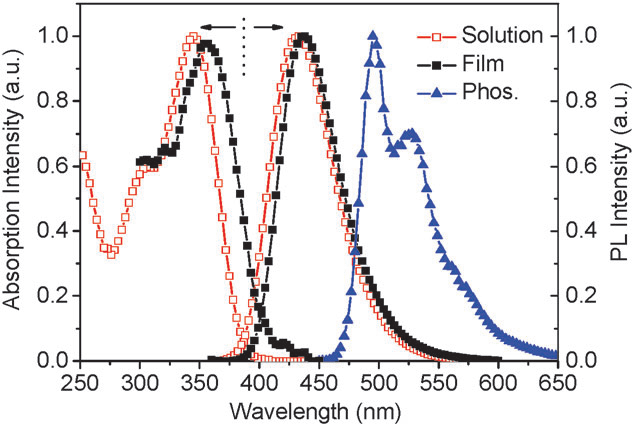
Room-temperature UV-Vis absorption spectra, PL spectra of POA in ethyl acetate and thin films, as well as its phosphorescence spectrum in 2-methyltetrahydrofuran at 77 K.
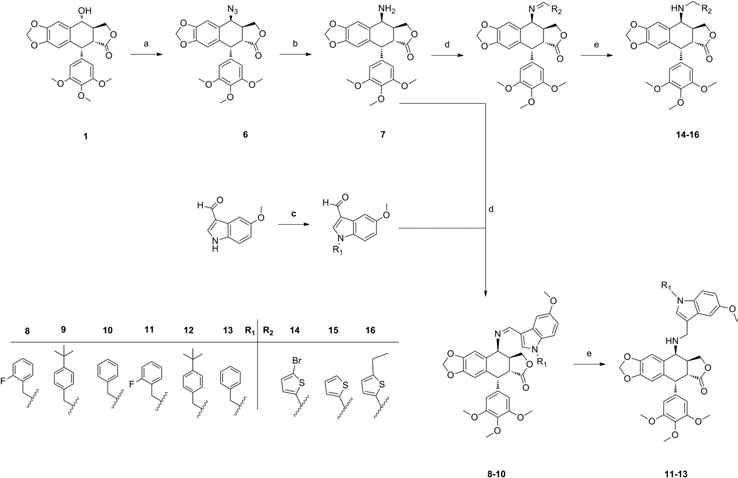
Synthesis route, conditions and reagents of the target compound: (a) NaN3, CF3COOH, CH2Cl2; (b) HCOONH4, 10% Pd/C, CH3COOC2H5; (c) NaH, DMF; (d) HAc, CH3OH; (e) NaBH4, CH3OH.
CAS number: 141-82-2
Malonic acid is an alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid in which the two carboxy groups are separated by a single methylene group. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a malonate(1-).
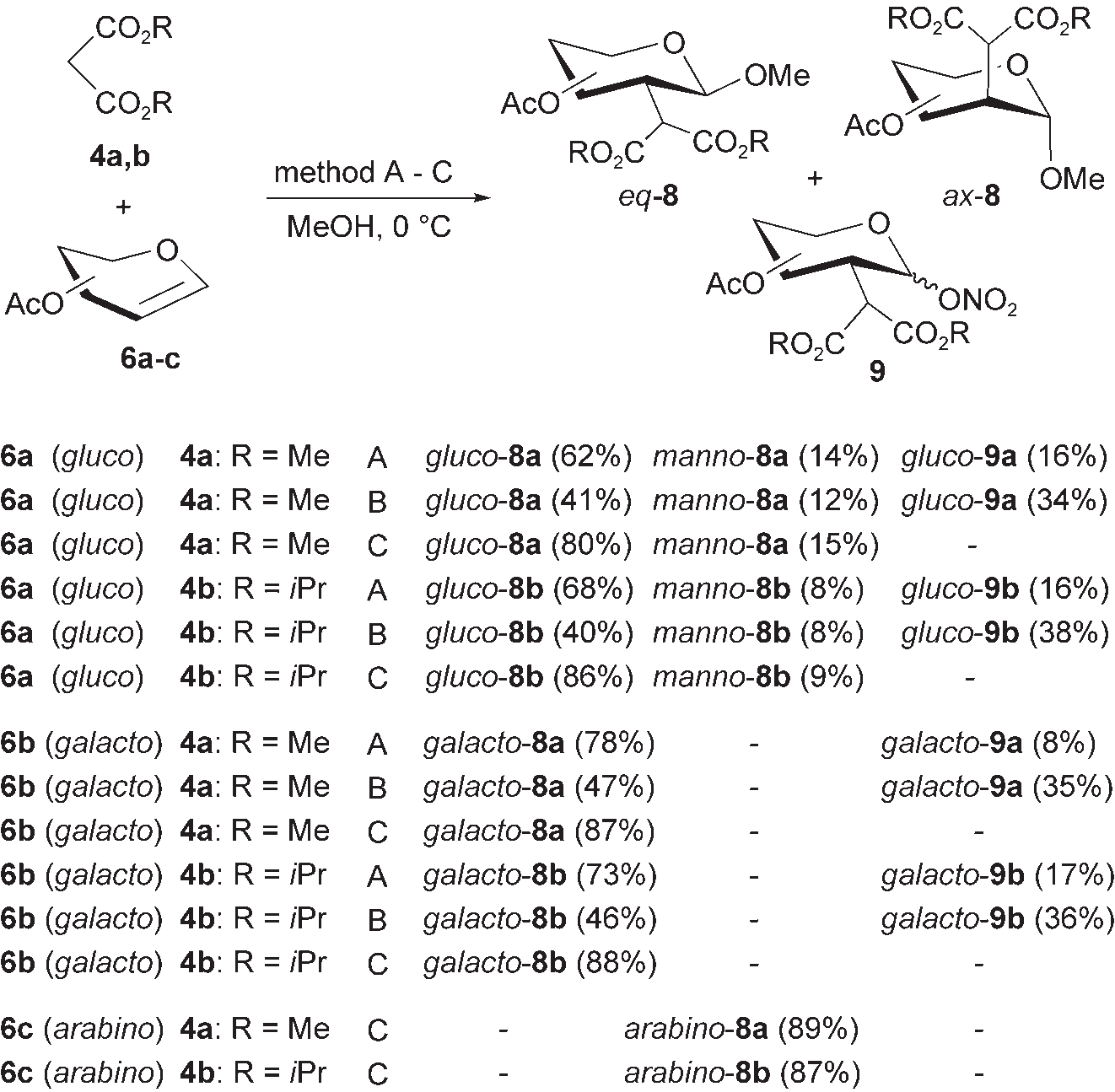
Addition of malonates 4 to glycals 6. Method A: 4 equiv CAN; method B: 4 equivCAN, 0.5 equivwater; method C: 4 equivanhy-drous CAN. Yields of isolated products after column chromatography are indicated in parentheses.
CAS number: 141-97-9
Ethyl acetoacetate is an ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of acetoacetic acid with ethanol.
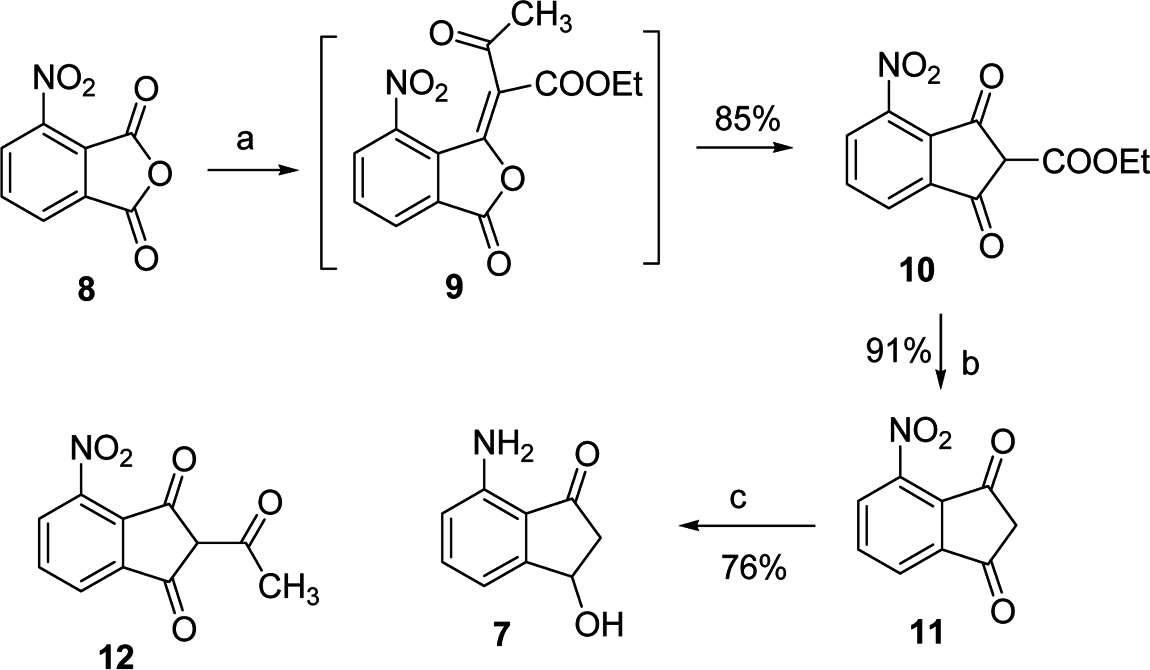
Reagents and conditions: (a) ethyl acetoacetate, acetic anhydride, triethylamine, dichloromethane, room temperature, 30 min; (b) trifluroacetic, acetonitrile, room temperature, 45 min; (c) 40 psi H2, 10% Pd=C, methanol, 24 h.
CAS number: 142-08-5
Pyridin-2-ol is a monohydroxypyridine that is pyridine substituted by a hydroxy group at position 2. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
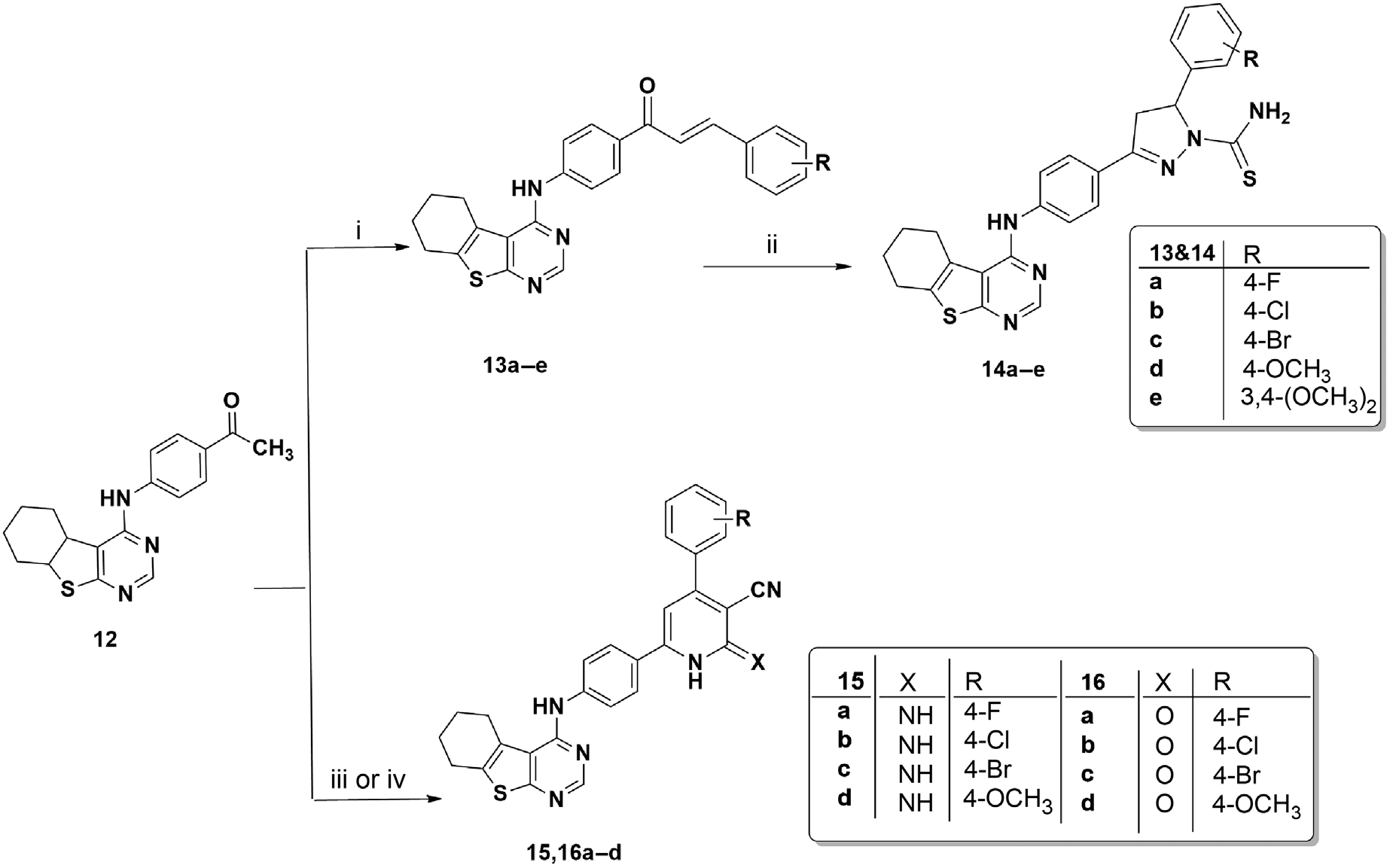
Synthesis of chalcones and pyrazoline derivatives (13a–e) in 50–70% yield, (14a–e) in 57–82% yield, 2-iminopyridine derivatives (15a–d) in 64–78% yield, and 2-oxopyridine derivatives (16a–d) in 62–71% yield.
CAS number: 142-29-0
Cyclopentene, a cyclic alkene, can be copolymerized with ethene or propene by heterogeneous and homogeneous Ziegler–Natta catalysts.
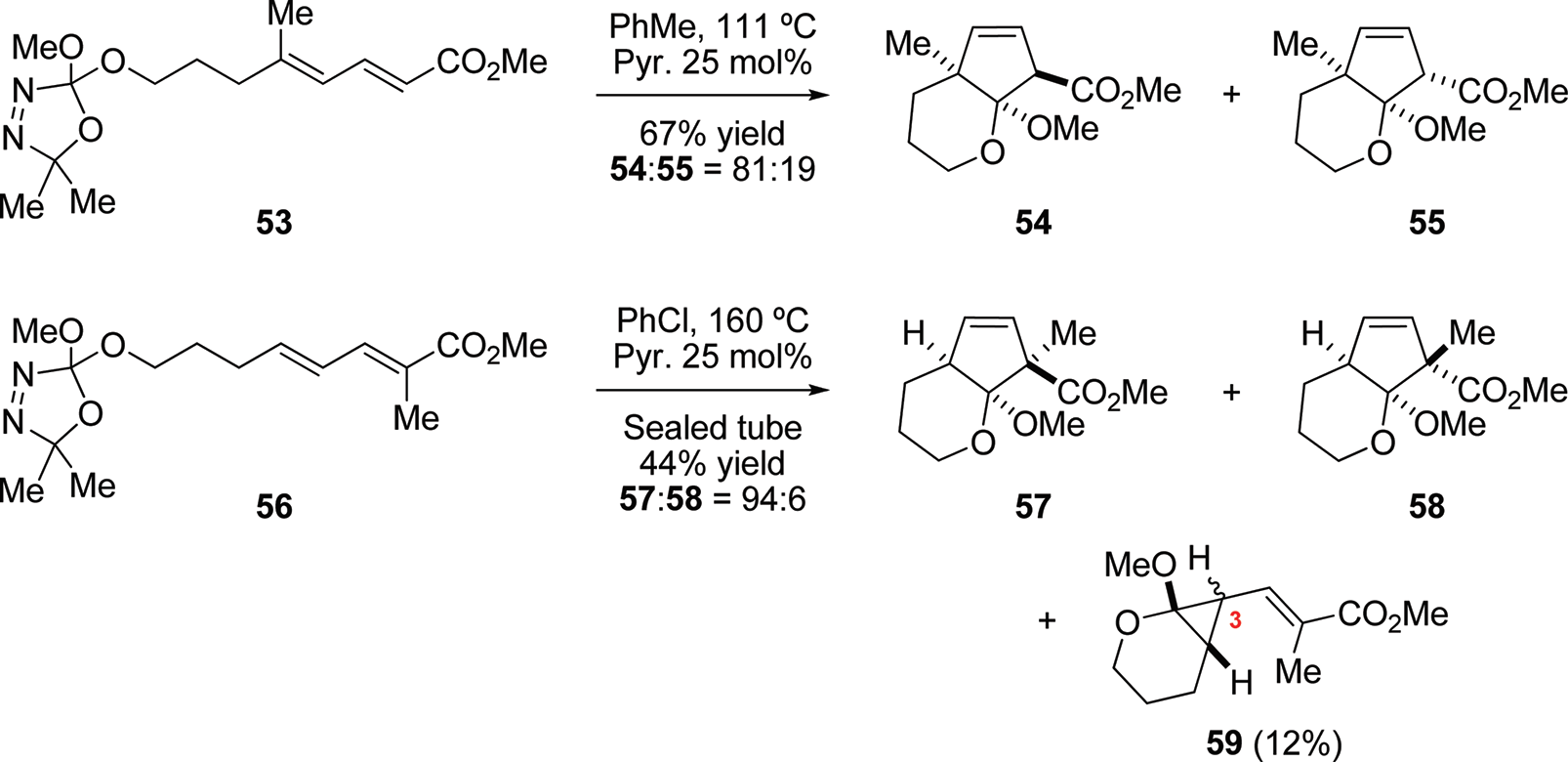
Formation of Cyclopentenes with Chiral Quaternary Carbons
CAS number: 142-82-5
Heptane is a straight-chain alkane with seven carbon atoms. It has been found in Jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi). It has a role as a non-polar solvent and a plant metabolite. It is a volatile organic compound and an alkane.
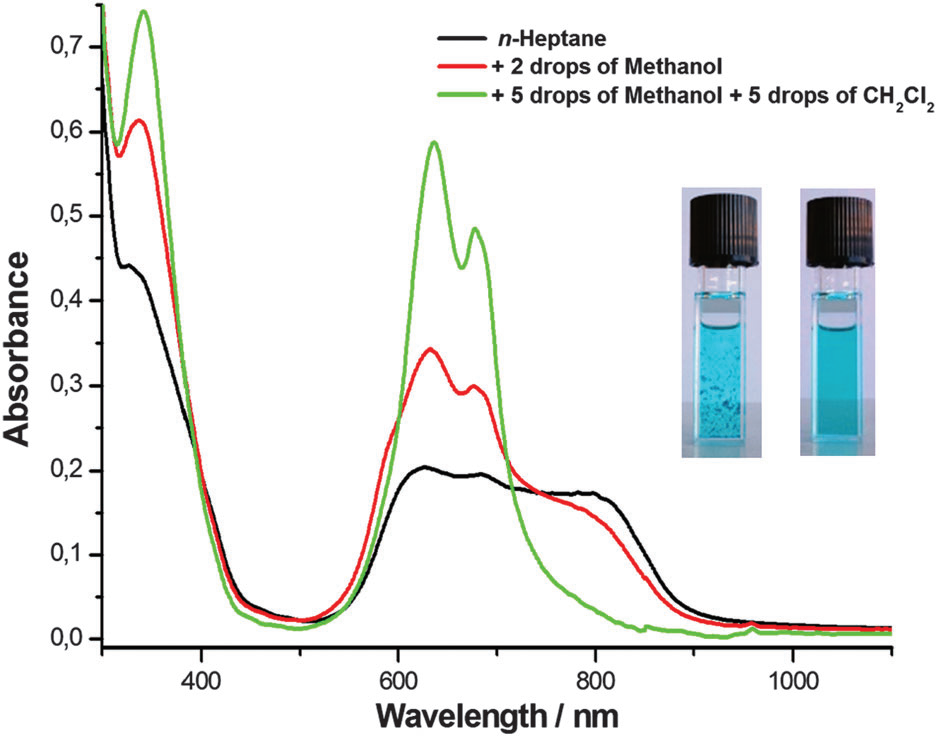
Absorption spectra of ZnPc-6d in dry n-heptane, after addition of two drops of methanol (red line) and followed by five more drops of methanol and five drops dichloromethane (the green line).
CAS number: 14333-33-6
C-11, also known as Carbon-11, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with a half-life of about 20.4 minutes. It is primarily used in positron emission tomography (PET) as a radioactive tracer to study various biological processes in living organisms.
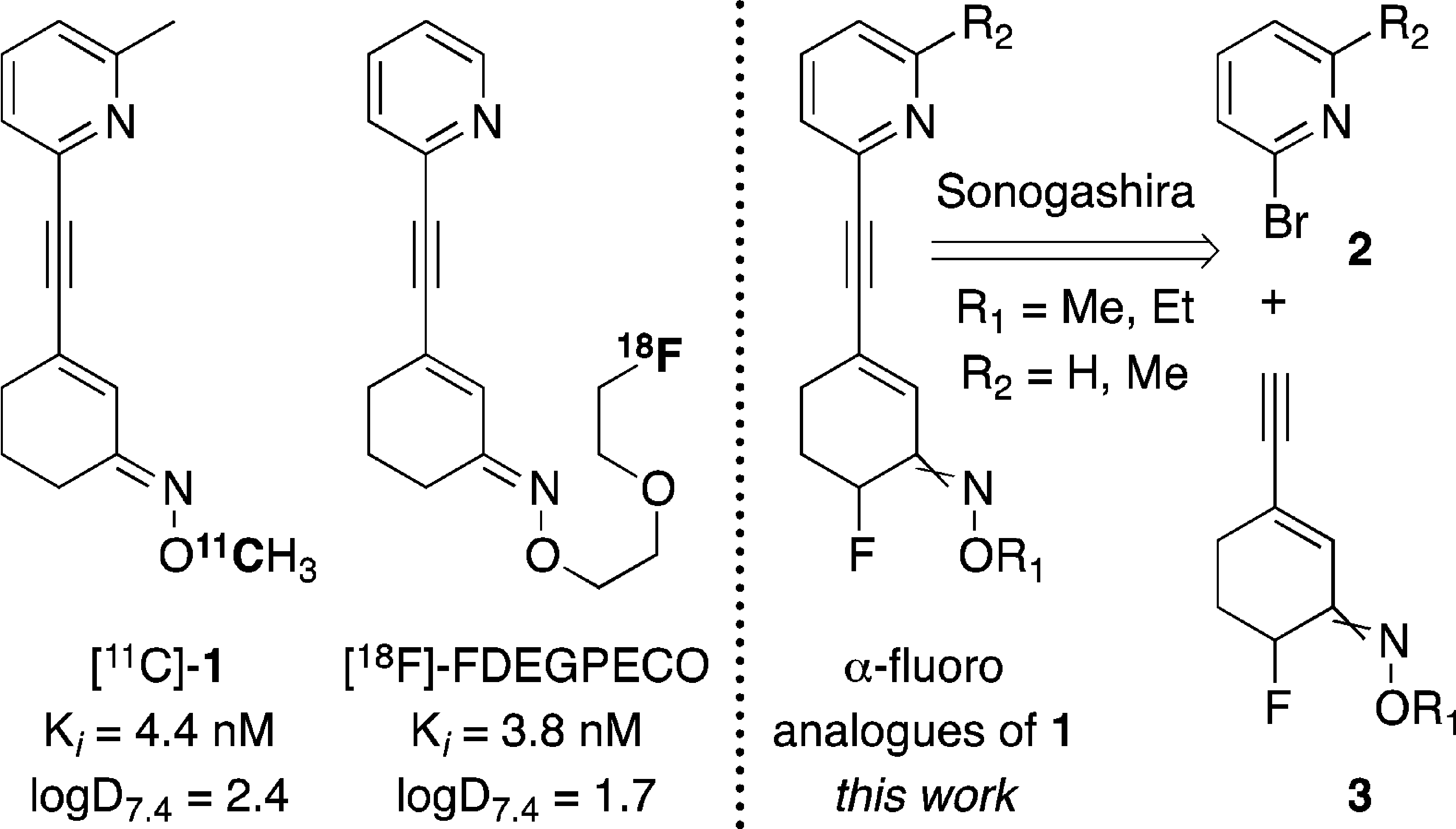
Structures of carbon-11 and fluorine-18 mGluR5 PET radiotracers from the Ametamey group and the synthetic plan to a new series of α-fluorinated analogues of 1. A crossed double bond is used to indicate double bond isomers (E and Z).
CAS number: 1438-30-8
A basic polypeptide isolated from Streptomyces netropsis. It is cytotoxic and its strong, specific binding to A-T areas of DNA is useful to genetics research.
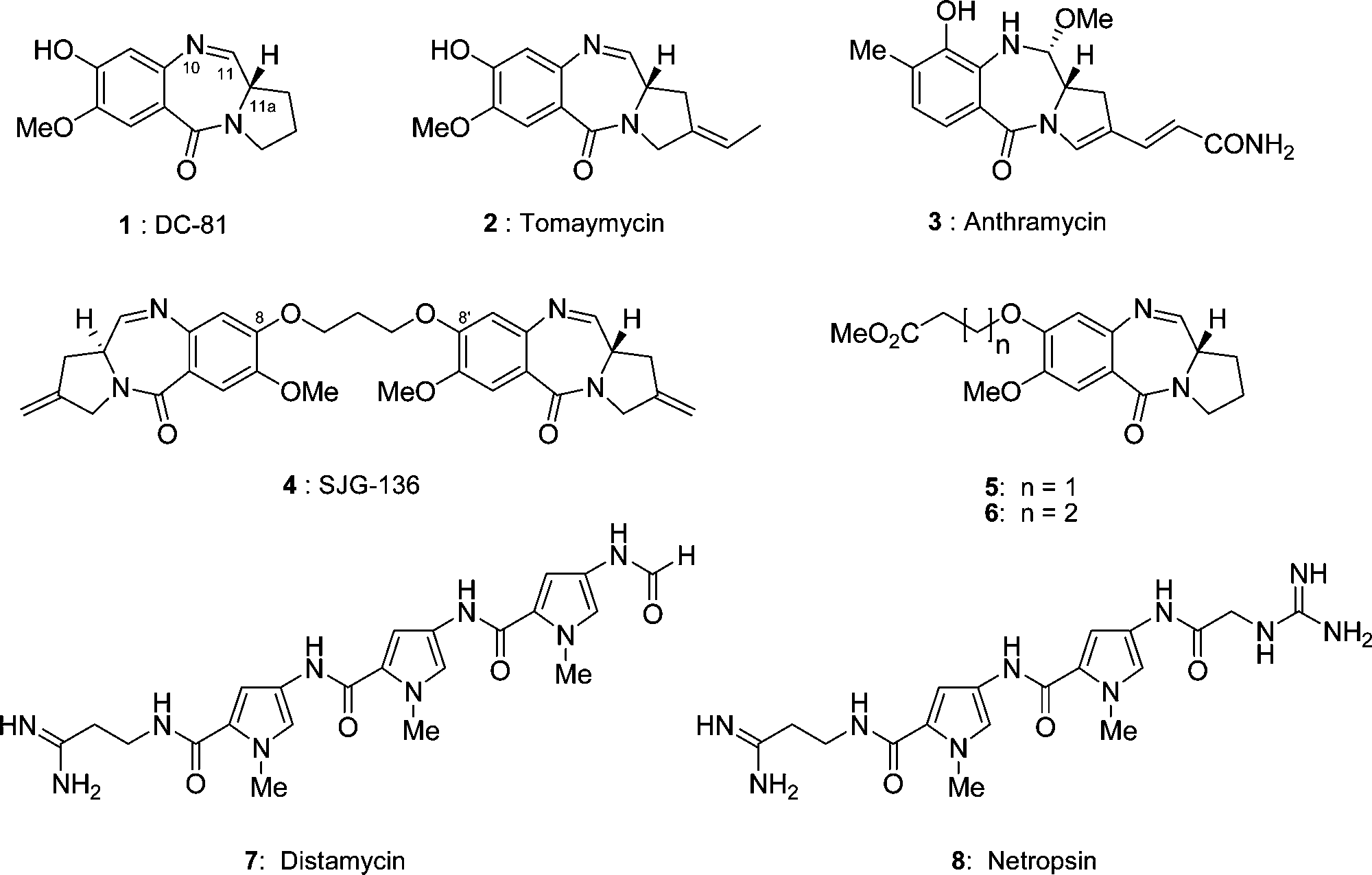
Structures of the PBD monomers (1, 2, 3, 5, and 6), the PBD dimer 4, and distamycin and netropsin (7 and 8).
CAS number: 144026-79-9
Scandium triflate, also known as scandium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate, is a highly effective and versatile Lewis acid catalyst used in organic chemistry, particularly for Friedel-Crafts reactions, Diels-Alder reactions, and other carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions.
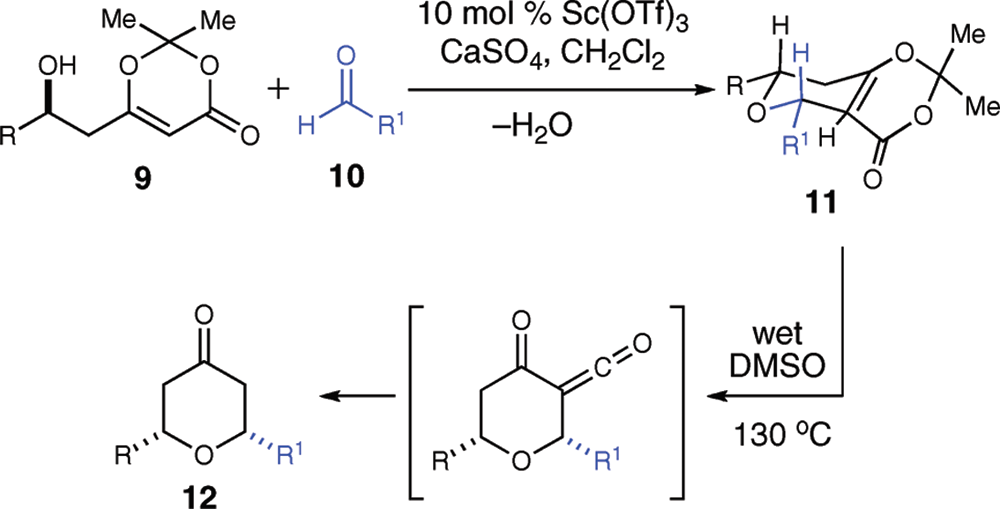
Scandium(III) triflate Methodology
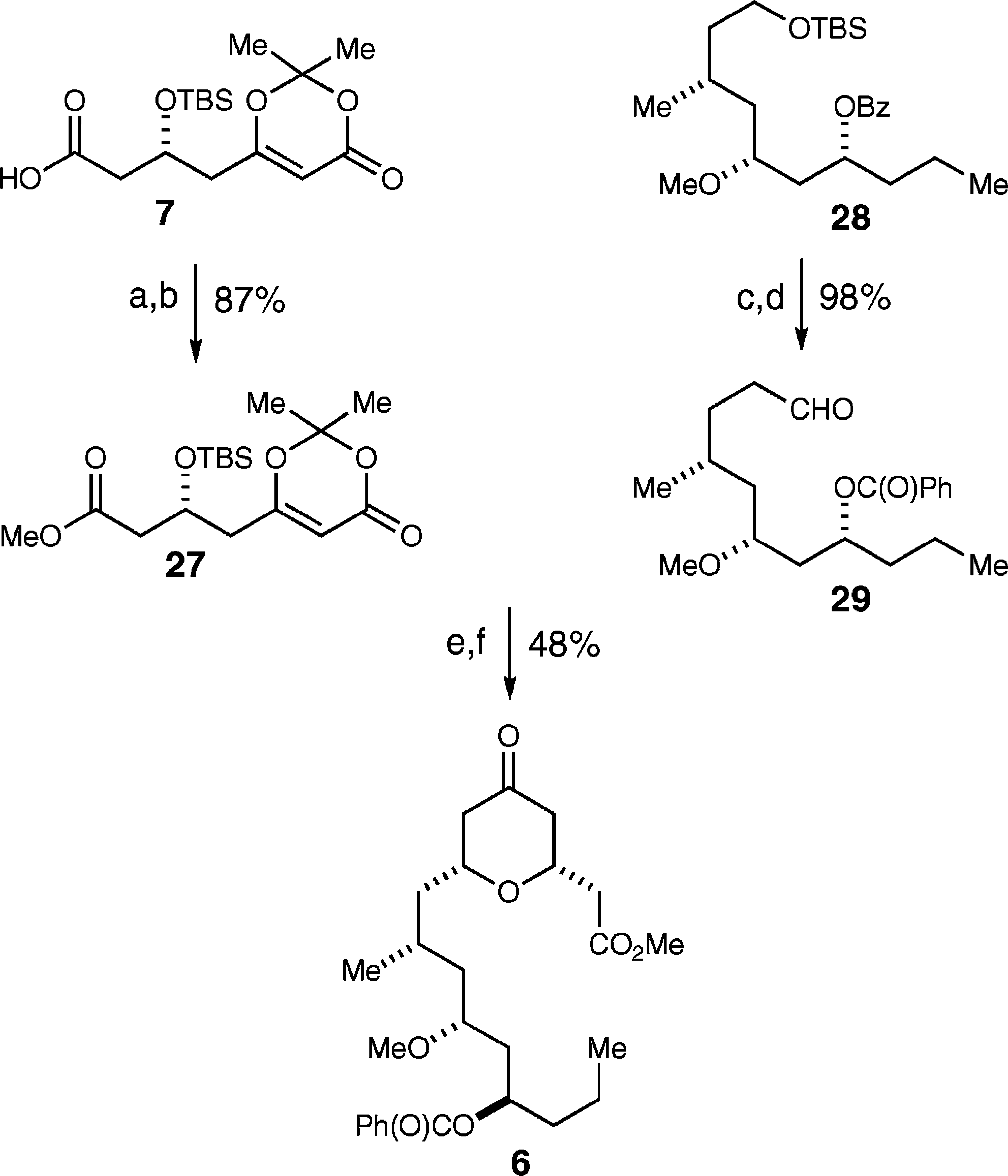
Intermolecular Scandium(III) triflate Methodology
CAS number: 14464-46-1
Cristobalite is defined as a high-temperature polymorph of silica that typically occurs in volcanic rocks, exhibiting structural transformations under varying pressure conditions, including a transition to lower symmetry phases or amorphization at high pressures.
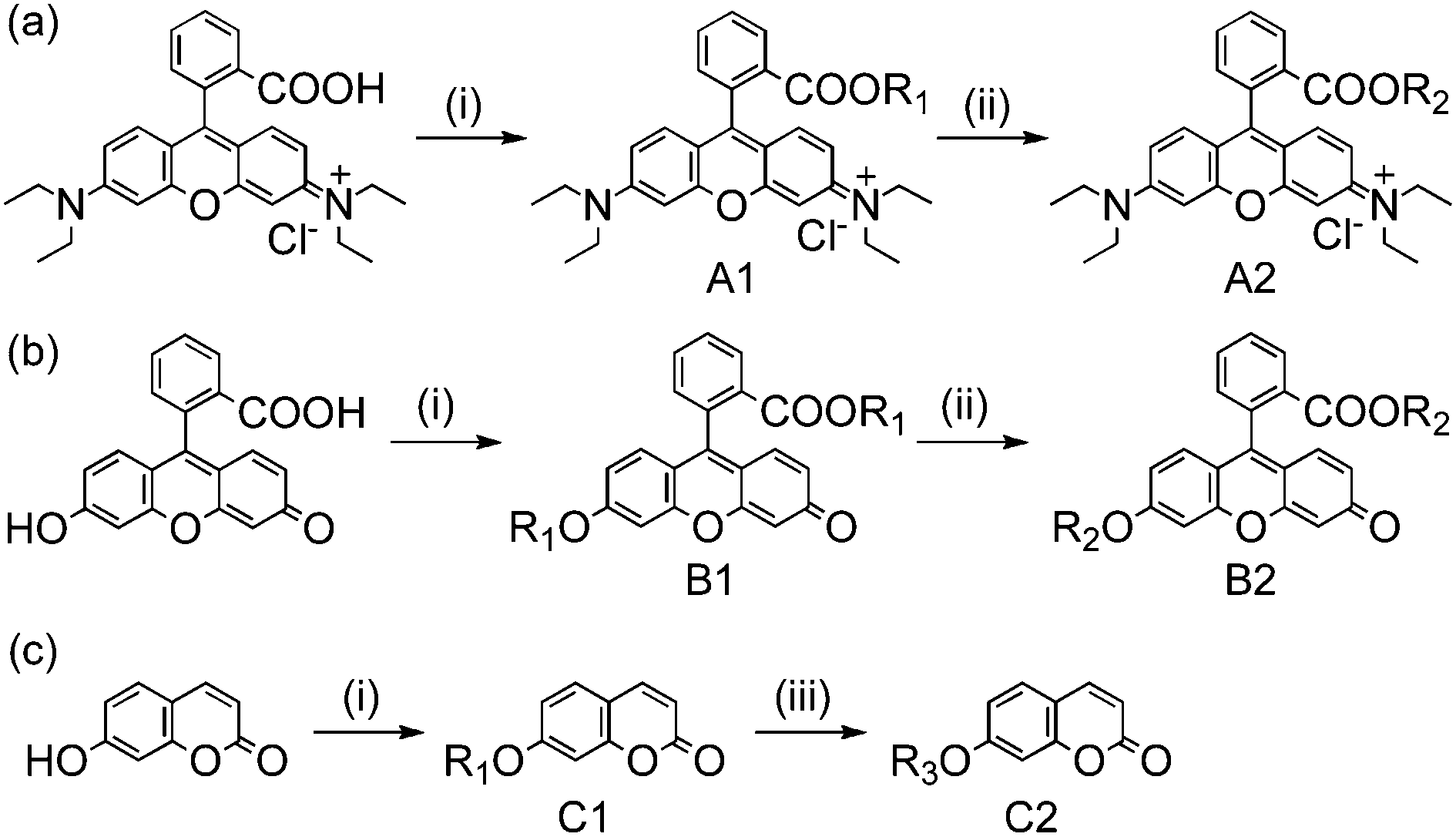
Derivatization of organic dyes for incorporation into silica matrices.
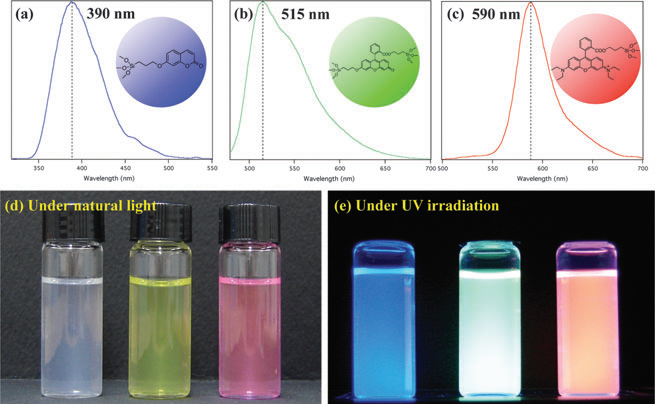
Photoluminescence spectra and photographs of 50 nm-sized, dye-doped silica nanoparticles in water.
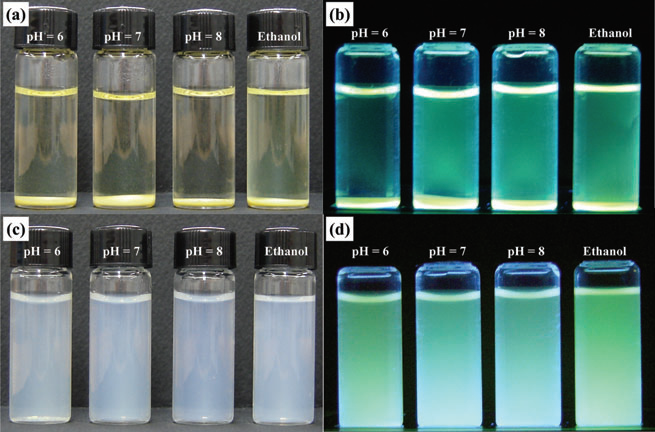
Stability of 50 nm fluorescent silica nanoparticles in water and ethanol at different pH values; (a) and (b) precipitated SiO2 prepared by FITC-APS conjugation; (c) and (d) dispersed SiO2 prepared by direct modification of fluorescein molecules as described in Scheme 1(b). Images of (b) and (d) were taken under UV illumination.
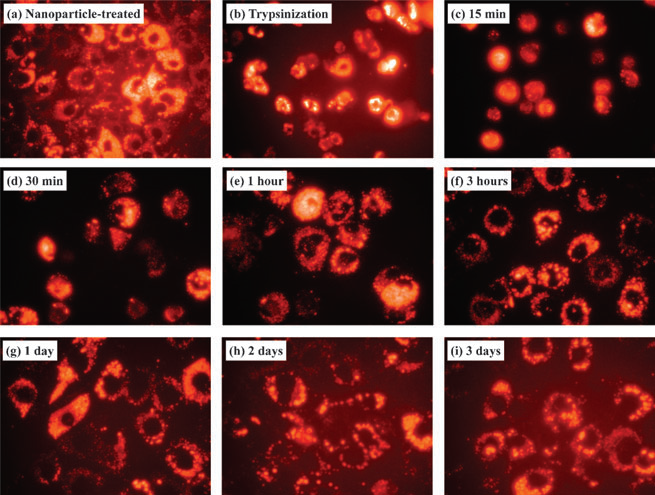
Fluorescent images of MC3T3-E1 cells incubated with 50 nm-sized, positively charged, orange fluorescent silica nano- particles; 100 mg mlÀ1 of nanoparticles were added to the medium.
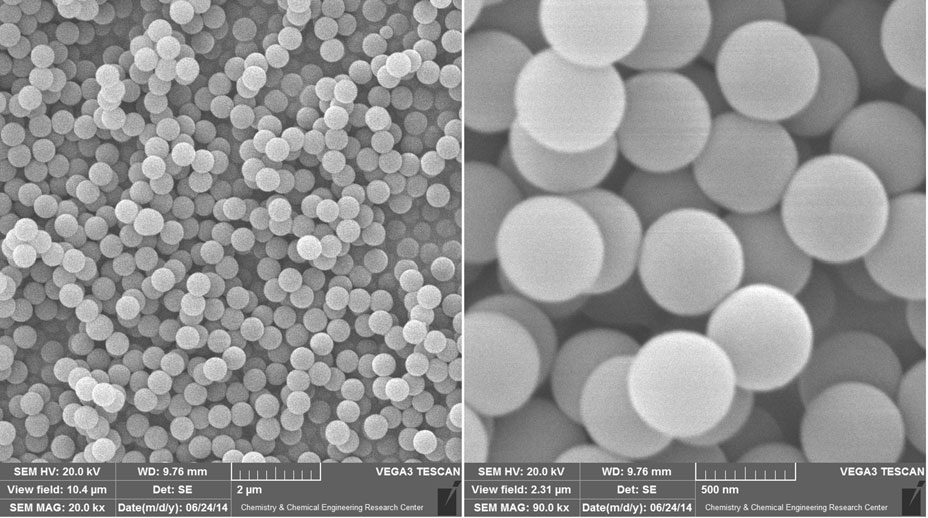
SEM images of silica particles prepared using the Stçber method.