Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 1211-29-6
(-)-methyl jasmonate is a jasmonate ester that is the methyl ester of jasmonic acid. It has a role as a member of jasmonates, a plant metabolite and a plant hormone. It is a jasmonate ester, a methyl ester and a member of Jasmonate derivatives.
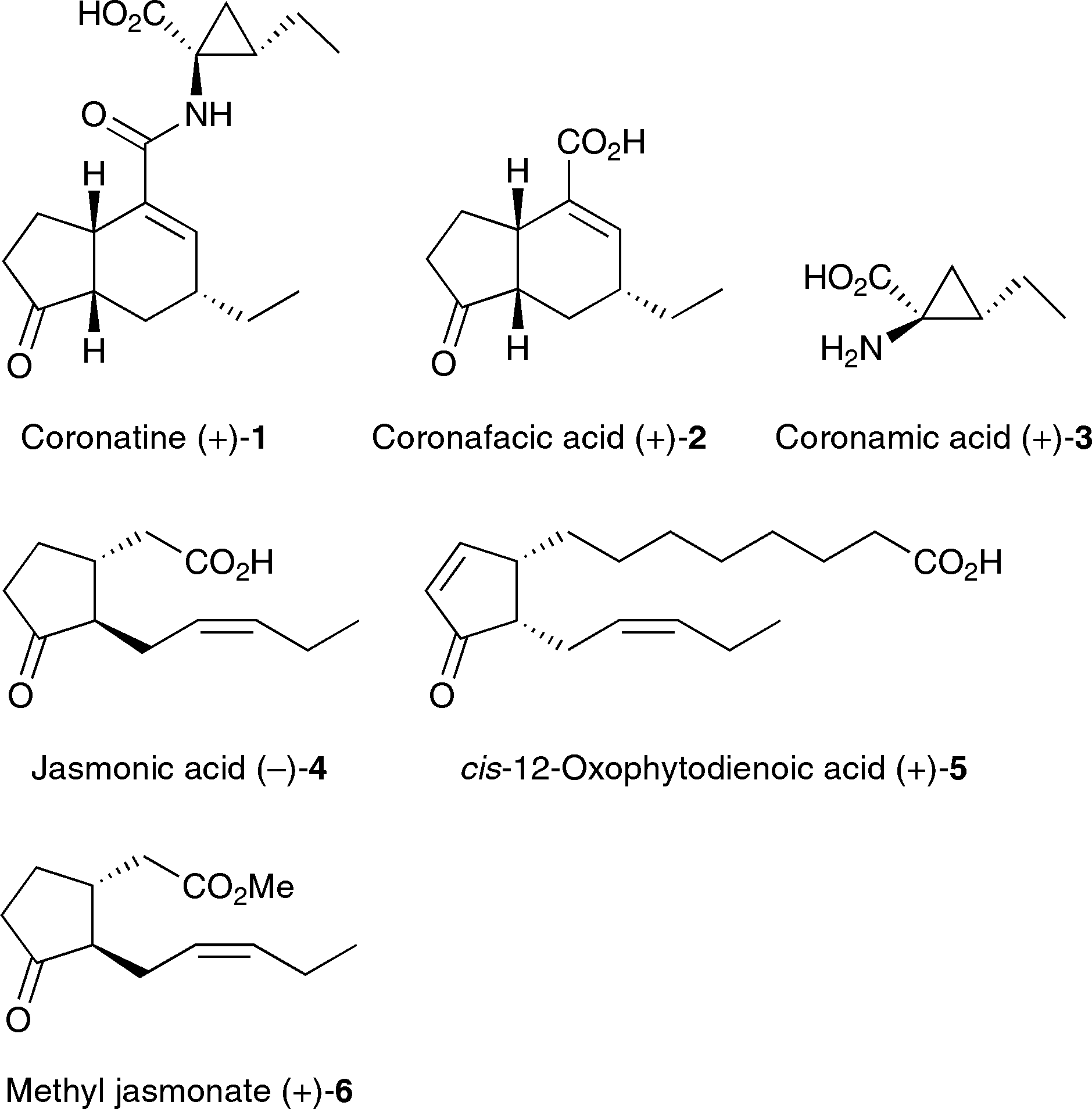
Structures of coronatine (+)-1, jasmonic acid (-)-4, and their derivatives.
CAS number: 12150-46-8
1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene (commonly abbreviated as dppf) is an organophosphorus compound featuring a ferrocene backbone substituted at the 1,1′-positions with two diphenylphosphino groups. It appears as an orange crystalline solid and is widely used as a bidentate ligand in coordination and organometallic chemistry due to its ability to form stable complexes with transition metals.
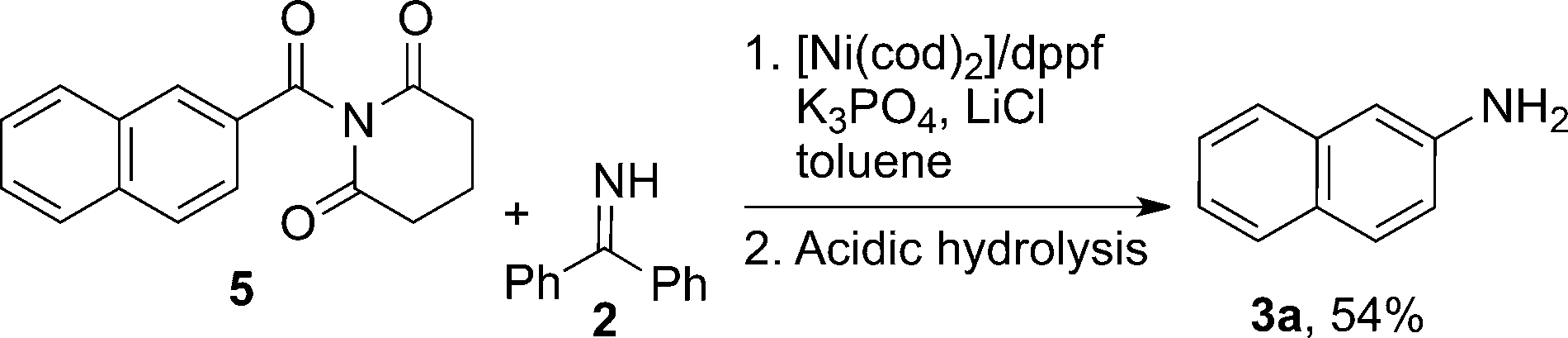
Nickel-catalyzed decarbonylative amination of naphthyl amide. dppf=1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)ferrocene.
CAS number: 121502-04-3
Maltosine, a 3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone derivative of lysine formed in the course of the advanced Maillard reaction, is an effective metal chelating agent.
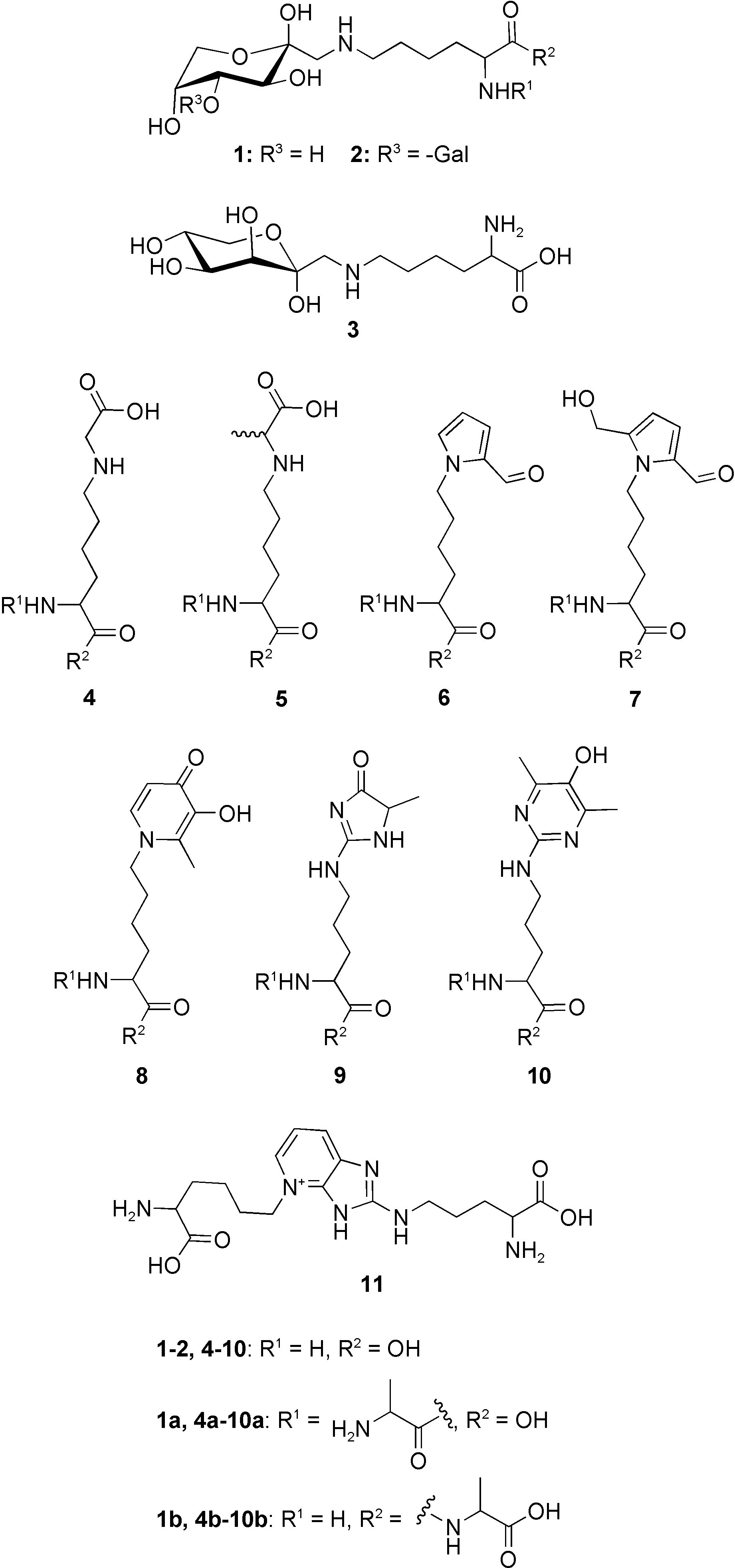
Chemical structures of the investigated Maillard reaction prod- ucts fructoselysine (1), lactuloselysine (2), tagatoselysine (3), CML (4), CEL (5), formyline (6), pyrraline (7), maltosine (8), MG-H1 (9), argpyrimidine (10), and pentosidine (11).
CAS number: 121749-39-1
Diethylnorspermine is a synthetic bis-ethyl analogue of spermine with potential antineoplastic activity. N(1),N(11)-bis(ethyl)norspermine (DENSPM), a N-terminally alkylated tetraamine and polyamine mimetics, disrupts polyamine pool homeostasis by modulating the activities of the biosynthetic enzymes, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), and S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (AdoMetDC). This agent also reduces polyamine concentrations through the induction of the catabolic enzyme spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SSAT). Polyamines, an integral part of the DNA helix structure, play a critical role in cell division, differentiation and membrane function. Disruption of normal polyamine concentrations by DENSPM may lead to cell growth inhibition.
![metabolism of diethylnorspermine [DENSPm; DE(3,3,3)] and diethylhomospermine [DEHSPm; DE(4,4,4)].](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4915294_02.png)
metabolism of diethylnorspermine [DENSPm; DE(3,3,3)] and diethylhomospermine [DEHSPm; DE(4,4,4)].
CAS number: 122-59-8
Phenoxyacetic acid is a monocarboxylic acid that is the O-phenyl derivative of glycolic acid. Phenoxyacetic acids are very important chemicals because of their wide distribution and extensive use as plant growth regulators.
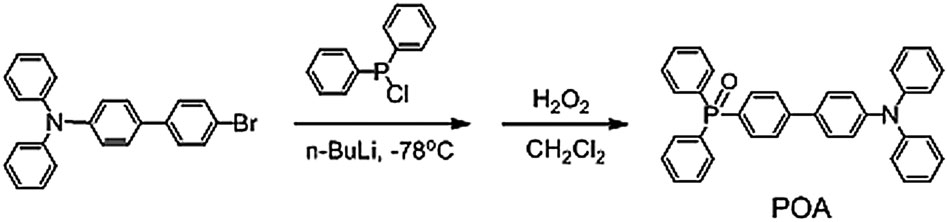
Synthetic route and molecular structure of POA.
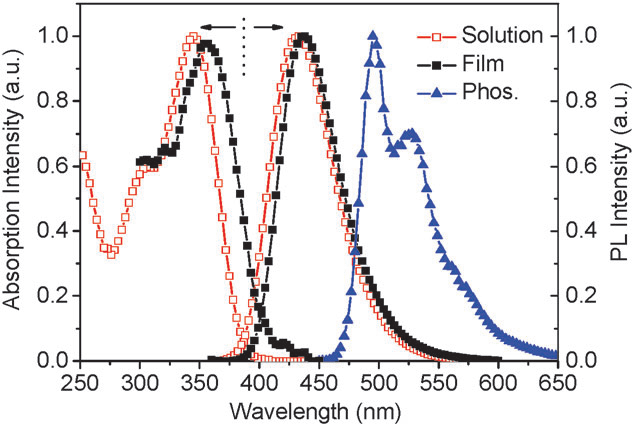
Room-temperature UV-Vis absorption spectra, PL spectra of POA in ethyl acetate and thin films, as well as its phosphorescence spectrum in 2-methyltetrahydrofuran at 77 K.
CAS number: 122-60-1
Phenyl glycidyl ether (PGE) is a colorless liquid used as a reactive diluent to reduce the viscosity of epoxy resins for coatings and composites, and as a solvent or additive in various household products, paints, lacquers, and adhesives. It is a toxic and potentially carcinogenic compound, causing moderate skin and eye irritation, and has shown carcinogenicity in animal studies.
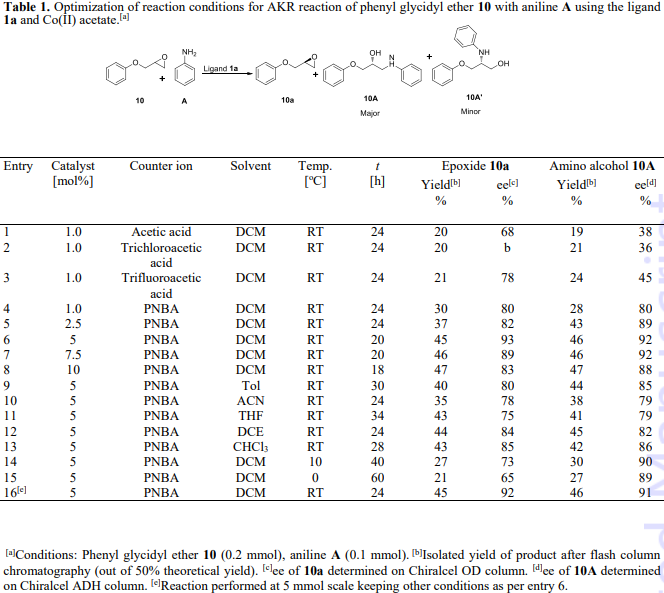
Optimization of reaction conditions for AKR reaction of phenyl glycidyl ether 10 with aniline A using the ligand 1a and Co(II) acetate.
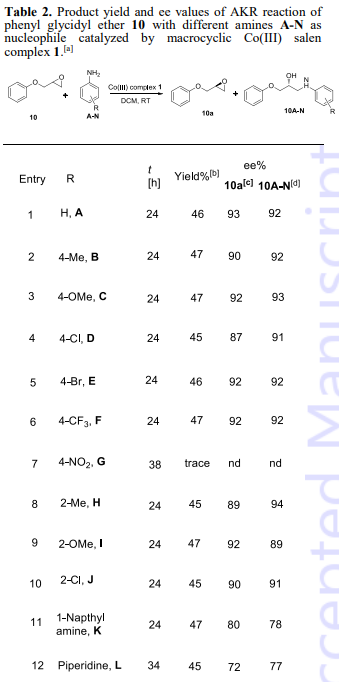
Product yield and ee values of AKR reaction of phenyl glycidyl ether 10 with different amines A-N as nucleophile catalyzed by macrocyclic Co(III) salen complex 1.
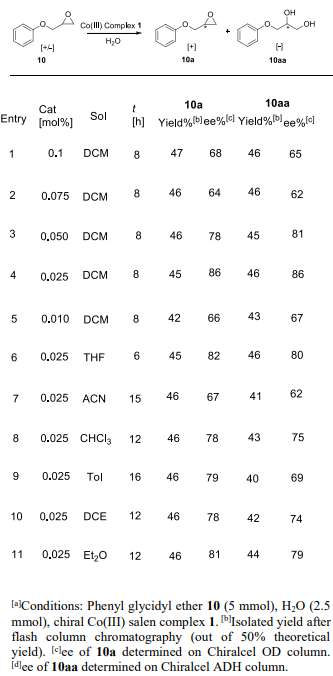
Optimization of reaction conditions for the hydrolytic kinetic resolution of phenyl glycidyl ether 10 using the macrocyclic Co(III) salen complex 1.
CAS number: 122-97-4
Benzenepropanol, also known as phenylpropanol, is an organic compound characterized by a benzene ring attached to a propanol group.
![O-Arylation of 3-phenylpropanol (1a) and phenol (1ab) by triarylsulfonium triflates in the presence of CsOH.[a] [a] Reaction conditions: 1a or 1ab (0.2 mmol), 2 (0.3 mmol), CsOH (0.3 mmol), 1,4-dioxane (2 mL), 508C, N2, 24 h. Isolated yield. [b] Toluene (2 mL) as solvent and at 808C. [c] 808C. [d] 0.4 mmol scale (1ab).](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/1296374_13.png)
O-Arylation of 3-phenylpropanol (1a) and phenol (1ab) by triarylsulfonium triflates in the presence of CsOH.[a] [a] Reaction conditions: 1a or 1ab (0.2 mmol), 2 (0.3 mmol), CsOH (0.3 mmol), 1,4-dioxane (2 mL), 508C, N2, 24 h. Isolated yield. [b] Toluene (2 mL) as solvent and at 808C. [c] 808C. [d] 0.4 mmol scale (1ab).
CAS number: 1222-57-7
Zolimidine is a member of imidazoles.
![Approved drugs containing imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines: zolpidem, Zolimidine, Olprinone](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/663811_02.png)
Approved drugs containing imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines: zolpidem, Zolimidine, Olprinone
CAS number: 123-54-6
Acetylacetone is a beta-diketone that is pentane in which the hydrogens at positions 2 and 4 are replaced by oxo groups. It is a conjugate acid of an acetylacetonate.
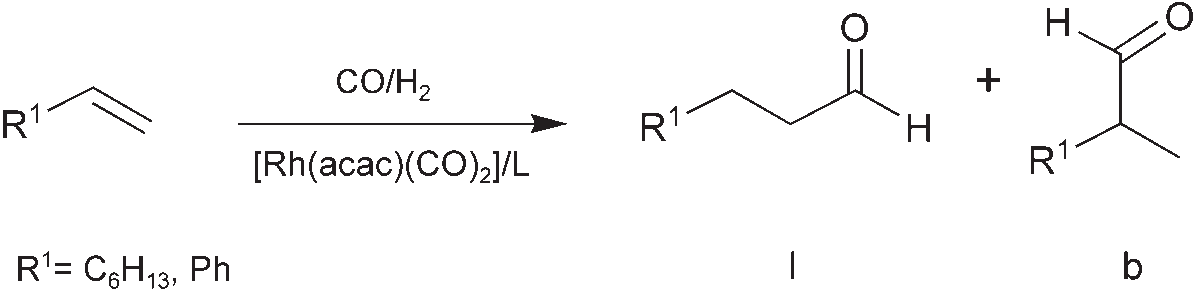
Rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation of 1-octene and styrene. acac=acetylacetone.
CAS number: 123-62-6
Propionic anhydride is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point 165 °F. Density 8.4 lb /gal. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
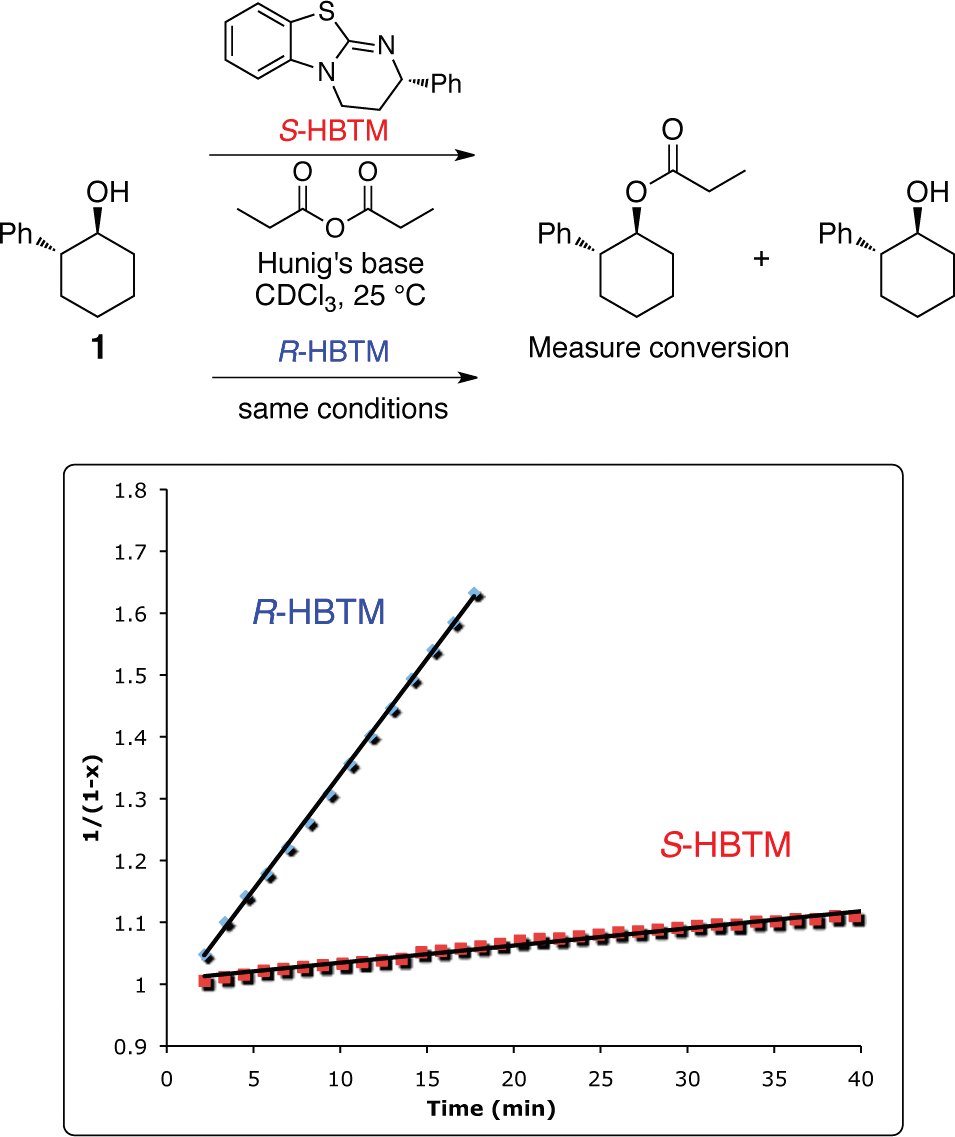
Optically pure alcohol 1 was reacted with propionic anhydride and either 5 mol % of S-HBTM or 5 mol % of R-HBTM catalyst.