Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 108736-35-2
Lanreotide is a drug employed in the management of acromegaly (a hormonal condition caused by excess growth hormone) in addition to symptoms caused by neuroendocrine tumors, especially carcinoid syndrome.
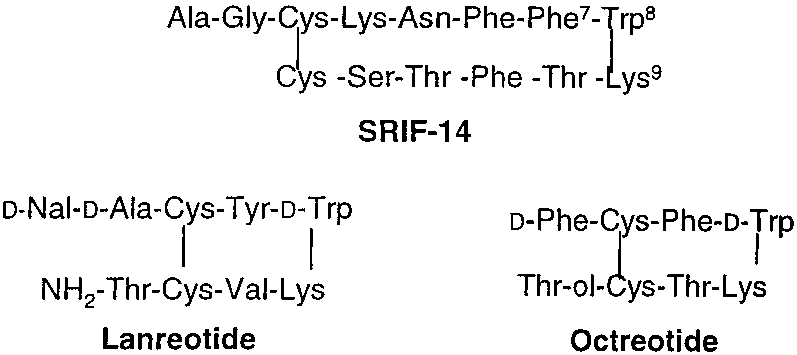
Chemical structures of SRIF-14, lanreotide, and octreotide.
CAS number: 109-01-3
1-Methylpiperazine is a N-methylpiperazine.
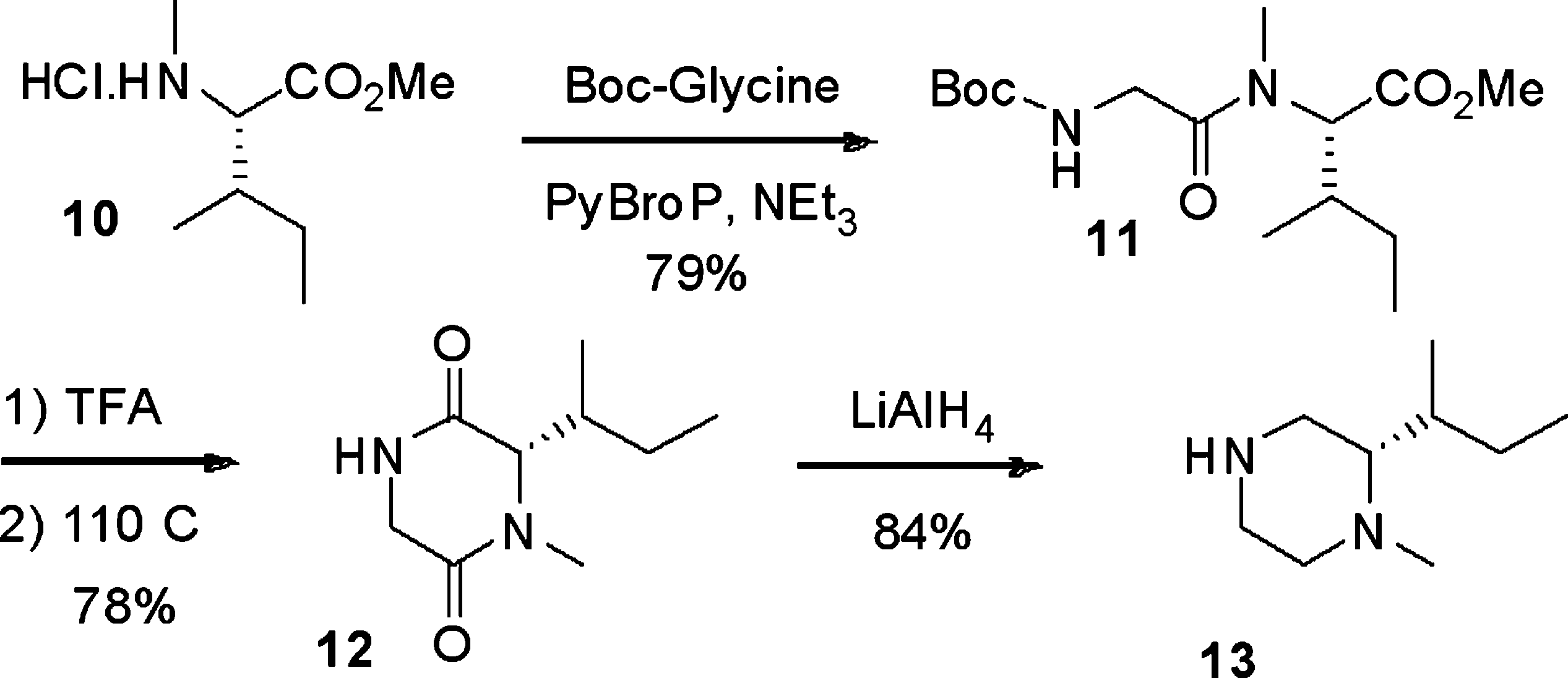
Synthesis of N-methyl-piperazine derivative 13.
CAS number: 109-02-4
4-methylmorpholine appears as a water-white liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. May be moderately toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Very irritating to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Used as a solvent and to make pharmaceuticals.
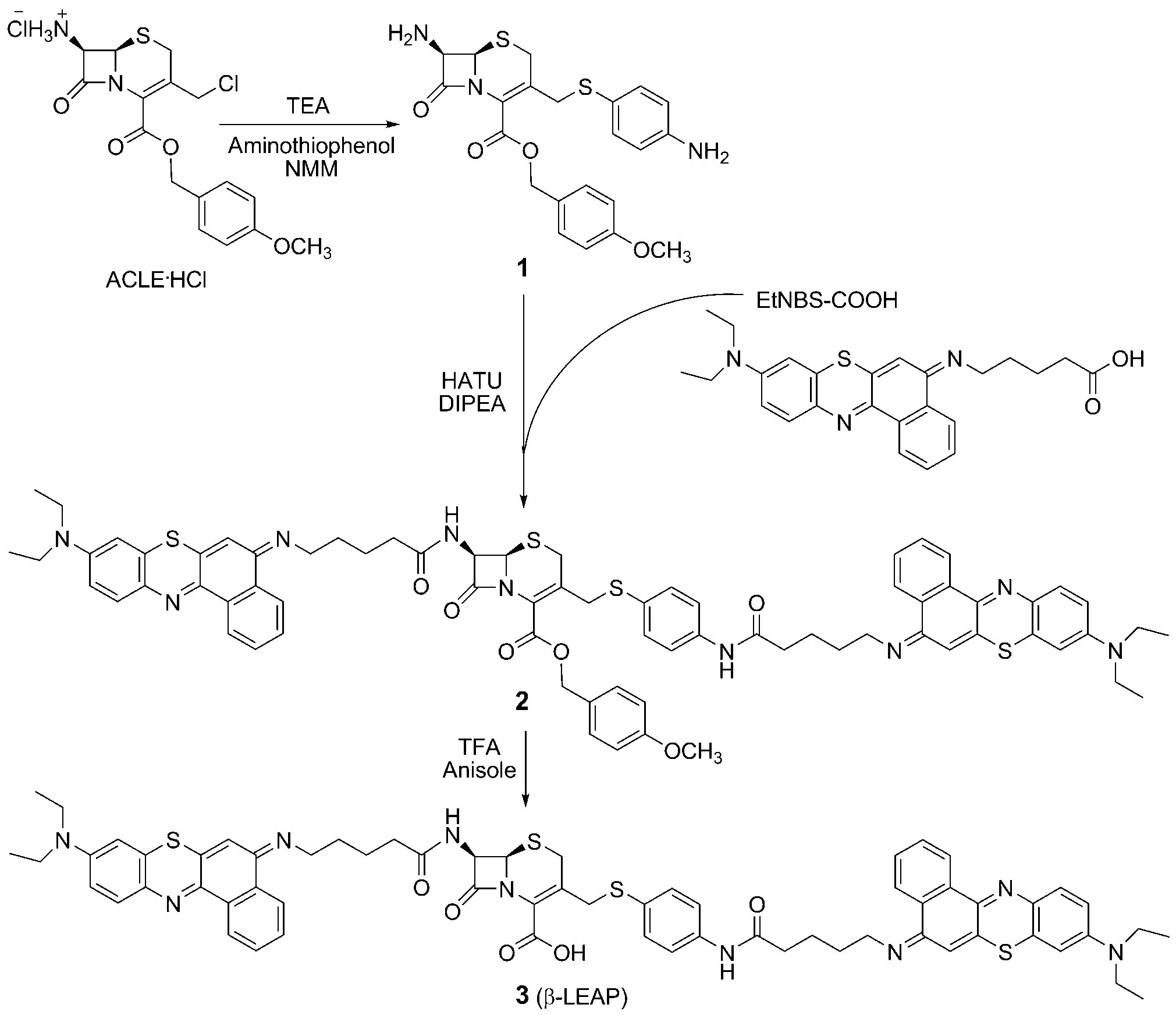
Synthesis of β-LEAP. DIPEA=N,N’-diisopropylethylamine, NMM=4-methylmorpholine, HATU=O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate, TEA=triethylamine, TFA=trifluoroacetic acid.
CAS number: 109-04-6
2-bromopyridine is a monobromopyridine.
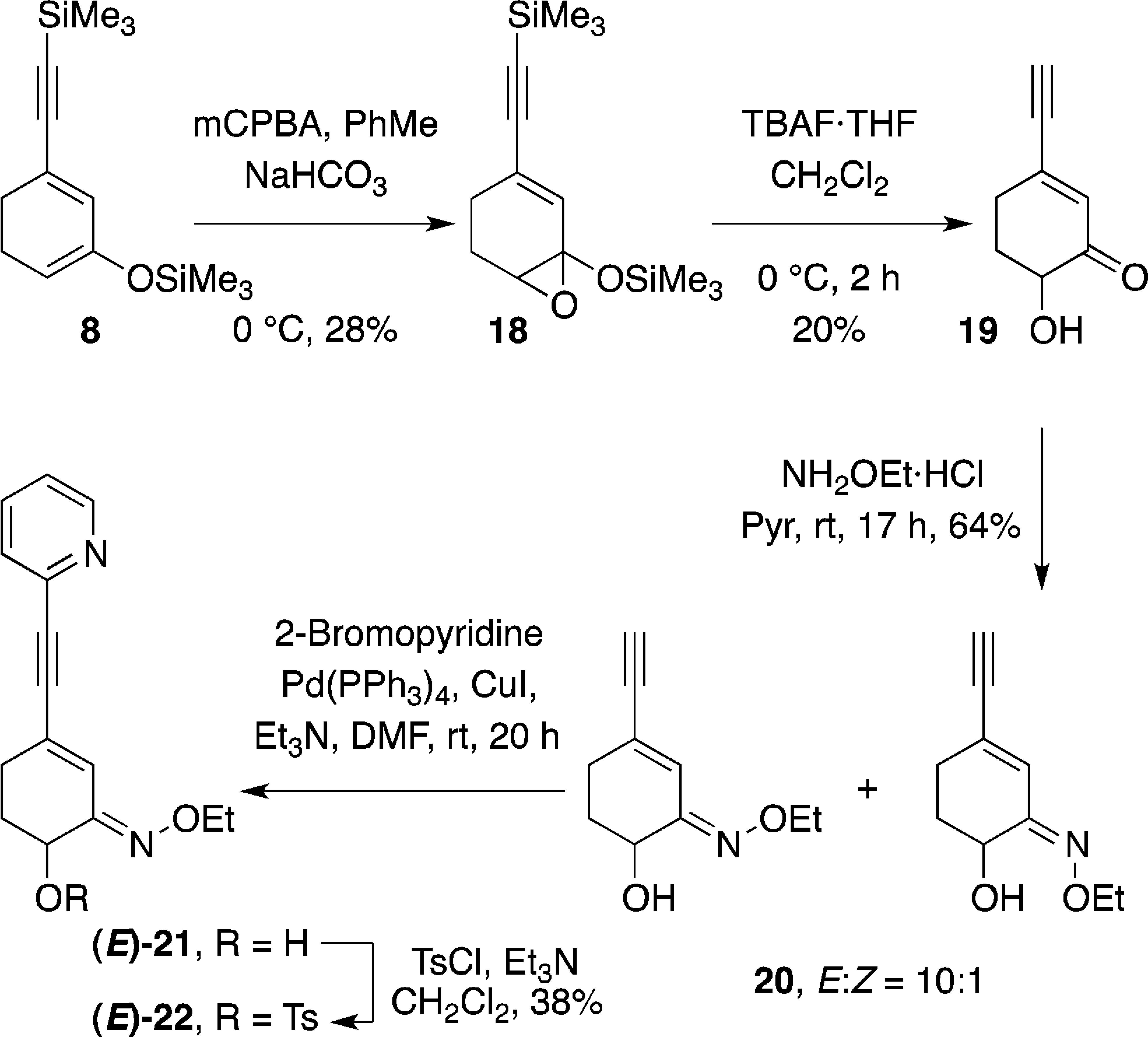
Synthesis of Radiolabelling Precursor Tosylate (E)-22 via the Rubottom Oxidation
CAS number: 109-66-0
Pentane is a straight chain alkane consisting of 5 carbon atoms. It has a role as a non-polar solvent and a refrigerant. It is a volatile organic compound and an alkane.
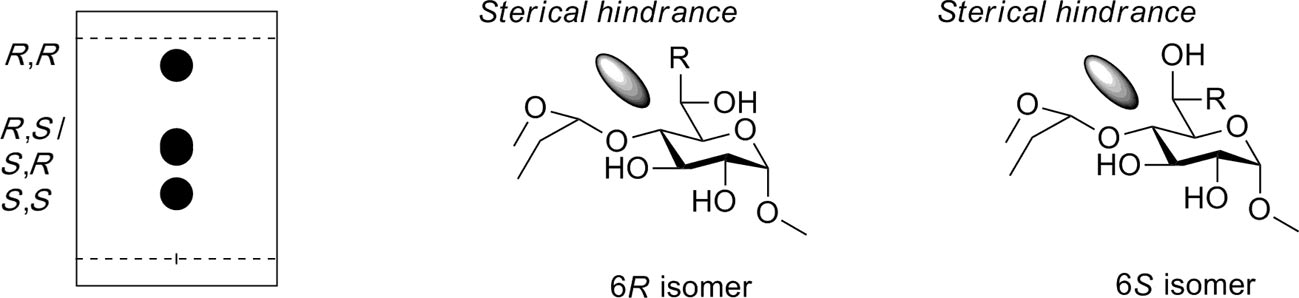
TLC plate showing the different polarities of diastereoisomers 6A,D-di-C-allyl-substituted nonadecaned-O-benzylated β-cyclodextrin in pentane/ethyl acetate 4:1 eluent (left). The figure shows how steric hindrance of the subsequent glucose residue prevents the C-6 substituent from entering the tg conformation, thus forcing each diastereomer to adopt the conformer shown (right).
CAS number: 109-72-8
Butyllithium is a highly reactive organolithium compound used as a strong base and a source of lithium in organic synthesis. It's a versatile reagent, particularly for deprotonation and metal-halogen exchange reactions, and is used in the production of polymers like synthetic rubber. However, it's also highly flammable and reactive, posing fire and explosion hazards.
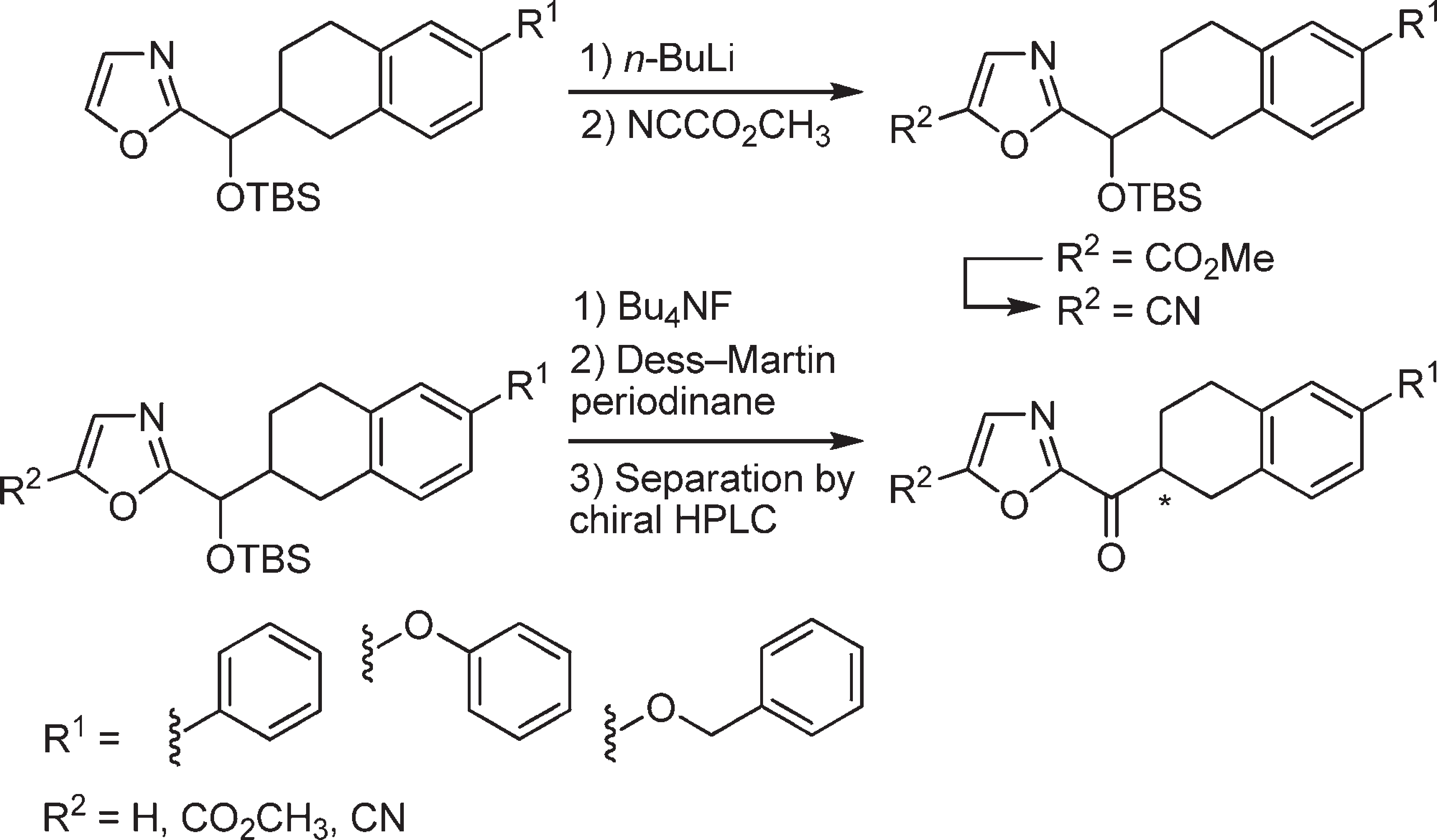
The synthesis of candidate inhibitors that bear a nonaro-matic oxazole C5-substituent.
CAS number: 109-92-2
Ethyl vinyl ether is a colorless, flammable liquid that is highly reactive due to the presence of both vinyl and ether functionalities. It is commonly used as a monomer in polymerization reactions to create various polymers and copolymers, as well as a building block in organic synthesis.
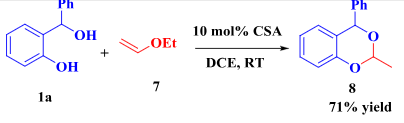
Ethyl vinyl ether was exploited as dienophile.
CAS number: 109-93-3
Vinyl ether is an ether.
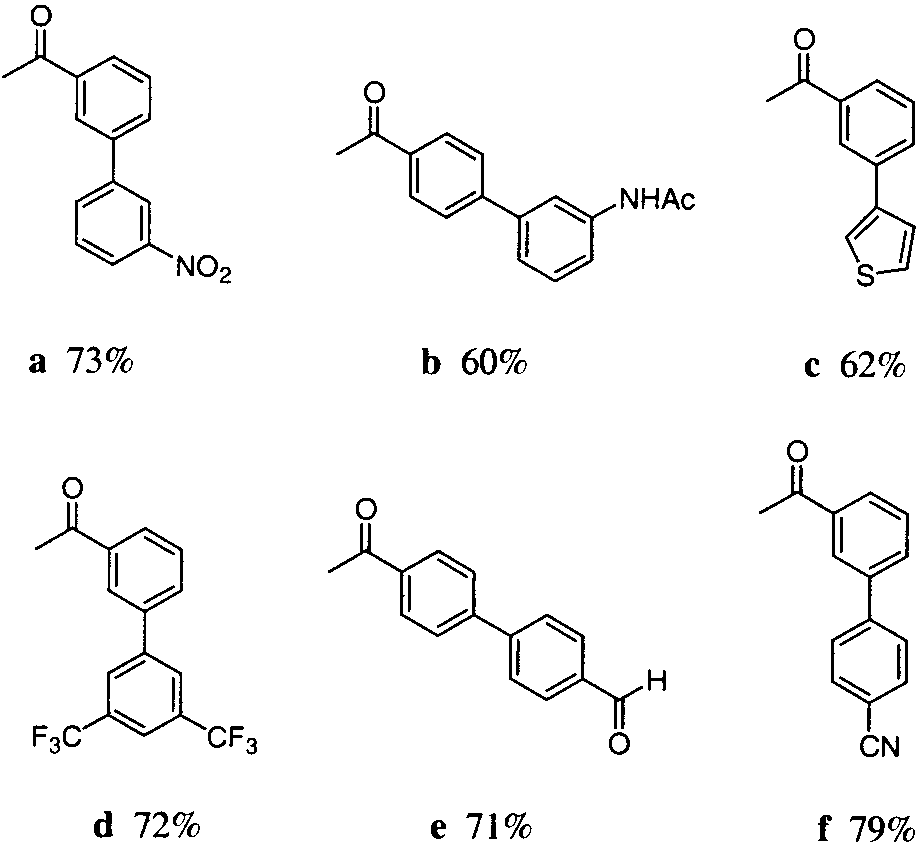
Synthesis of biarylic ketones 8 via Suzuki couplings onto vinyl ether 2.
CAS number: 109-97-7
PYRROLE is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of III and has 1 investigational indication.
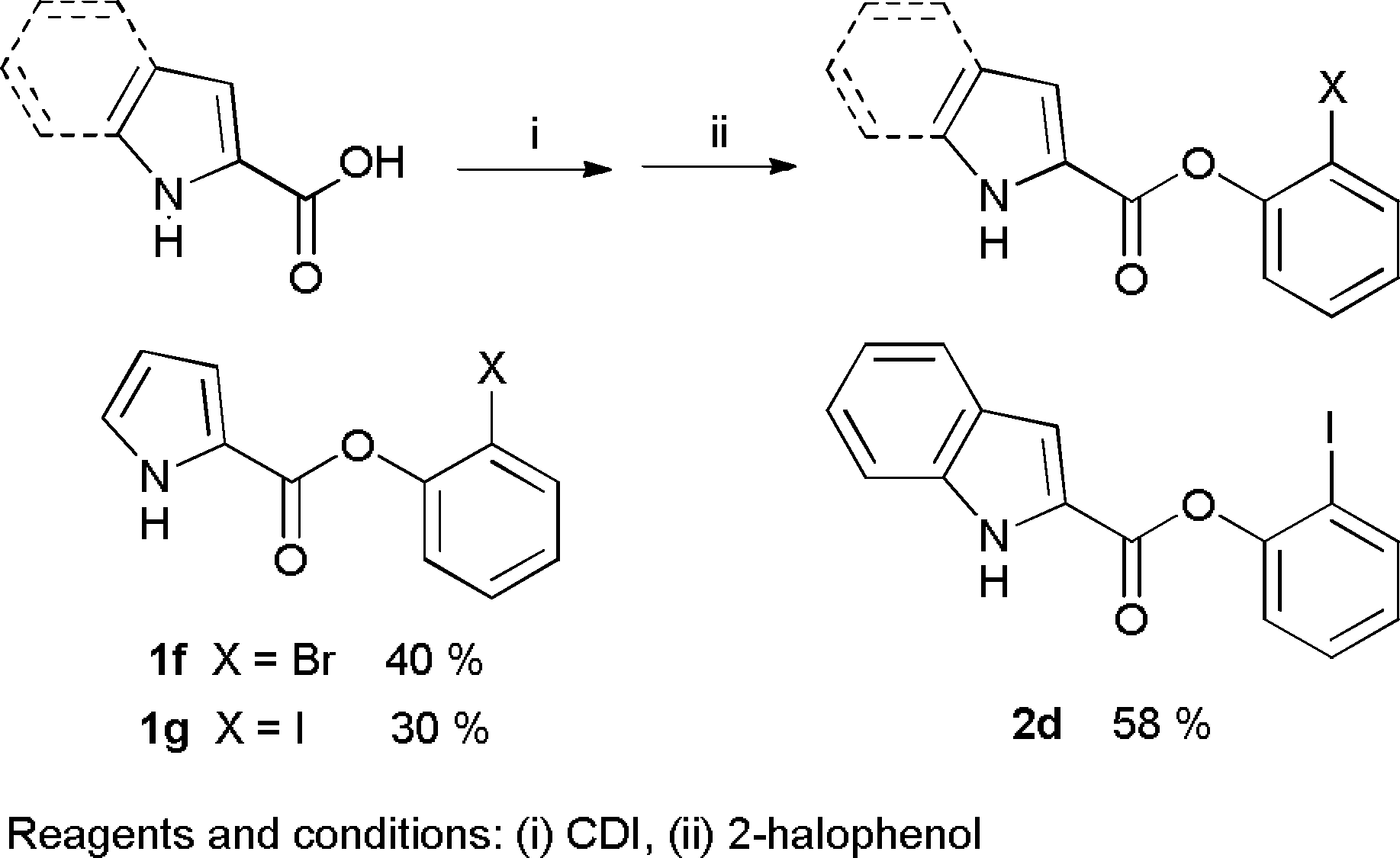
Synthesis of pyrrole and indole ester derivatives.
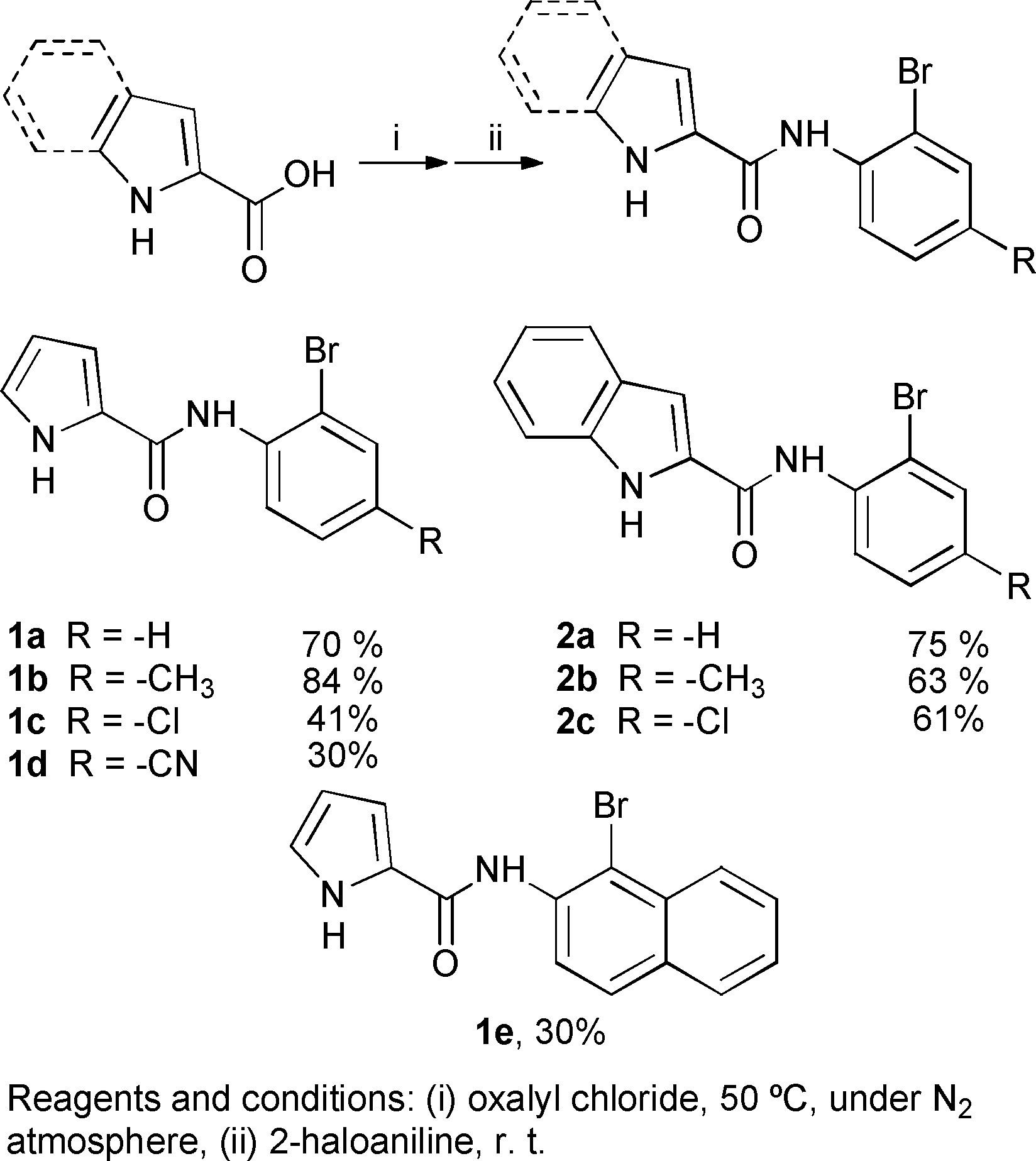
Synthesis of pyrrole and indole carboxamides.
CAS number: 109-99-9
Tetrahydrofuran appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ethereal odor. Less dense than water. Flash point 6 °F. Vapors are heavier than air.
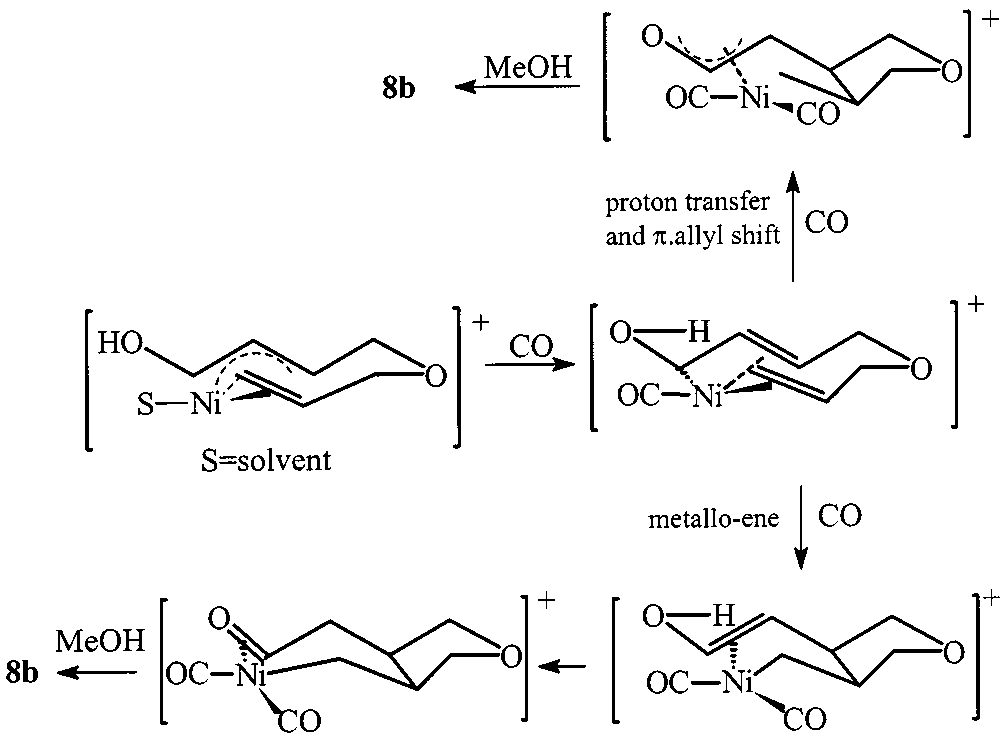
Two plausible paths for the formation of tetrahydrofuran.
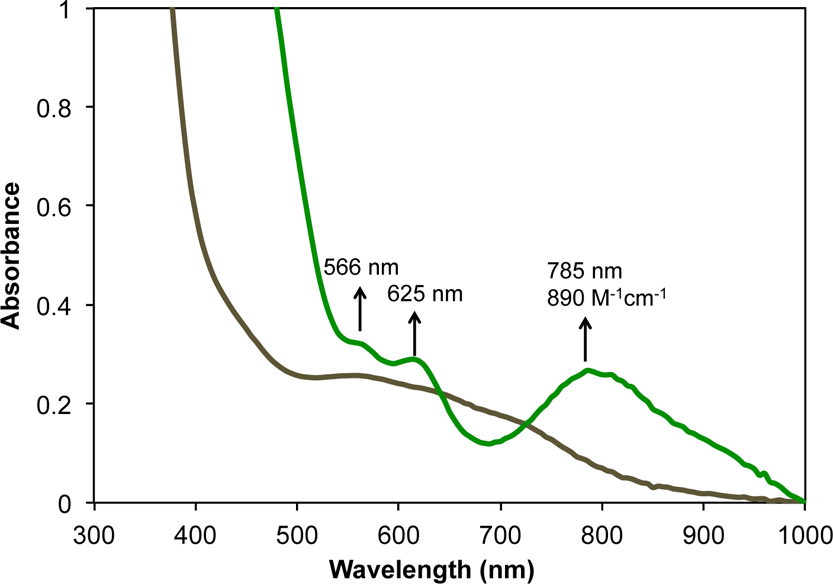
UV-vis spectral change for the conversion of 3 (brown trace) to 4 (green trace) with 0.5% Na/Hg amalgam in tetrahydrofuran (THF).