Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 2230724-66-8
BTK inhibitor 27, also known as BTK inhibitor 1 (Compound 27), is a potent and selective covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). It is a small molecule that has been shown to inhibit the activation of B cells and has potential applications in treating B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases.
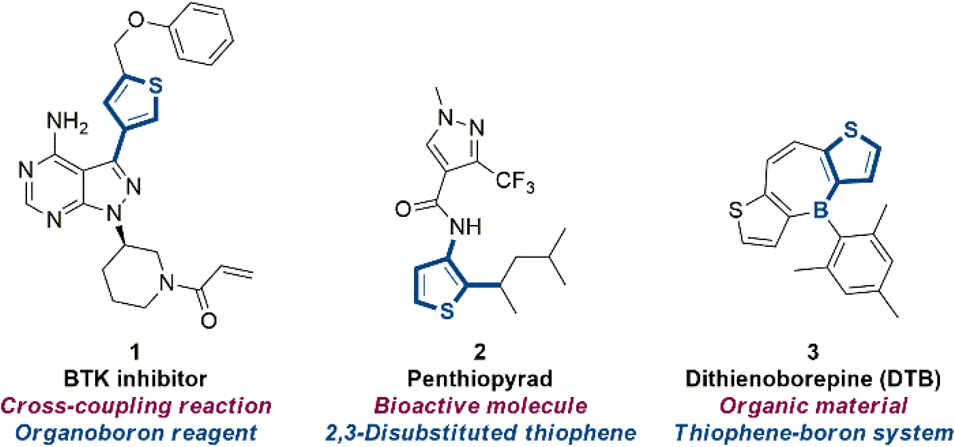
Synthetic importance of thiophene building blocks.
CAS number: 22345-98-8
3-Phenyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)prop-2-enenitrile is an organic chemical compound contains a phenyl group, a pyridine ring, and a nitrile group, linked by a propene chain, and is sold by chemical suppliers for research and development purposes.
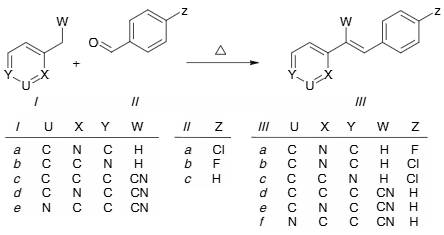
Synthesis of (E)-2-(4-fluorostyryl)pyridine IIIa, (E)-2-(4-chlorostyryl)pyridine IIIb, (E)-4-(4-chlorostyryl)pyridine IIIc, 2,3-diphenylacrylonitrile IIId, 3-phenyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)acrylonitrile IIIe, and 3-phenyl-2-(pyridin-3-yl)acrylonitrile IIIf.
CAS number: 224585-45-9
SCH-79687 is a synthetic small molecule that functions as a selective histamine H₃ receptor antagonist. Originally described pharmacologically in 2003, it exhibits both in vitro and in vivo H₃-blocking activity and has demonstrated wake-promoting properties, potential anti-obesity effects, and nasal decongestion (particularly when administered alongside an H₁ antagonist) .
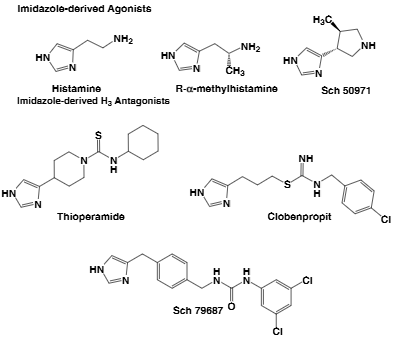
Examples of imidazole-derived agonists and antagonists:Thioperamide, clobenpropit, SCH-79687, r-alpha-methylhistamine.
CAS number: 22559-70-2
Quinolinium is a positively charged ion (cation) formed by protonating quinoline. It is similar to ammonium but derived from quinoline, a nitrogen-containing aromatic compound. Quinolinium salts, where the cation is paired with a counterion (like chloride or iodide), are a class of organic compounds with various applications, particularly in photocatalysis and medicinal chemistry.
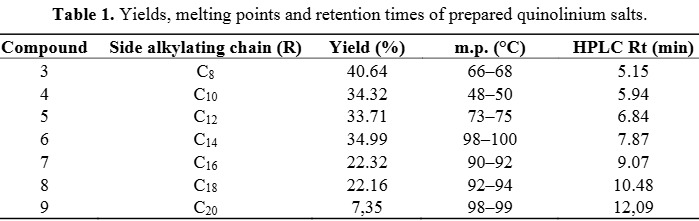
Yields, melting points and retention times of prepared quinolinium salts.
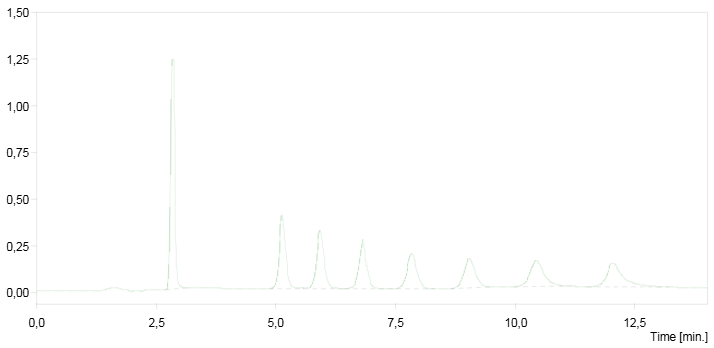
HPLC chromatogram of a quinolinium compound mixture.
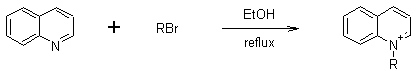
Preparation of quinolinium salts.
CAS number: 2259-96-3
Cyclothiazide is 3,4-Dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide substituted at positions 3, 5 and 6 by a 2-norbornen-5-yl group, chlorine, and a sulfonamide group, respectively. A thiazide diuretic, it has been used in the management of hypertension and oedema. It has a role as a diuretic and an antihypertensive agent.
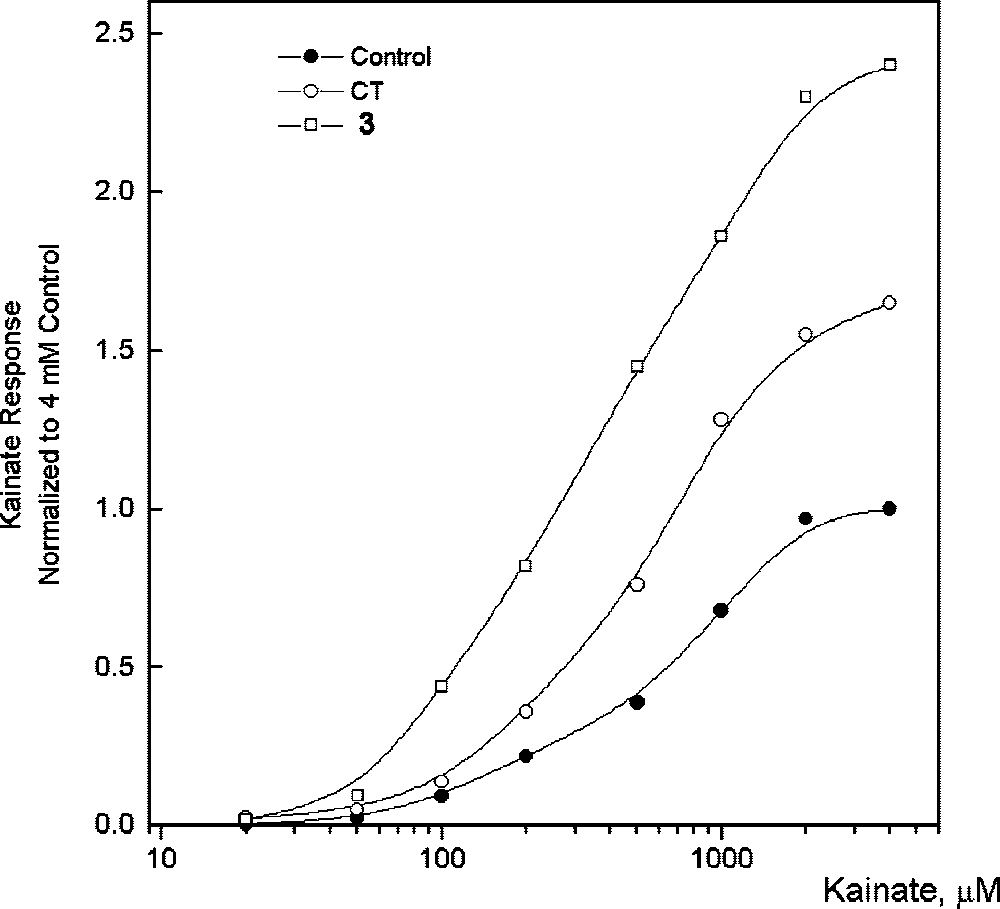
Effect of CT (cyclothiazide) and 3 on dose-dependent response for the currents induced by kainic acid in Purkinje neurons.
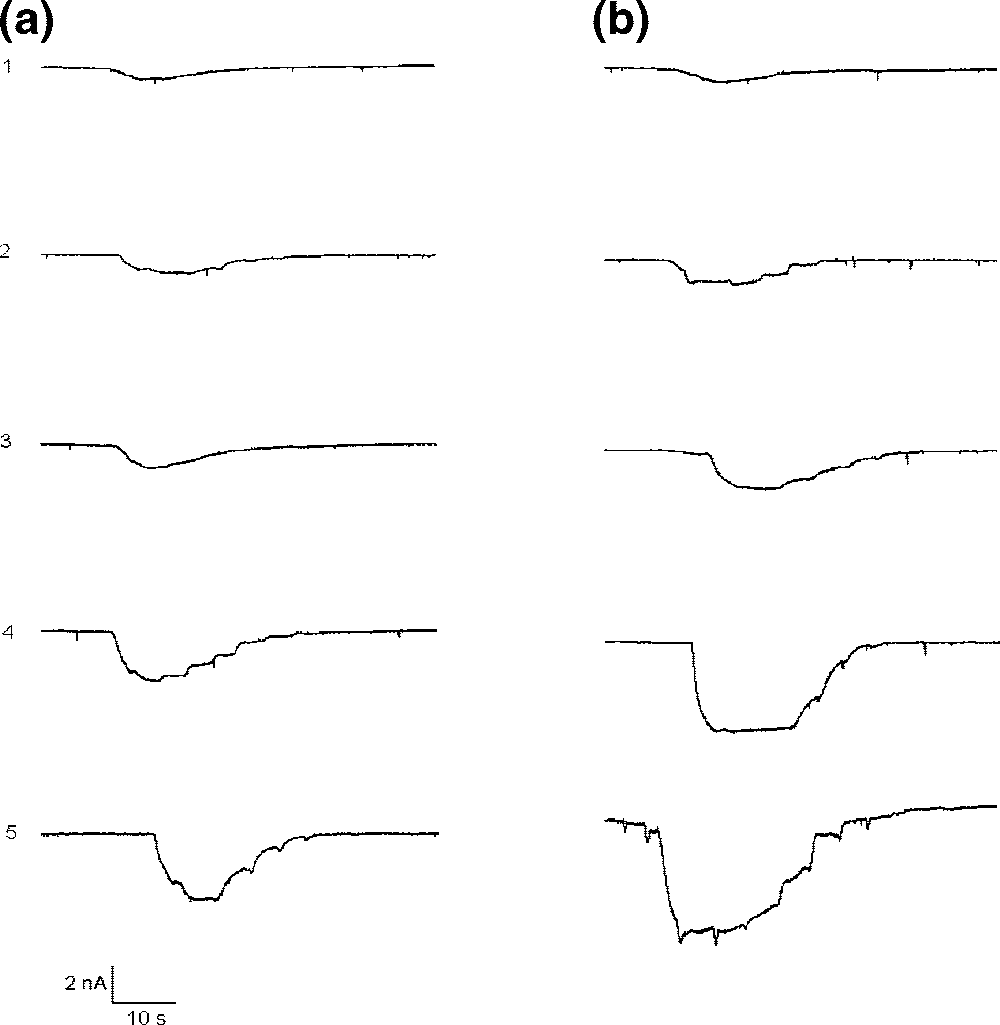
Comparative effect of different doses of CT (cyclothiazide) and 1 on currents, induced by the fixed concentration of kainic acid (KA).
CAS number: 226256-56-0
Cinacalcet is a calcimimetic sold by Amgen under the trade name Sensipar® in North America and Australia and as Mimpara® in Europe. It is used to treat hyperparathyroidism due to parathyroid tumours or renal failure.
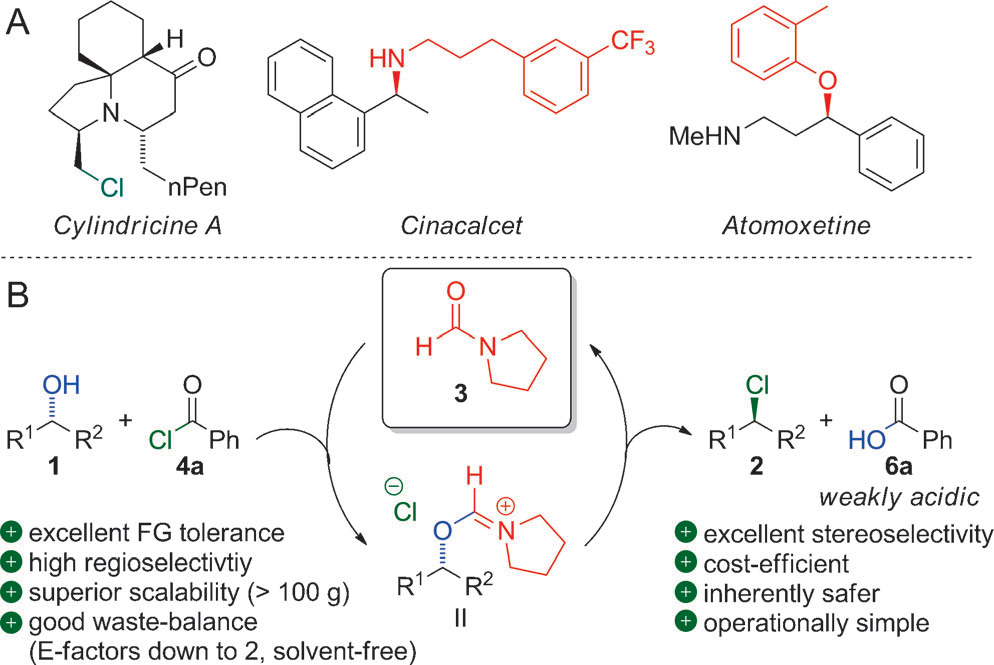
Selected chloride-containing natural products and pharmaceuticals containing amino and ether functionalities (A); presented method (B).
CAS number: 22638-09-1
Phosphoramidic acid, ion(2−), also known as phosphoramidate dianion, is the conjugate base of phosphoramidic acid (H₂PO₂NH₂). It has the molecular formula [H₂NPO₂]²⁻ and consists of a phosphorus atom centrally bonded to an amino group (–NH₂), two oxygen atoms (one double-bonded and one single-bonded with a negative charge), and a lone pair of electrons. This dianion plays a role in biochemical and pharmaceutical research, particularly in the study of phosphoryl transfer reactions and enzyme inhibitors. It is typically encountered as part of salts or coordination compounds, and its structure is stabilized by resonance between the phosphorus–oxygen bonds.
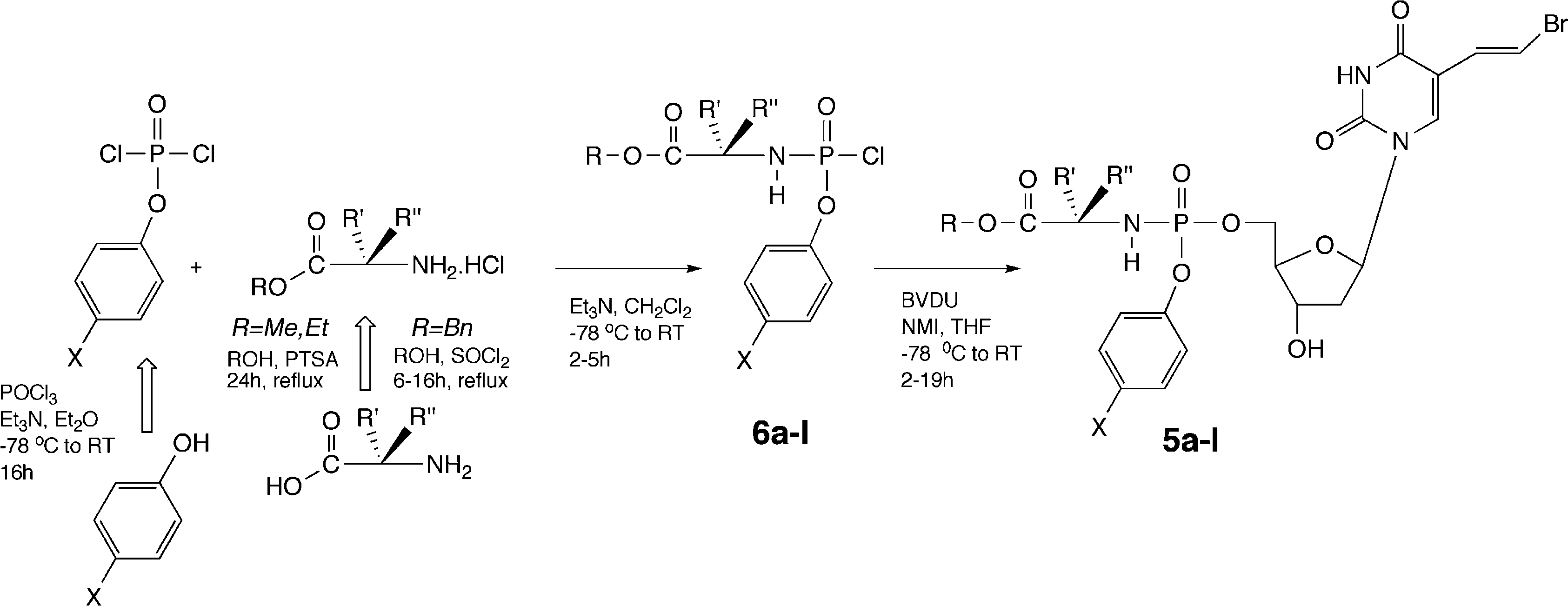
Synthetic route to target phosphoramidates.
CAS number: 22694-45-7
Pyridine moieties which are partially saturated by the addition of two hydrogen atoms in any position.
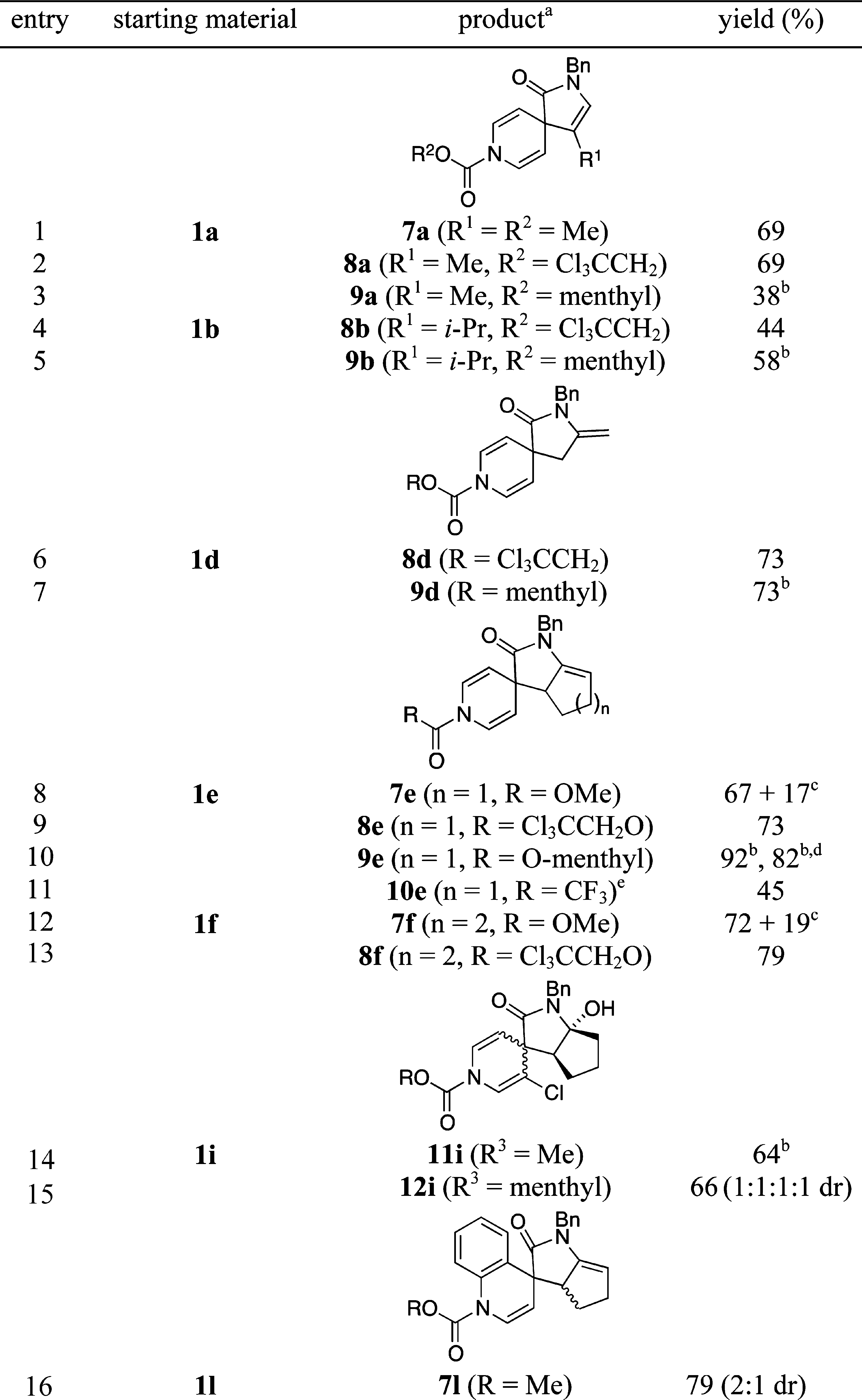
Dihydropyridines by Spirocyclization with Chloroformates
CAS number: 2280-44-6
Glucose is a simple sugar (monosaccharide) generated during phosynthesis involving water, carbon and sunlight in plants. It is produced in humans via hepatic gluconeogenesis and breakdown of polymeric glucose forms (glycogenolysis). It circulates in human circulation as blood glucose and acts as an essential energy source for many organisms through aerobic or anaerobic respiration and fermentation.
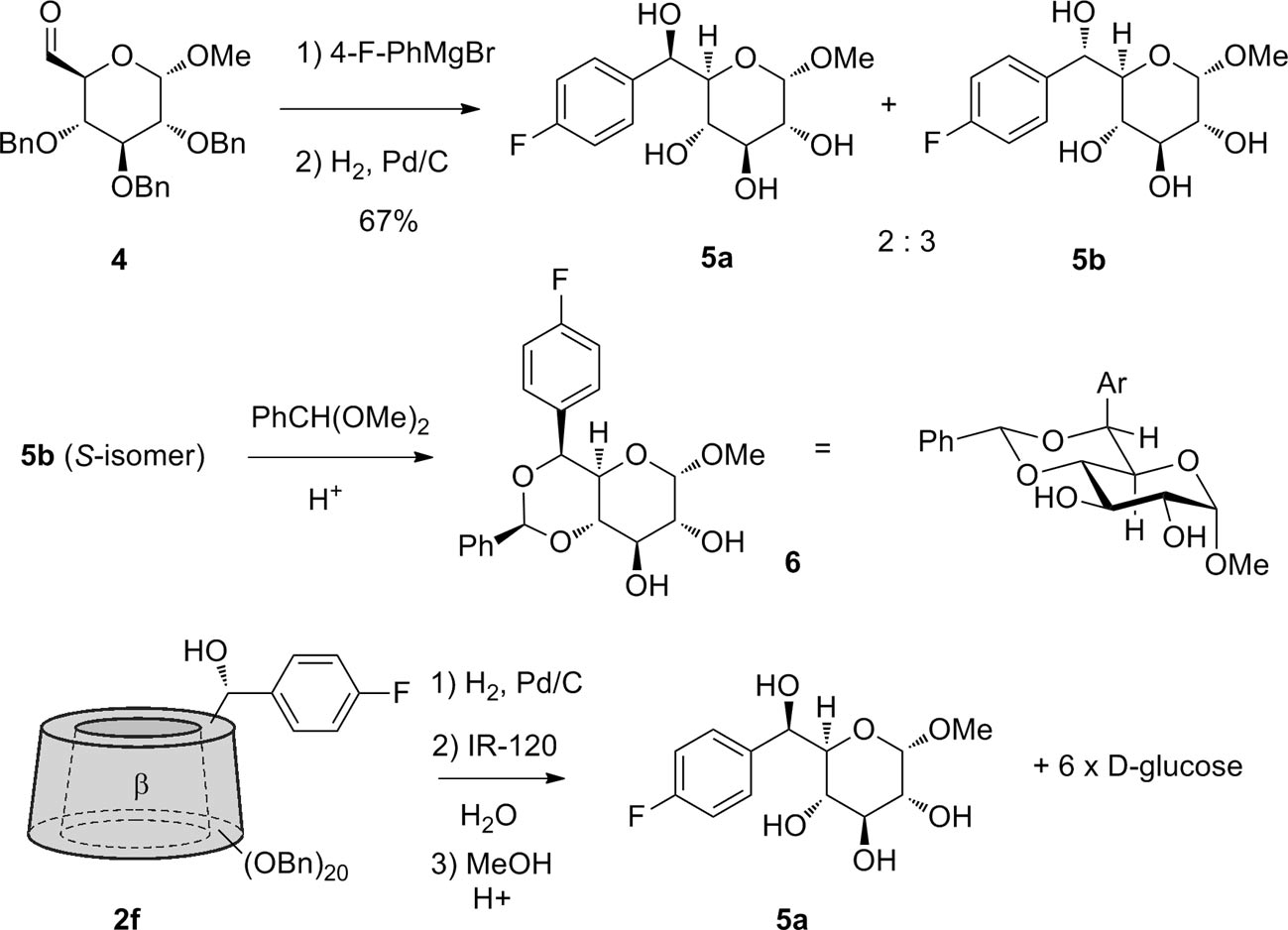
Two reference monosaccharide derivatives 5a and 5b were prepared to determine the stereochemistry at the C-6 position. The major isomer 5b obtained by addition of (4-fluorophenyl)magnesium bromide to glucose-6-aldehyde 4 was converted to the benzylidene derivative 6. This compound has a small J5,6 and only conforms to the S-stereochemistry. The β-cyclodextrin derivative 2f was hydrolyzed and converted to the methyl glycoside to give the minor R-isomer 5a.
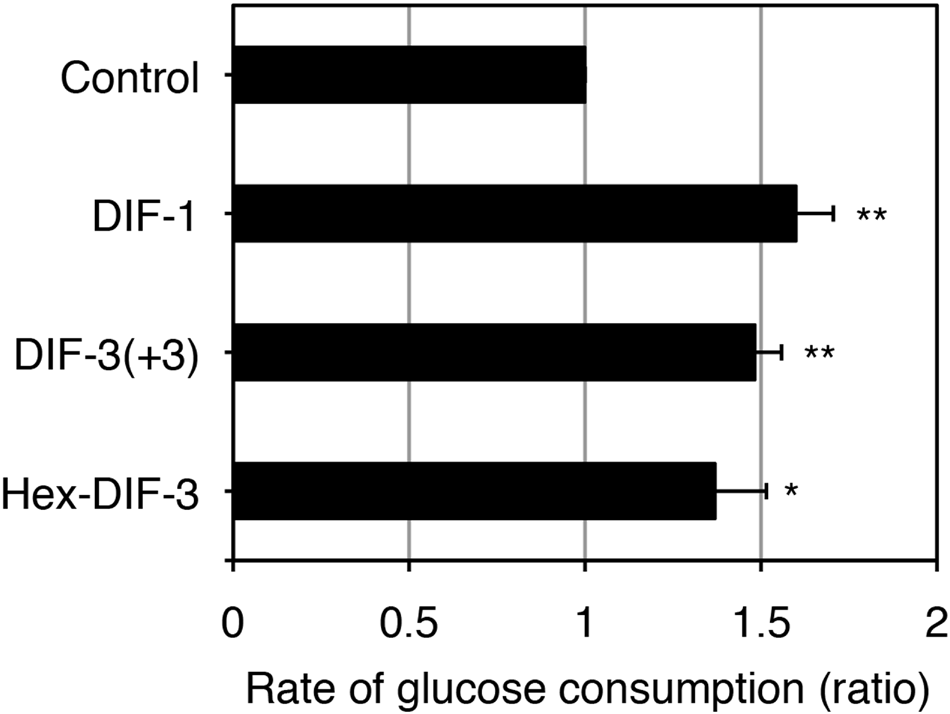
Effects of DIF Derivatives on Glucose Consumption in 3T3-L1 Cells
CAS number: 2281-74-5
4-Thiazolidinone is a heterocyclic organic compound, specifically a saturated form of thiazole, characterized by a carbonyl group at the 4-position. It's a significant scaffold in medicinal chemistry, known for its diverse biological activities, including antimicrobial, antifungal, antiviral, and anticonvulsant properties.
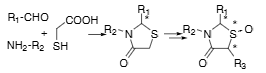
Synthetic scheme for 4-thiazolidinones.
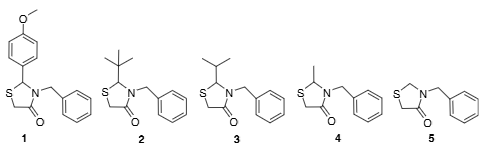
4-Thiazolidinones synthesized for this study
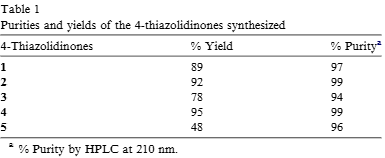
Purities and yields of the 4-thiazolidinones synthesized