Vanillic Acid
CAS number: 121-34-6
Vanillic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid that is 4-hydroxybenzoic acid substituted by a methoxy group at position 3. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is a monohydroxybenzoic acid and a methoxybenzoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a vanillate.
Related images
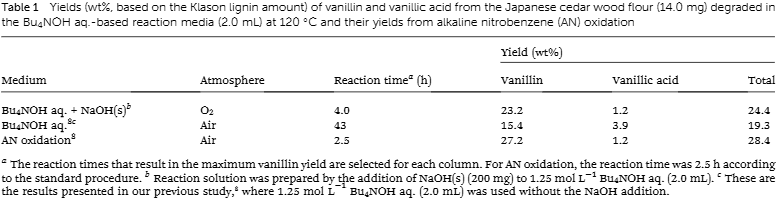
Yields (wt%, based on the Klason lignin amount) of vanillin and vanillic acid from the Japanese cedar wood flour (14.0 mg) degraded in the Bu4NOH aq.-based reaction media (2.0 mL) at 120 ℃ and their yields from alkaline nitrobenzene (AN) oxidation
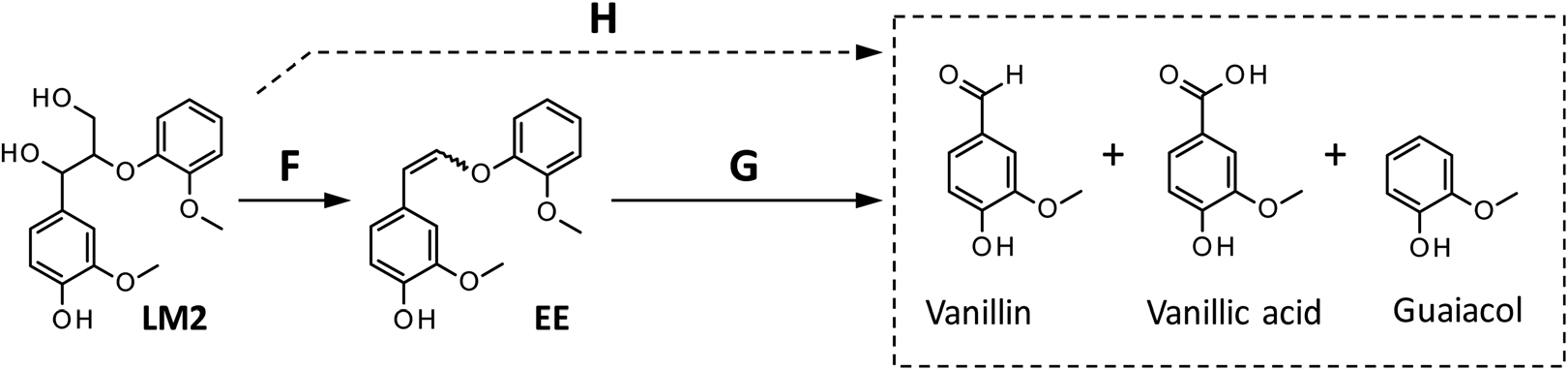
Reaction pathways from Lm2 to the products detected in this study. The formation of vanillic acid via pathway H is less significant than that via pathway G
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet