Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 100-09-4
4-methoxybenzoic acid is a methoxybenzoic acid substituted with a methoxy group at position C-4. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is functionally related to a benzoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a 4-methoxybenzoate.
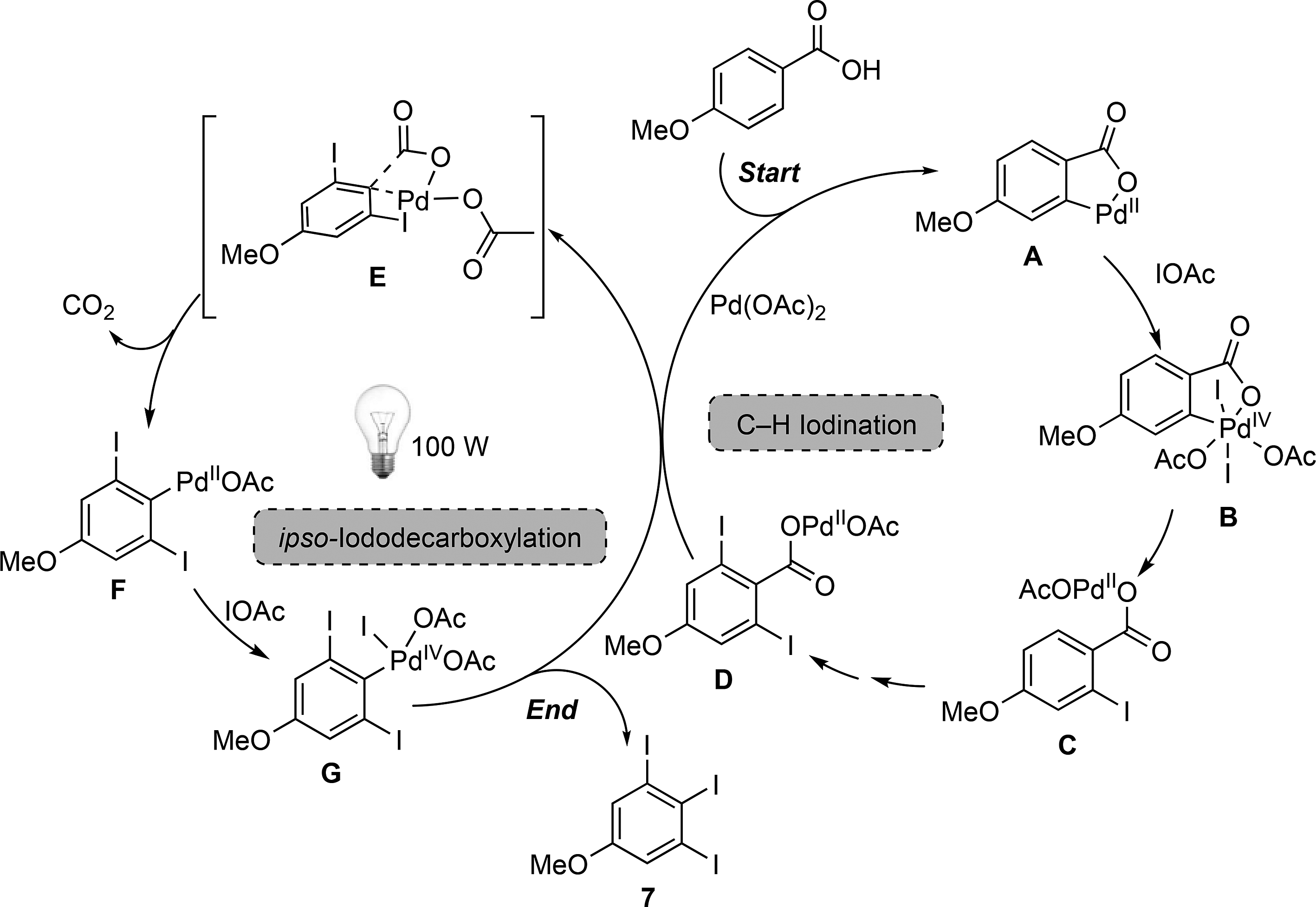
Proposed mechanism for the one-pot PdII-catalyzed C–H iodination/ipso-iododecarboxylation of para-anisic acid.
CAS number: 100-10-7
4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde is a member of the class of benzaldehydes that is benzaldehyde carrying a dimethylamino substituent at position 4. Used as an indicator for detection of indoles and hydrazine. It has a role as a chromogenic compound. It is a member of benzaldehydes, a substituted aniline and a tertiary amino compound.
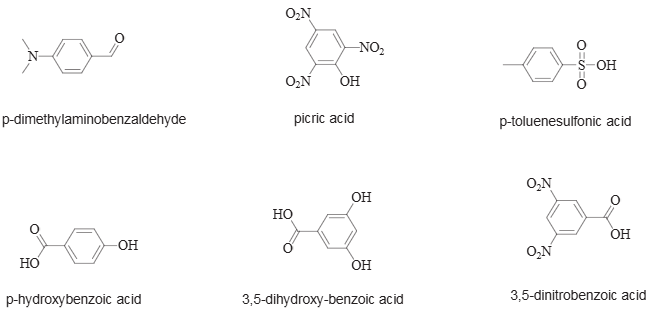
The building blocks discussed in this paper: p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, picric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3,5-dihydroxy-benzoic acid, 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid.
CAS number: 100-39-0
Benzyl bromide is a member of the class of benzyl bromides that is toluene substituted on the alpha-carbon with bromine. It has a role as a lachrymator.
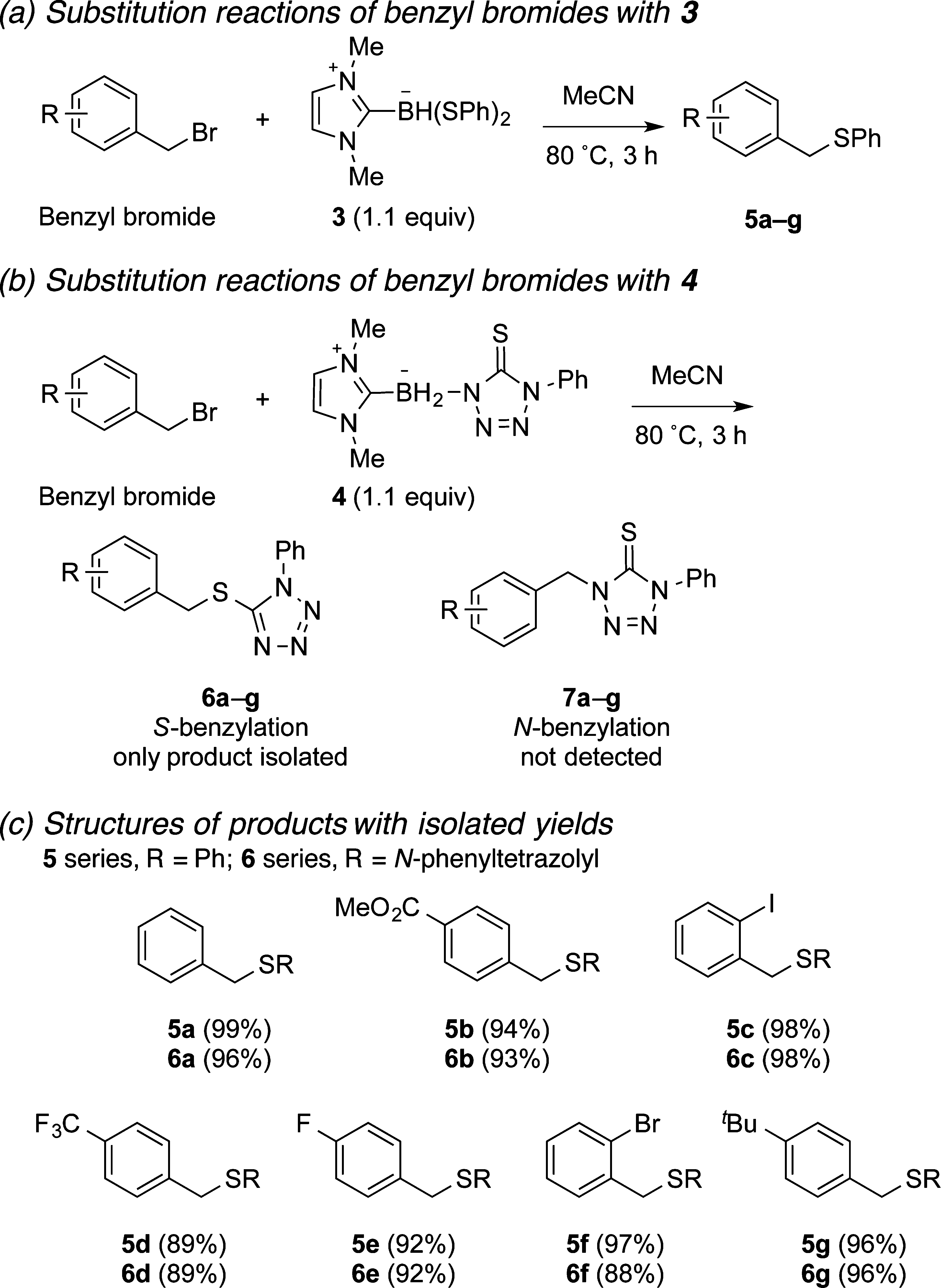
Scope study of substitution reactions of benzyl bromides by 3 under standard conditions
CAS number: 100-42-5
Styrene is a colorless, flammable liquid, which has a sweet odor and is highly volatile.
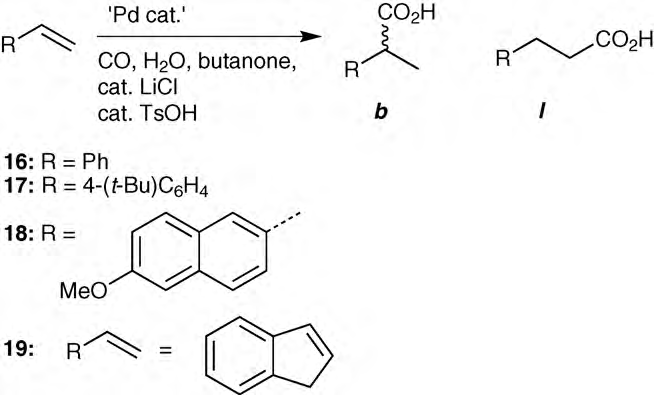
Hydroxycarbonylation of styrene, 4-butyl styrene, 9-methoxy- naphthalene and indene gives mainly branched carboxylic acids.
CAS number: 100-47-0
Benzonitrile is a nitrile that is hydrogen cyanide in which the hydrogen has been replaced by a phenyl group. It is a member of benzenes and a nitrile.
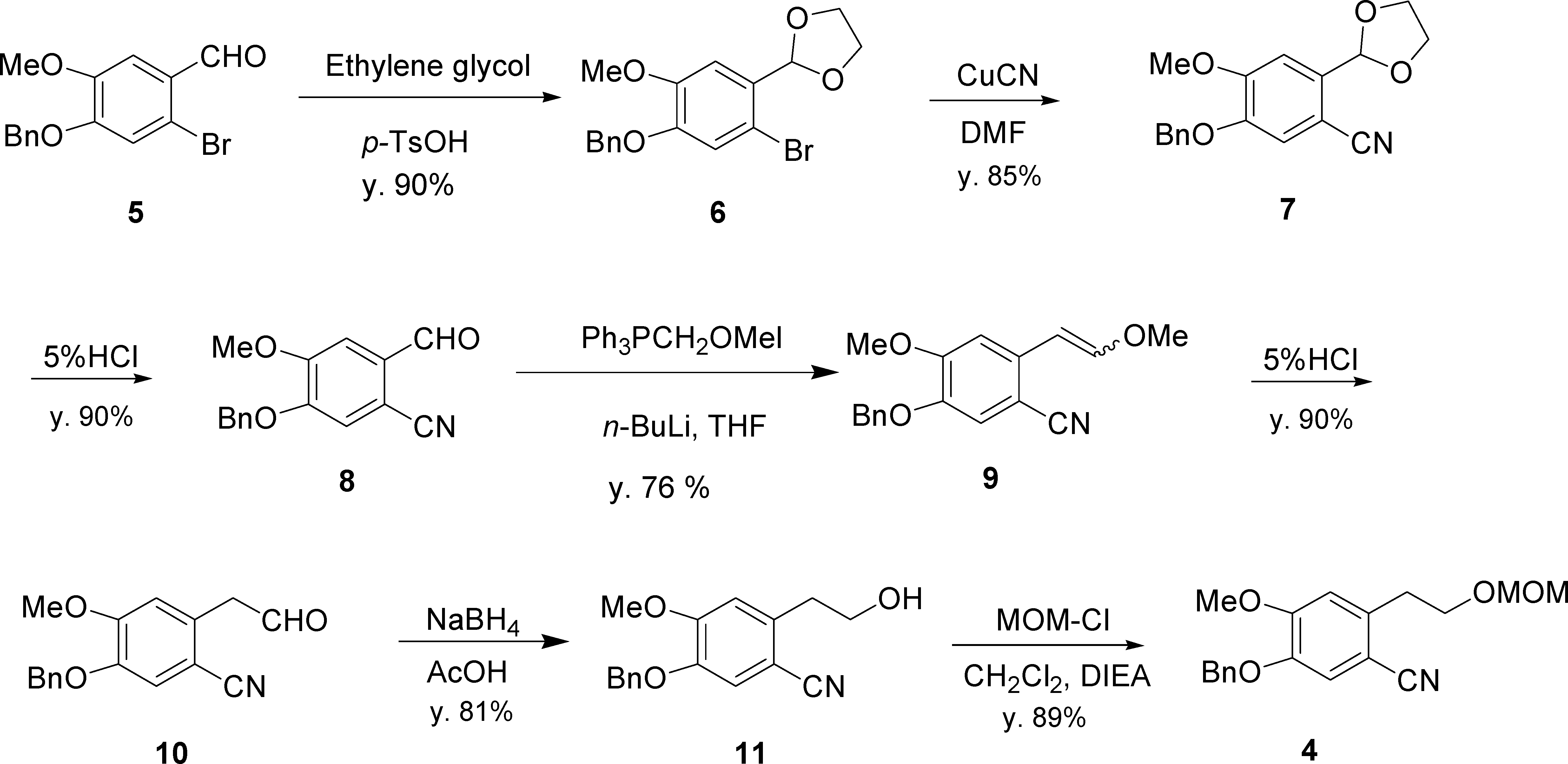
Synthesis of Benzonitrile 4
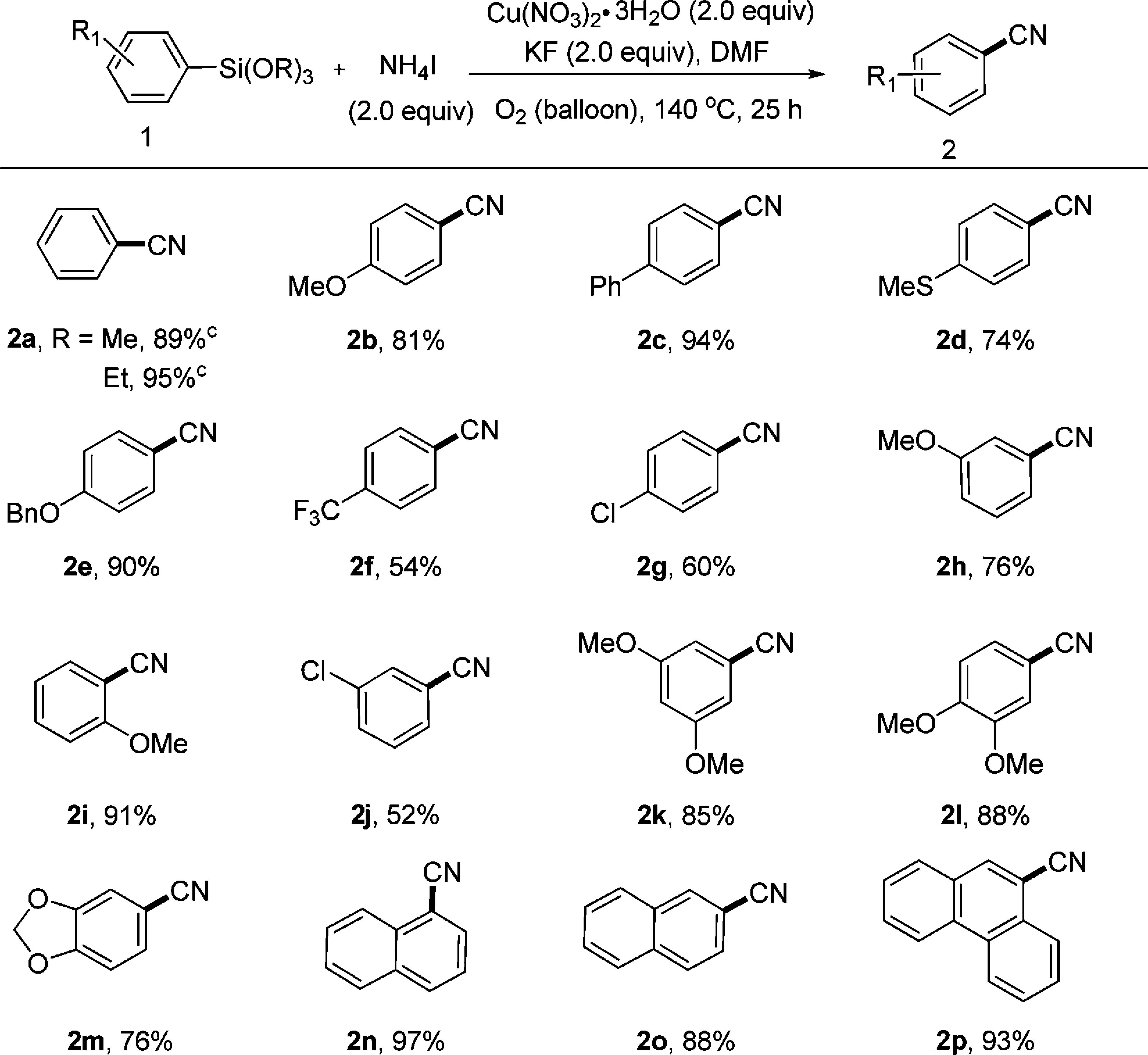
A variety of functional groups (e.g., alkoxy, phenyl, methylthio, benzyloxy, trifluoromethyl, or chloro) were compatible with the conditions used. Arylsilanes bearing substituents at the para-, meta-, and ortho-positions were all converted to the corresponding benzonitriles (2b, 2h, and 2i, respectively) in good yields.
CAS number: 100-51-6
Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid with a mild, pleasant, aromatic odor.
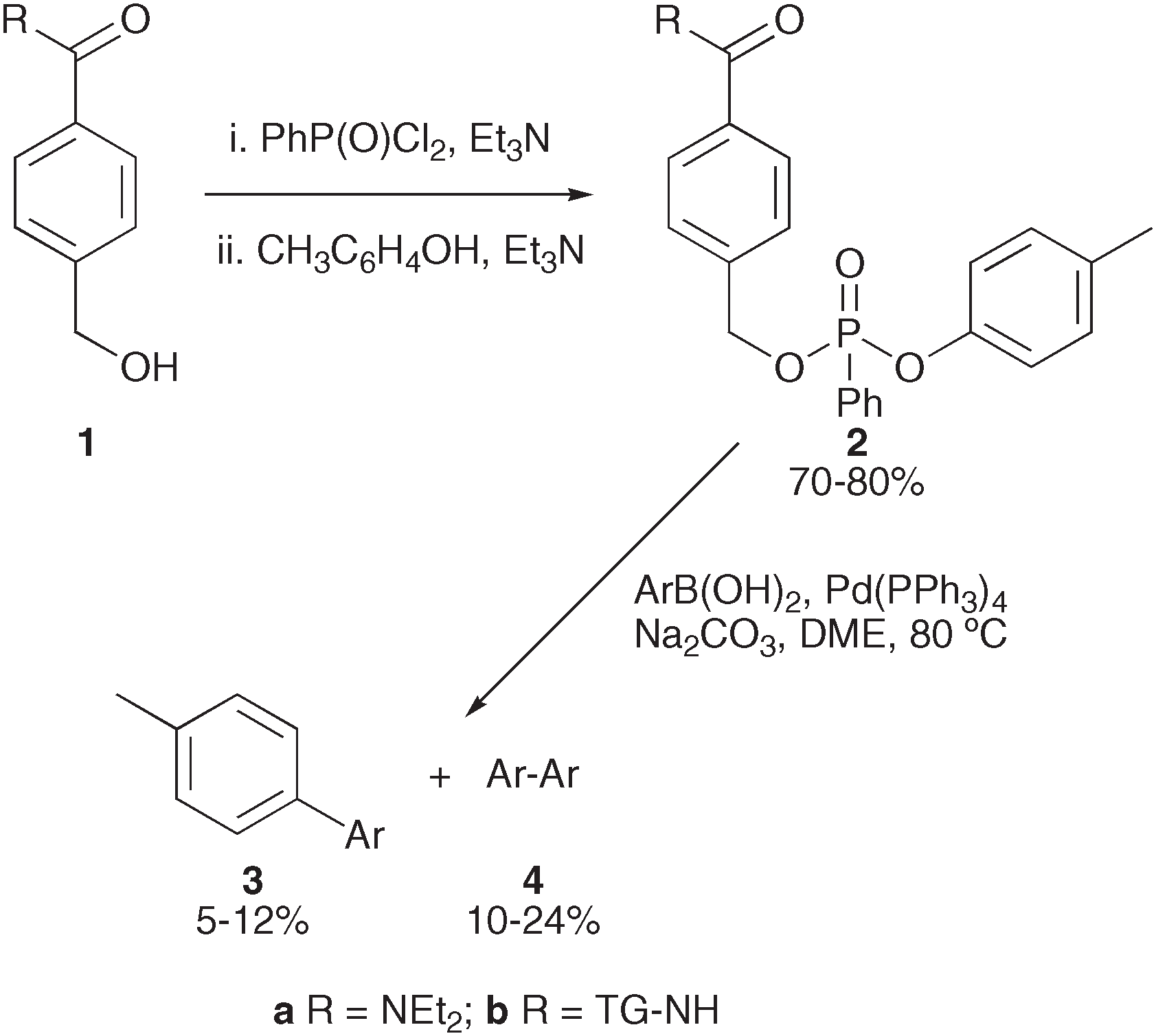
Benzyl alcohol 1a was reacted with 1.25 equivalents of phenylphosphonyl dichloride (PPDC; PhP(O)Cl2) in the presence of triethylamine (Et3N) to afford a mixture of mono- and bis-phosphates. The monosubstituted product was reacted directly with p-cresol without purification to afford the desired phenylphosphonate 2a.
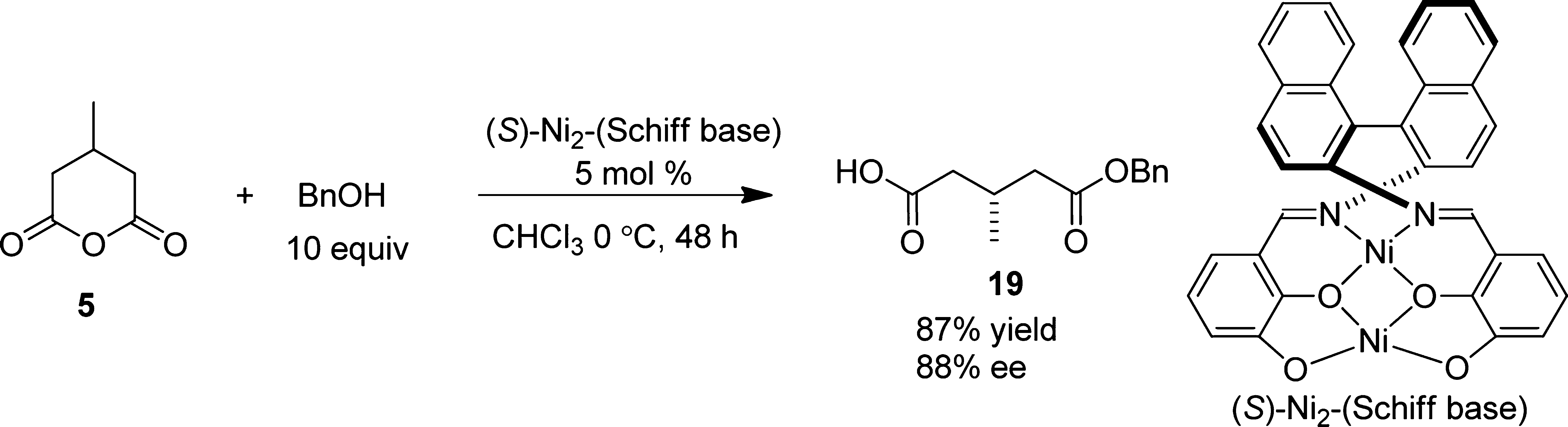
Desymmetrization of 3-Methylglutaric Anhydride 5 with Benzyl Alcohol
CAS number: 100-52-7
A chemical used in flavorings and in some dyes, perfumes, and medicines. It is found in essential oils made from almonds and peach pits and in other foods.
![Peptoid-synthesis-inspired modular assembly of azaxylylene precursors and their cyclizations. [a] Acetal hydrolysis step is required only in the a (i.e. benzaldehyde) series. [b] Major diastereomer is shown, the minor hydroxy epimer (not shown) is denoted with a prime, 16’a etc. Bn=benzyl, DIPEA=diisopropylethylamine, PTS=pyridinium para-tolue-nesulfonate.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3047941_09.png)
Peptoid-synthesis-inspired modular assembly of azaxylylene precursors and their cyclizations. [a] Acetal hydrolysis step is required only in the a (i.e. benzaldehyde) series. [b] Major diastereomer is shown, the minor hydroxy epimer (not shown) is denoted with a prime, 16’a etc. Bn=benzyl, DIPEA=diisopropylethylamine, PTS=pyridinium para-tolue-nesulfonate.
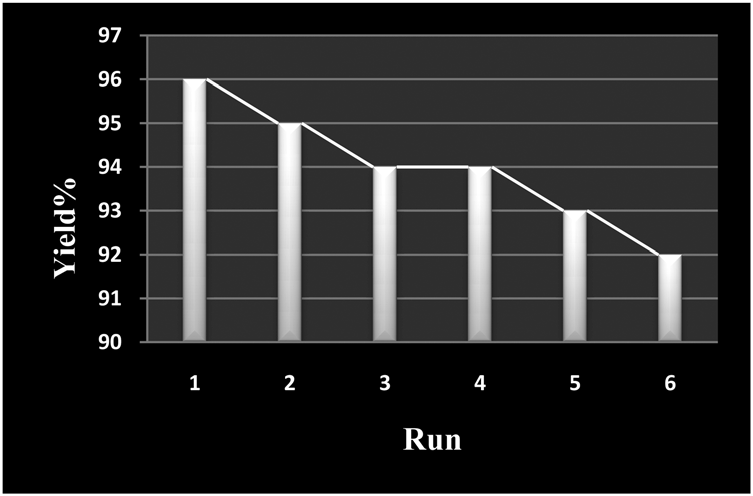
Condensation of benzil, benzaldehyde, ammonium acetate and n-Pr amine using recycled catalysts.

Scheme of preparation of ligand L.
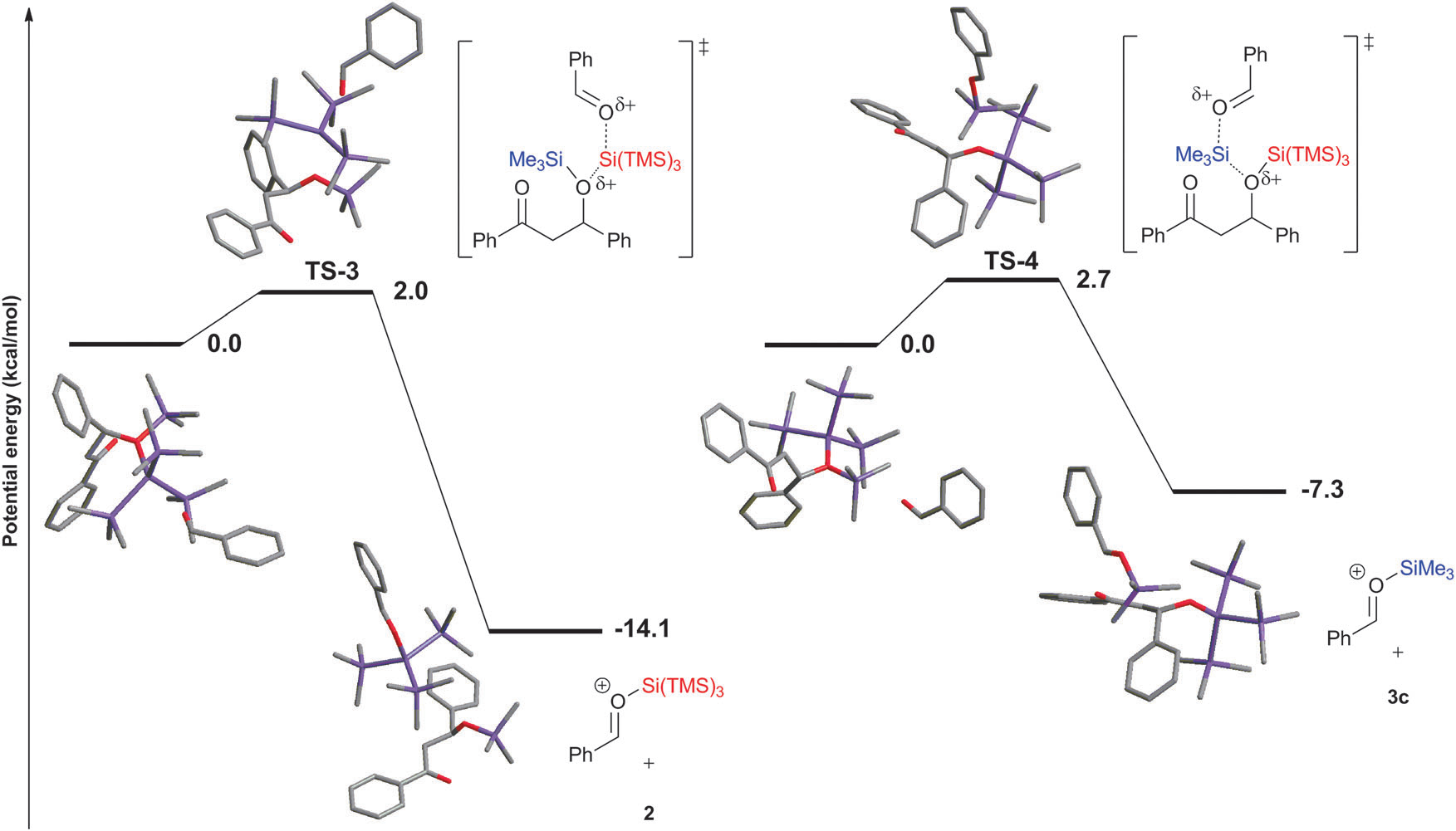
Potential energy profiles for the addition of benzaldehyde to (TMS)3Si+ and Me3Si+.
CAS number: 100-66-3
Anisole is a monomethoxybenzene that is benzene substituted by a methoxy group. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
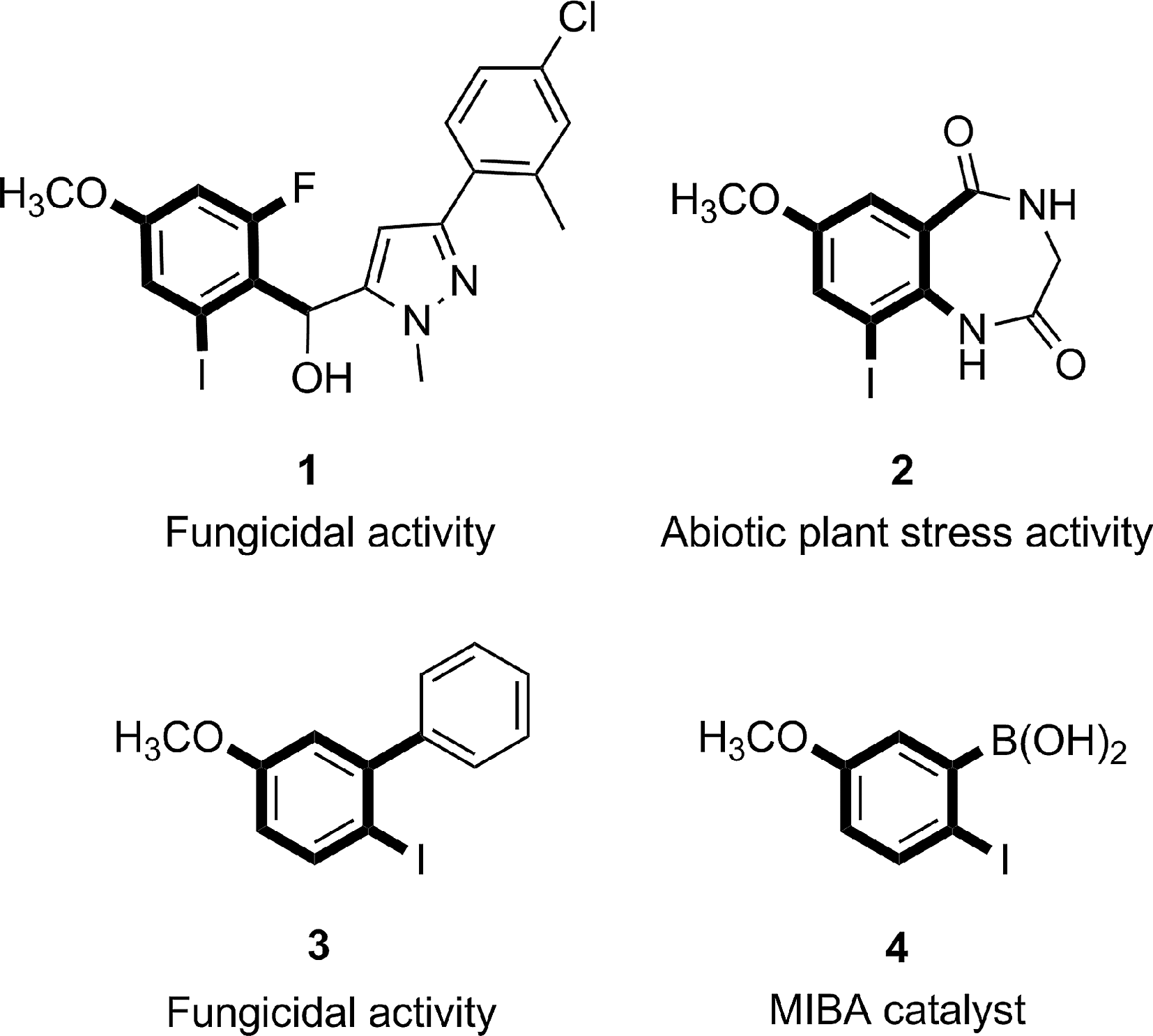
Some important iodinated anisole derivatives in medicine and industry.
CAS number: 100043-29-6
1H-tetrazole is an odorless white to light-yellow crystalline powder. Mp:1 55-157 °C. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic oxides of nitrogen fumes. Can explode if exposed to shock or heat from friction or fire. The primary hazard is from blast effect where the entire load can explode instantaneously and not from flying projectiles and fragments.
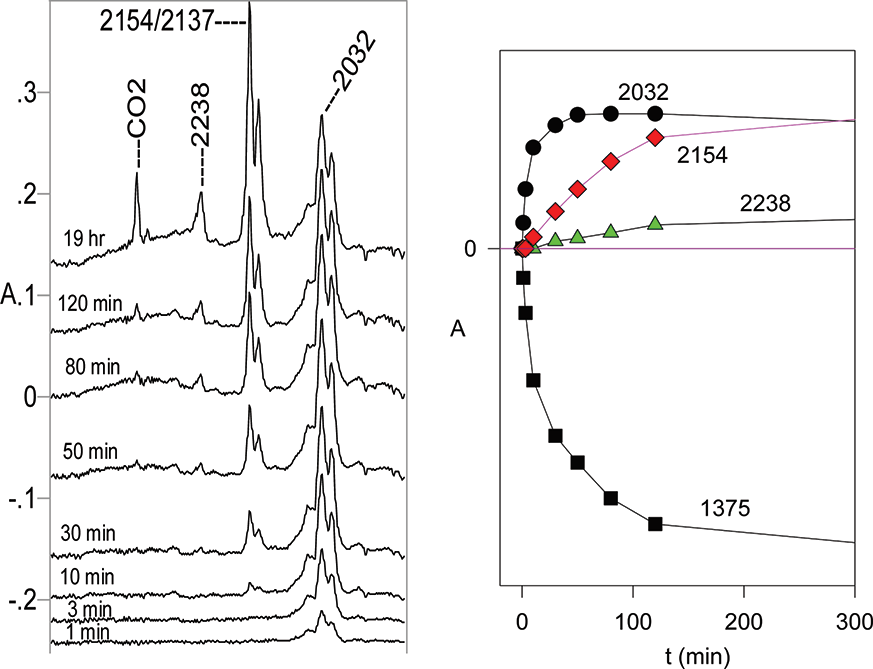
(Left) Partial IR difference spectra of tetrazole 16 at 12 K in Ar matrix at different photolysis times at 254 nm. The positive peaks are due to the photolysis products. The peaks at 2154 and 3137 cm−1 belong to the same compound, N-methyl-N′-phenylcarbodiimide 20. Abscissa 1900−2500 cm−1. (Right) Plots of IR absorbances at different wavenumbers versus photolysis time. The 1375 cm−1 band belongs to the starting material 16. Ordinates in arbitrary absorbance units.
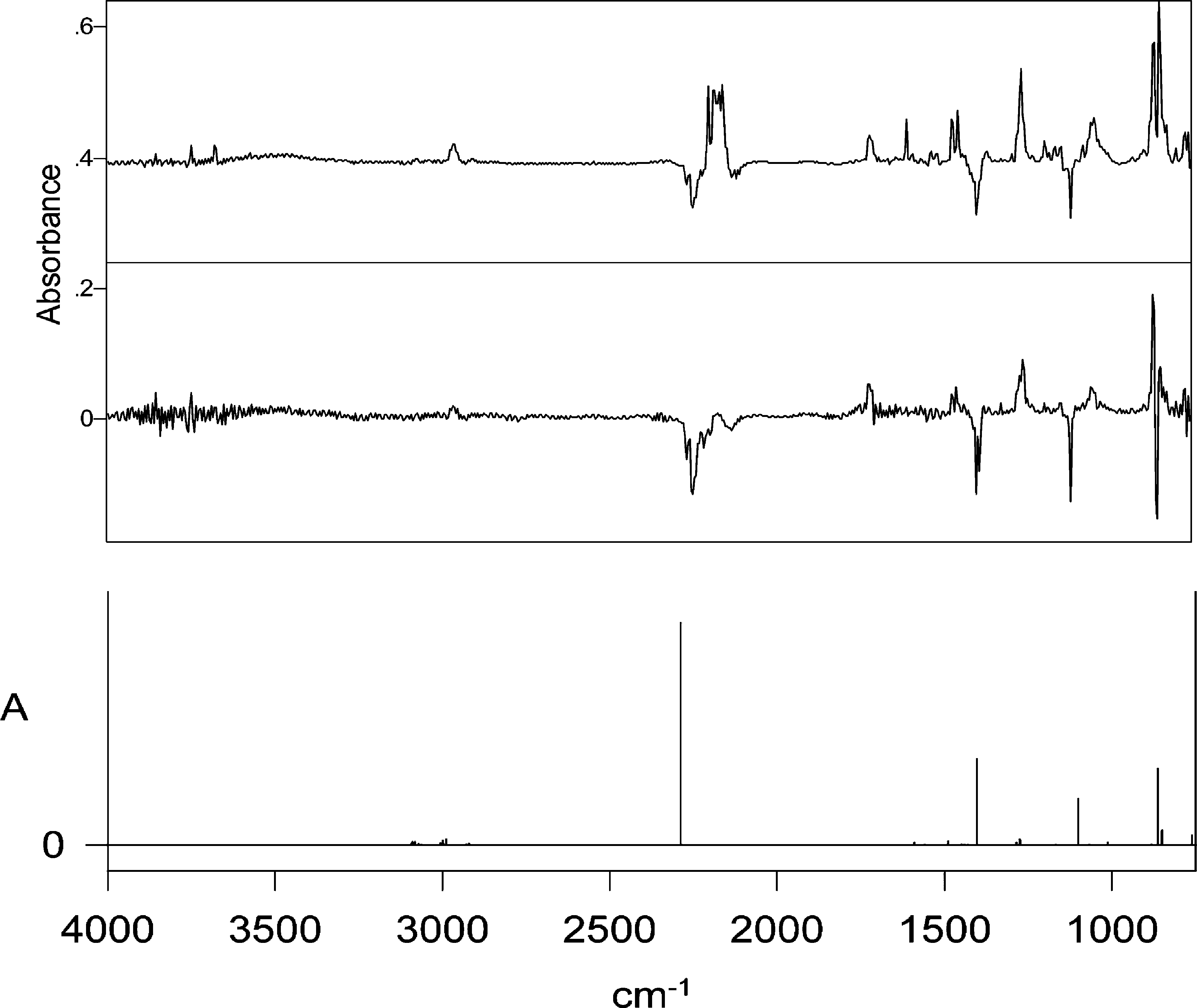
(a, bottom) Calculated IR spectrum of C-phenyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)nitrile imine 23 (B3-LYP/631G*, harmonic wave-numbers scaled by 0.9613; ordinate in arbitrary absorbance units). (b, middle) C-Phenyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)nitrile imine 23 obtained by photolysis of tetrazole 22 at 254 nm for 1 min in Ar matrix at 12 K and then destroyed by photolysis at 314 nm for 7 min, giving rise to the difference spectrum. Negative peaks are due to the nitrile imine 23: 2245, 1394, 1385, 1108, and 851 cm−1. Positive peaks are due to the formed N-phenyl-N′-(trimethylsilyl)carbodiimide 25: 2140−2175, 1590, 1466, 1451, 1256, 1150, 862, and 848 cm−1. (c, top) IR difference spectrum after photolysis of 22 for 45 min in Ar matrix at 12 K.
CAS number: 100045-73-6
Ulapualide A is an extraordinary bioactive tris-oxazole based macrolide which was isolated from the egg masses of the marine sponge Hexabranchus sanguineus and exhibits potent antifungal activity with inhibition of leukaemia cell proliferation.
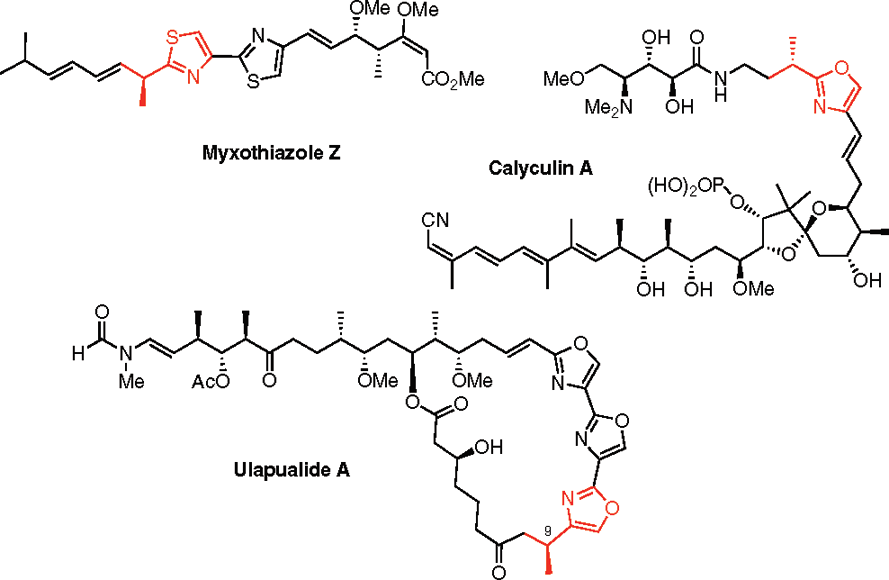
Structure of myxothiazole Z, calyculin A, and ulapualide A.