Benzyl Bromide
CAS number: 100-39-0
Benzyl bromide is a member of the class of benzyl bromides that is toluene substituted on the alpha-carbon with bromine. It has a role as a lachrymator.
Related images
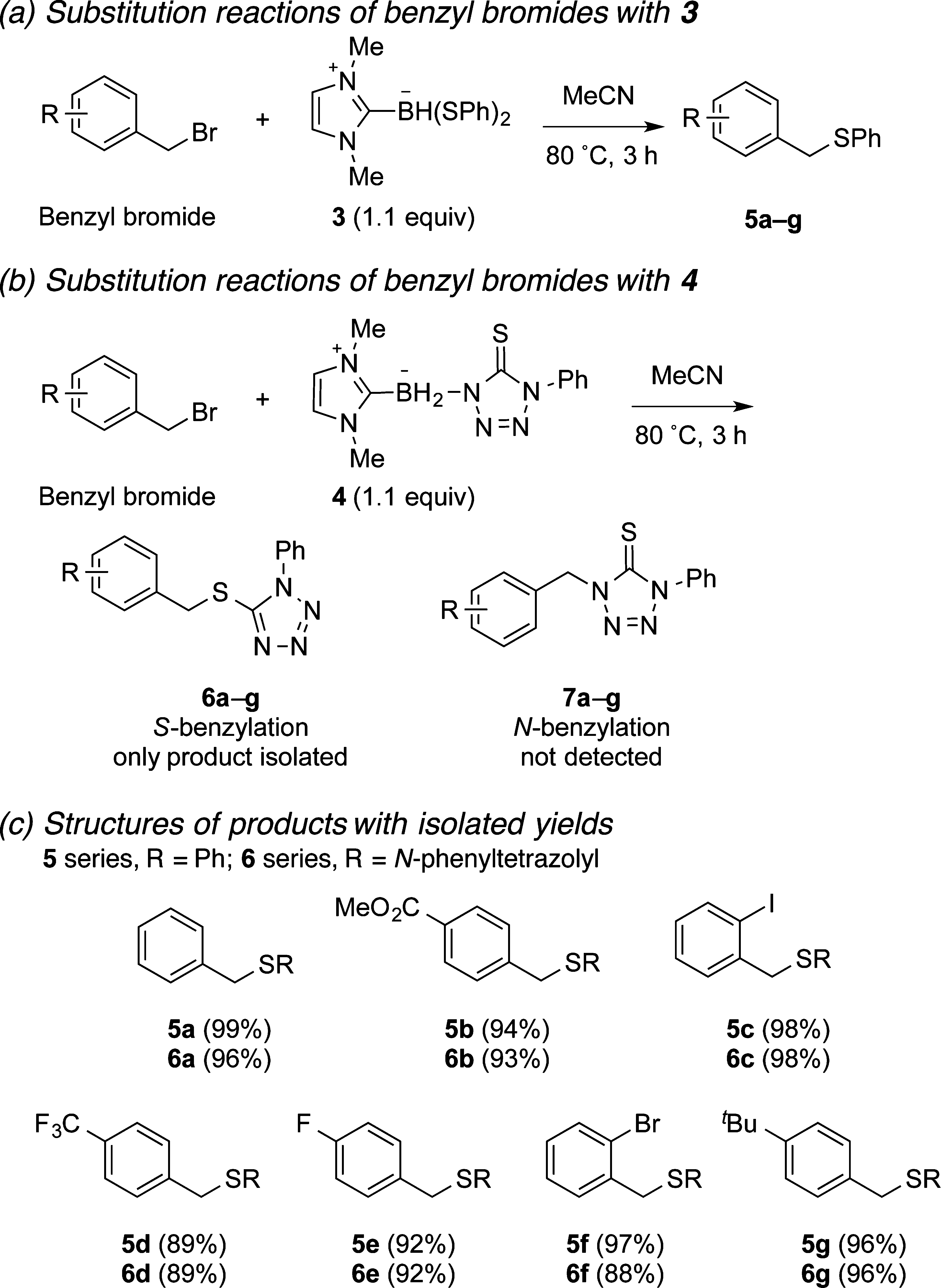
Scope study of substitution reactions of benzyl bromides by 3 under standard conditions
Related Questions and Answers
A: The proposed mechanism involves the formation of a quaternary ammonium salt, followed by hydrolysis to form a hydroxyl intermediate. DMP oxidizes this intermediate to an enamide, which then undergoes bromophilic attack and isomerization to form the key intermediate. Further oxidation by DMP leads to the final isoquinolinone product.
A: Benzyl bromides bearing electron-donating substituents such as methyl and methoxy groups, as well as those with 3-chloro and 3-bromo substituents, were successfully tolerated, yielding the corresponding isoquinoline-1,3-diones in excellent yields. Even benzyl bromides with strong electron-withdrawing nitro groups provided the desired products in good yields.
A: DMP acts as an efficient oxidant in the oxidative coupling reaction of isoquinoline with benzyl bromide, facilitating the formation of isoquinoline-1,3-dione or isoquinoline-1,3,4-trione derivatives under metal-free, mild, and practical conditions.