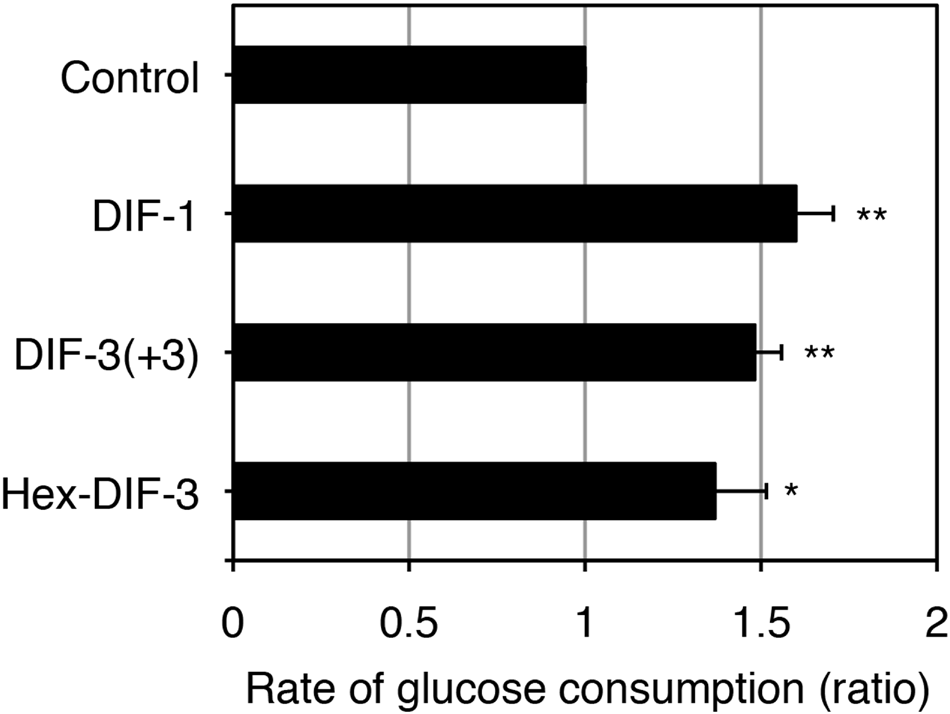
D-Glucose
CAS number: 2280-44-6
Glucose is a simple sugar (monosaccharide) generated during phosynthesis involving water, carbon and sunlight in plants. It is produced in humans via hepatic gluconeogenesis and breakdown of polymeric glucose forms (glycogenolysis). It circulates in human circulation as blood glucose and acts as an essential energy source for many organisms through aerobic or anaerobic respiration and fermentation.
Related images
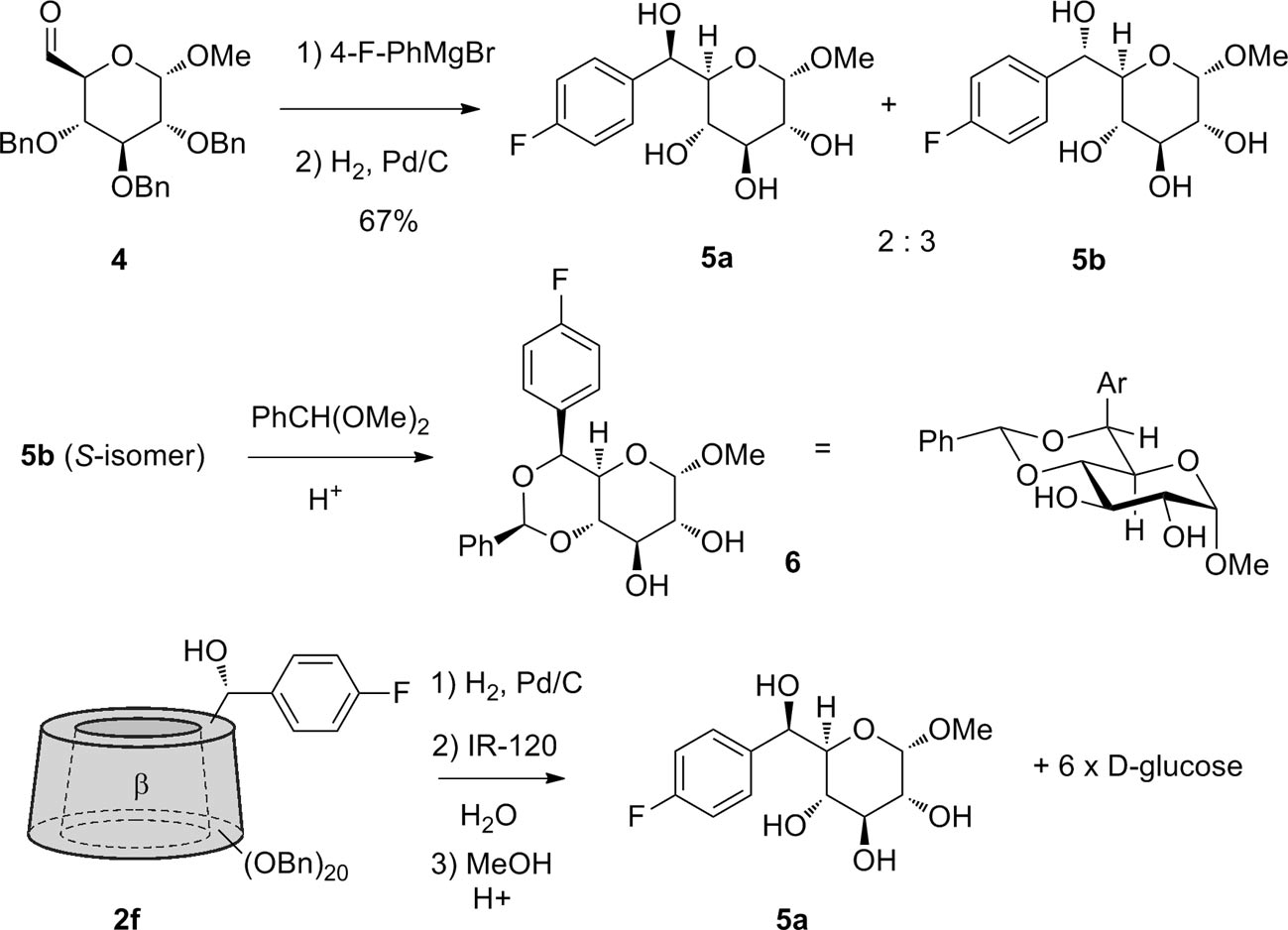
Two reference monosaccharide derivatives 5a and 5b were prepared to determine the stereochemistry at the C-6 position. The major isomer 5b obtained by addition of (4-fluorophenyl)magnesium bromide to glucose-6-aldehyde 4 was converted to the benzylidene derivative 6. This compound has a small J5,6 and only conforms to the S-stereochemistry. The β-cyclodextrin derivative 2f was hydrolyzed and converted to the methyl glycoside to give the minor R-isomer 5a.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet