Phosphoramidic acid, ion(2-)
CAS number: 22638-09-1
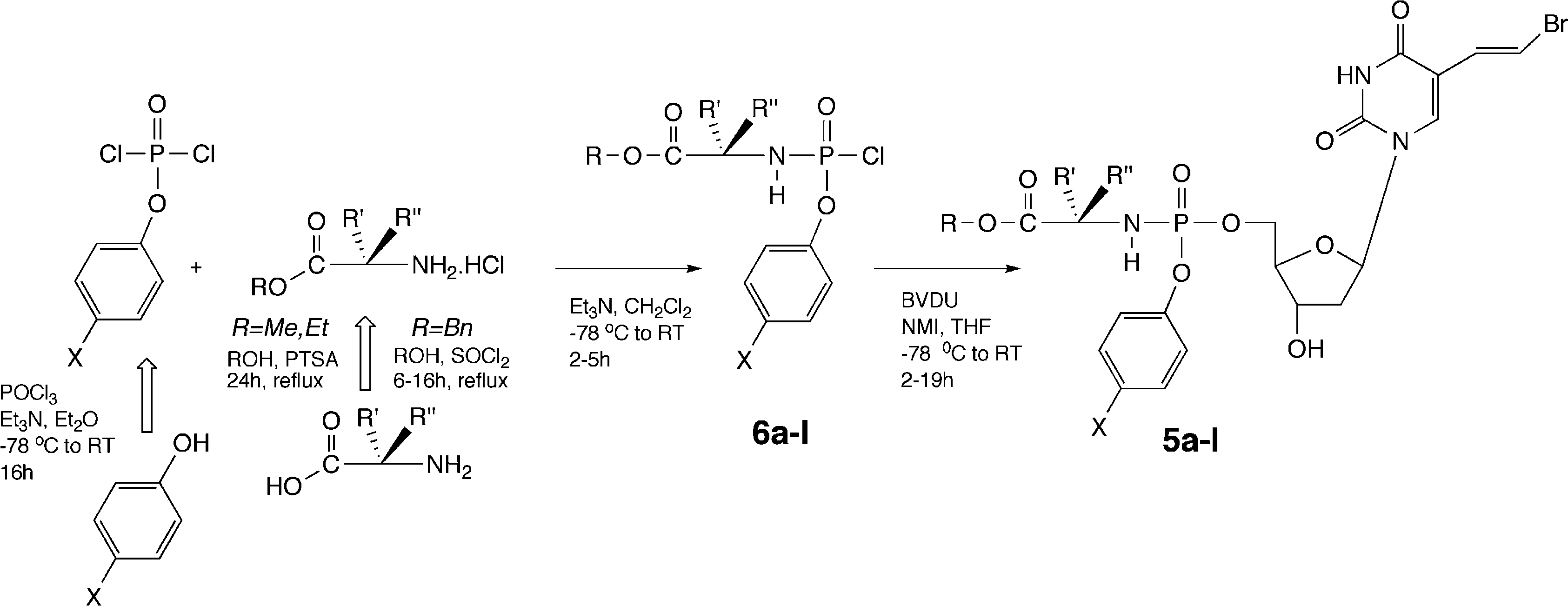
Phosphoramidic acid, ion(2−), also known as phosphoramidate dianion, is the conjugate base of phosphoramidic acid (H₂PO₂NH₂). It has the molecular formula [H₂NPO₂]²⁻ and consists of a phosphorus atom centrally bonded to an amino group (–NH₂), two oxygen atoms (one double-bonded and one single-bonded with a negative charge), and a lone pair of electrons. This dianion plays a role in biochemical and pharmaceutical research, particularly in the study of phosphoryl transfer reactions and enzyme inhibitors. It is typically encountered as part of salts or coordination compounds, and its structure is stabilized by resonance between the phosphorus–oxygen bonds.
Related images
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet