Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 1634-04-4
Methyl tert-butyl ether appears as a colorless liquid with a distinctive anesthetic-like odor. Vapors are heavier than air and narcotic (cause drowsiness when inhaled). This liquid has a flash point lower than most ambient temperatures, so it will readily ignite under most conditions. It is less dense than water and moderately soluble in water. Used as a octane booster in gasoline.
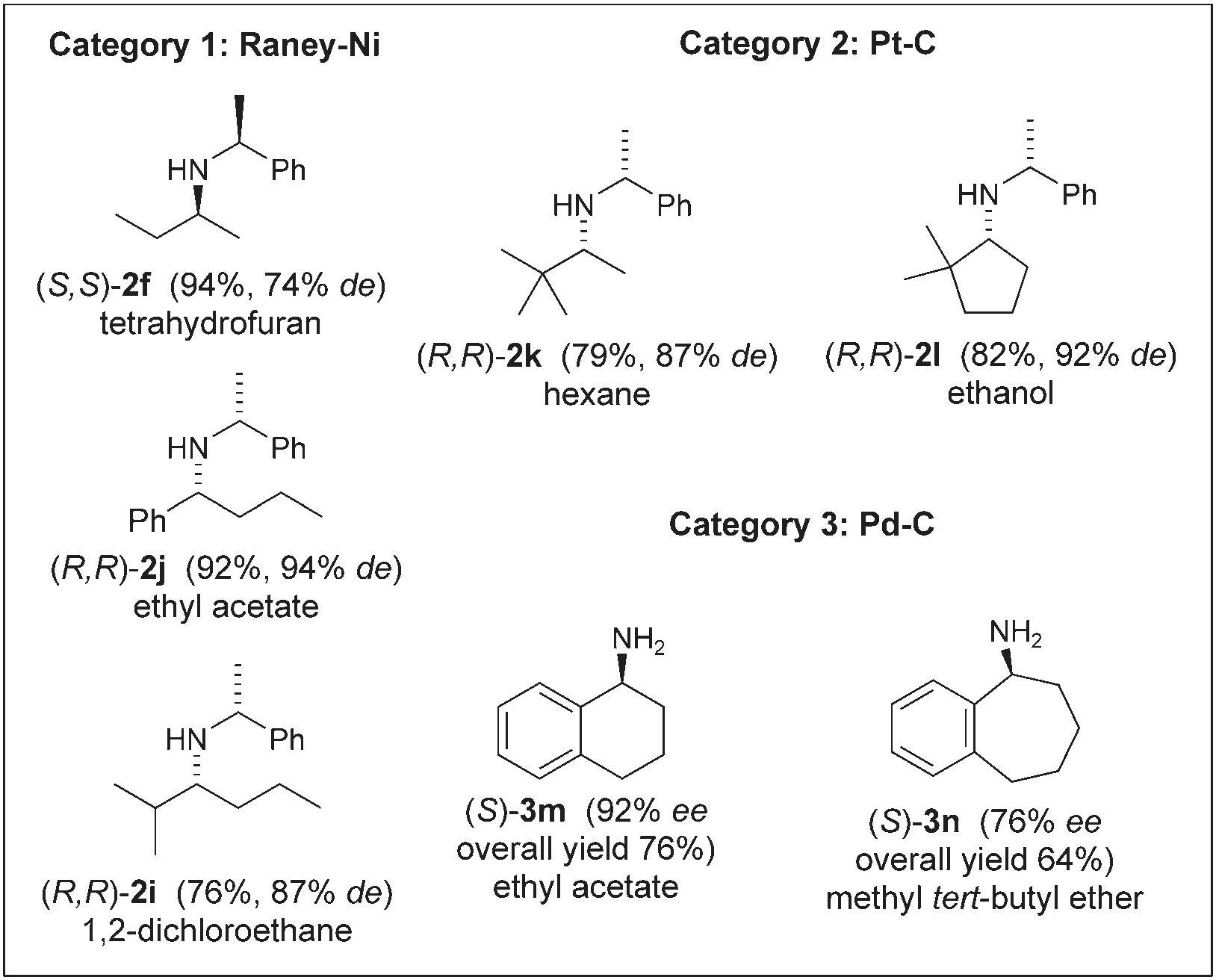
Correlation of structure, heterogeneous H2 catalyst, and diastereoselectivity: terahydrofuran, hexane, ethanol, ethyl acetate, 1,2-dichloroethane, methyl tert-butyl ether.
CAS number: 163815-24-5
The SV40 large T antigen Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) is a specific amino acid sequence within the SV40 large T antigen protein that directs its transport into the cell nucleus. This NLS, located at residues 47-55 (PKKKRKV), is crucial for the protein's function in viral replication and cellular transformation. The NLS acts as a signal that is recognized by importin proteins, which then facilitate the protein's movement through the nuclear pore and into the nucleus.
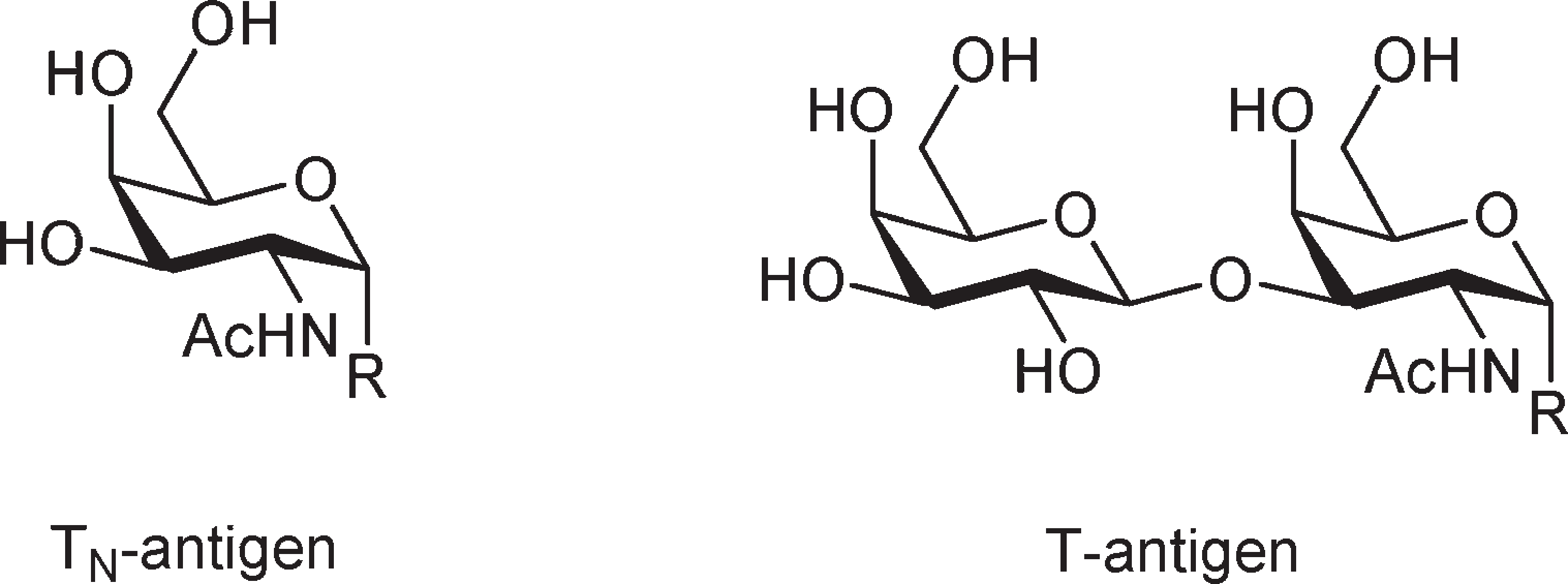
Structures of the TN- and the T-antigen.
CAS number: 165170-94-5
Hyperolactone C is a naturally occurring spirolactone, a type of organic compound, found in plants of the genus Hypericum, like Hypericum chinense and Hypericum lloydii. It's structurally interesting due to its unique spirocyclic structure with adjacent quaternary stereocenters.
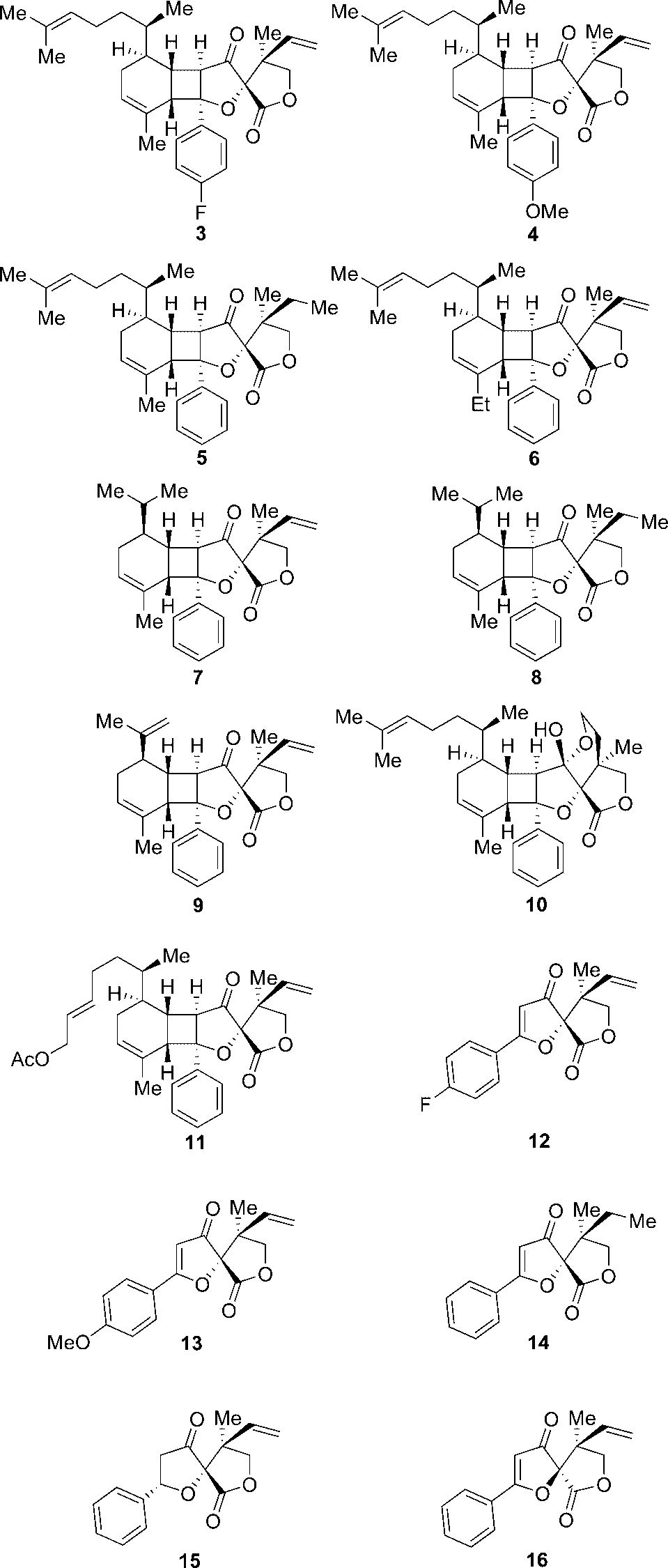
Synthesized biyouyanagin A (3-11) and hyperolactone C (12-16) analogues.
CAS number: 1656-44-6
2,4-Dinitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride, also known as benzenesulfonyl chloride, 2,4-dinitro-, is an aromatic sulfonyl chloride compound. It features a benzene ring substituted with two electron-withdrawing nitro groups at the 2 and 4 positions and a sulfonyl chloride group, making it a highly reactive electrophile.
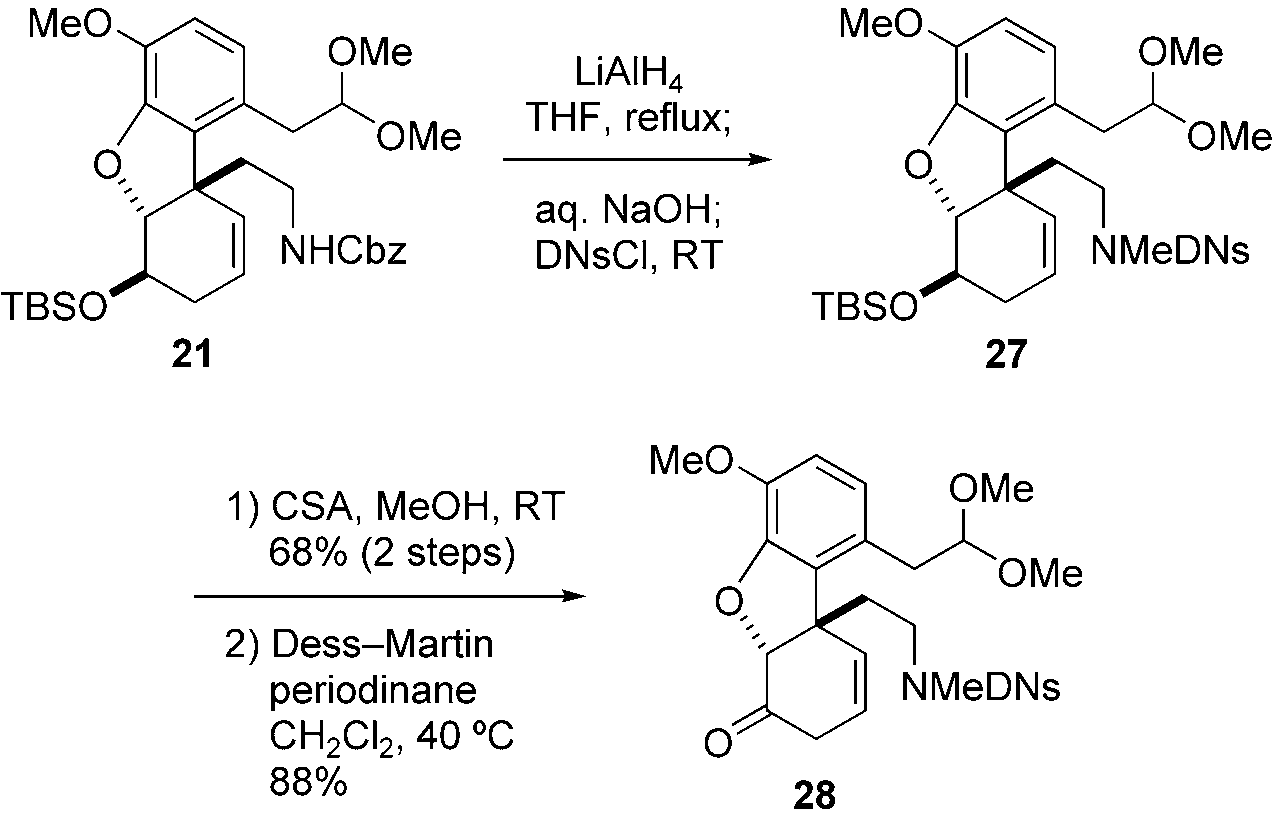
Preparation of key intermediate 28. DNsCl=2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride.
CAS number: 165877-95-2
Maremycin B is a natural product, specifically an indole diketopiperazine (DKP) alkaloid, isolated from the culture broth of a marine Streptomyces strain. It features a unique 3-hydroxyindolin-2-one structure derived from (2S,3S)-β-methyltryptophan. Maremycin B is structurally related to other diketopiperazines like Tryprostatin A and maremycin A.
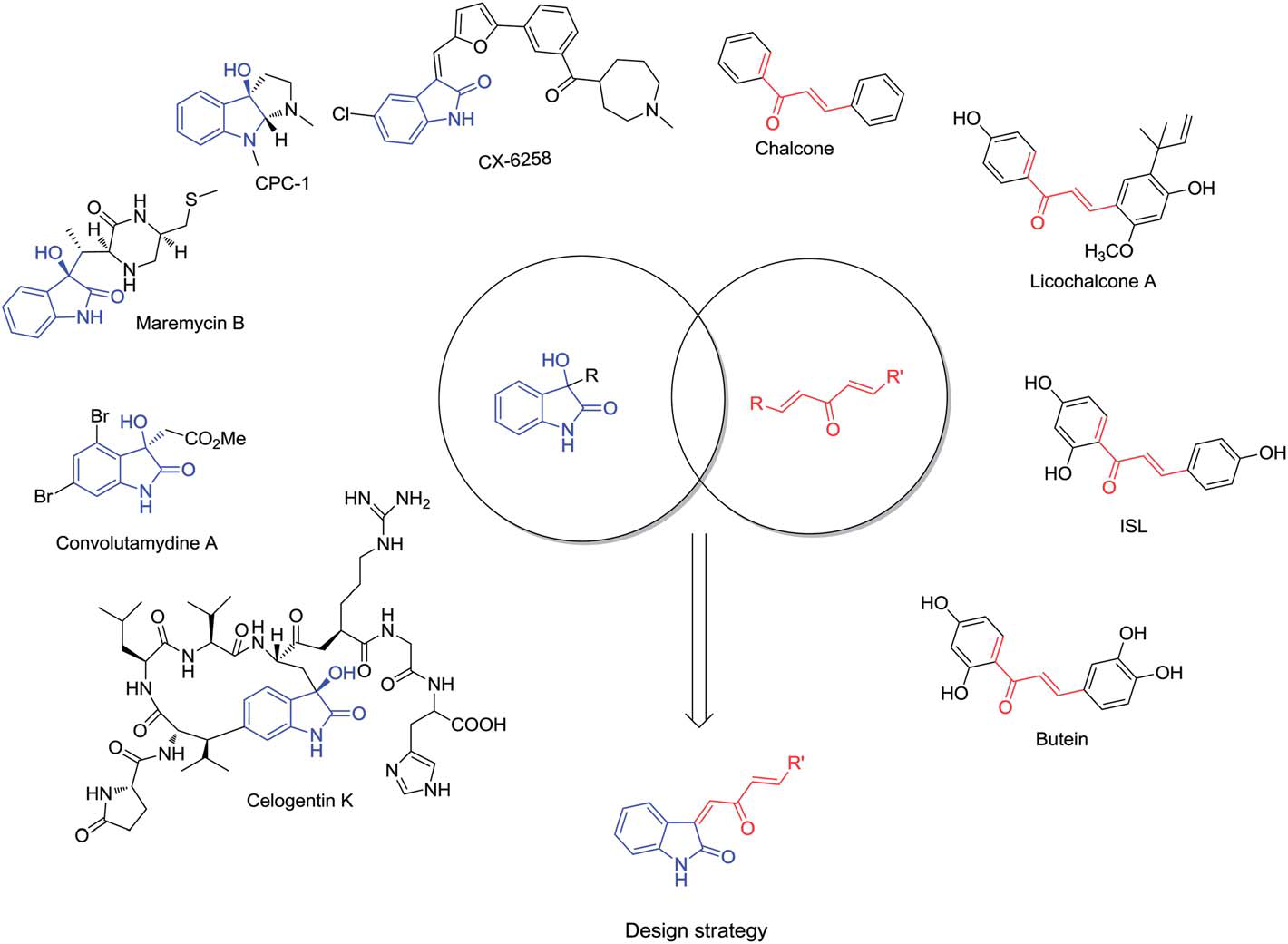
Biologically important molecules containing C3-functionalized oxindoles or a,b-unsaturated ketones, and the design strategy of combinatorial chemistry for new compound.
CAS number: 16590-41-3
Naltrexone is an organic heteropentacyclic compound that is naloxone substituted in which the allyl group attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a cyclopropylmethyl group. A mu-opioid receptor antagonist, it is used to treat alcohol dependence. It has a role as a mu-opioid receptor antagonist, a central nervous system depressant, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and an antidote to opioid poisoning. It is an organic heteropentacyclic compound, a morphinane-like compound and a member of cyclopropanes. It is a conjugate base of a naltrexone(1+).
![Competition curves of naltrexone (◼) and compounds 8 (△), 9 (▼), 10 (+), 12 (▲), 15 (◇), 31 (○) and 32 (●) for [3H]-DAMGO binding to Wistar rat forebrain membranes.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/2127528_10.png)
Competition curves of naltrexone (◼) and compounds 8 (△), 9 (▼), 10 (+), 12 (▲), 15 (◇), 31 (○) and 32 (●) for [3H]-DAMGO binding to Wistar rat forebrain membranes.
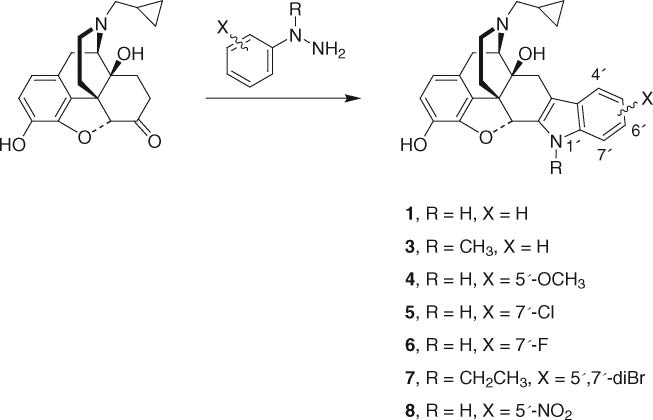
Fischer synthesis of naltrindole and analogs from naltrexone.
CAS number: 16619-14-0
2-phenyl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-one is a chemical compound, specifically a dihydroquinoline derivative. It is also known as 2,3-Dihydro-2-phenyl-4(1H)-quinolinone or azaflavanone.
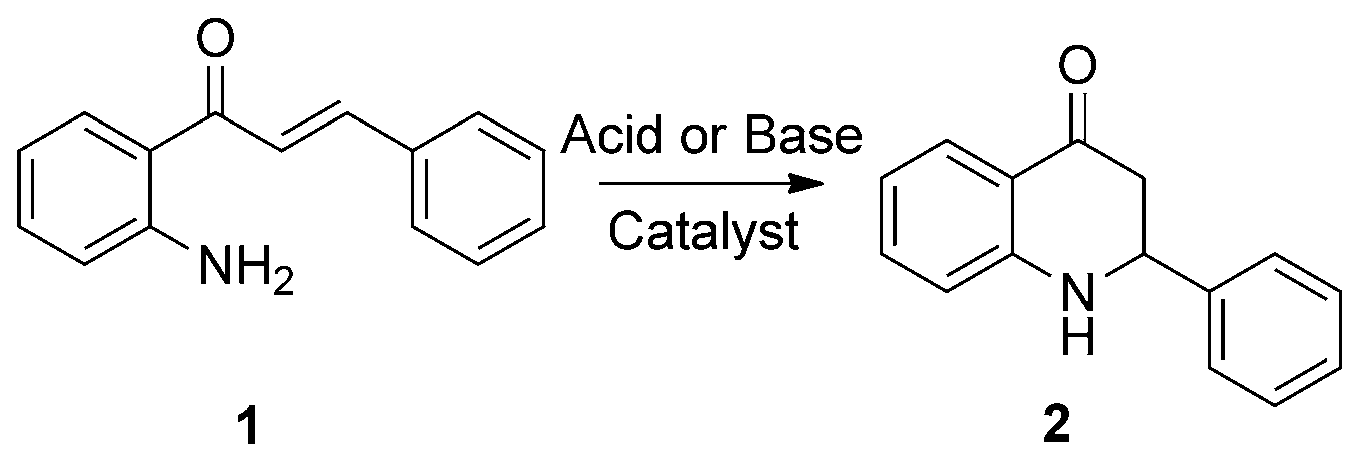
Synthesis of 2-phenyl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-one (2) from 2'-aminochalcone (1).
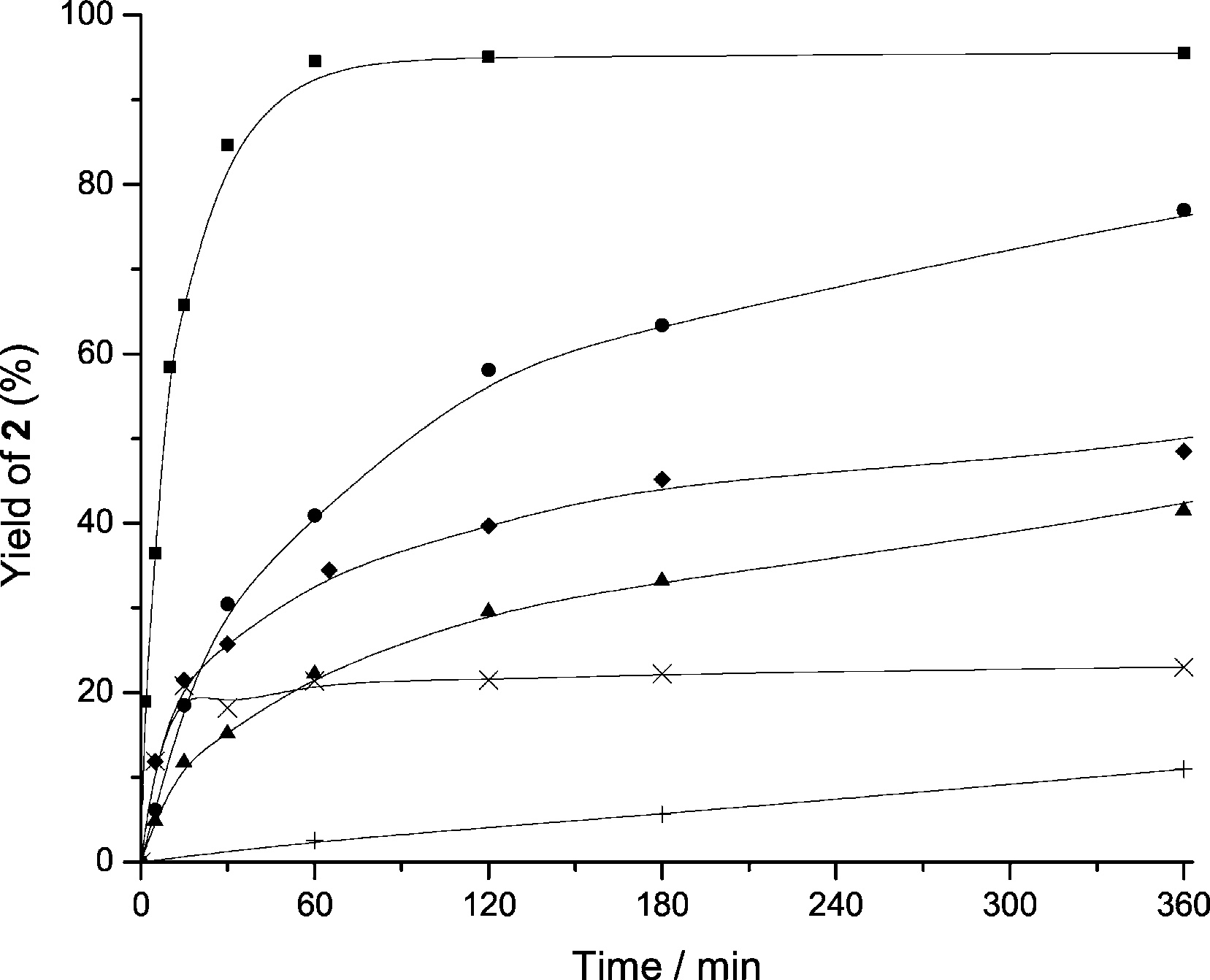
Kinetics curves of the yield to 2-phenyl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-one obtained with different solid acid catalysts (8 wt%) starting from 2'-Aminochalcone (1 mmol) in toluene (0.5 mL) at 1008C. MCM-41 (■), ITQ-2 (●), HBeta (▲), USY (◆), 15 wt% Mordenite (x), 15 wt% Sn-MCM-41(+).
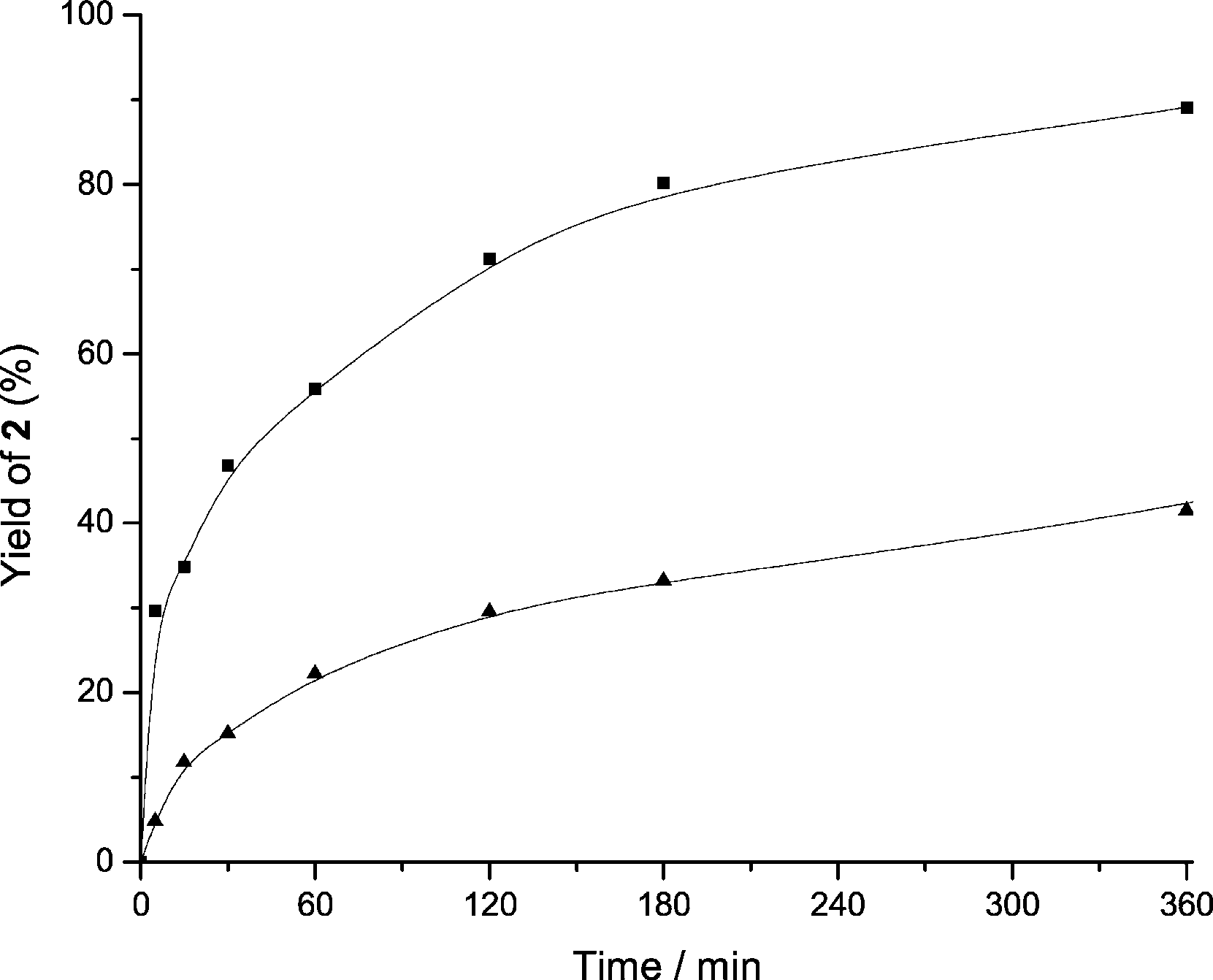
Yield of 2-phenyl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-one (2) versus time obtained for HBeta (▲) and Betanano (■) using 2'-aminochalcone (1 mmol) in toluene (0.5 mL) at 1008C.
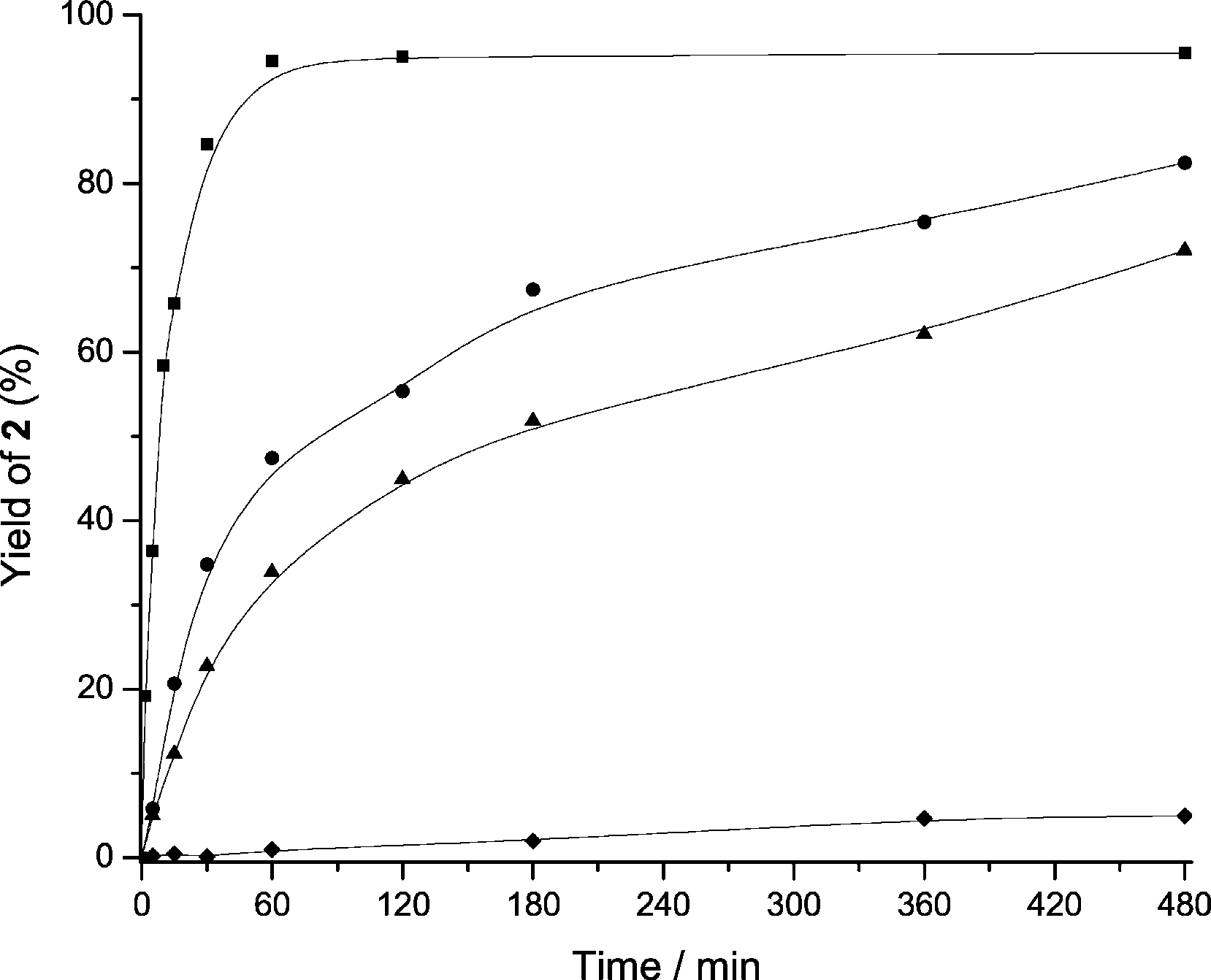
Yield of 2-phenyl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-one (2) versus time when the aza-Michael addition was performed using MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios. Si/Al=15 (■), 30 (●), 50 (▲), Si-MCM-41 (◆). Reaction conditions: 2;-aminochalcone (1 mmol), MCM-41 (8 wt%), at 1008C, in toluene (0.5 mL).
CAS number: 16619-60-6
3,5-Diphenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole is a chemical compound, specifically a derivative of pyrazole. It features a pyrazole ring (a five-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms) that is saturated at the 4,5 positions, and it is substituted at the 3 and 5 positions with phenyl groups.

Effect of varying concentrations of chalcone hydrazones (I), 1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazolines (II), N-acetyl-3,5-diphenyl pyrazolines (III), 3,5-diphenyl-2-pyrazolines (IV) and 1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazoles (V) at pH 6.0 on cathepsin B activity in presence of 2.5 mM concentration of BANA. Results are the mean of the experiment conducted in triplicates taking different concentrations of compounds. Activities are expressed as percent of control which contains equivalent amount of solvent and Lineweaver–Burk plot for cathepsin B activity on varying concentrations of BANA in presence of minimum concentration of chalcone hydrazones (VI), 1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazolines (VII), N-acetyl-3,5-diphenyl pyrazolines (VIII), 3,5-diphenyl-2-pyrazolines (IX) and 1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazoles (X).
CAS number: 166330-10-5
Bis[2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl] ether, also known as DPEphos, is a diphosphine ligand commonly used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. It features a diphenyl ether backbone with two diphenylphosphino groups attached.
![Synthetic routes to prepare compound ASDSN. (i) K2CO3, Me–I, acetone, 50 ℃, 6 h. (ii) Bu4NBr (5 mol%), HNO3 (15% w/w), dichloroethane, 20 ℃. (iii) AcOH, H2O2, CH2Cl2, 0 ℃-reflux, 2 h. (iv) I2, dioxane/pyridine, 0 ℃ to rt, 3 h. (v) LiAlH4. (vi) PCC. (vii) Ph3PMeBr, KOtBu, THF, rt, 18 h. (viii) Pd(OAc)2 (1.2–1.8 mol%), bis[(2-diphenylphosphino)phenyl] ether (DPEPhos) (2.5–3.6 mol%), K2CO3, DMF, 120 ℃, 6–12 h.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3214957_05.png)
Synthetic routes to prepare compound ASDSN. (i) K2CO3, Me–I, acetone, 50 ℃, 6 h. (ii) Bu4NBr (5 mol%), HNO3 (15% w/w), dichloroethane, 20 ℃. (iii) AcOH, H2O2, CH2Cl2, 0 ℃-reflux, 2 h. (iv) I2, dioxane/pyridine, 0 ℃ to rt, 3 h. (v) LiAlH4. (vi) PCC. (vii) Ph3PMeBr, KOtBu, THF, rt, 18 h. (viii) Pd(OAc)2 (1.2–1.8 mol%), bis[(2-diphenylphosphino)phenyl] ether (DPEPhos) (2.5–3.6 mol%), K2CO3, DMF, 120 ℃, 6–12 h.
CAS number: 1665-00-5
Dichloromethane-d2, also known as methylene chloride-d2 or dideuteromethylenechloride, is a deuterated form of the solvent dichloromethane (CH2Cl2).
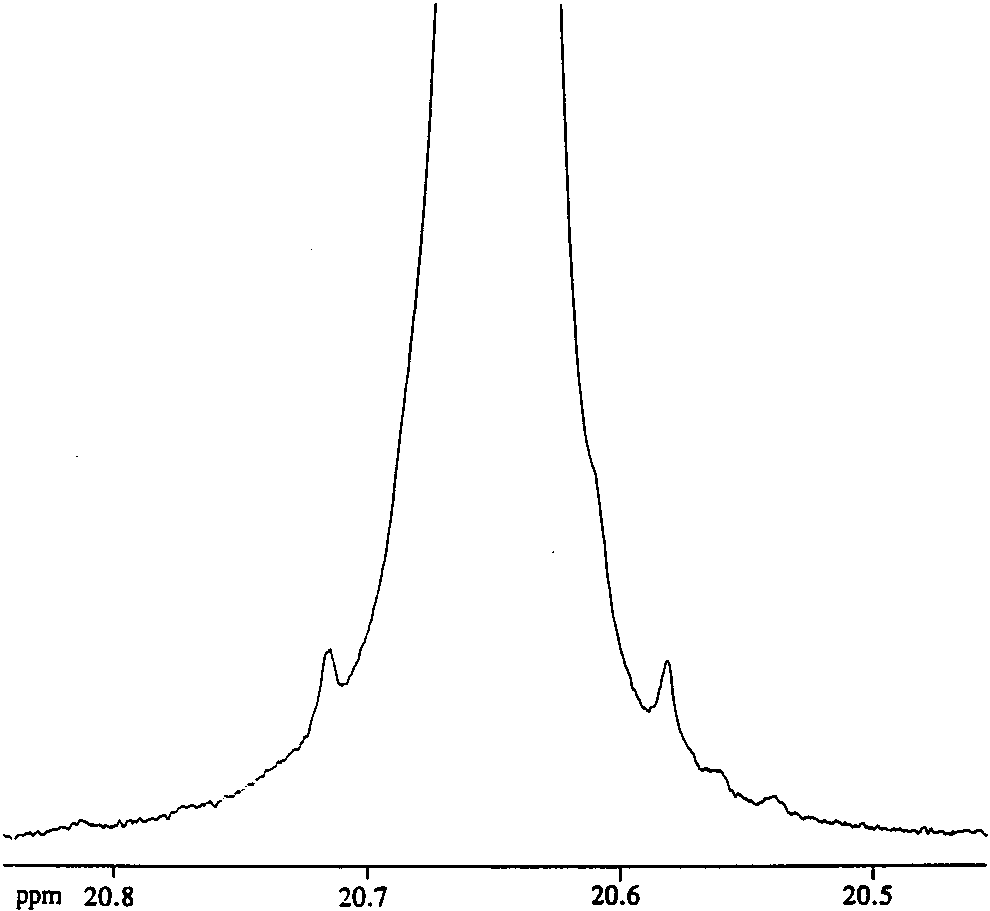
Zoom-in of the nitroxyl protons in the 1H NMR spectrum of 3a (CD2Cl2, 400 MHz, 20 °C).
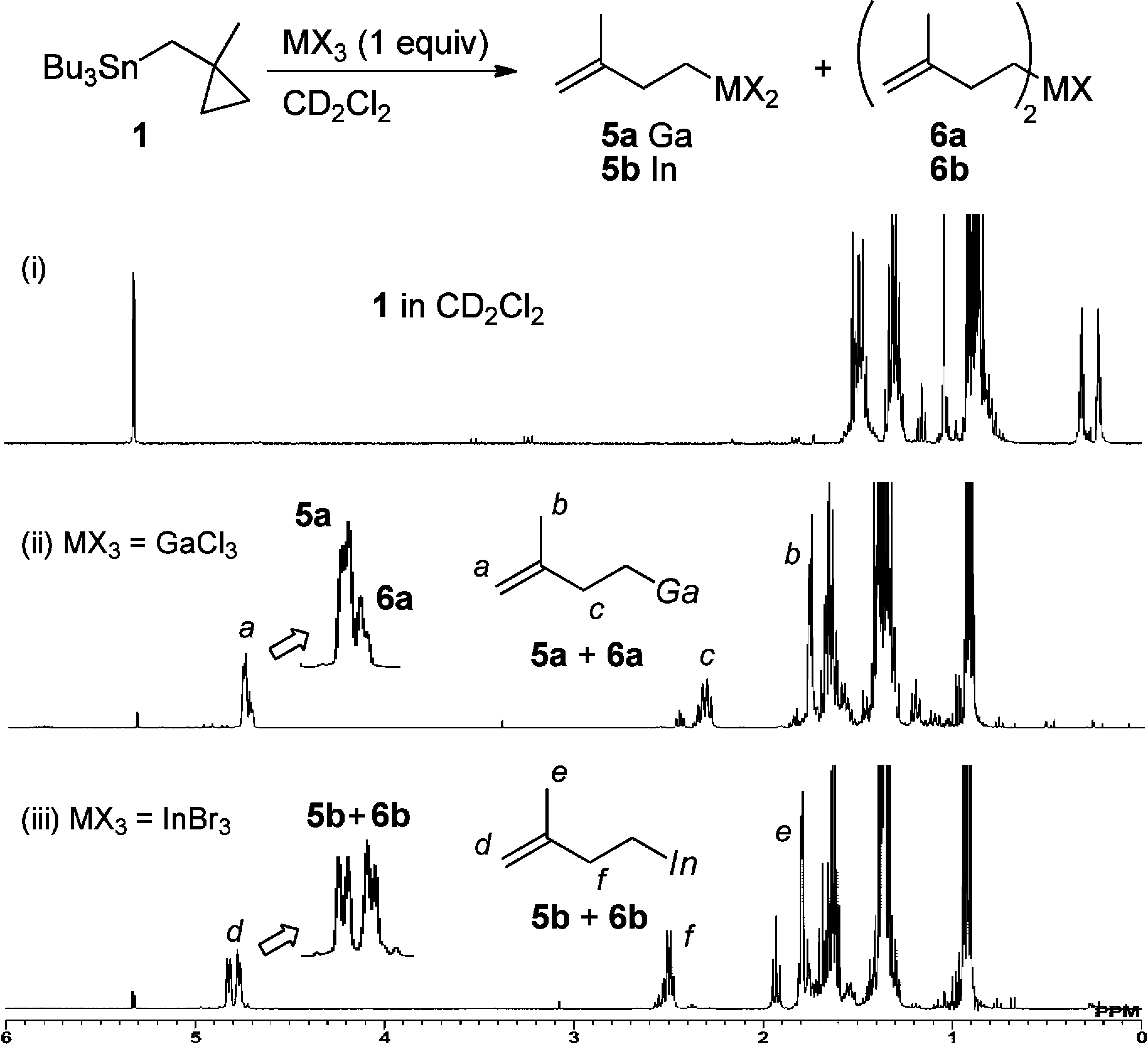
1H NMR spectra of (i) 1, (ii) the mixture of GaCl3 and 1, and (iii) the mixture of InBr3 and 1 in CD2Cl2.
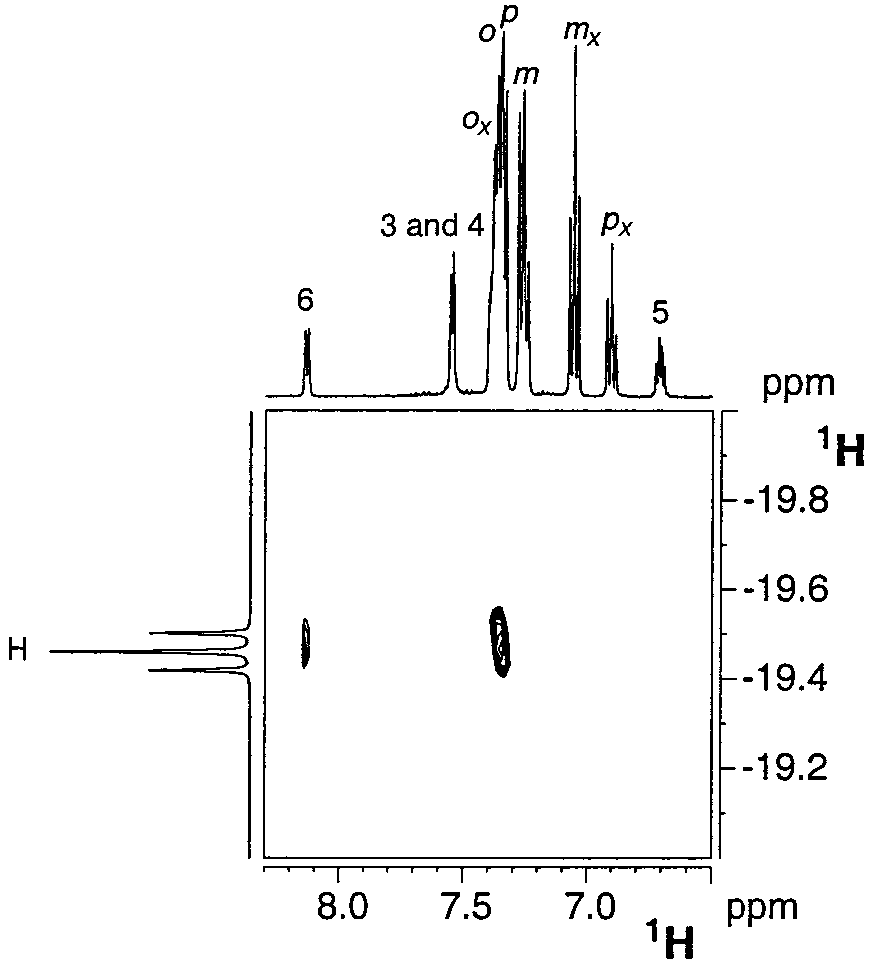
Section of the 1H-NOESY NMR spectrum of complex 1d recorded at 400.13 MHz in methylene chloride-d2 (298 K) showing the selective intramolecular interactions of the hydrides with protons H-6 and H-o.