Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 158959-32-1
SC-57666 is a stilbenoid.
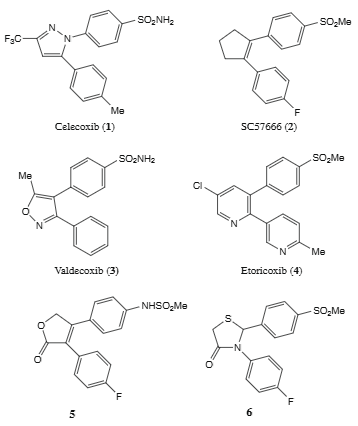
Representative examples of selective COX-2 inhibitors: Celecoxib, SC57666, Valdecoxib, Etoricoxib.
CAS number: 159026-30-9
Aplysamine-1 is a naturally occurring bromotyrosine alkaloid, and a potent antagonist of the histamine H3 receptor. It's found in marine sponges and has been the subject of research for its potential as a drug candidate.
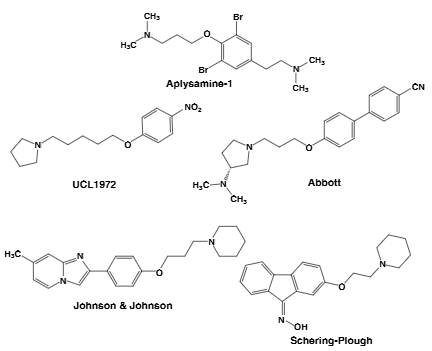
Examples of non-imidazole-derived H3 antagonists: Aplysamine-1, UCL-1972, Abbott(A-10749).
CAS number: 15956-28-2
Dirhodium tetraacetate, also known as Rhodium(II) acetate dimer, is well-known for its use as a catalyst in various organic reactions and is also a subject of research in materials science and medicinal chemistry.
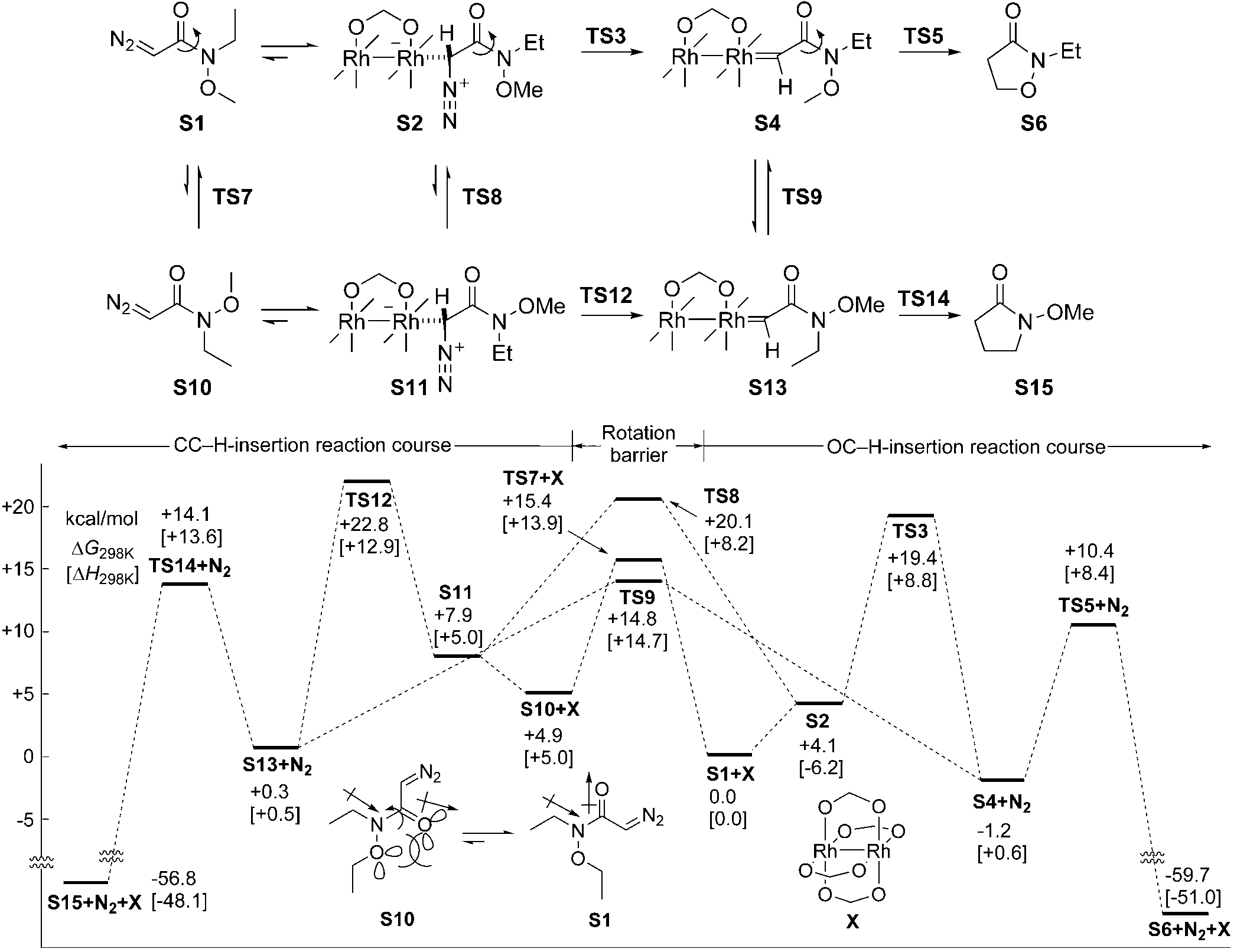
Reaction pathways and the potential surface of the C H insertion model reaction at the B3LYP/631GLAN level. The simpler dirhodium catalyst X and substrate S1 were used instead of dirhodium tetraacetate and more complex substrates to make the computation more manageable.
CAS number: 15980-15-1
1,4-Oxathiane is a heterocyclic compound containing one oxygen atom and one sulfur atom at opposite corners of a saturated six-membered ring.
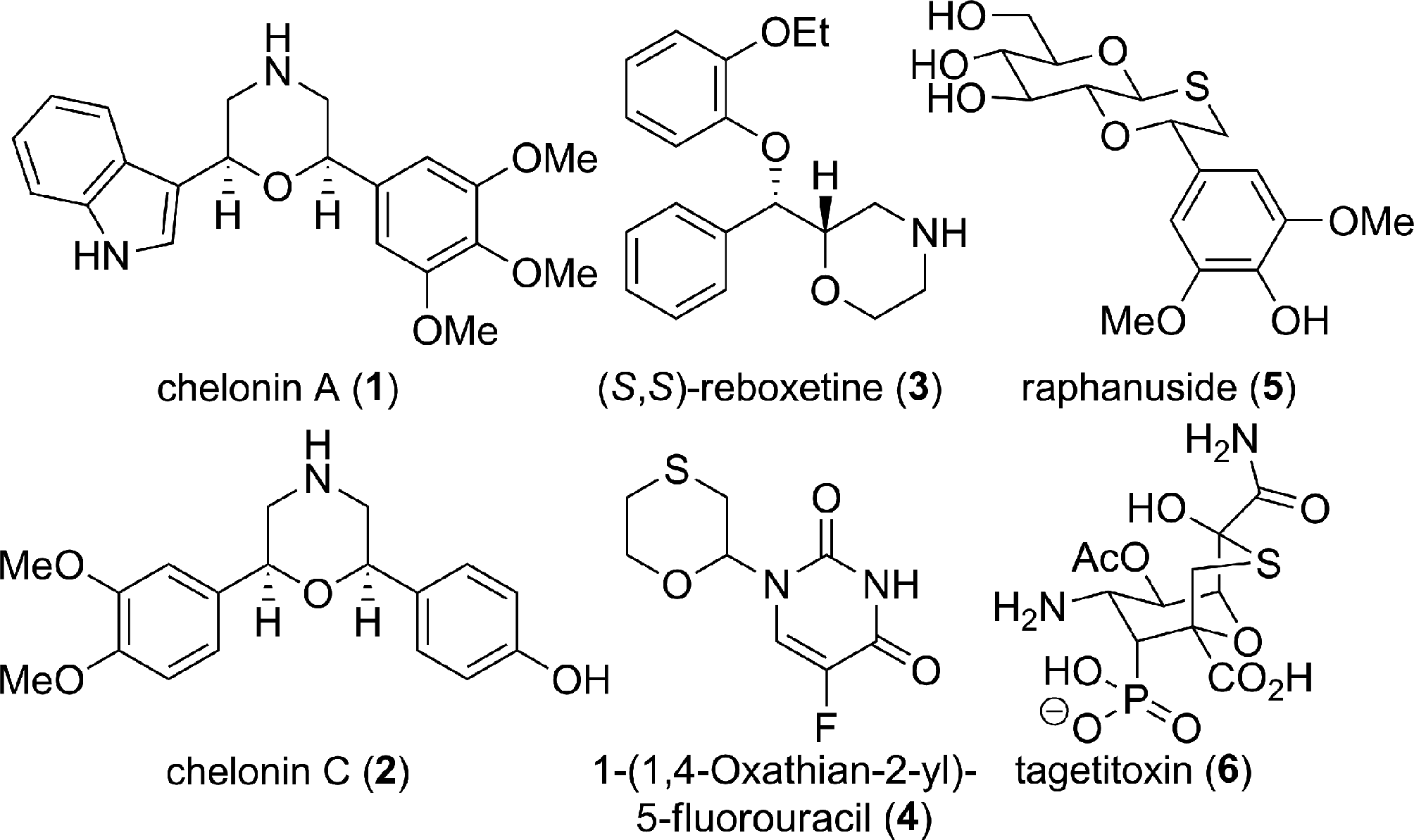
Morpholines and 1,4-oxathiane ring bearing natural products and bioactive molecules.
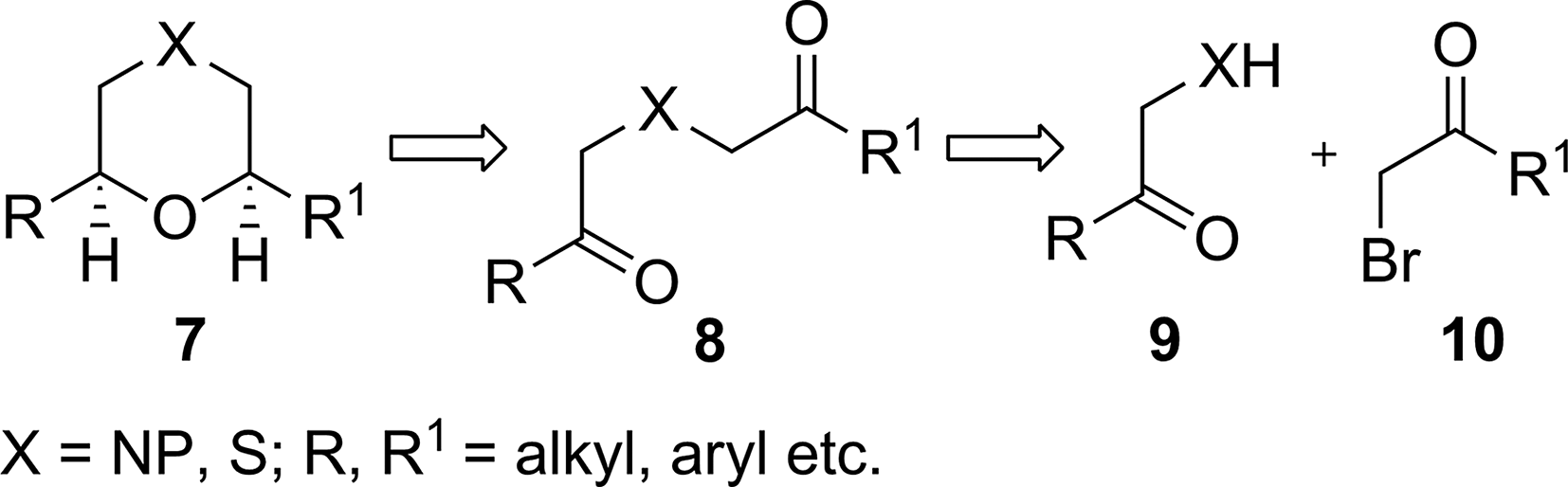
Retrosynthesis for 2,6-disubstituted morpholine and 1,4-oxathianes 7.
CAS number: 1605-68-1
Taxane is a terpenoid fundamental parent and a diterpene.
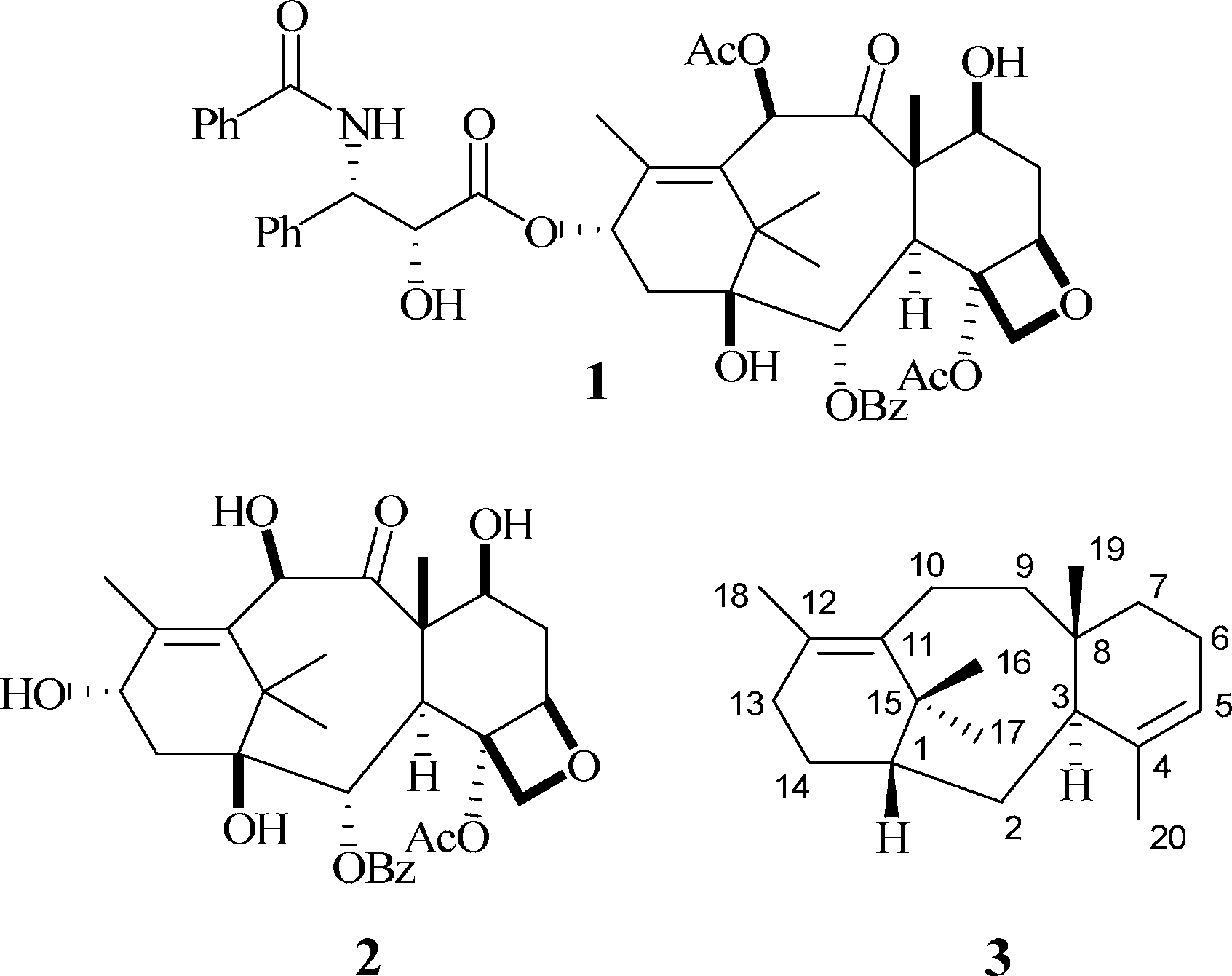
Structures of taxane diterpenes.
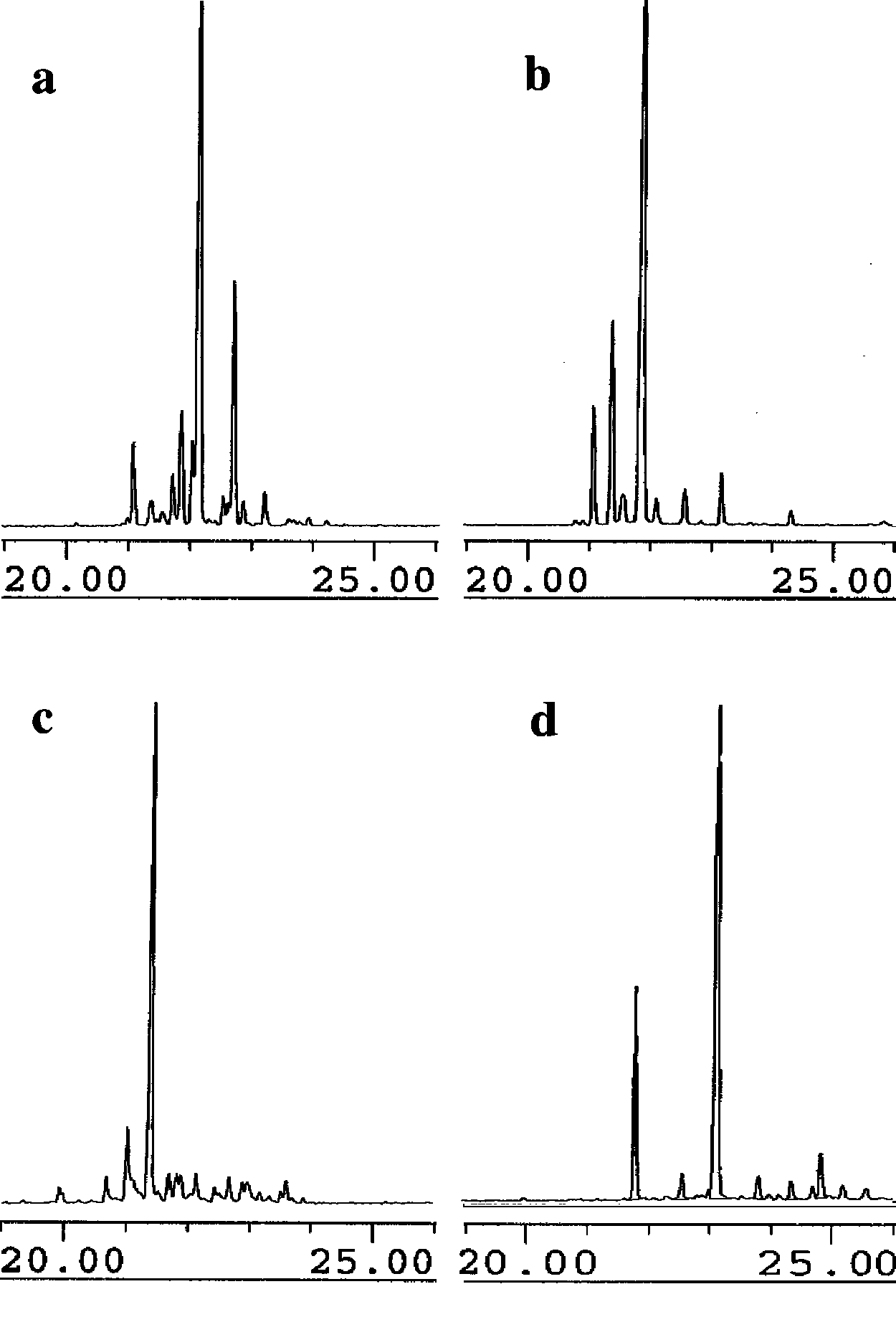
GCMS analyses, displaying the total ion current of the hydrocarbon products from the incubation of taxadiene synthase with analogues 10 (panel a), 11 (panel b), 12 (panel c), and 13 (panel d).
CAS number: 1605-72-7
Dichlorocarbene is a chemical compound that is formed when chloroform reacts with a base.
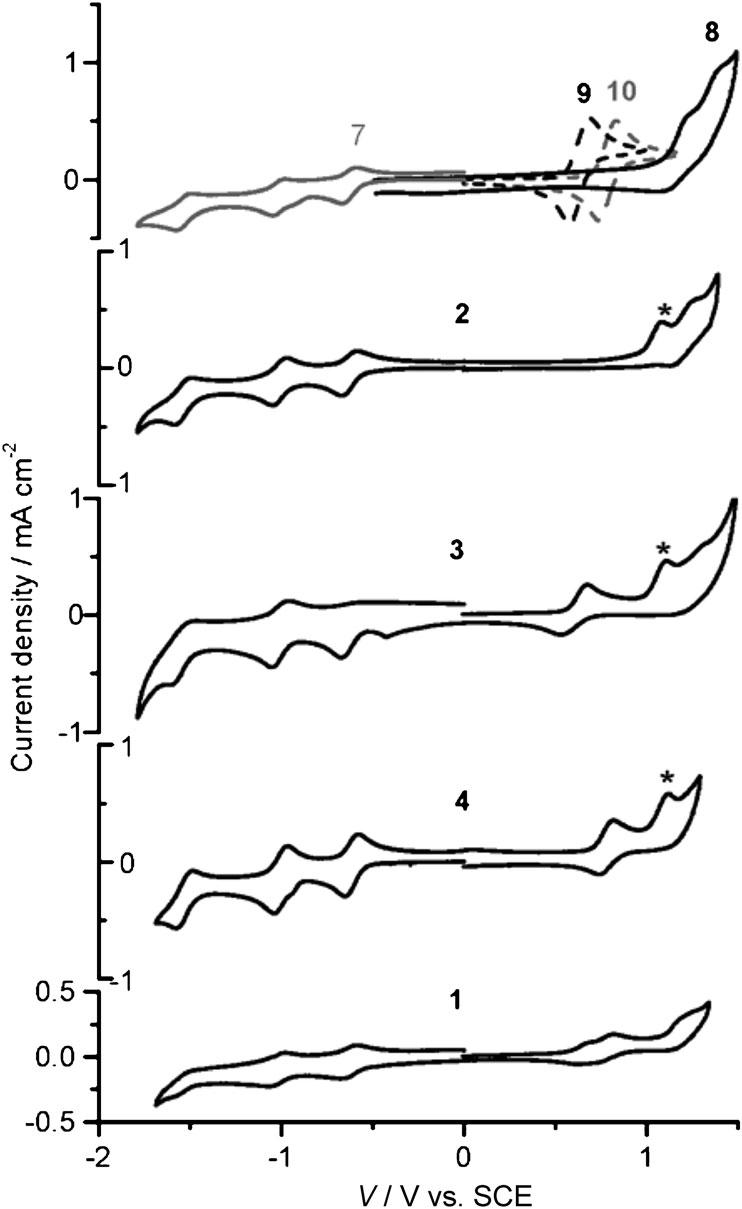
Voltammograms of reference molecular subunits 7-10 and multicomponent systems 1-4 were measured in CH2Cl2 with 0.1 mol/L▔1 nBu4NClO4 (TBAP) as supporting electrolyte. Scan rate: 0.2 Vs▔1
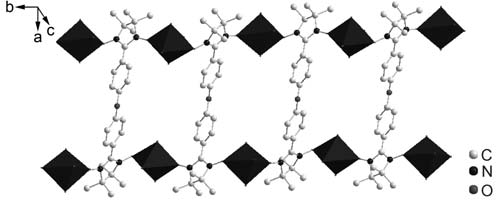
The ladder-like chain structure of the complex 2. The copper atoms are displayed as octahedrons, hexfluoroacetylacetone, hydrogen atoms and the disordered dichloromethane are omitted for clarity.
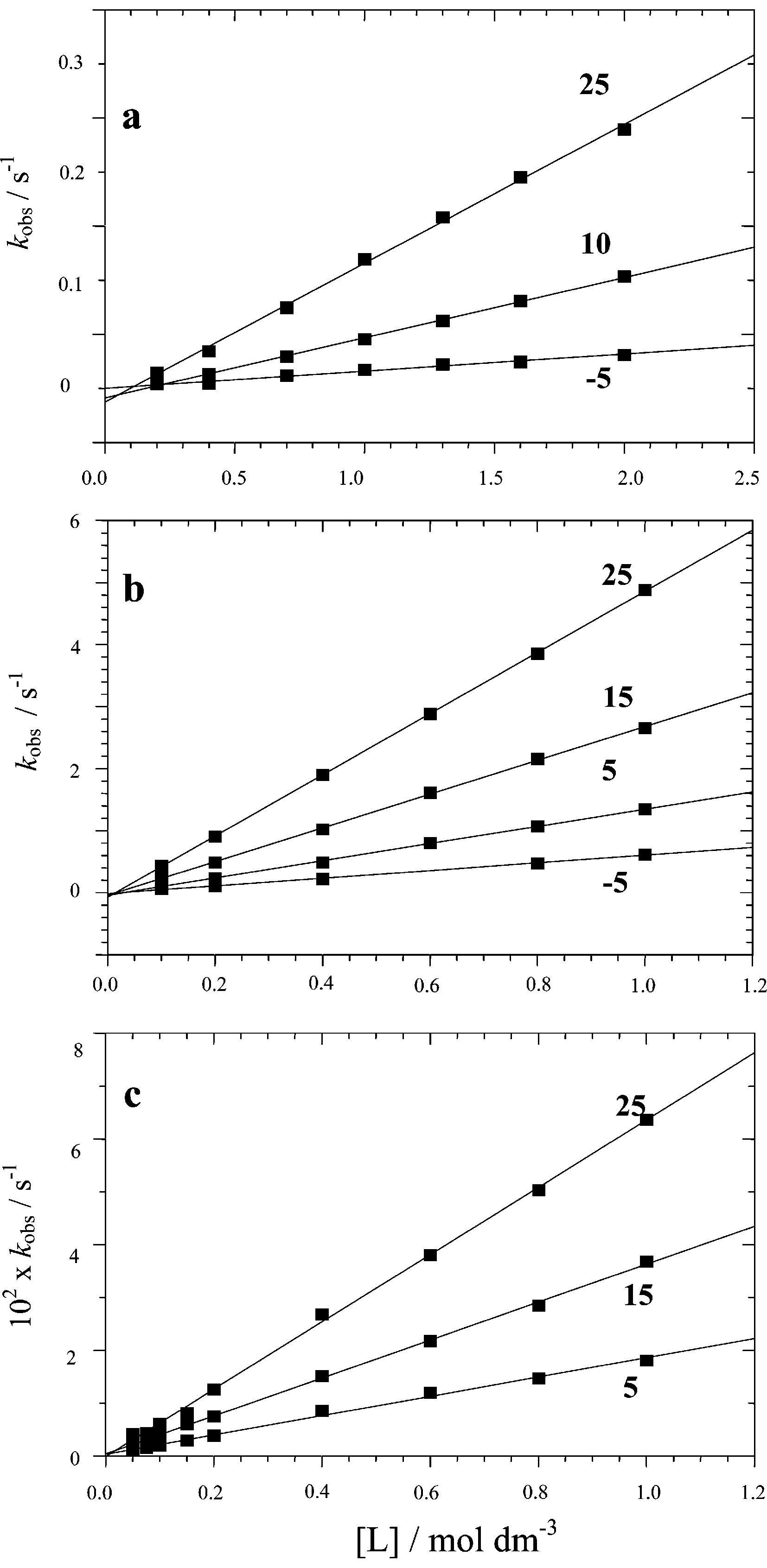
Bridge splitting of 1 with MeOH (a), MeCN (b) and cyclooctene (c) in dichloromethane at various temperatures.
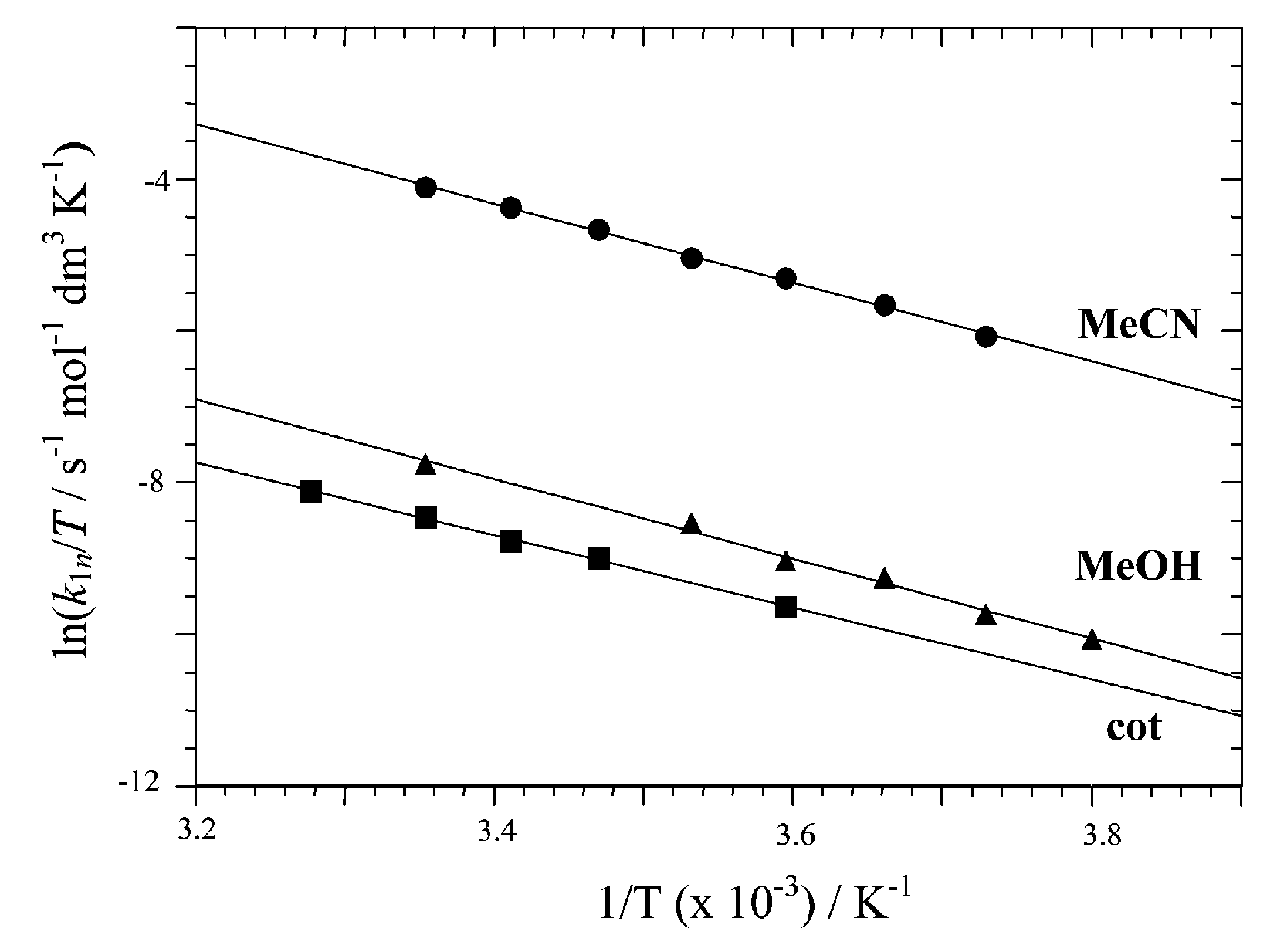
Eyring plots for bridge splitting of 1 with MeOH, MeCN and cyclooctene in dichloromethane.
CAS number: 161265-03-8
Xantphos is a wide bite angle bisphosphine ligand. It contains two phosphine moieties that can strongly bind to a metal centre in a bidentate fashion.
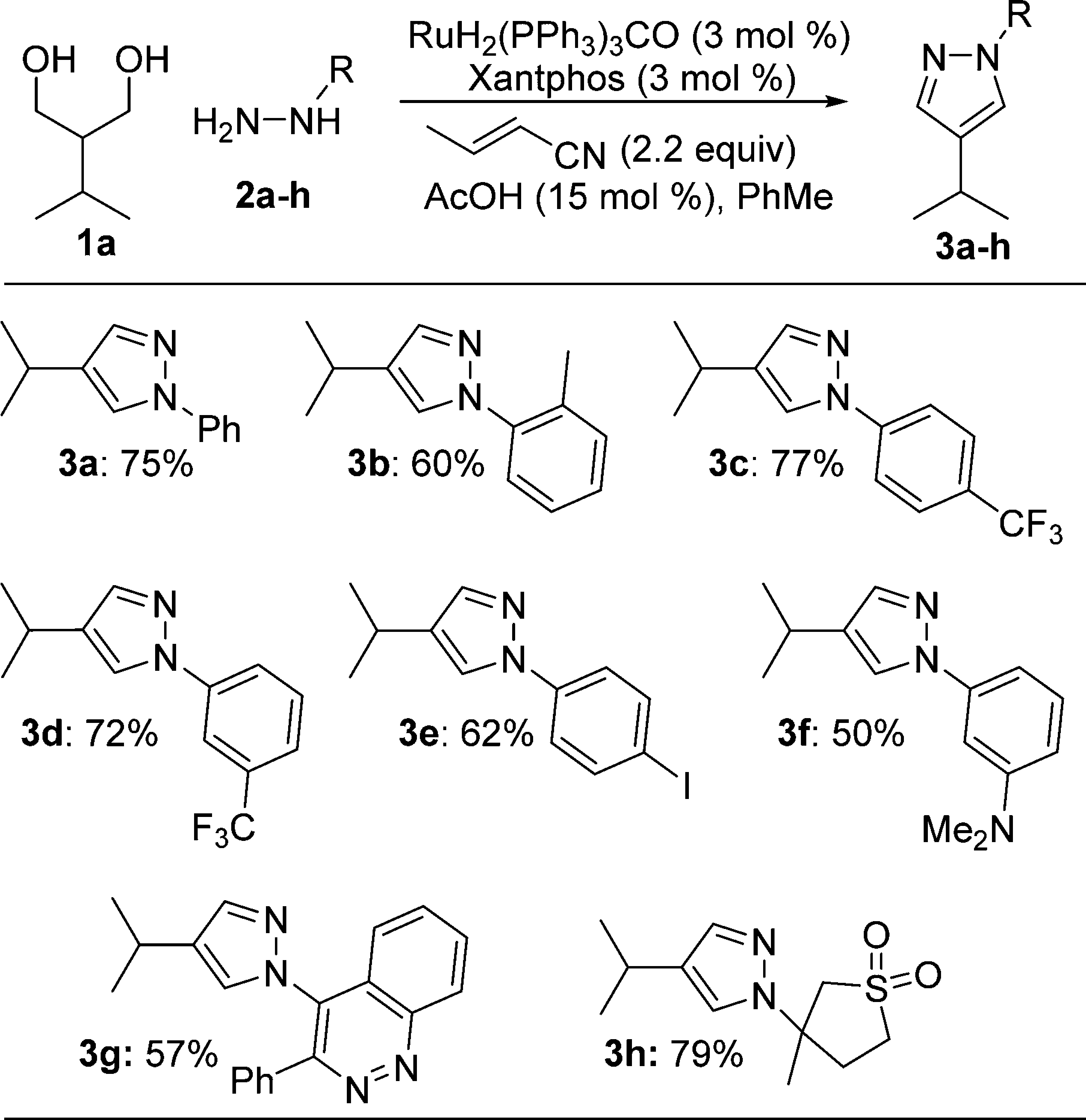
Hydrazine Scope
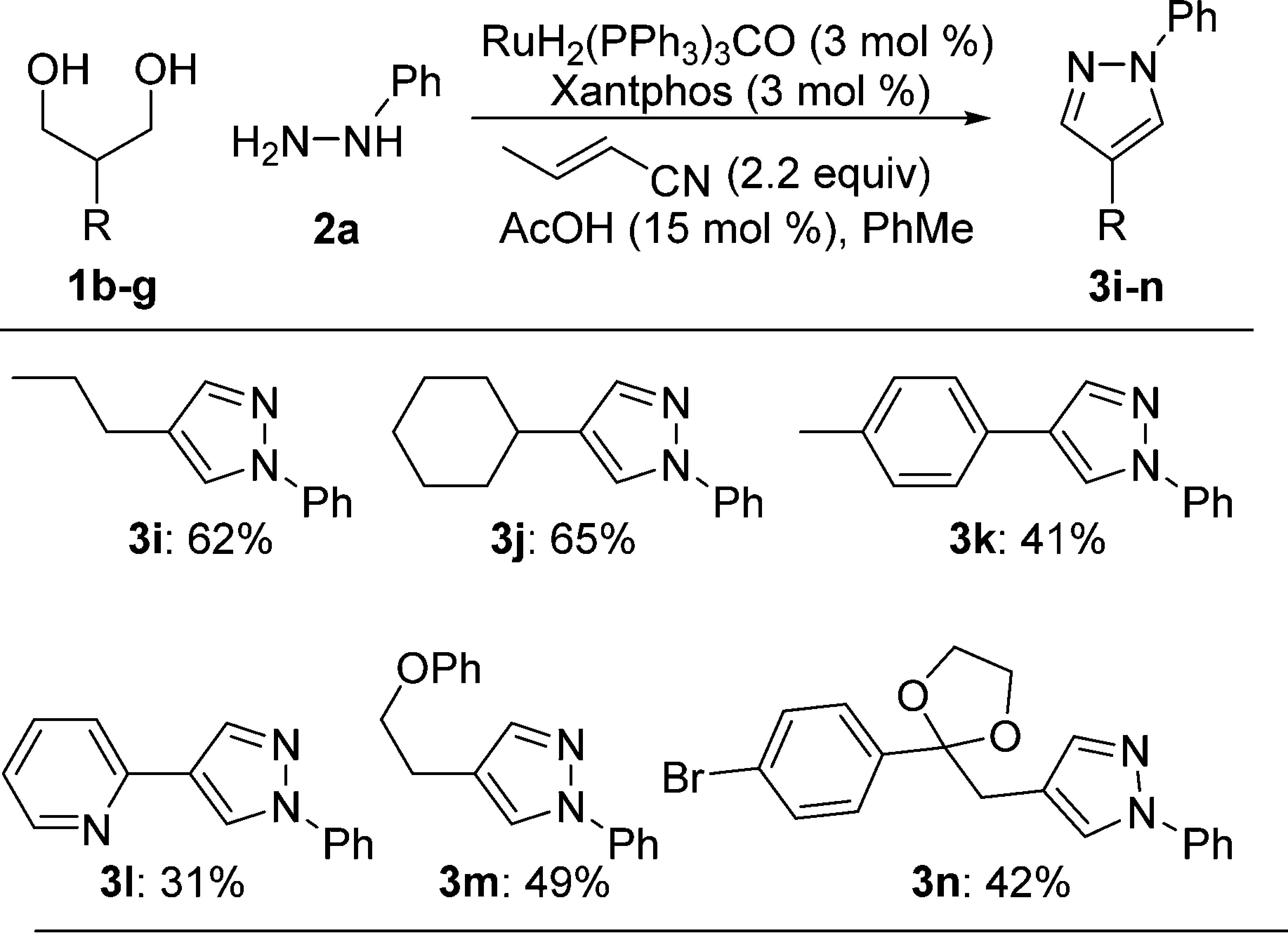
Diol Scope
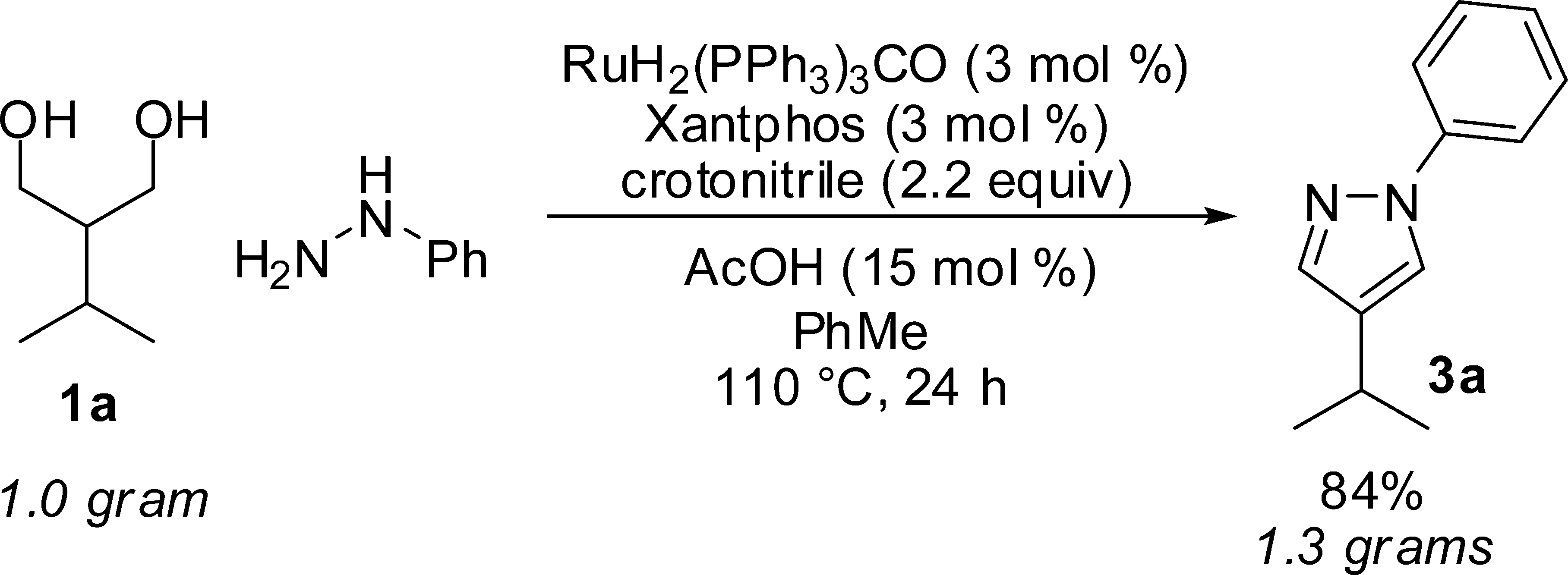
Gram-Scale Reaction
CAS number: 16165-40-5
2-Cyclopropen-1-ylidene, also known as cyclopropenylidene, is a highly reactive and unstable carbene. It consists of a three-membered cyclopropene ring with a divalent carbon atom (a carbene) replacing one of the ring's hydrogen atoms, resulting in a structure featuring both ring strain and a reactive lone pair.

Cyclopropenes can be selectively detected on model proteins.
CAS number: 16275-44-8
Butenolide is a mycotoxin found in various species of fungi of the genus Fusarium. It can often be found in contaminated agricultural products.
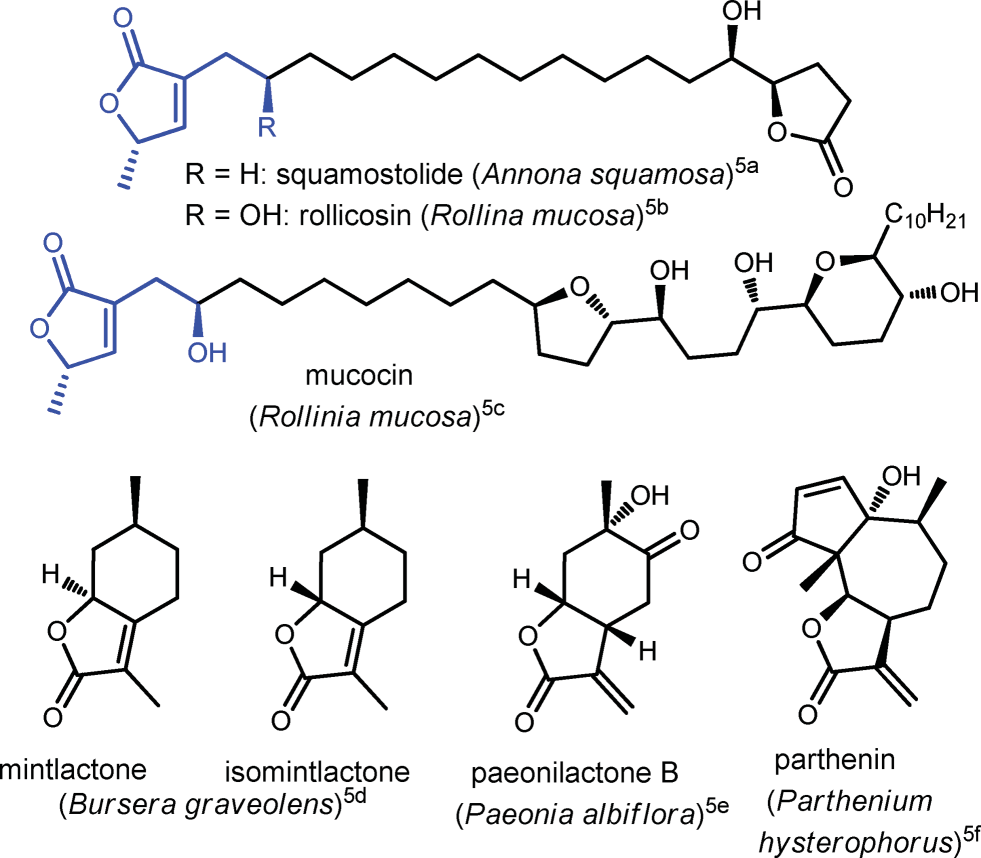
Naturally occurring bioactive butenolides and fused butenolides.
CAS number: 163042-96-4
Namodenoson is an orally bioavailable, synthetic, highly selective adenosine A3 receptor (A3AR) agonist with potential antineoplastic activity. Namodenoson selectively binds to and activates the cell surface-expressed A3AR, deregulating Wnt and NF-kB signal transduction pathways downstream, which may result in apoptosis of A3AR-expressing tumor cells. A3AR, a G protein-coupled receptor, is highly expressed on the cell surfaces of various solid tumor cell types, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, and plays an important role in cellular proliferation.
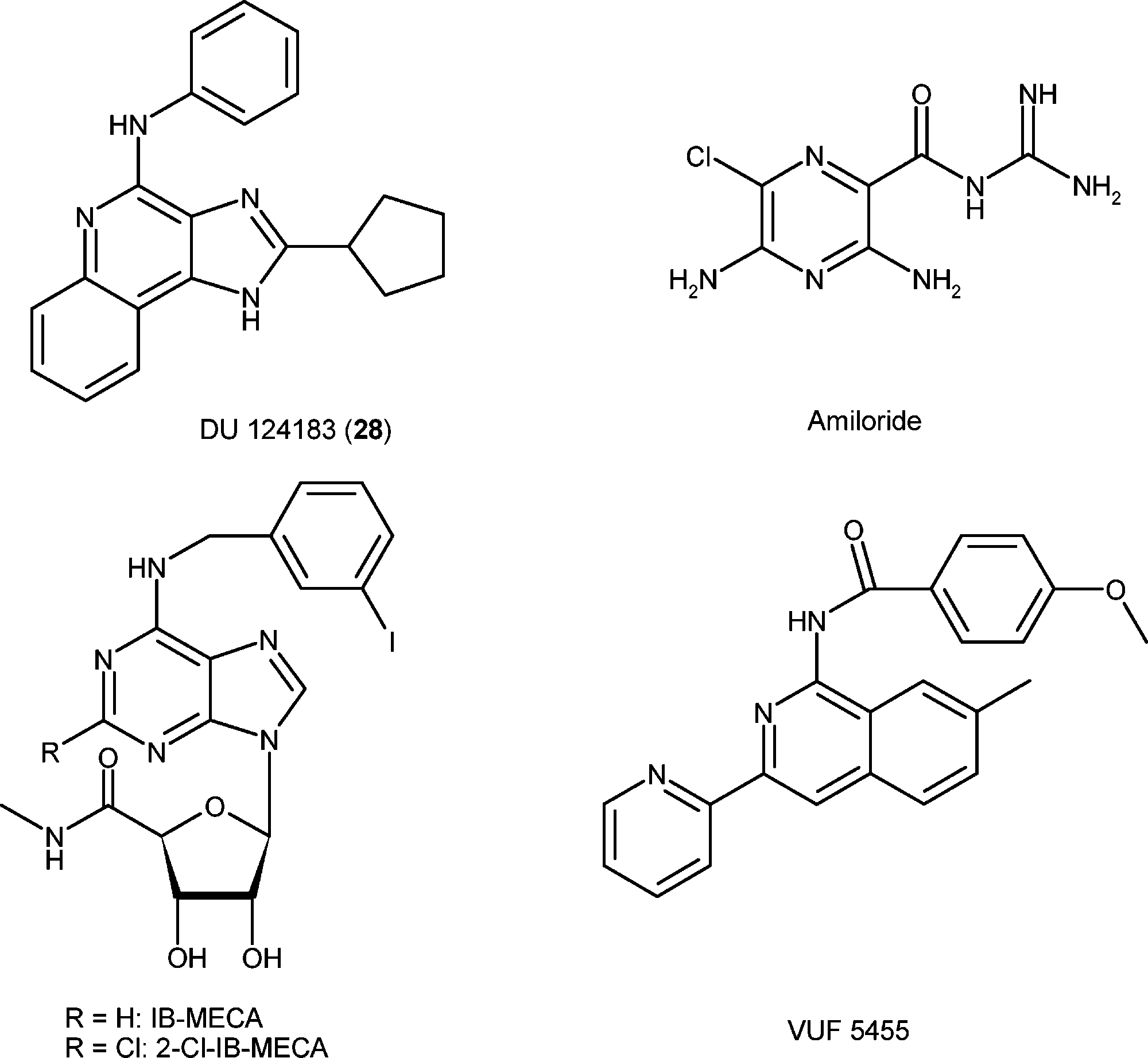
Structures of reference agonists (IB-MECA and 2-Cl-IB-MECA) and allosteric modulators (DU 124183, amiloride, and VUF5455) of the A3AR.