Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 50-36-2
Cocaine is an intense, euphoria-producing stimulant drug with strong addictive potential.
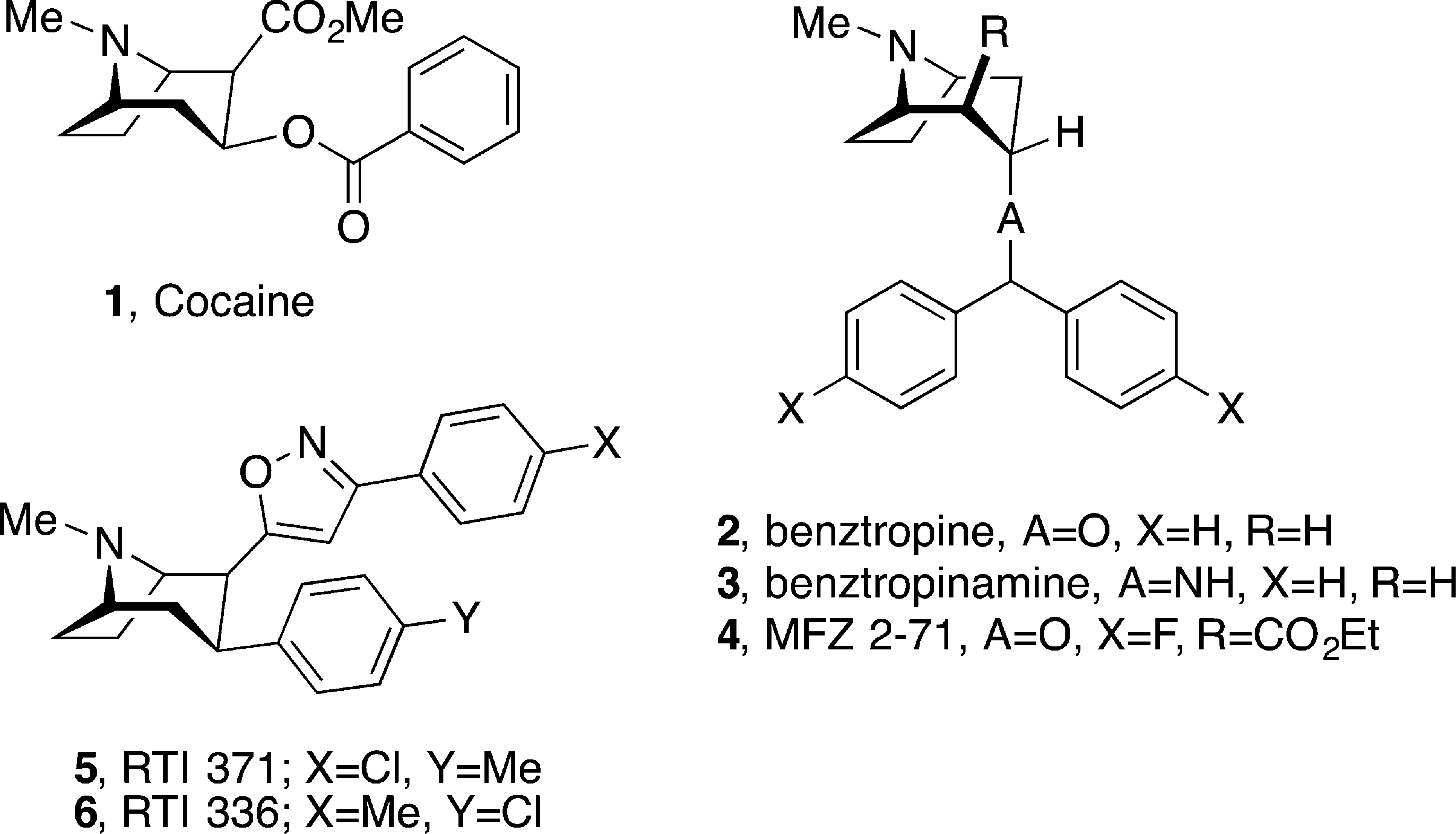
Chemical structures of cocaine and other tropane-based DAT inhibitors.
CAS number: 50-44-2
Mercaptopurine (also known as 6-mercaptopurine or 6-MP) is used for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
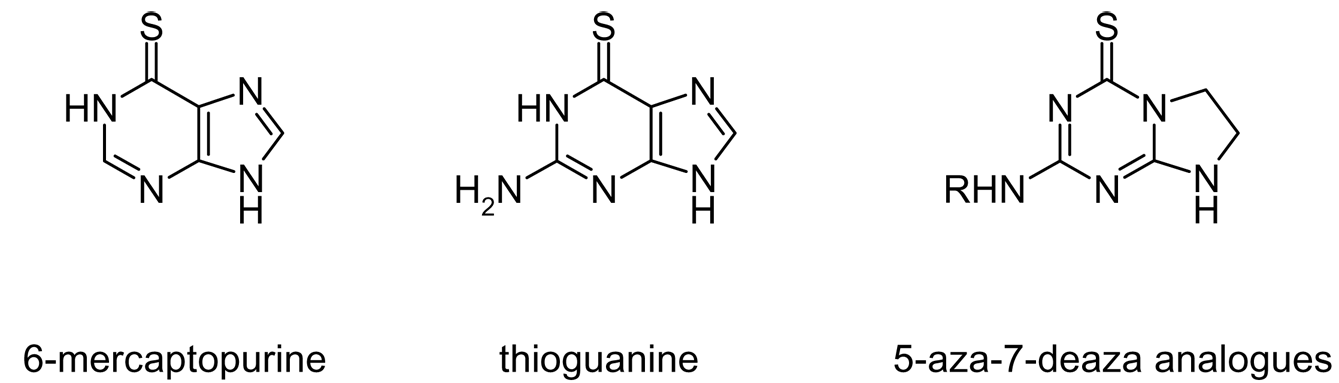
Structures of 6-mercaptopurine and thioguanine and their 5-aza-7-deaza analogs.
CAS number: 50-69-1
D-ribopyranose is a D-ribose and the D-enantiomer of ribopyranose. It is a ribopyranose and a D-ribose. It is an enantiomer of a L-ribopyranose.
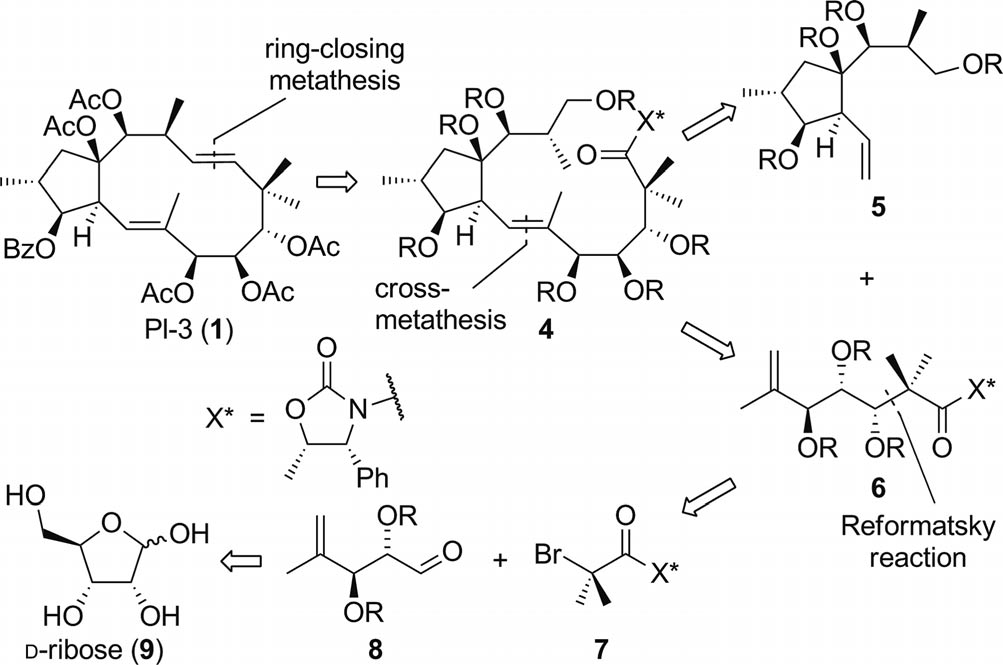
Retrosynthetic analysis.
CAS number: 50-81-7
L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is a powerful water-soluble antioxidant, essential for the correct functioning of the body.
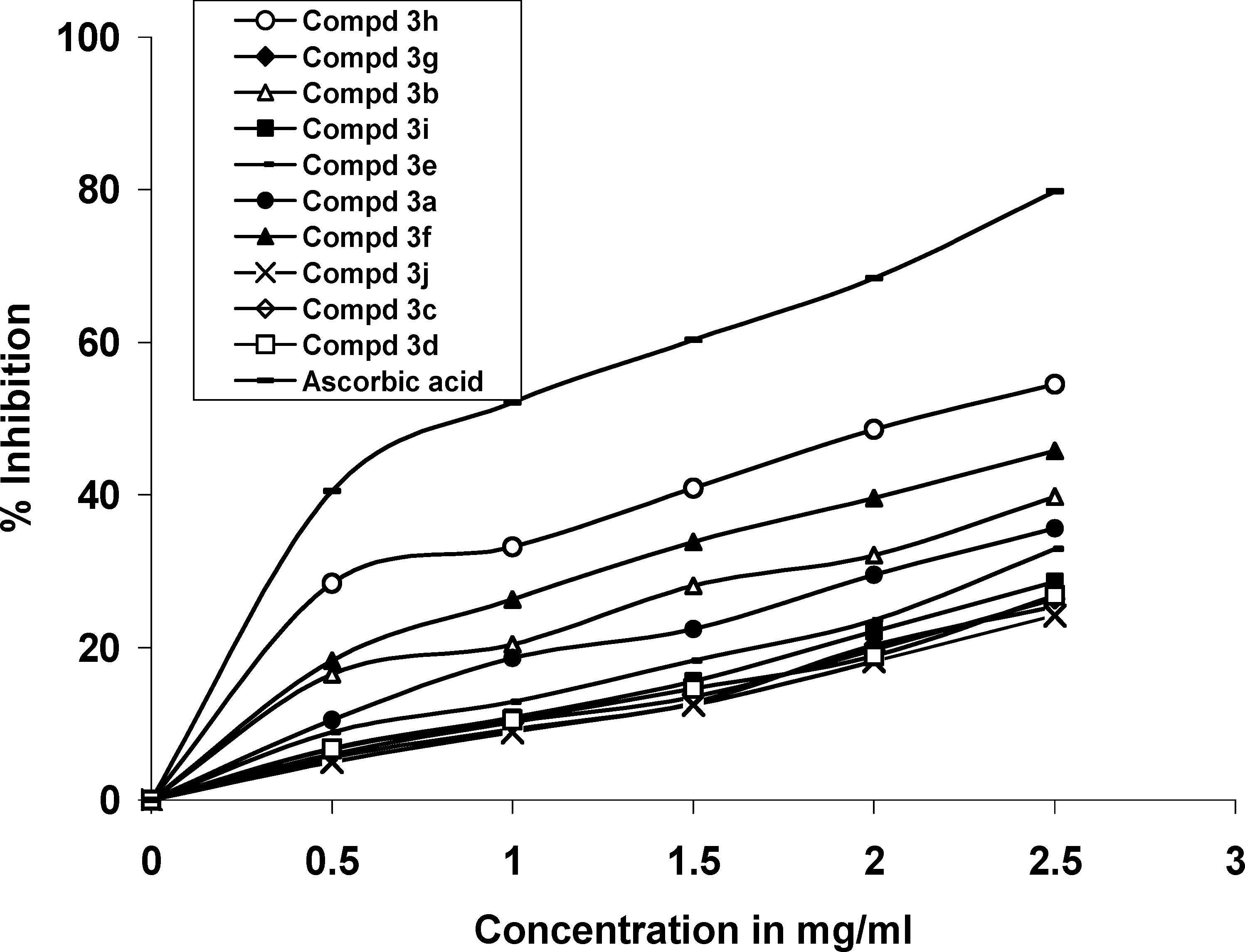
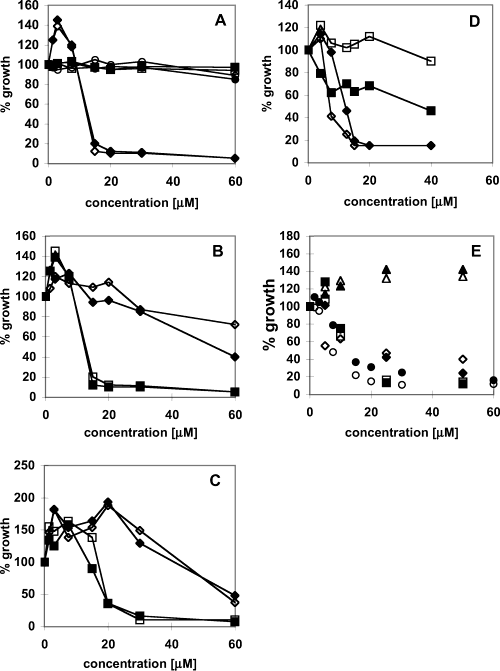
Effect of Compounds on Ferric Ion and Ascorbic Acid Induced Lipid Peroxidation
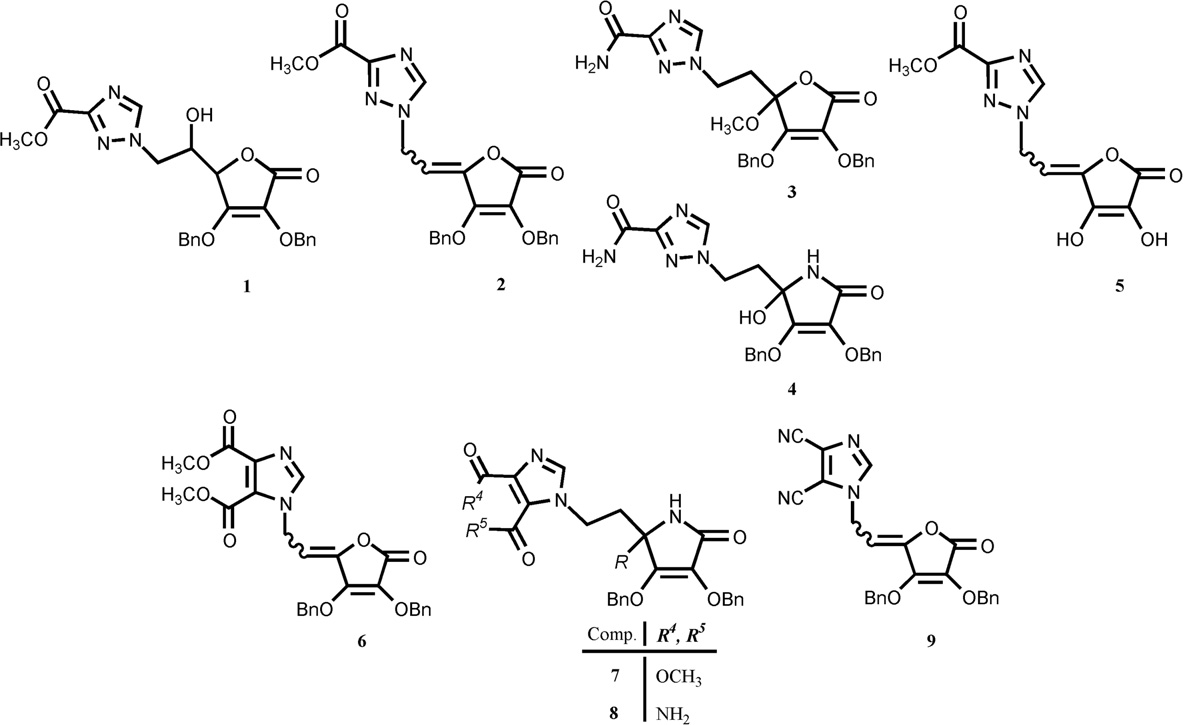
The novel 1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and 4,5-disubstituted-imidazole L-ascorbic acid (1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 9) and imino-ascorbic acid (4, 7 and 8) derivatives.
CAS number: 50-99-7
Glucose is a simple sugar that serves as the body's primary source of energy. It's a type of carbohydrate, and is found in foods like fruits, vegetables, and grains.
Systematic chemical modification of the glucopyranoside backbone inhibits the growth of glioblastoma cells.
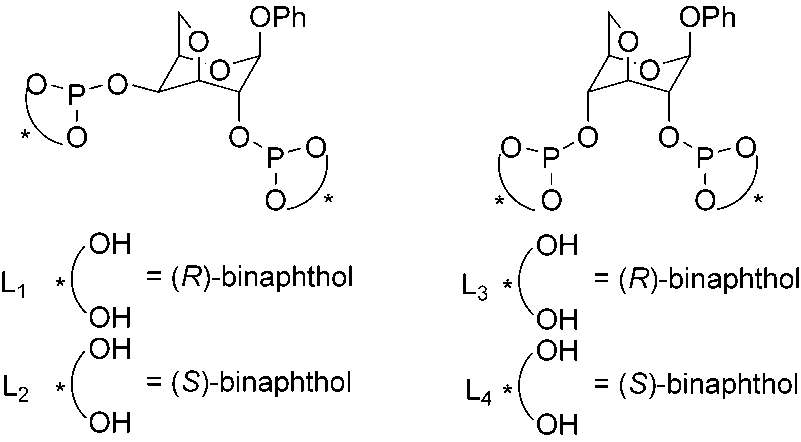
The chiral diphosphite ligands with the pyranoside backbone of galactose (L1 and L2) and glucose (L3 and L4).
CAS number: 500287-72-9
Rilpivirine is an aminopyrimidine that is pyrimidine-2,4-diamine in which the amino groups at positions 2 and 4 are substituted by 4-cyanophenyl and 4-[(E)-2-cyanovinyl]-2,6-dimethylphenyl groups respectively. Used for treatment of HIV. It has a role as a HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor and an EC 2.7.7.49 (RNA-directed DNA polymerase) inhibitor. It is a nitrile and an aminopyrimidine. It is a conjugate base of a rilpivirine(1+).
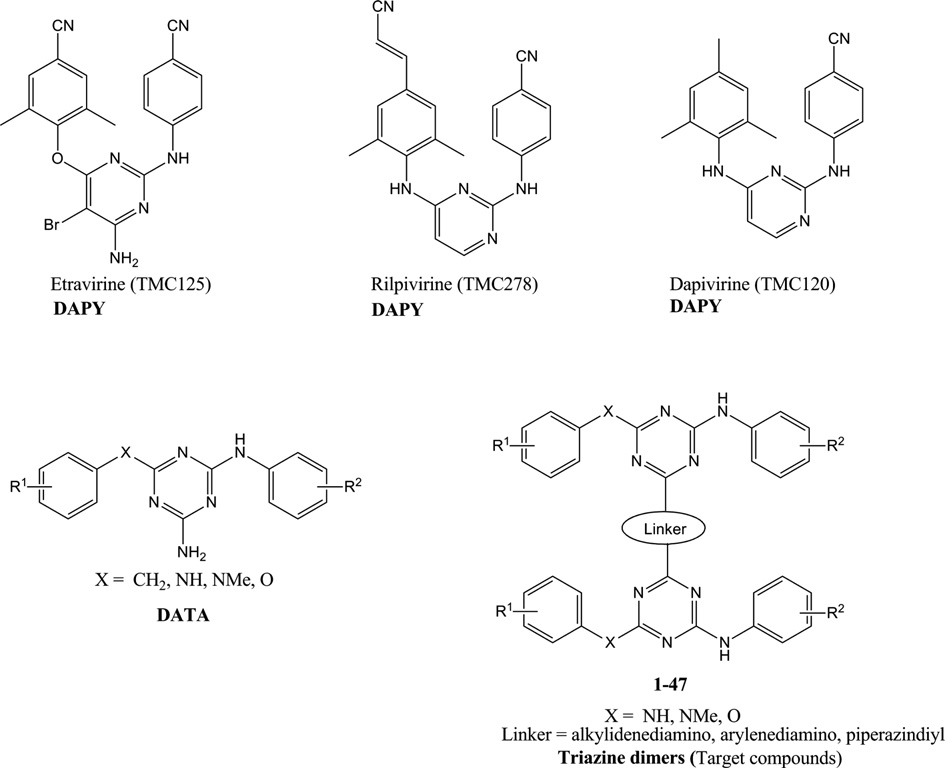
Chemical structures of DAPY, DATA and target compounds.
CAS number: 501-36-0
Resveratrol is a plant polyphenol found in high concentrations in red grapes that has been proposed as a treatment for hyperlipidemia and to prevent fatty liver, diabetes, atherosclerosis and aging. Resveratrol use has been associated with rare instances of serum enzyme elevations during therapy but has not been convincingly linked to episodes of clinically apparent liver injury.
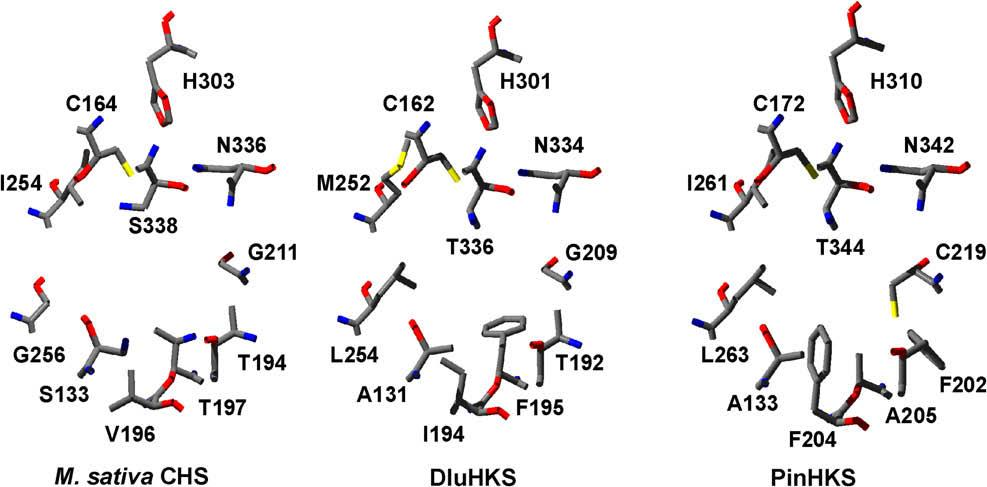
Models of the active sites of M. sativa CHS2, DluHKS and PinHKS. The structures of DluHKS and PinHKS were modeled based on the structure of M. sativa CHS2 complexed with resveratrol (PDB code 1CGZ, resveratrol not shown).
CAS number: 504-29-0
Aminopyridine is a white or clear colored crystalline solid. It is soluble in water and alcohol. It is toxic by ingestion and by inhalation of the dust. It is used to make pharmaceuticals and dyes.
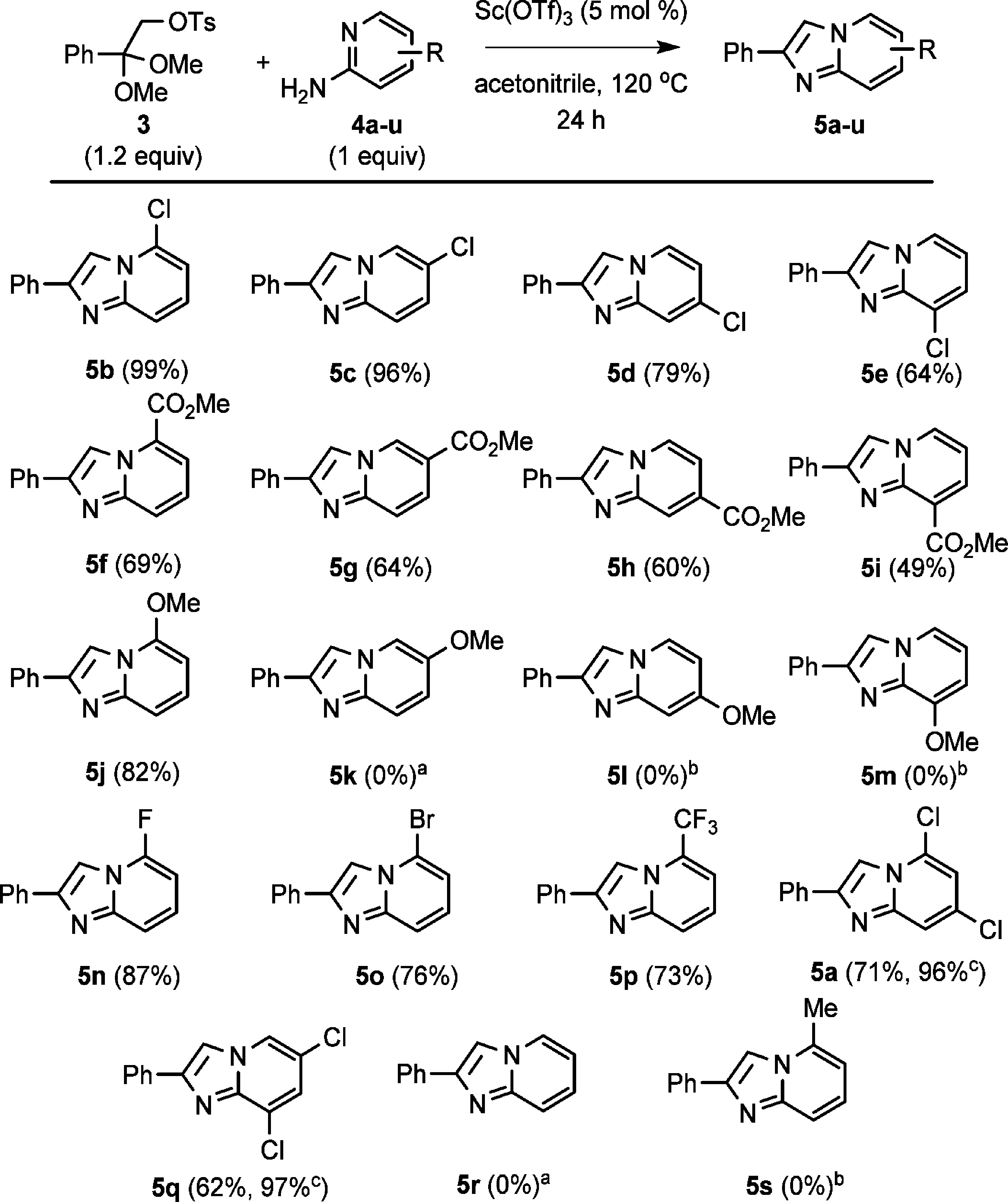
Having identified optimal conditions, we investigated the scope and generality of the annulation reaction using a series of substituted 2-aminopyridine substrates (Scheme 3).
CAS number: 504-78-9
Thiazolidine is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
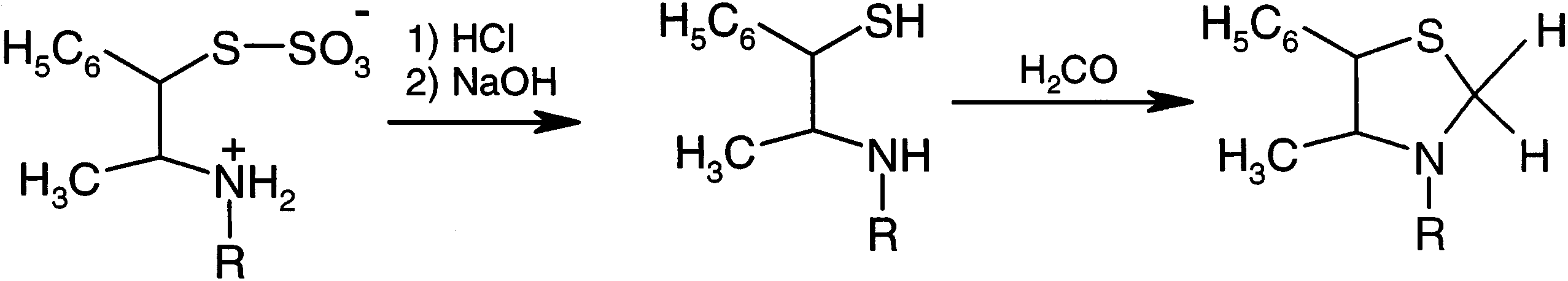
Syntheses of thiazolidines.
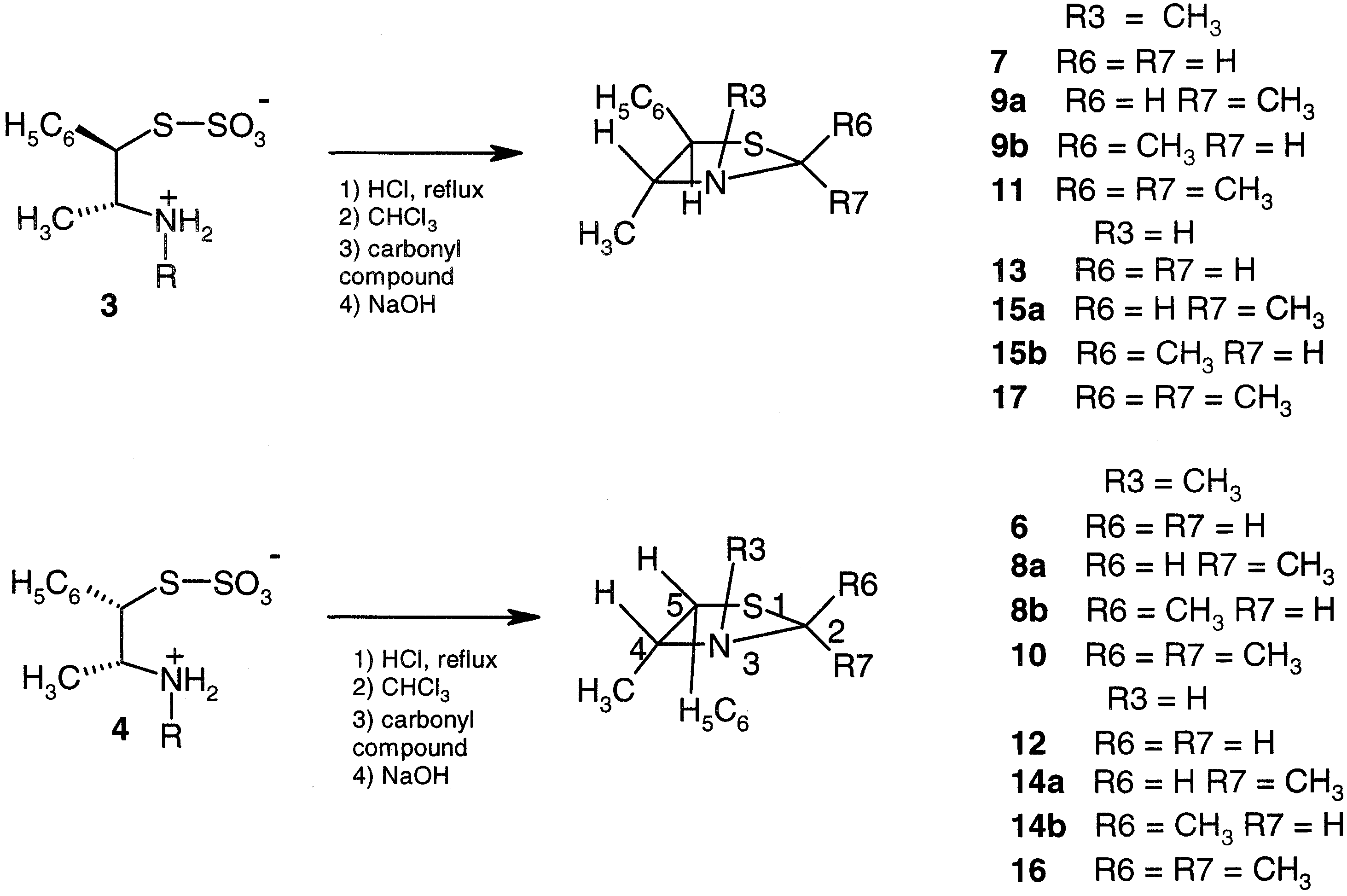
Preparation of thiazolidines 7–17.
CAS number: 50439-45-7
(2S,5R)-5-Hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylic acid is a specific stereoisomer of 5-hydroxypipecolic acid, also known as a trans-5-hydroxy-L-pipecolic acid. It is a cyclic amino acid with a piperidine ring, containing both a carboxylic acid group at the 2-position and a hydroxyl group at the 5-position.
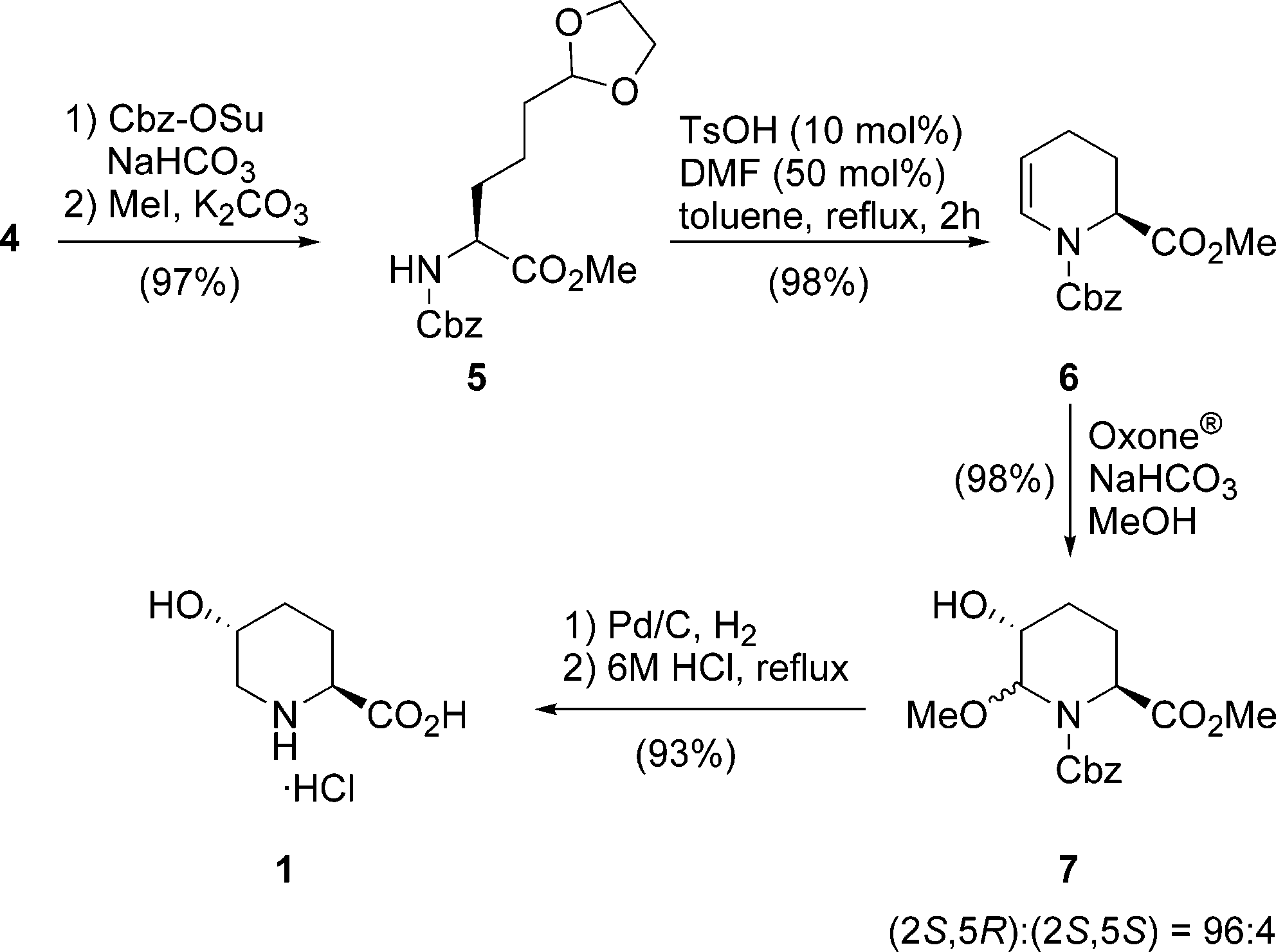
Synthesis of (2S,5R)-5-Hydroxypipecolic Acid