Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 505-66-8
Hexahydro-1,4-diazepine, also known as homopiperazine, is a saturated version of the heterocyclic compound 1,4-diazepine. It has a seven-membered ring structure containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 4.
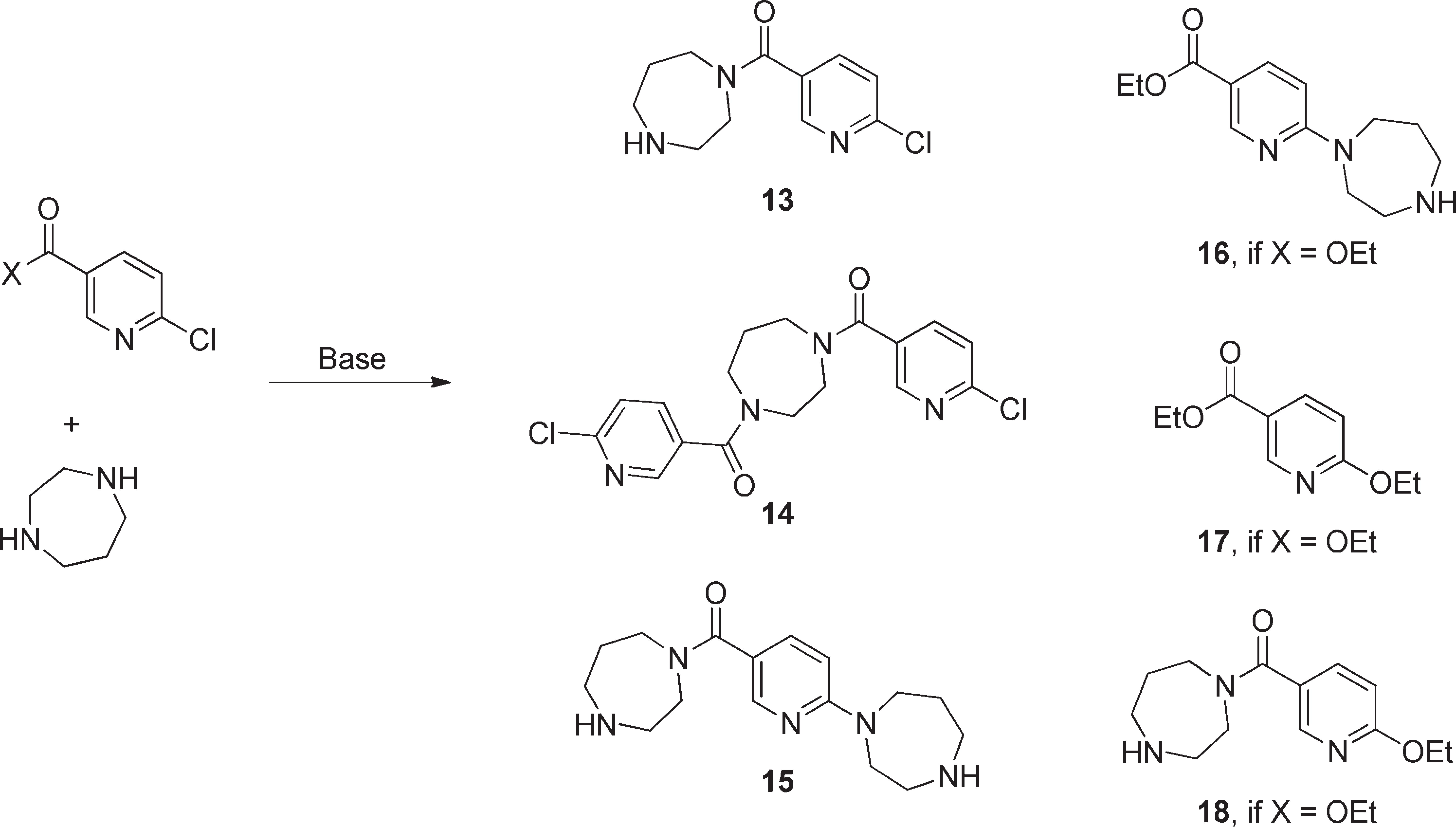
Potential Products in Reaction between 6-Chloronicotinic Acid Derivatives and Homopiperazine
CAS number: 506-32-1
Arachidonic acid is a long-chain fatty acid that is a C20, polyunsaturated fatty acid having four (Z)-double bonds at positions 5, 8, 11 and 14. It has a role as a human metabolite, an EC 3.1.1.1 (carboxylesterase) inhibitor, a Daphnia galeata metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is an icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid and a long-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of an arachidonate. It derives from a hydride of a (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraene.
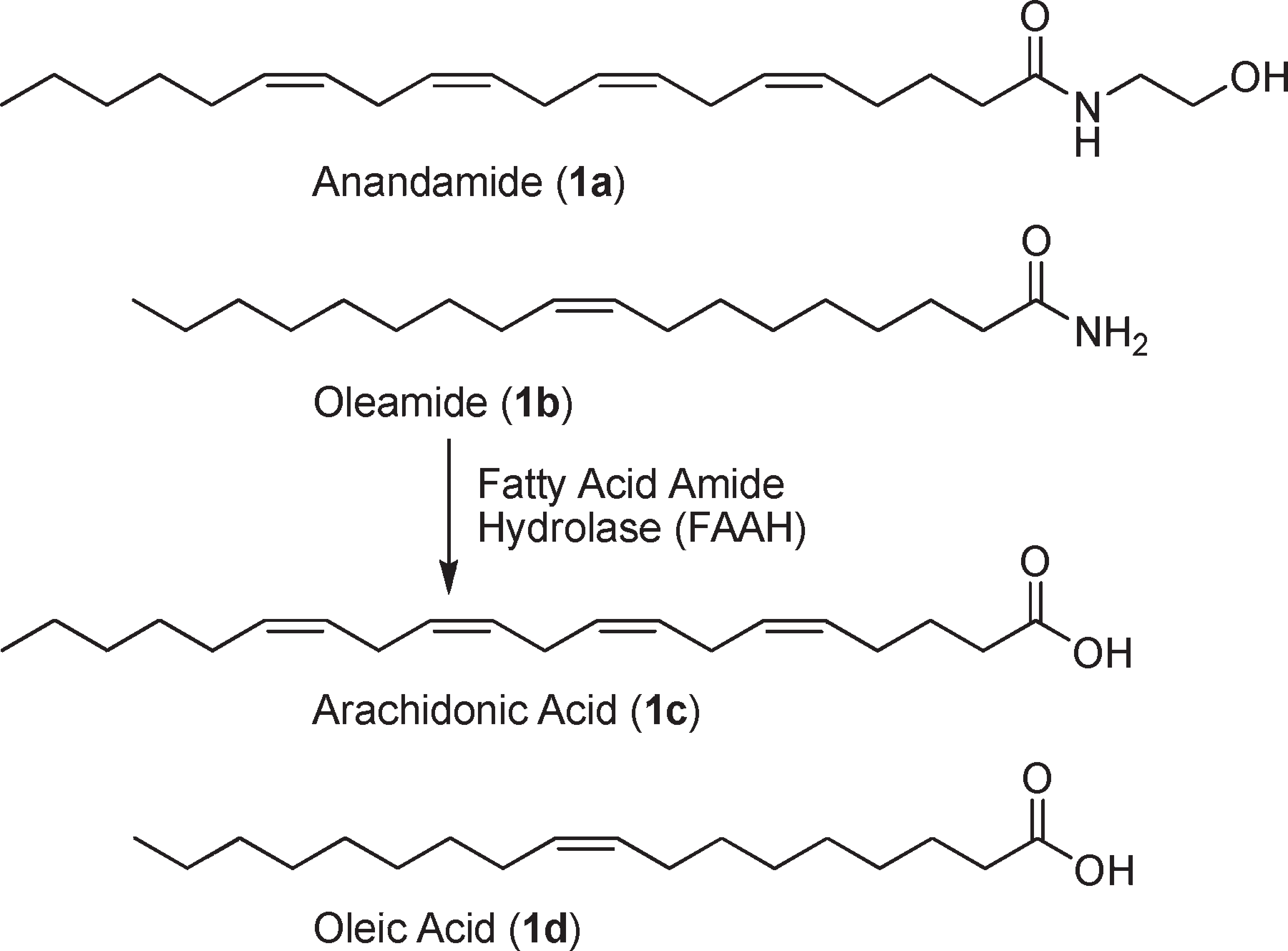
Substrates of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
CAS number: 50741-46-3
Ethyl quinoline-3-carboxylate is an organic compound that is the ethyl ester of quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, which means it contains a quinoline ring system with a carboxylic acid group and an ethyl group attached to the third carbon of the quinoline ring.
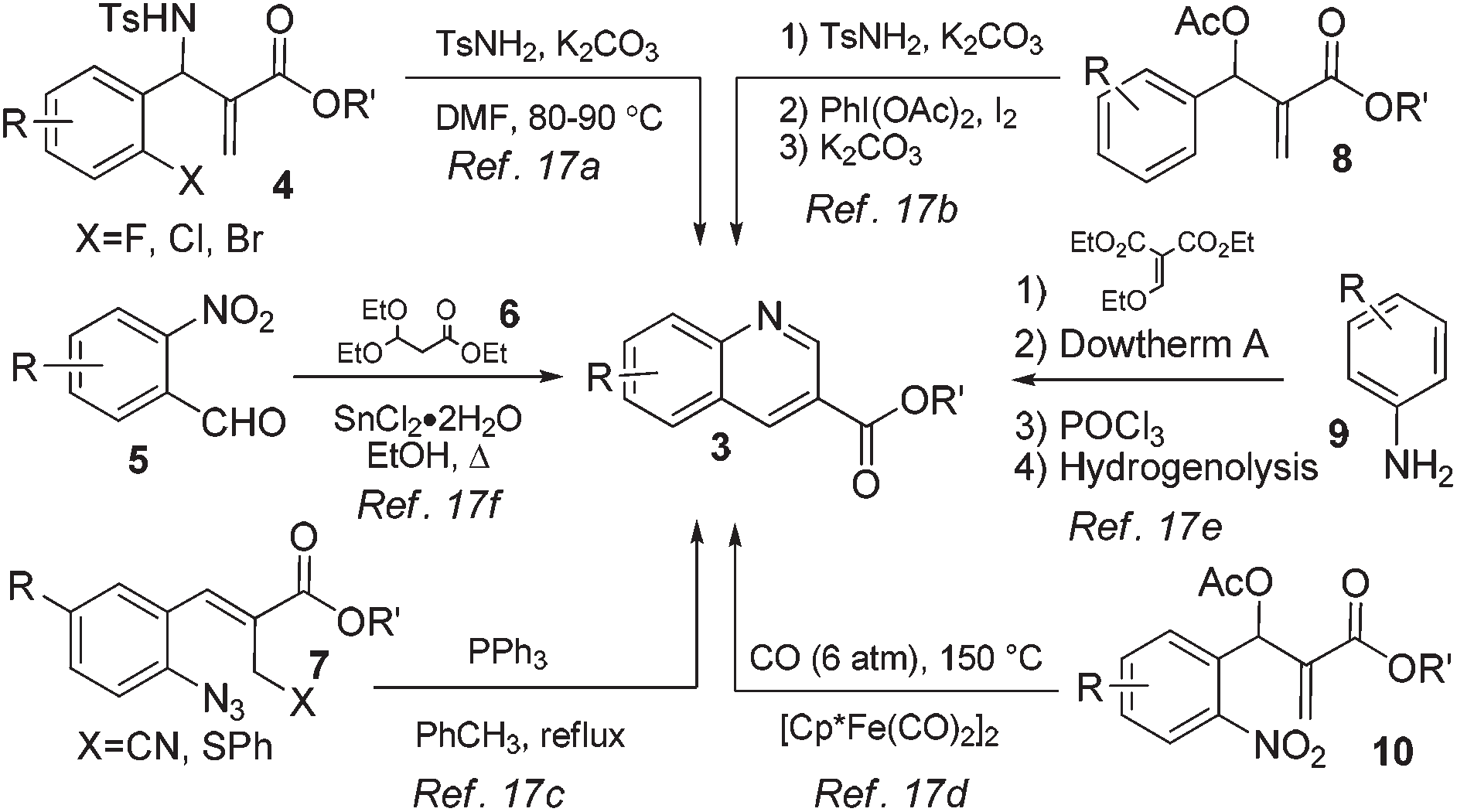
Synthesis of 2,4-unsubstituted quinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 3.
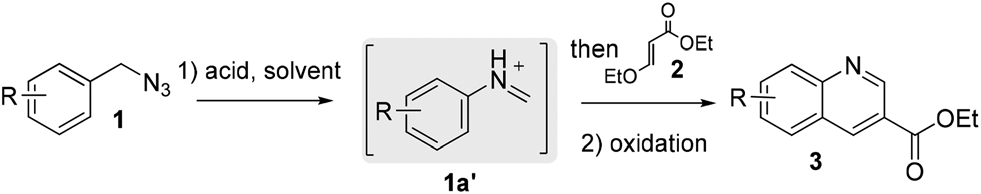
Synthetic strategy for the synthesis of 2,4-unsubstituted quinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 3.
CAS number: 50926-11-9
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a transparent, conductive material made of a mixture of indium(III) oxide (In2O3) and tin(IV) oxide (SnO2). It is widely used in electronic devices like touchscreens, displays, and solar cells due to its ability to conduct electricity while remaining transparent.
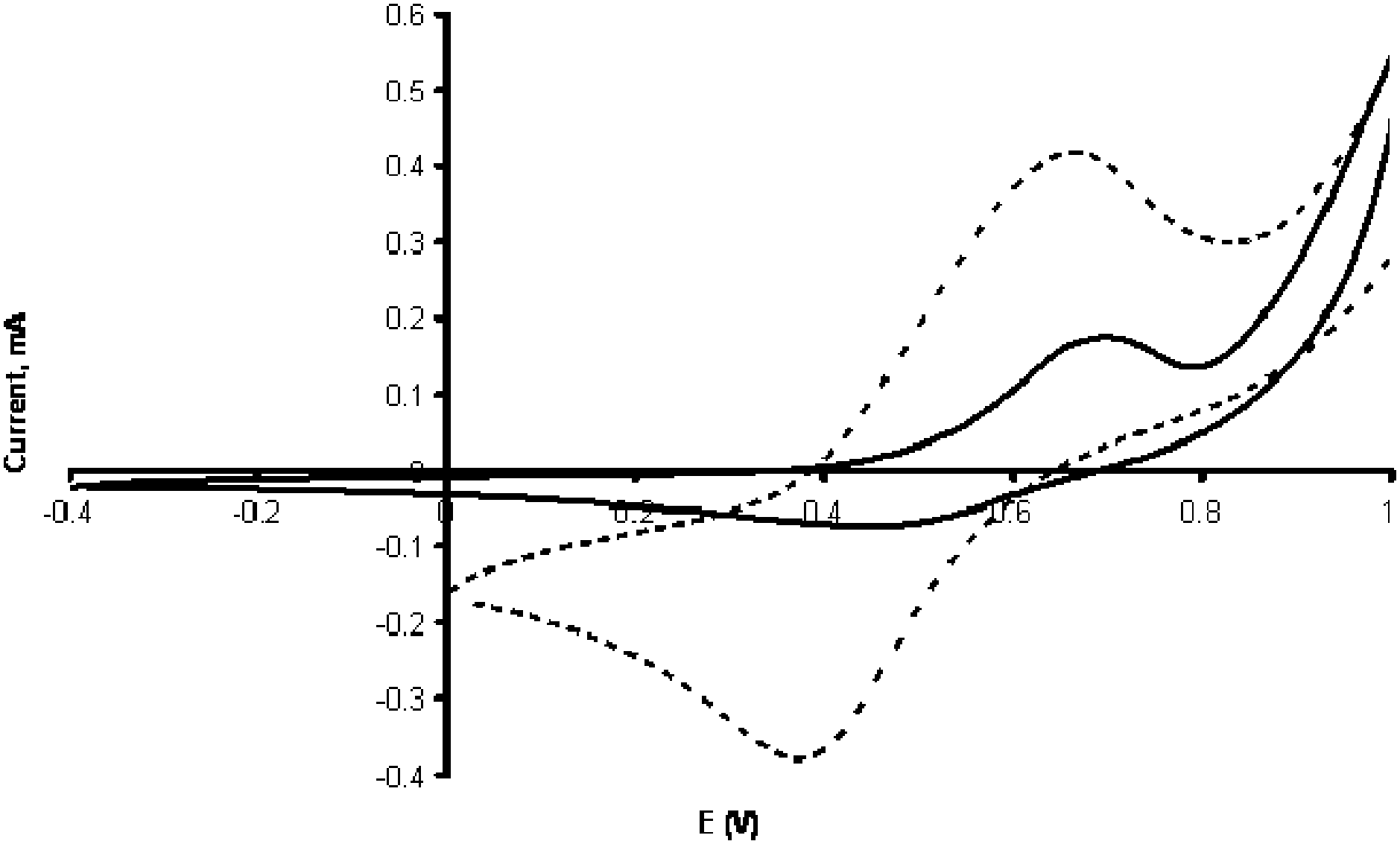
Cyclic voltammograms obtained when electropolymerized N-phenylethylenediaminemethacrylamide films were deposited on gold (solid line) and indium tin oxide (dashed line) electrodes.
CAS number: 50935-04-1
Carubicin is an anthracycline antineoplastic antibiotic isolated from the bacterium Actinomadura carminata. Carubicin intercalates into DNA and interacts with topoisomerase II, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and repair and RNA and protein synthesis.
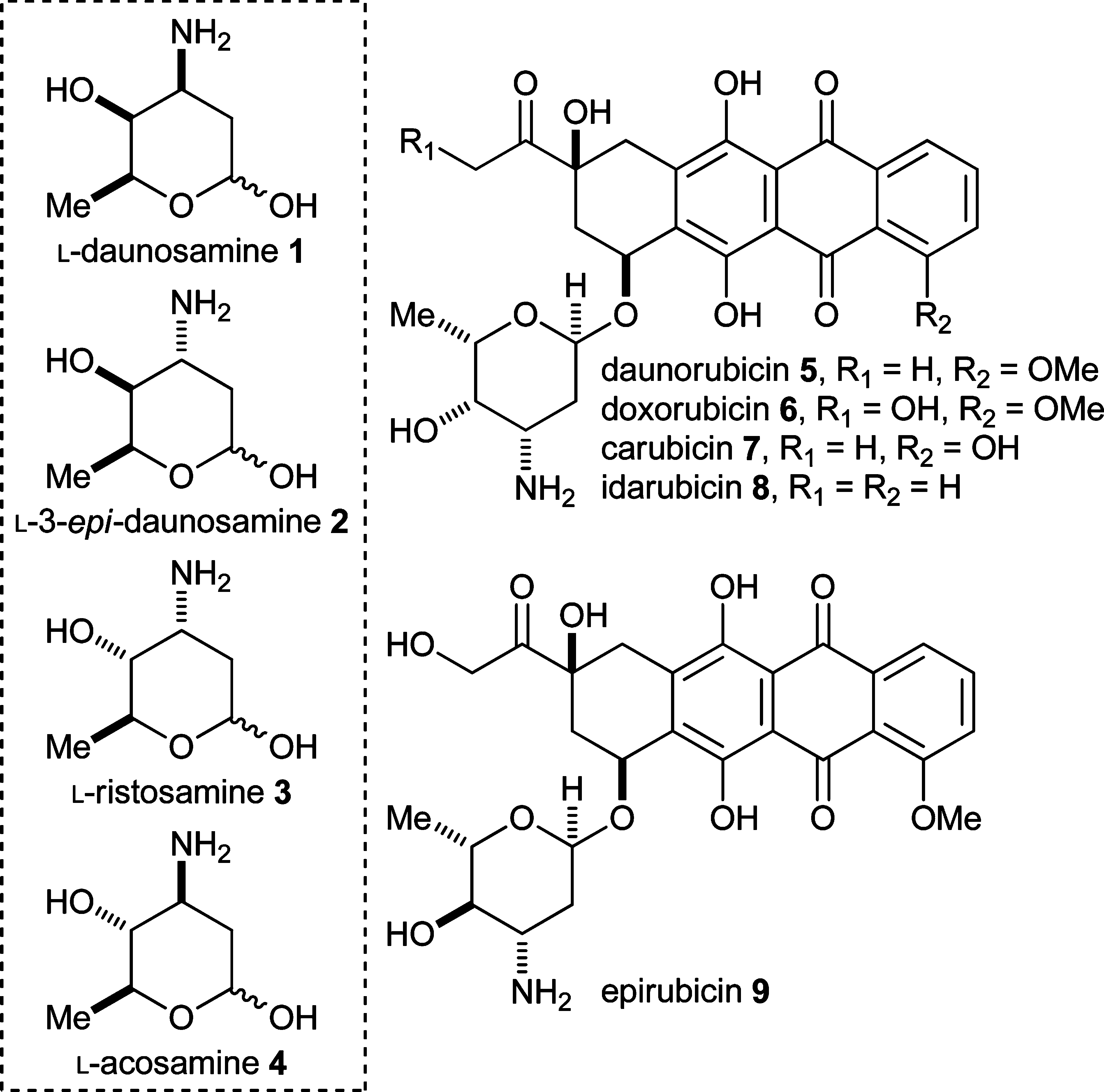
Structures of L-daunosamine 1, L-3-epi-daunosamine 2, L-ristosamine 3, L-acosamine 4, and the anthracycline antibiotics daunorubicin 5, doxorubicin 6, carubicin 7, idarubicin 8, and epirubicin 9.
CAS number: 51-17-2
1H-benzimidazole is the 1H-tautomer of benzimidazole. It is a benzimidazole and a polycyclic heteroarene. It is a conjugate acid of a benzimidazolide. It is a tautomer of a 4H-benzimidazole, a 2H-benzimidazole and a 3aH-benzimidazole.
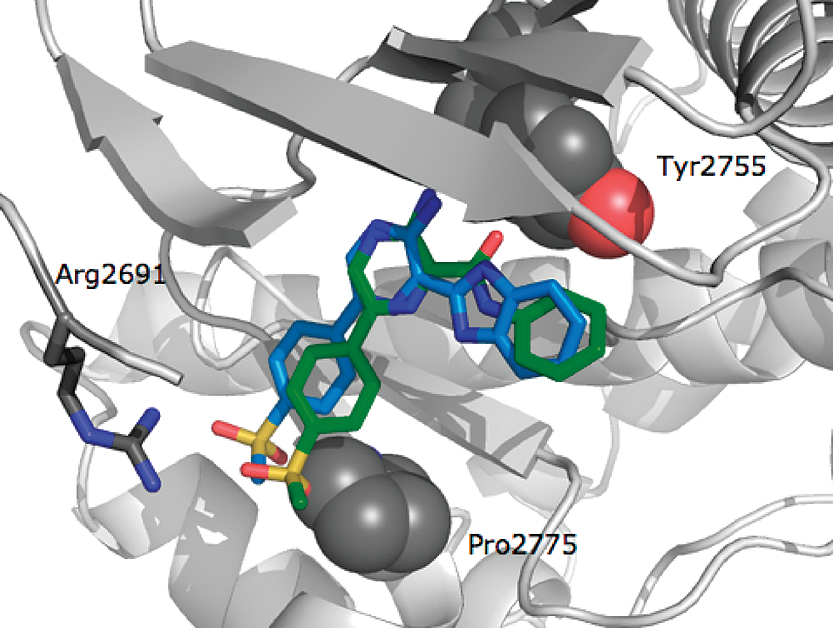
Cartoon of the ATM homology model in complex with phenylamide 27 (green) and benzimidazole isostere 49 (blue). The sulfone group in 49 interacts with the ATM-specific Pro2775 (grey spheres) to create less steric hindrance than the sulfone group in 27.
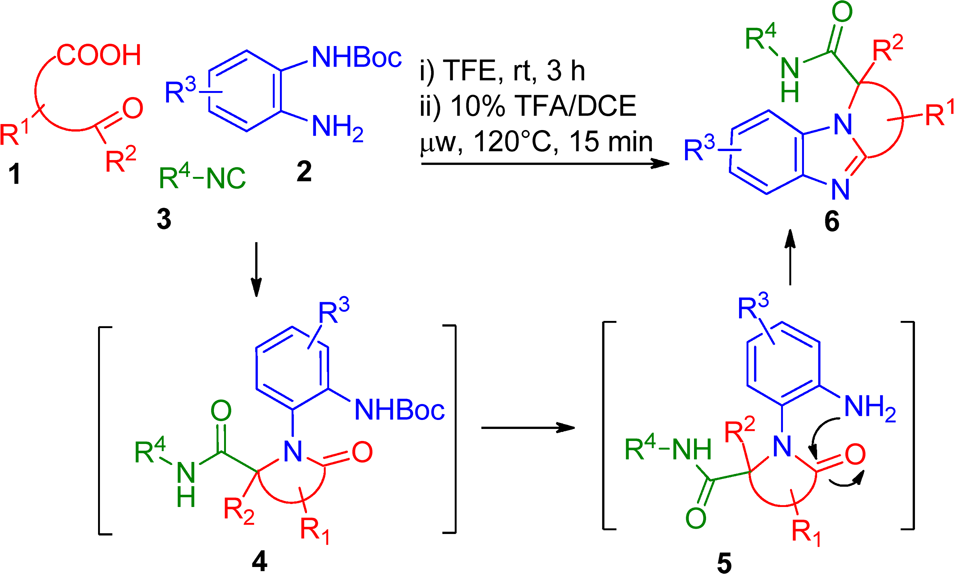
Synthesis of α-Quaternized Benzimidazole-Carboxamides
CAS number: 51-21-8
5-fluorouracil is a nucleobase analogue that is uracil in which the hydrogen at position 5 is replaced by fluorine. It is an antineoplastic agent which acts as an antimetabolite - following conversion to the active deoxynucleotide, it inhibits DNA synthesis (by blocking the conversion of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid by the cellular enzyme thymidylate synthetase) and so slows tumour growth.
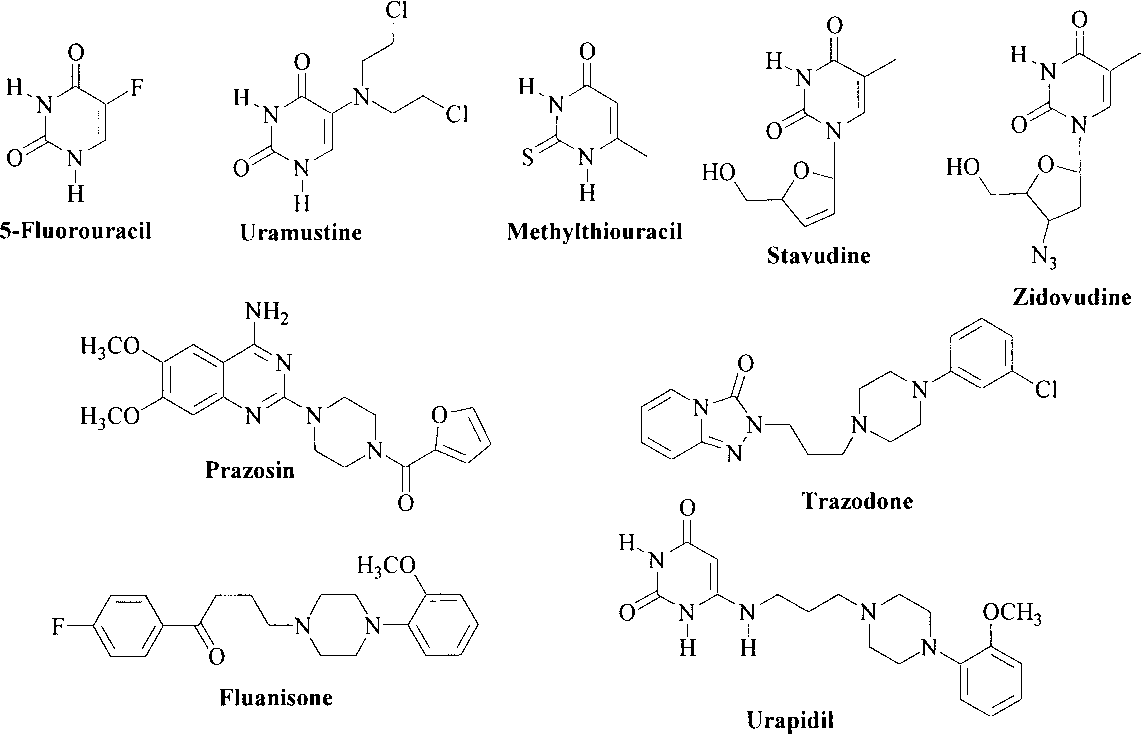
Several Pharmacologically Useful Agents Containing Uracil and Piperazine Moieties: 5-Fluorouracil, Uramustine, Methylthiouracil, stavudine, zidovudine, prazosin, trazodone, Fluanisone, urapidil.
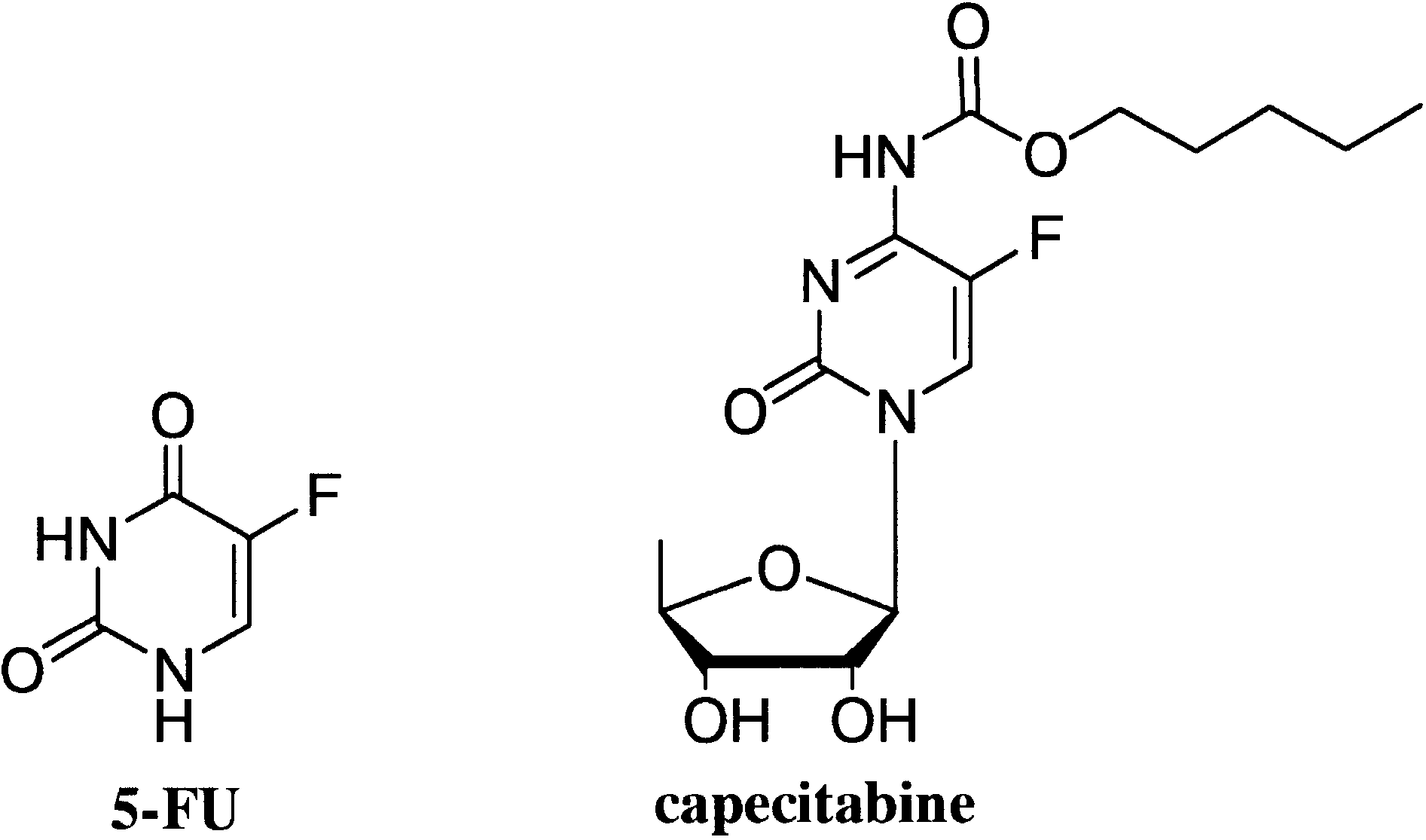
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and capecitabine.
CAS number: 51-61-6
Dopamine is catechol in which the hydrogen at position 4 is substituted by a 2-aminoethyl group. It has a role as a cardiotonic drug, a beta-adrenergic agonist, a dopaminergic agent, a sympathomimetic agent, a human metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a conjugate base of a dopaminium(1+).
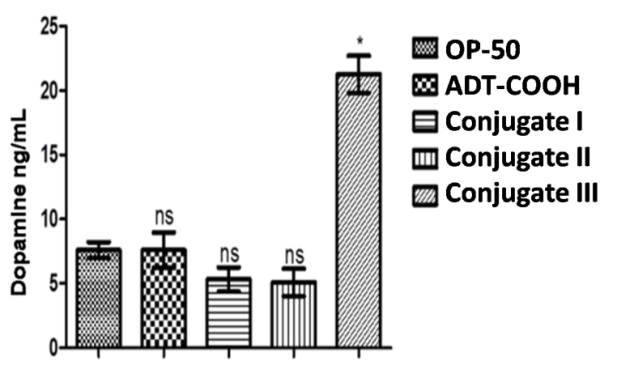
HPLC/MS quantification of dopamine levels on treatment with compound ADT-COOH, I, II and III in NL5901 transgenic C. elegans (Expressing human Alpha synuclein YFP). Conjugate III significantly increases dopamine content.
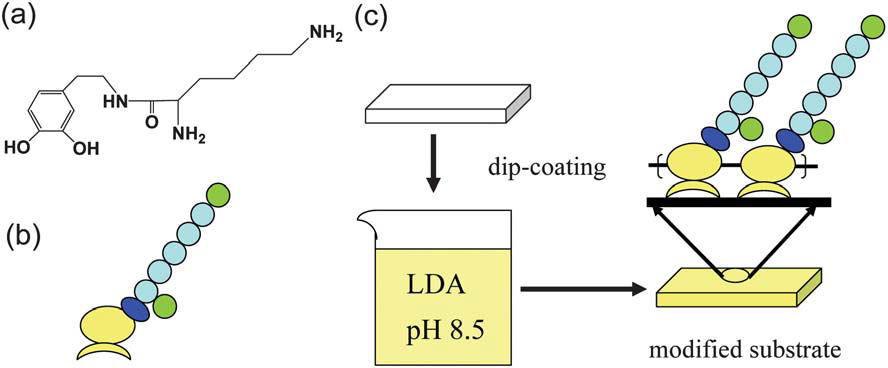
Lysine-dopamine (LDA): chemical structure (a) and schematic representation (b); surface modification of LDA by dip-coating (c).
CAS number: 514-10-3
Abietic acid is an abietane diterpenoid that is abieta-7,13-diene substituted by a carboxy group at position 18. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is an abietane diterpenoid and a monocarboxylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of an abietate.
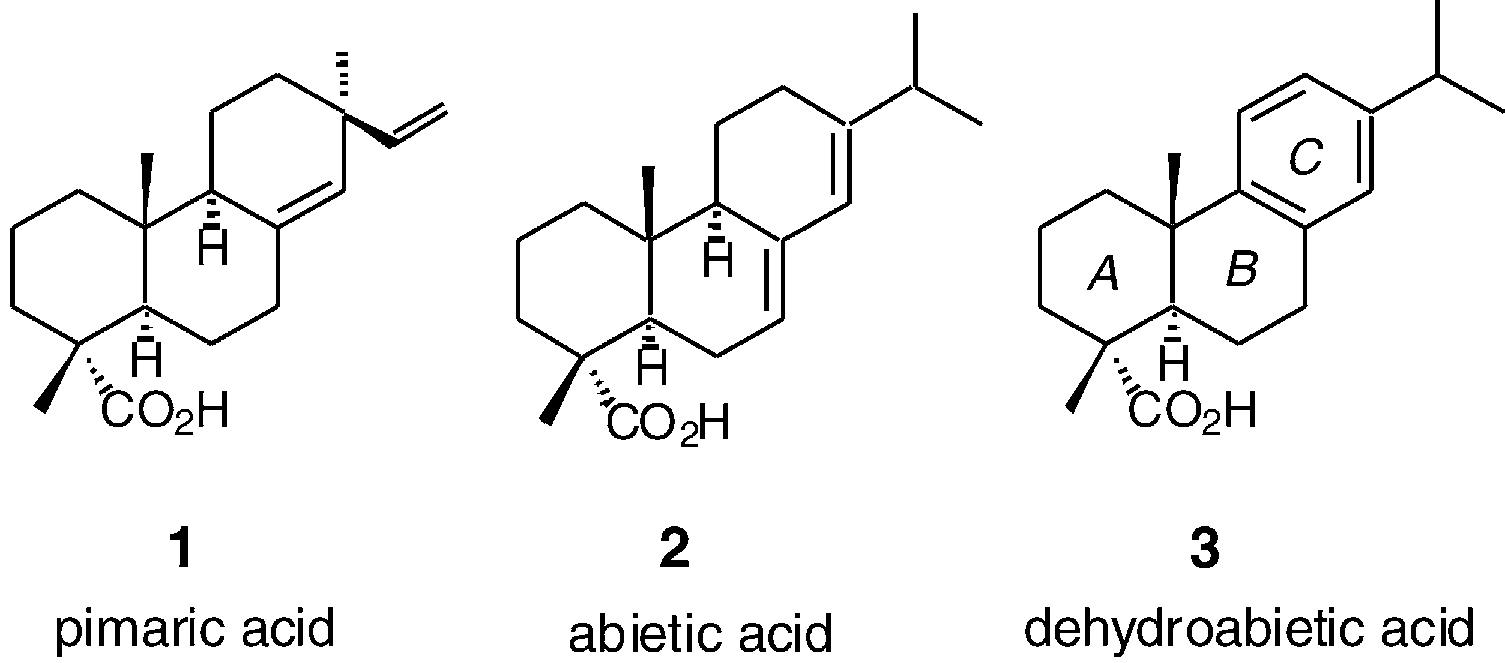
Scaffolds for BK channel modulators in this study.
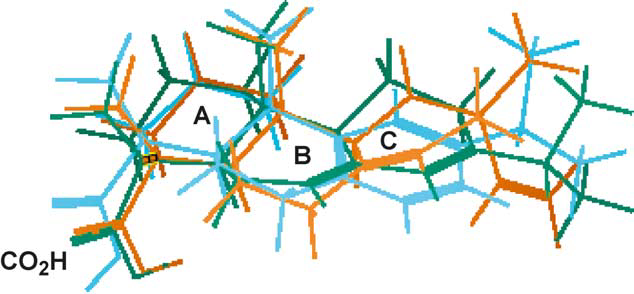
Superimposed structures of pimaric acid (1, green), abietic acid (2, brown) and dehydroabietic acid (3, blue).
CAS number: 515-03-7
Sclareol is a labdane diterpenoid that is labd-14-ene substituted by hydroxy groups at positions 8 and 13. It has been isolated from Salvia sclarea. It has a role as an antimicrobial agent, an apoptosis inducer, a fragrance, an antifungal agent and a plant metabolite.
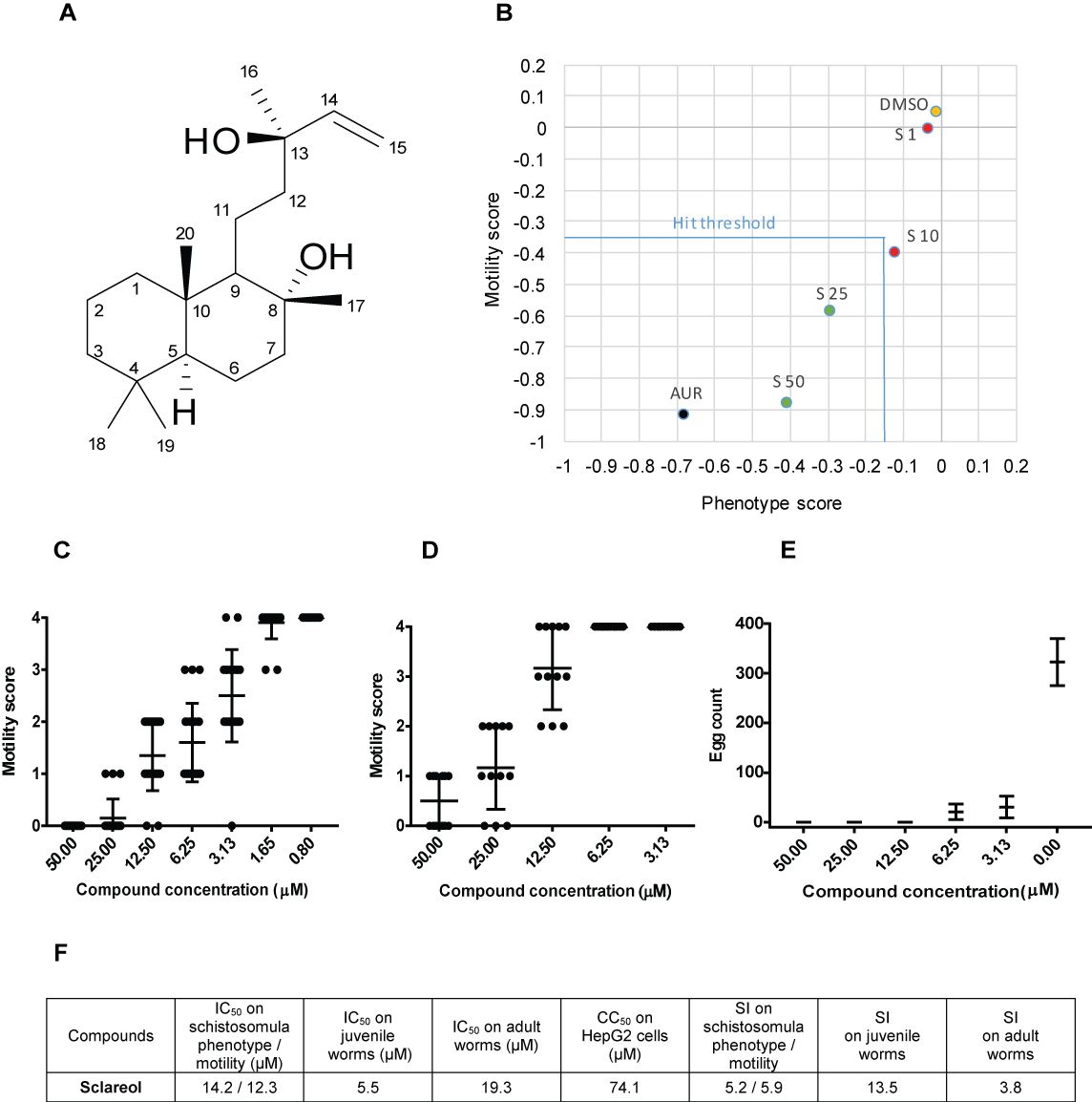
Structure and anti-schistosomal activity of (-)-sclareol.