Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 3641-08-5
1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide is a member of the class of triazoles that is 1H-1,2,4-triazole substituted by an aminocarbonyl group at position 3. It is the major catabolite and aglycon of ribavirin. It has a role as a human urinary metabolite and a drug metabolite. It is a member of triazoles, a primary carboxamide, a monocarboxylic acid amide and an aromatic amide.
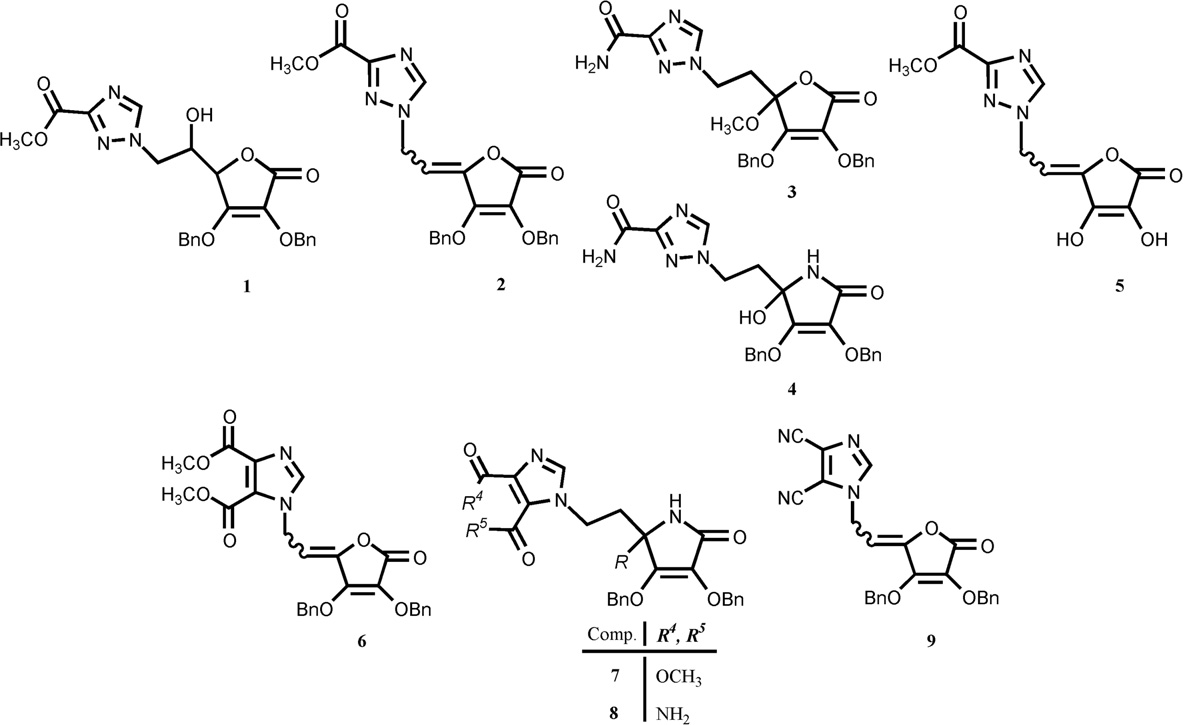
The novel 1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and 4,5-disubstituted-imidazole L-ascorbic acid (1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 9) and imino-ascorbic acid (4, 7 and 8) derivatives.
CAS number: 36480-36-1
3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-L-lyxo-hexose is a branched-chain amino sugar also known as L-vancosamine. It's a key component of the antibiotic vancomycin and other related antibiotics. Specifically, it's found as a sugar component in the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin, which is important in treating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It also appears in other antibiotic structures as an O-glycoside or a C-glycoside.
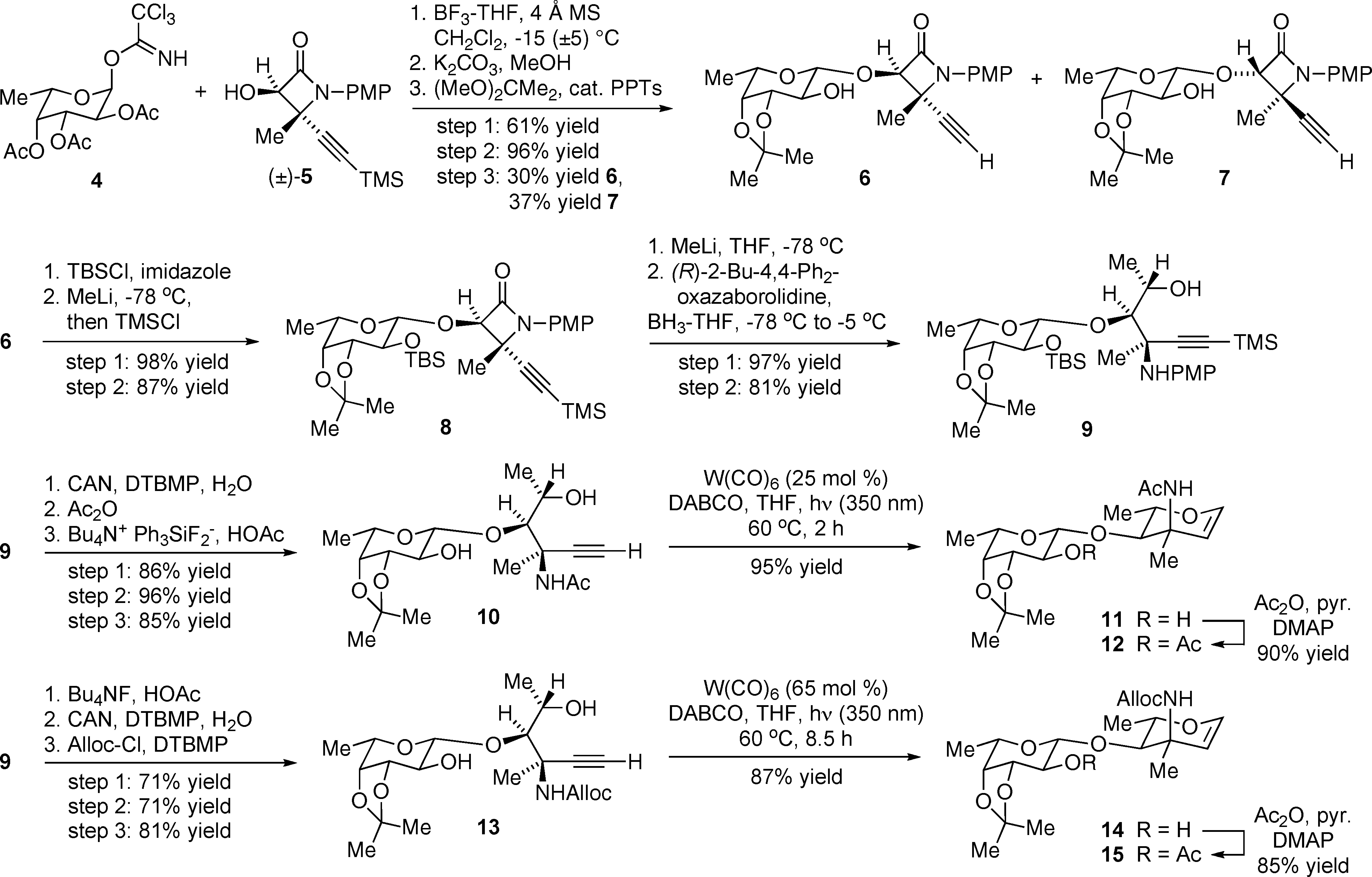
Preparation of Fucose-Saccharosamine Disaccharide Glycals 11-12 and 14-15
CAS number: 366-18-7
2,2'-Bipyridine, also known as bipy or bpy, is a symmetrical bipyridine, meaning it has two pyridine rings connected at the 2 and 2' positions. It's a versatile bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry, forming stable complexes with various metal ions.
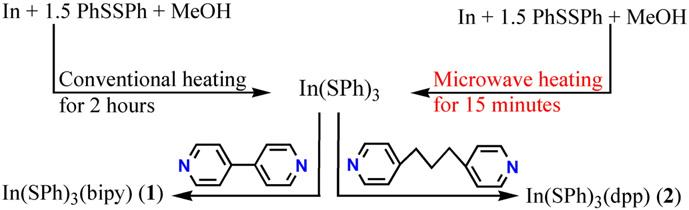
The contrast between the microwave heating and conventional heating for the synthesis of In(SPh)3, and its use as precursor for the self-assembly of two new one-dimensional indium thiolate-dipyridyl compounds.
CAS number: 36622-29-4
Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker that widens your blood vessels and relaxes your heart muscle.

Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of (S)-verapamil. LDA=lithium diisopropylamide.
CAS number: 366789-02-8
Rivaroxaban is an anticoagulant and the first orally active direct factor Xa inhibitor. Unlike warfarin, routine lab monitoring of INR is not necessary. However there is no antidote available in the event of a major bleed. Only the 10 mg tablet can be taken without regard to food. The 15 mg and 20 mg tablet should be taken with food. FDA approved on July 1, 2011.
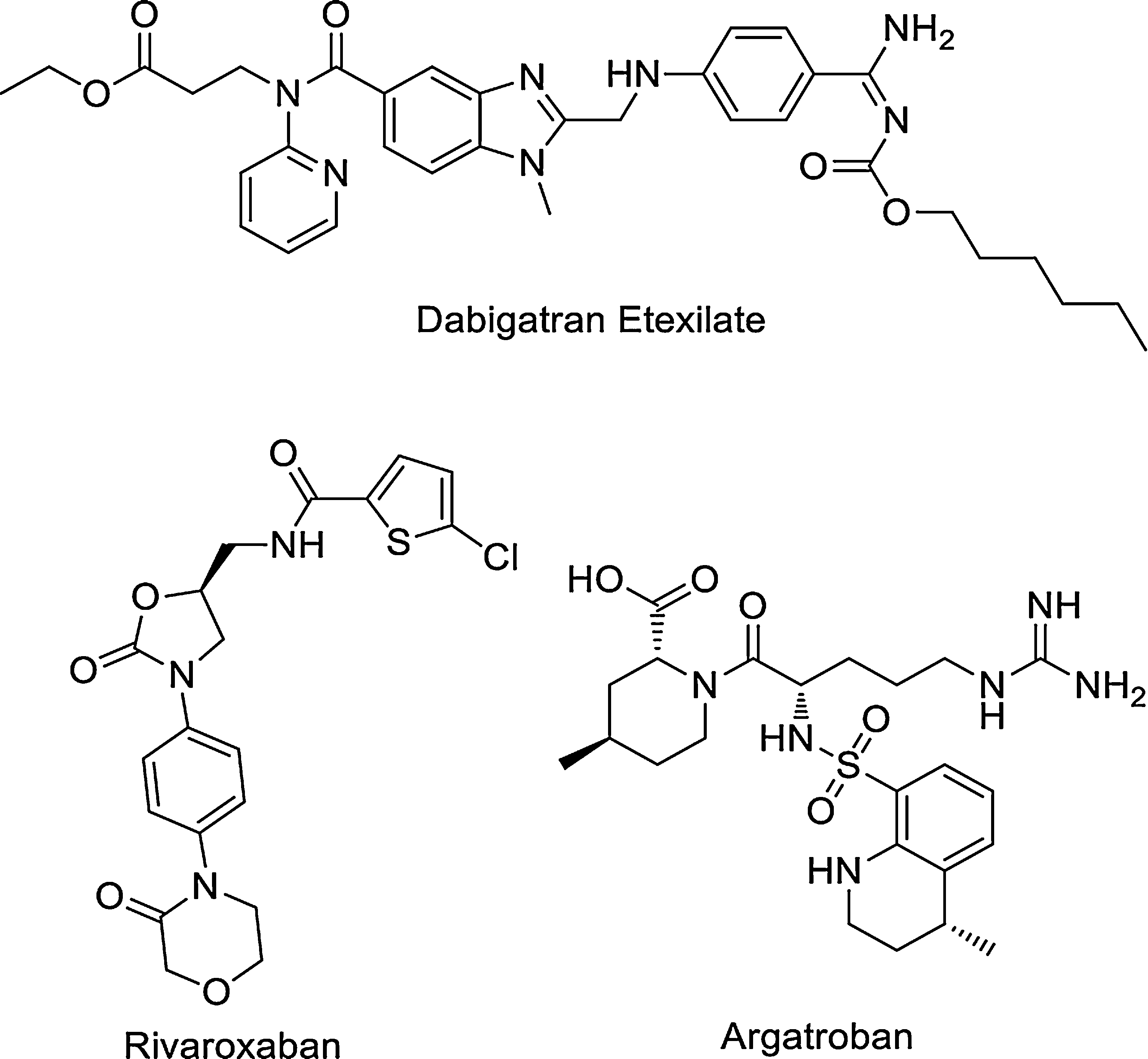
Structures of commercial thrombin inhibitory drugs.
CAS number: 36791-04-5
Ribavirin is a 1-ribosyltriazole that is the 1-ribofuranosyl derivative of 1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. A synthetic guanosine analogue, it is an inhibitor of HCV polymerase and possesses a broad spectrum of activity against DNA and RNA viruses.
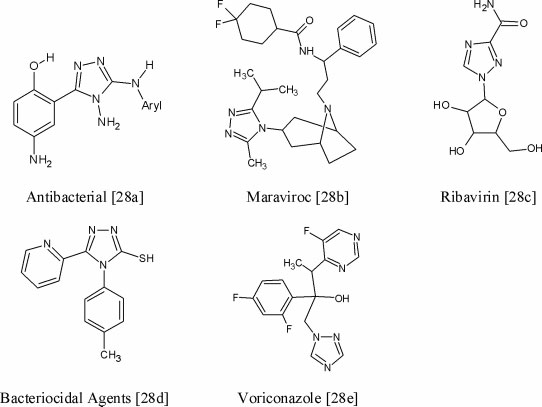
Examples of some bioactive compounds containing 1,2,4-triazole moiety.
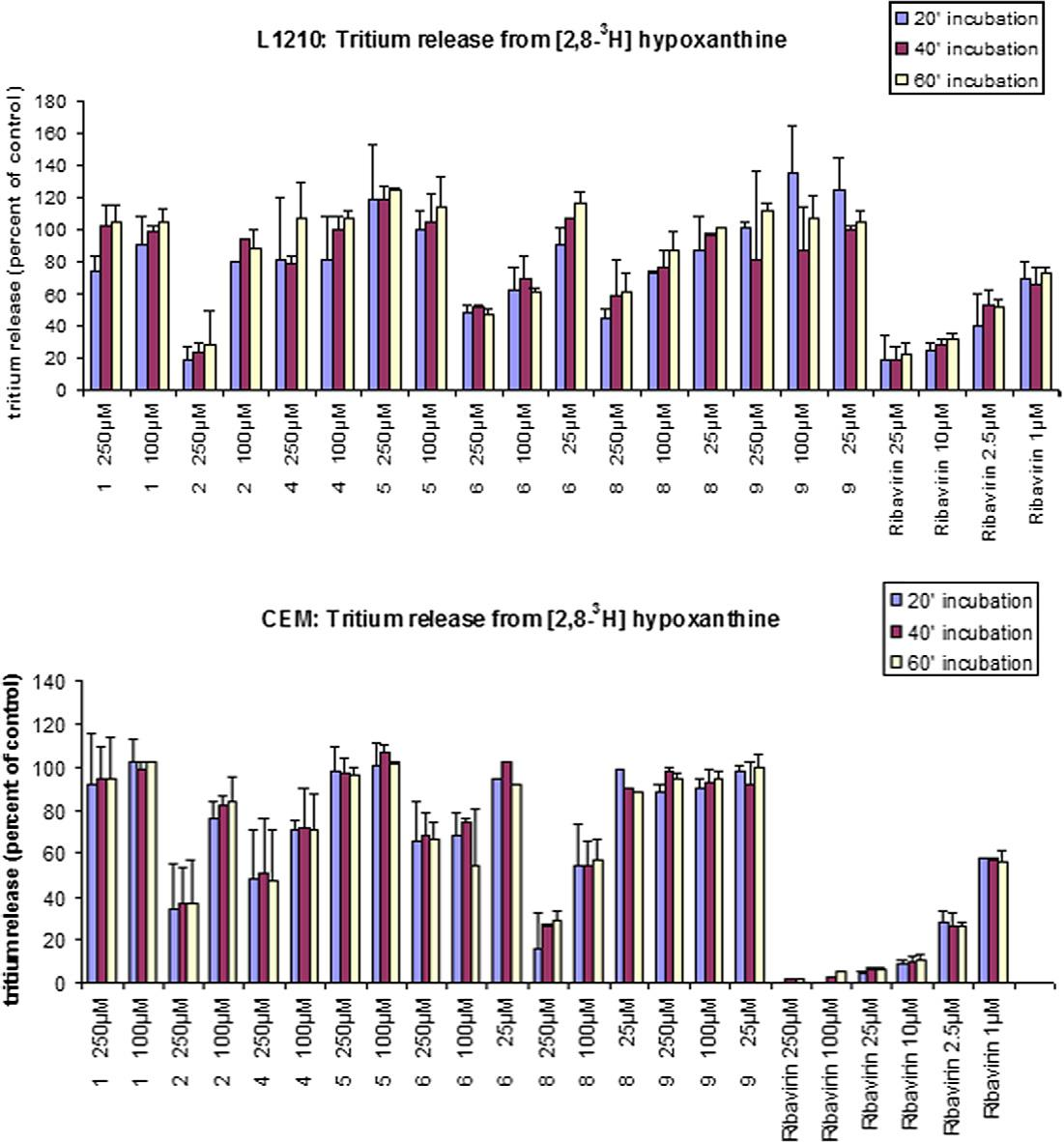
IMP dehydrogenase activity measurements in L1210 and CEM cell cultures in the presence of ribavirin and the test compounds.
CAS number: 37112-31-5
Levoglucosenone (LGO) is a chiral, bio-based molecule produced from the pyrolysis of cellulose and other biomass materials.
![Synthesis of racemic levoglucosenone [(±)-1]](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/2903988_03.png)
Synthesis of racemic levoglucosenone [(±)-1]
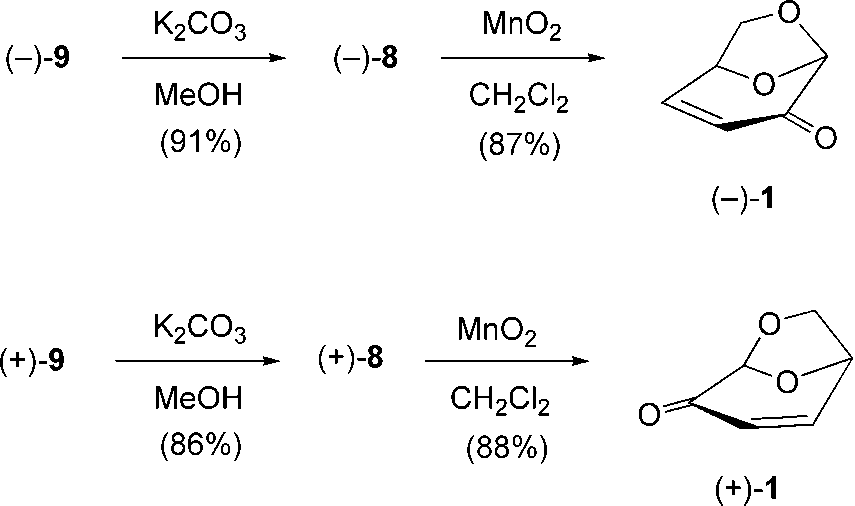
Synthesis of enantiopure levoglucosenone
CAS number: 37181-39-8
Triflate is an organosulfonate oxoanion resulting from the removal of a proton from the sulfonic acid group of triflic acid. It is a conjugate base of a triflic acid.
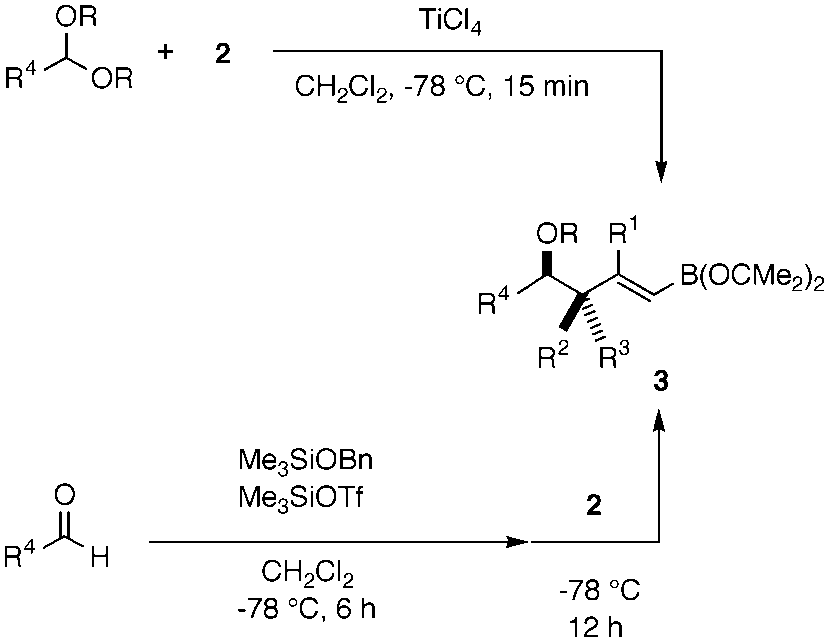
Allylation of acetals or aldehydes as allylic silanes. Bn = benzyl, OTf = trifluoromethanesulfonate.
CAS number: 37231-75-7
Quinocycline A, also known as PA-371-A''1, is a quinocycline-class natural product derived from Streptomyces species, characterized by a tetracyclic core with a unique quinoline moiety. It exhibits potent antibacterial activity, particularly against Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and drug-resistant strains such as MRSA. Structurally, it combines features of both tetracyclines and quinolines, contributing to its mechanism of action, which is believed to involve inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis. Quinocycline A is of interest in antibiotic discovery for its novel scaffold and promising bioactivity, offering a potential lead compound for addressing antibiotic resistance.
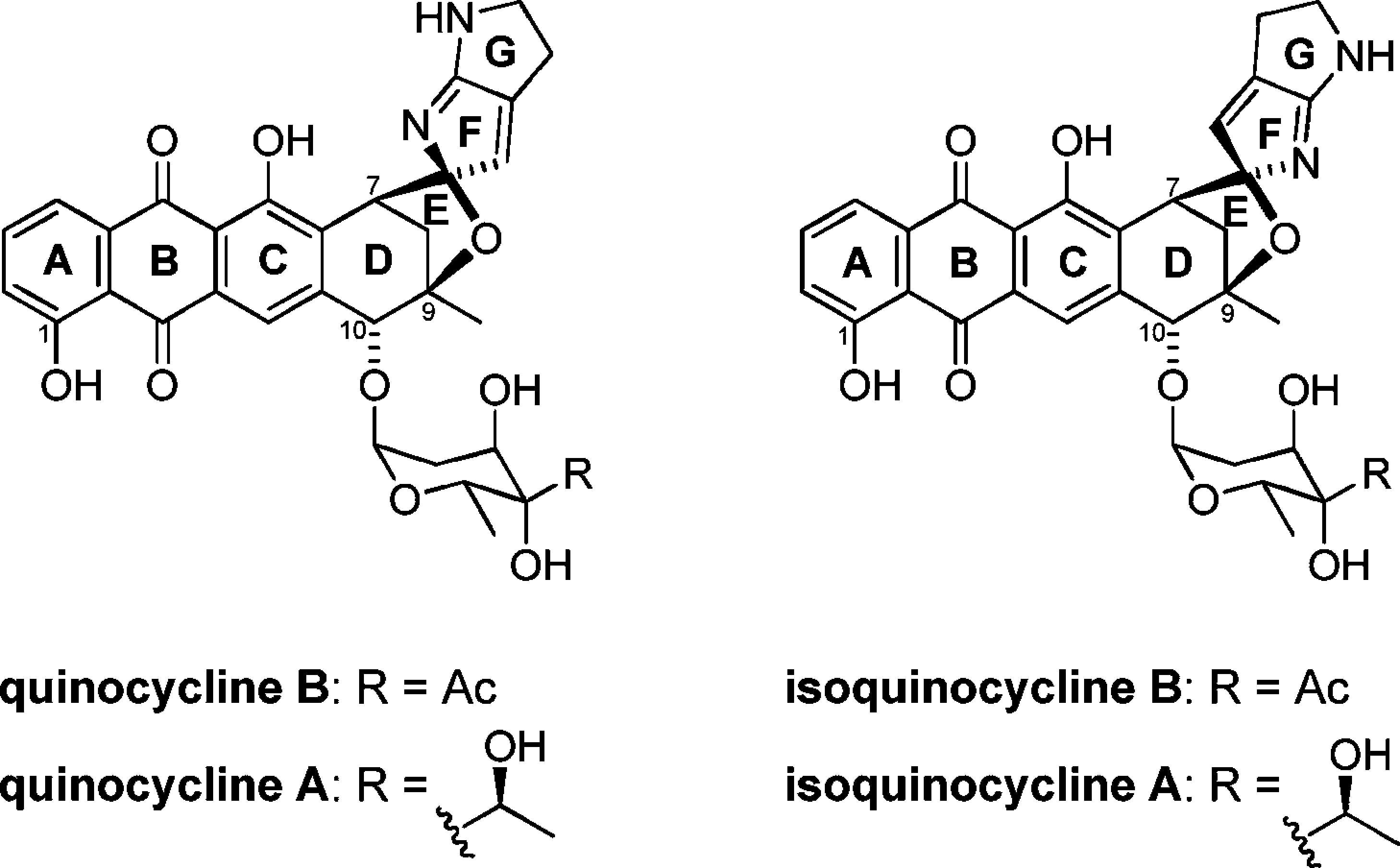
Quinocyclines are a class of anthracycline related natural products consisting of the four compounds quinocycline A, quinocycline B, isoquinocycline A, and isoquinocycline B (Figure 1).
CAS number: 37231-76-8
Quinocycline B, also known as PA-371-D'', is a synthetic tetracycline derivative with broad-spectrum antibacterial and potential anticancer properties. It was originally developed for its antimicrobial activity but has since attracted interest for its ability to inhibit tumor cell growth, particularly in drug-resistant cancer cells. Quinocycline B functions by targeting mitochondrial function and inducing apoptosis through pathways independent of p53, making it a promising candidate for overcoming resistance mechanisms in cancer therapy.

Quinocyclines are a class of anthracycline related natural products consisting of the four compounds quinocycline A, quinocycline B, isoquinocycline A, and isoquinocycline B (Figure 1).