Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 352-13-6
4-Fluorophenylmagnesium bromide is an organomagnesium compound classified as a Grignard reagent, commonly used in organic synthesis. It consists of a fluorinated phenyl ring (4-fluorophenyl group) bonded to a magnesium atom, which is also coordinated with a bromine atom.
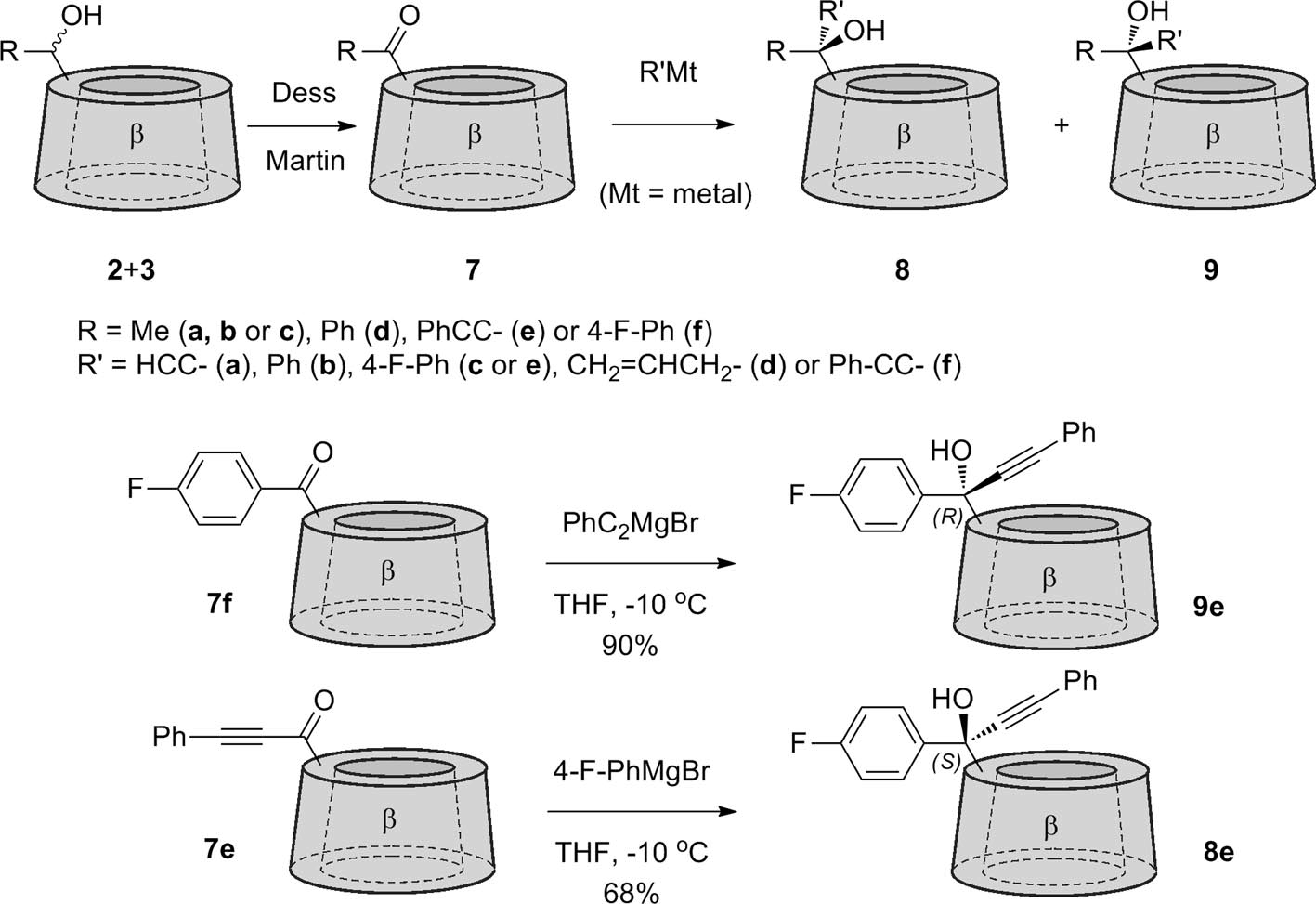
Oxidation of secondary alcohols to the β-cyclodextrin ketone 4, 7e and 7f followed by reaction with organometallic reagents to give tertiary alcohols.
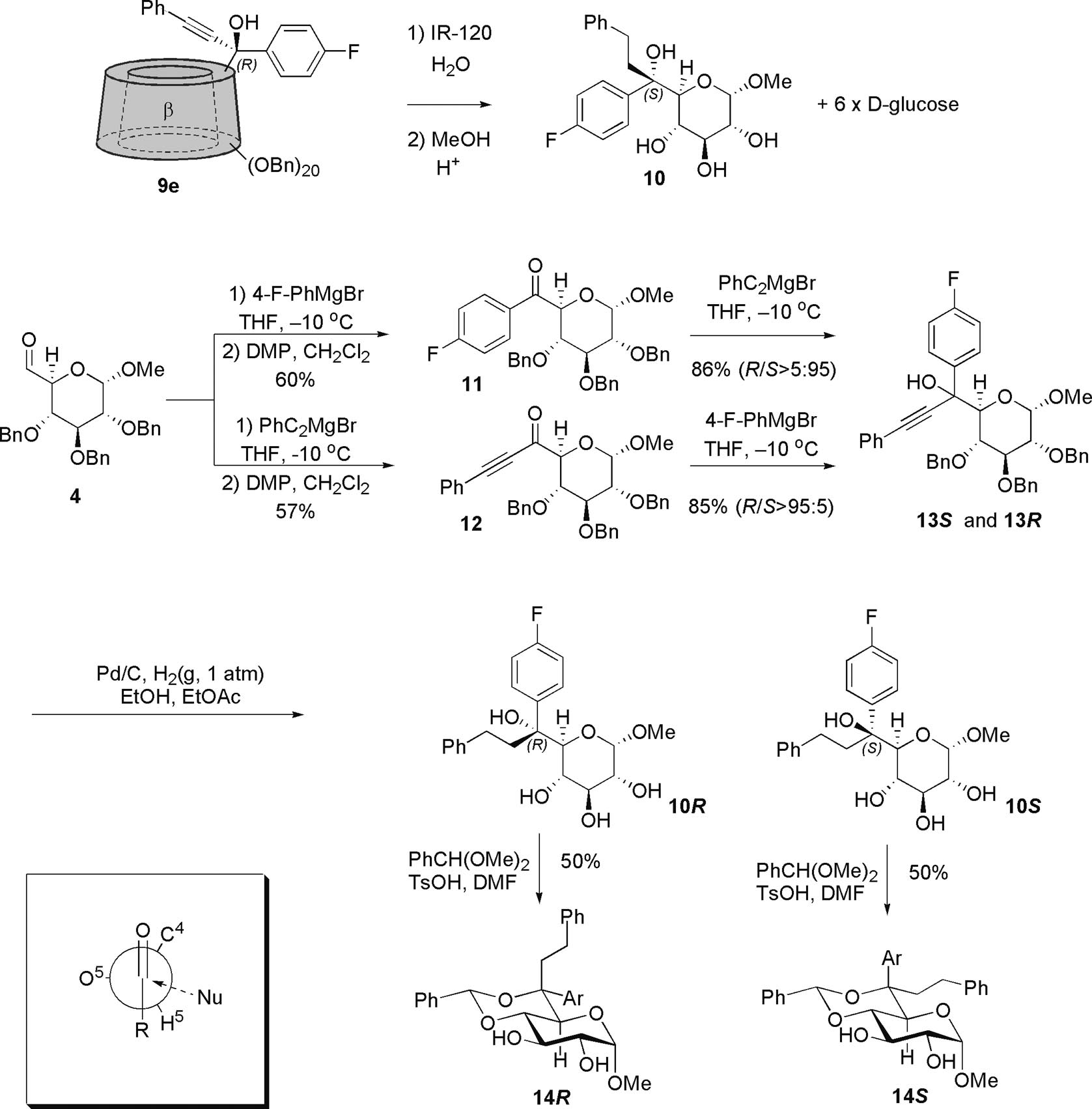
Preparation of two reference monosaccharide derivatives, 10S and 10R that could be used to determine the stereochemistry at C-6 of tertiary alcohols 8e and 9e.
CAS number: 35225-79-7
Dibenzylideneacetone or dibenzalacetone, often abbreviated dba, is an organic compound with the formula C17H14O. It is a bright-yellow solid insoluble in water, but soluble in ethanol. Dibenzylideneacetone is used as a sunscreen component and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry, for instance in tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0).
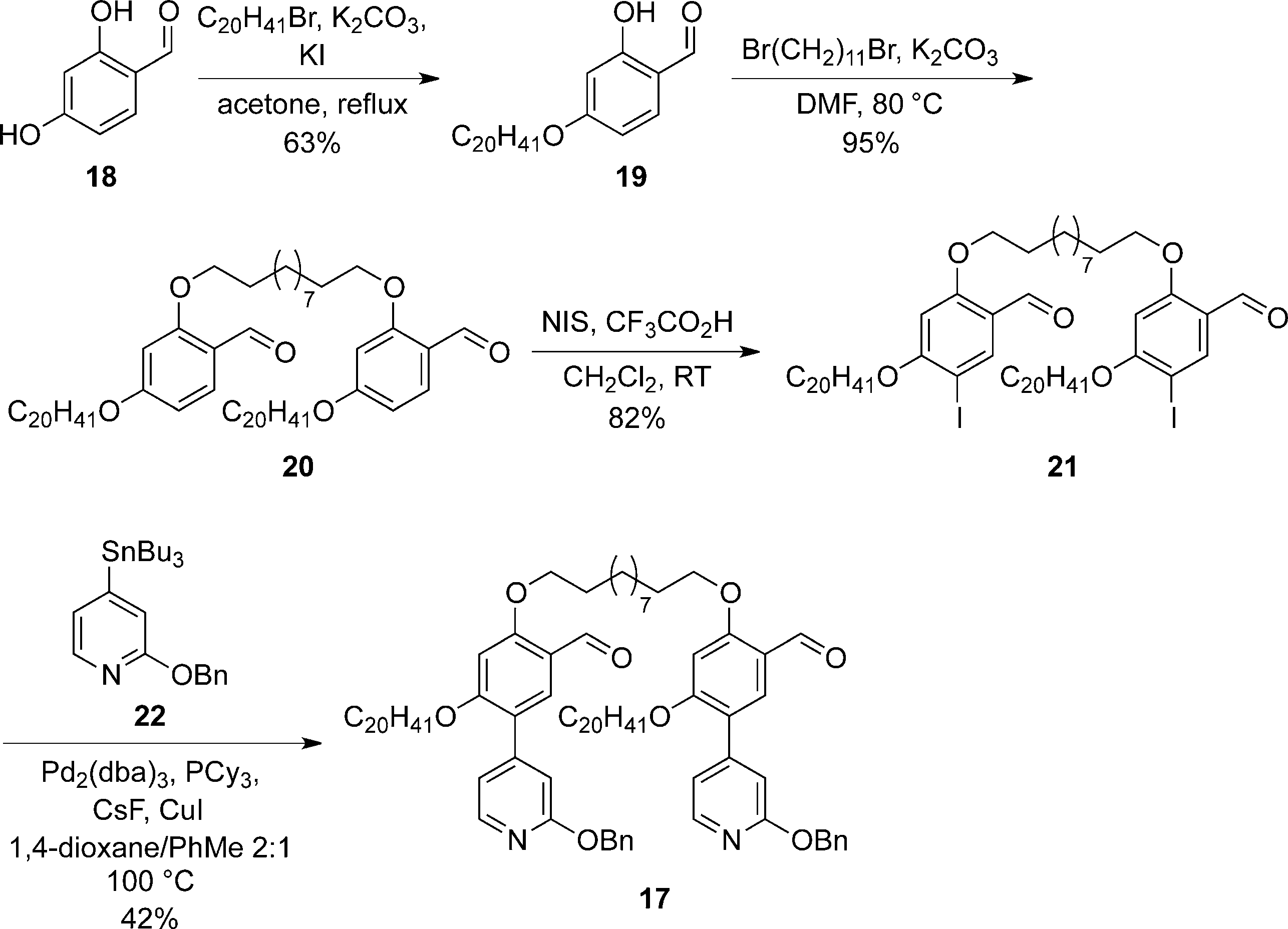
Synthesis of aldehyde 17 required for the porphyrin condensation. Cy=cyclohexyl, dba=dibenzylideneacetone.
CAS number: 35457-80-8
Midecamycin is a naturally occurring 16-membered macrolide that fits under the category of acetoxy-substituted macrolide antibiotics. In this molecule, an acetoxy group is substituted on the position 9 of the 16-member ring and on position 4 of the terminal sugar. Until 2017, midecamycin was still under the list of approved antimicrobial active pharmaceutical ingredients by Health Canada.
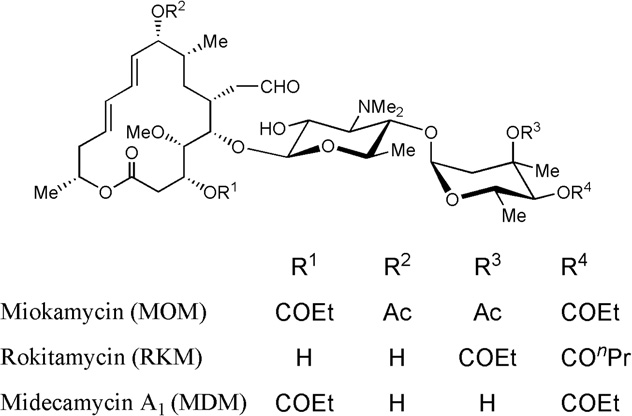
Natural antibiotic, midecamycin A1 and representative semisynthetic 16-membered macrolides, miokamycin and rokitamycin.
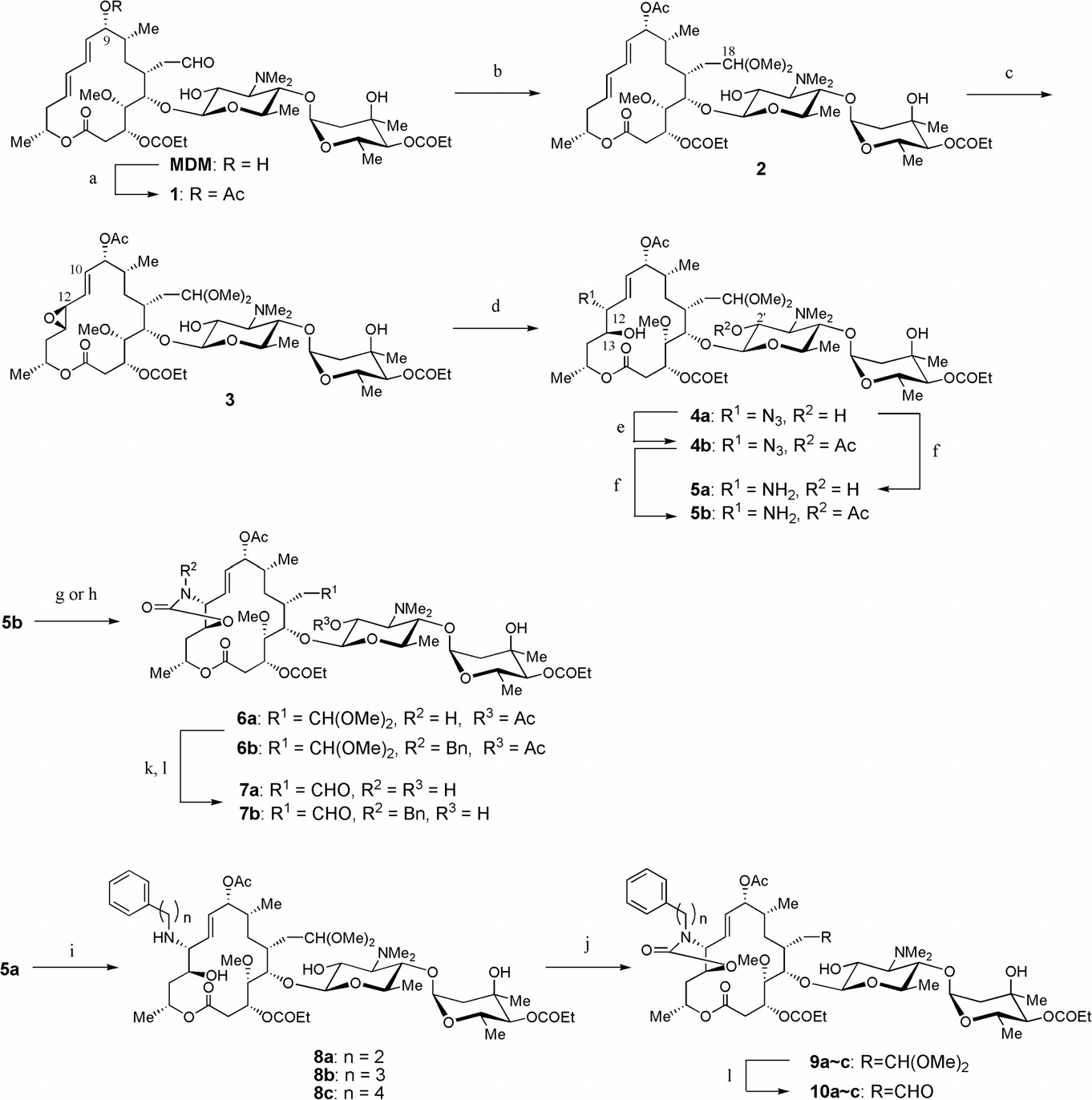
Synthesis of 12,13-cyclic carbamates of MDM (Midecamycin).
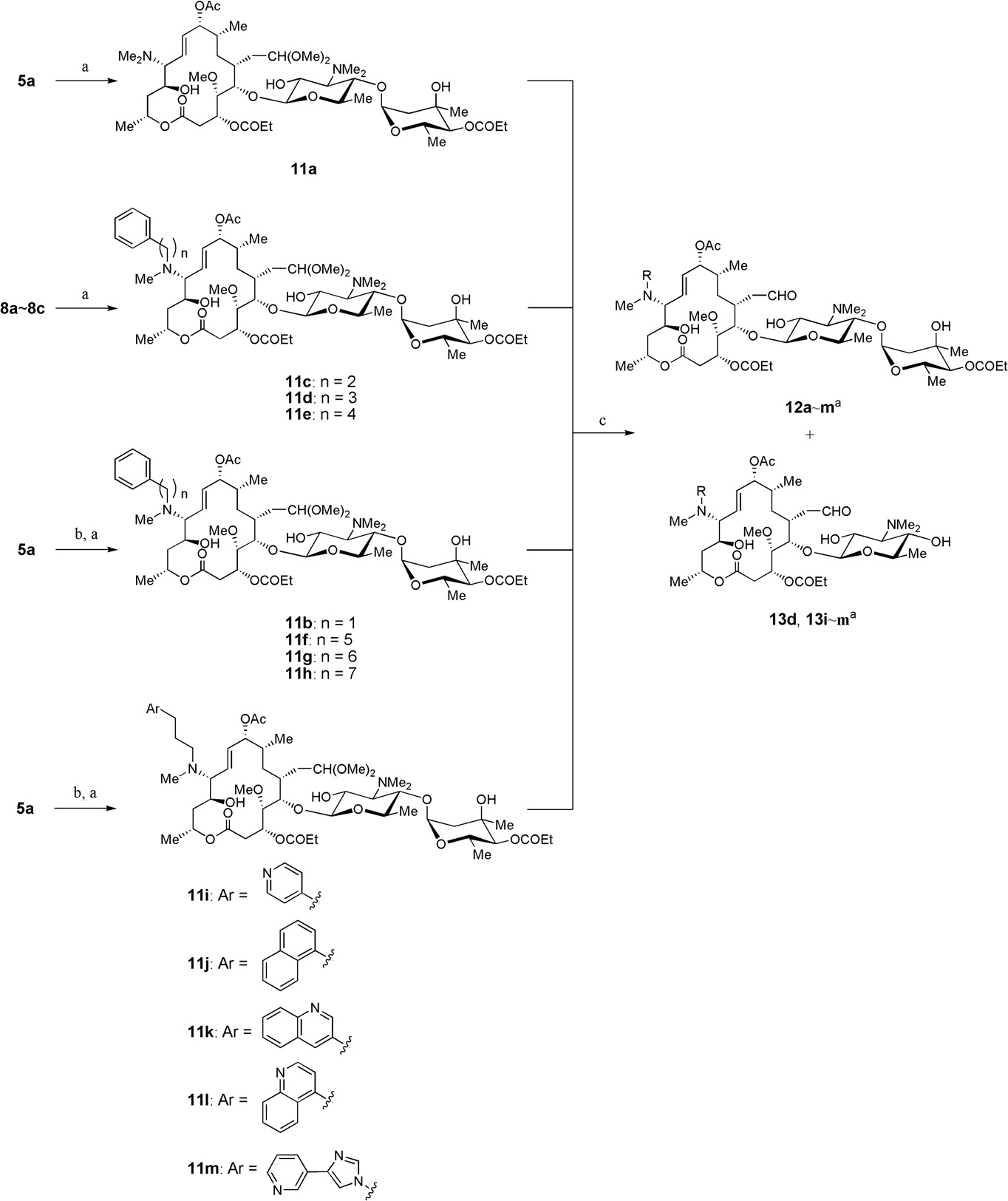
Synthesis of 12-arylalkylamino analogues of MDM (Midecamycin).
CAS number: 3546-21-2
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is a chemical compound commonly used in molecular biology laboratories to visualize DNA and RNA in gel electrophoresis.
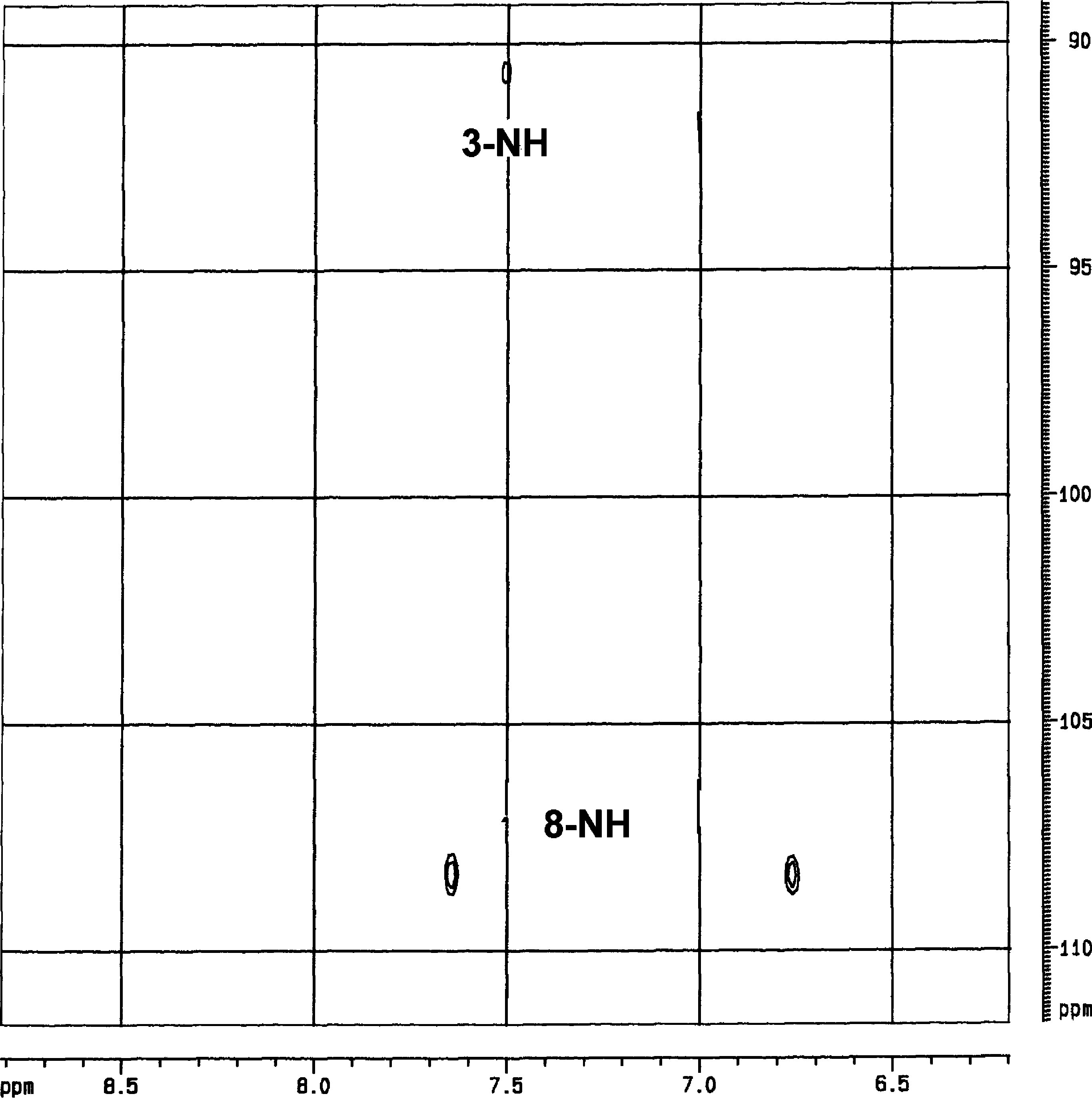
NH–HSQC of ethidium nucleoside 5 .
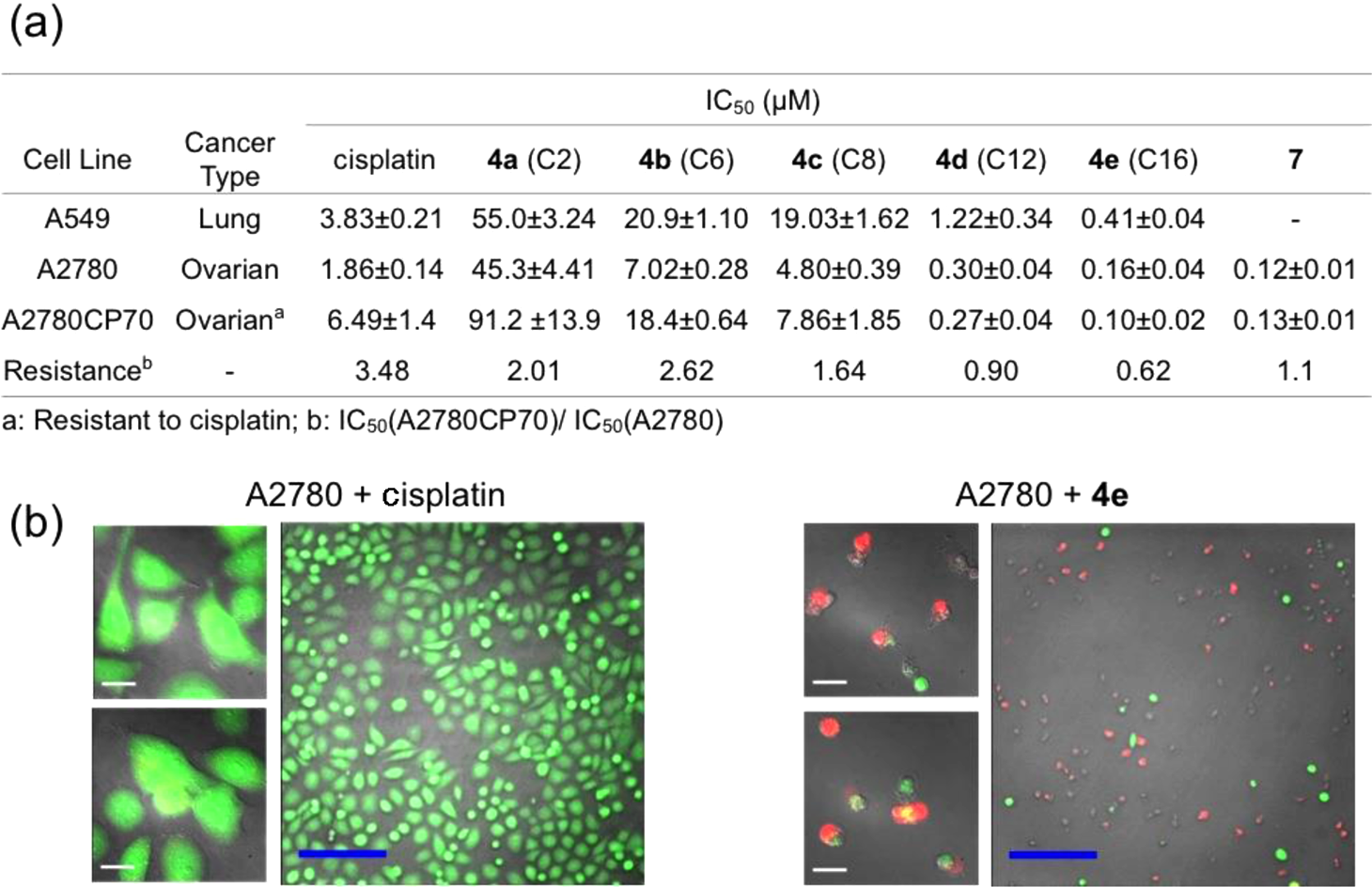
Cytotoxicity profiles of Pt(IV) prodrugs: (a) Table of IC50 values of 4a-e and 7 measured in A549, A2780, and A2780CP70 cell lines; (b) Calcein AM/ethidium homodimer-1 cell viability assay, details of which can be found in the main text and Supporting Information (white scale bar, 20 μm; blue scale bar, 200 μm).
CAS number: 35523-89-8
Saxitoxin is an alkaloid isolated from the marine dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria that causes paralytic shellfish poisoning. It has a role as a neurotoxin, a toxin, a sodium channel blocker, a marine metabolite and a cyanotoxin. It is a carbamate ester, a member of guanidines, an alkaloid, a pyrrolopurine, a ketone hydrate and a paralytic shellfish toxin. It is a conjugate base of a saxitoxin(2+).
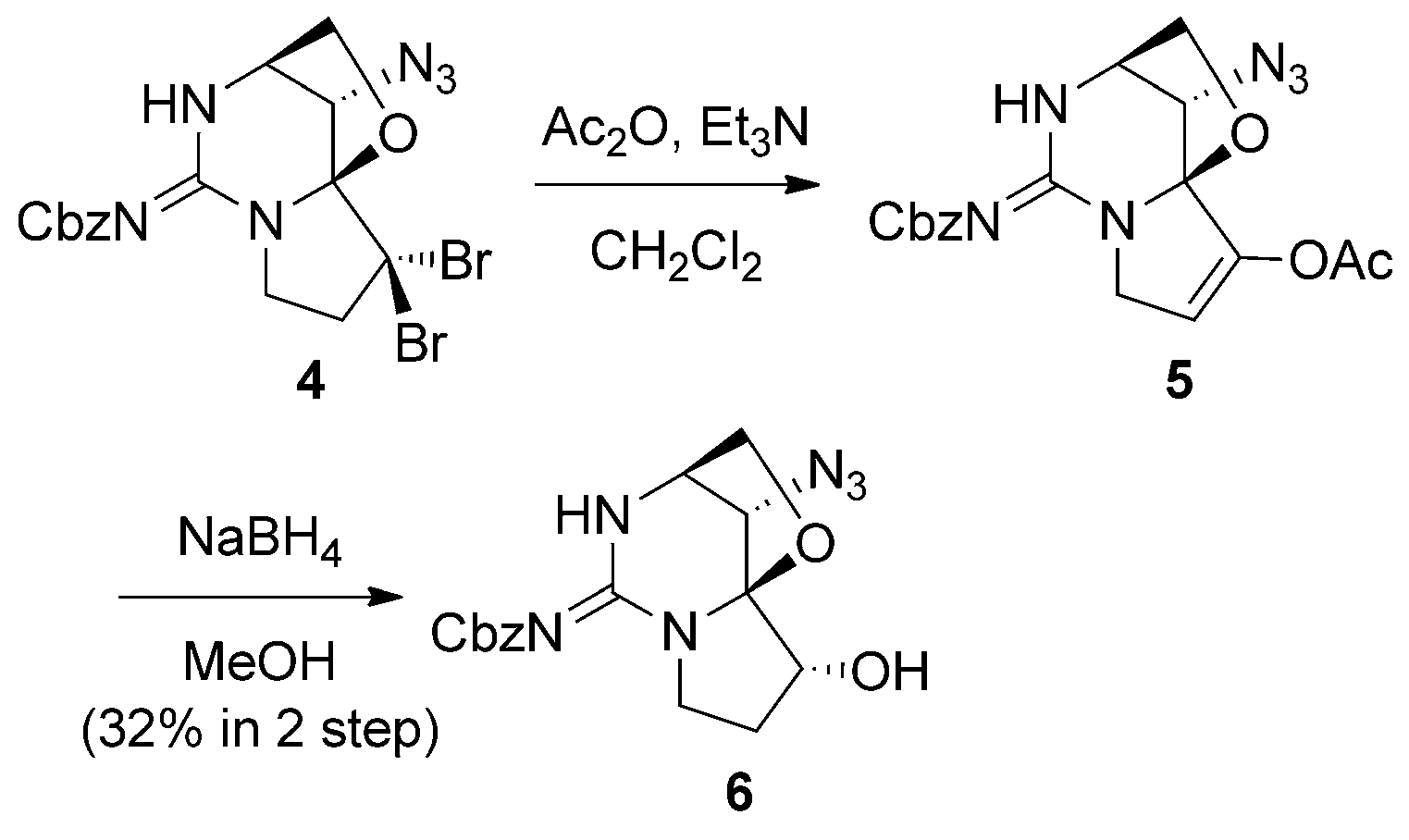
The novel transformation of a gem-CBr2 group to enol acetate followed by reduction, employed in the total synthesis of an analogue of saxitoxin.
CAS number: 35661-40-6
Fmoc-phenylalanine is an essential amino acid derivative used in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) that has a protective Fmoc group attached to the amino group of phenylalanine. This modification makes it a stable building block for creating complex peptides, and it can be selectively removed when needed. Its applications include developing peptide-based drugs, creating novel materials for drug delivery, and researching protein interactions.
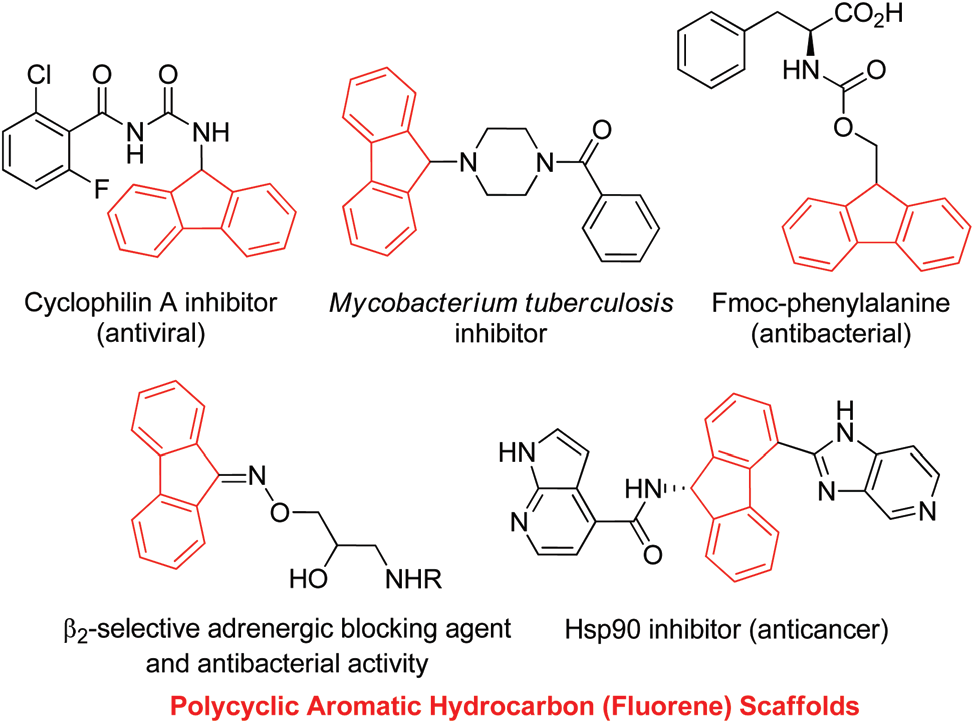
Selected examples of pharmaceuticals and bioactive compounds that contain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) scaffolds: Cyclophilin A inhibitor, Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Inhibitor, FMOC-PHENYLALANINE, Hsp90 inhibitor. The fluorene core is shown in red.
CAS number: 35907-63-2
Carbon-13C monoxide-18O (¹³C¹⁸O) is an isotopically labeled variant of carbon monoxide, composed of the carbon-13 isotope and the oxygen-18 isotope, giving it the molecular formula ¹³C¹⁸O. As a diatomic molecule, it retains the linear geometry and bonding characteristics of regular carbon monoxide (CO), but its isotopic composition alters its physical properties, such as molecular weight (approximately 31 g/mol) and vibrational spectra, making it useful in advanced spectroscopic studies, tracer experiments, and reaction mechanism investigations in chemistry and environmental science. This gas is colorless, toxic, and flammable, similar to regular CO, and must be handled with appropriate safety precautions.
2 as a catalyst.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/541095_12.png)
Products synthesized by reductive amination using carbon monoxide as a reducing agent and [2b](SbF6)2 as a catalyst.
CAS number: 36148-89-7
Amphotericin B methyl ester is the methyl ester of amphotericin B. It has a role as an antifungal agent, an antiinfective agent and a metabolite. It is a macrolide, a monosaccharide derivative and a methyl ester. It is functionally related to an amphotericin B.
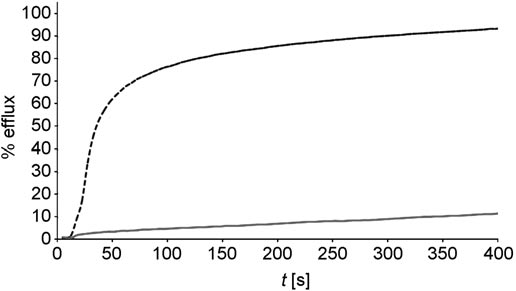
KCl efflux from LUV induced by 53 (c) and amphotericin B methyl ester (a) measured via potentiometry.
CAS number: 36193-36-9
(R)-Rhazinilam is a benzenoid aromatic compound.
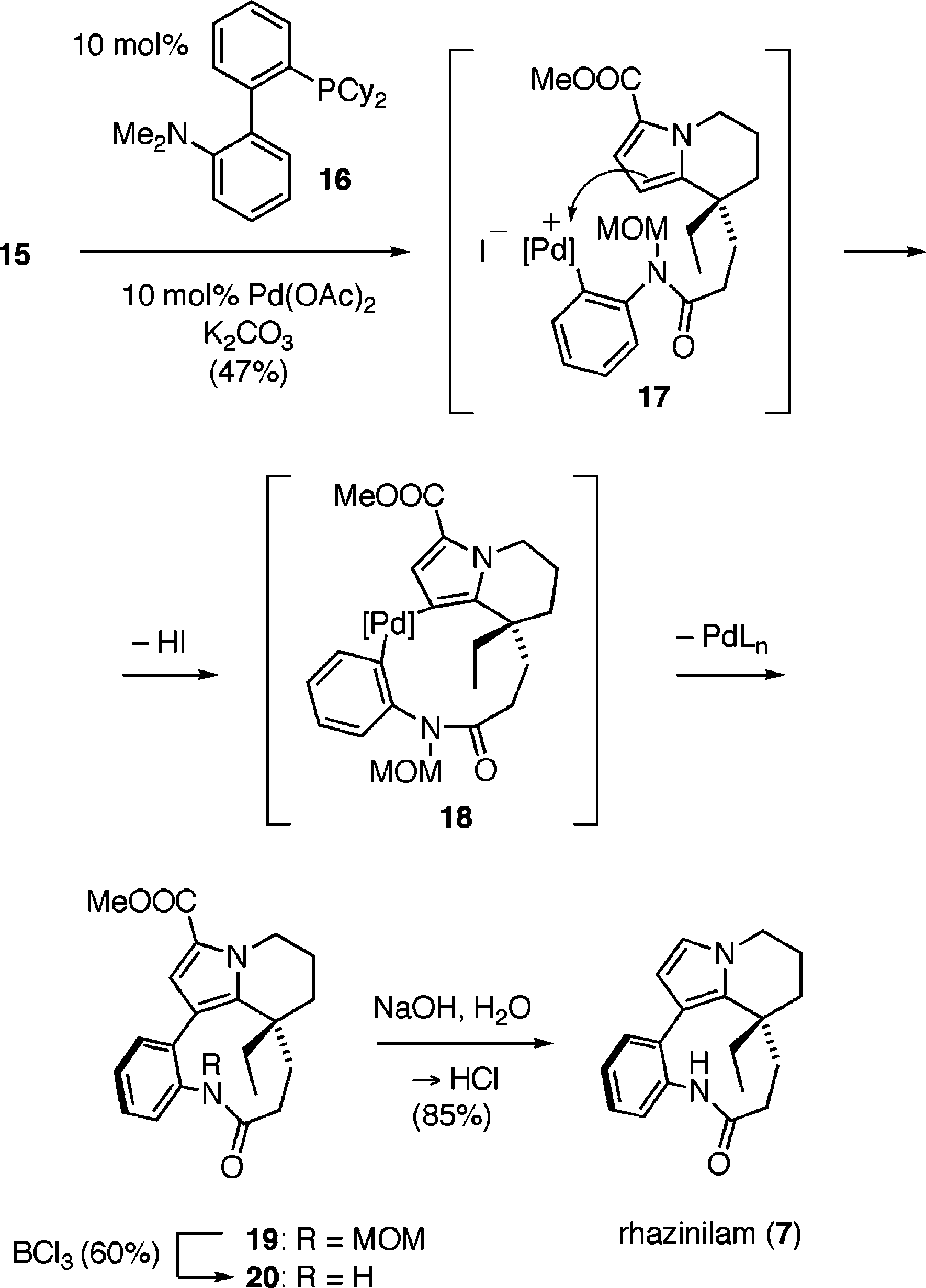
Key Coupling and Total Synthesis of Rhazinilam
CAS number: 36312-17-1
2,3-dihydrofuran is a dihydrofuran.
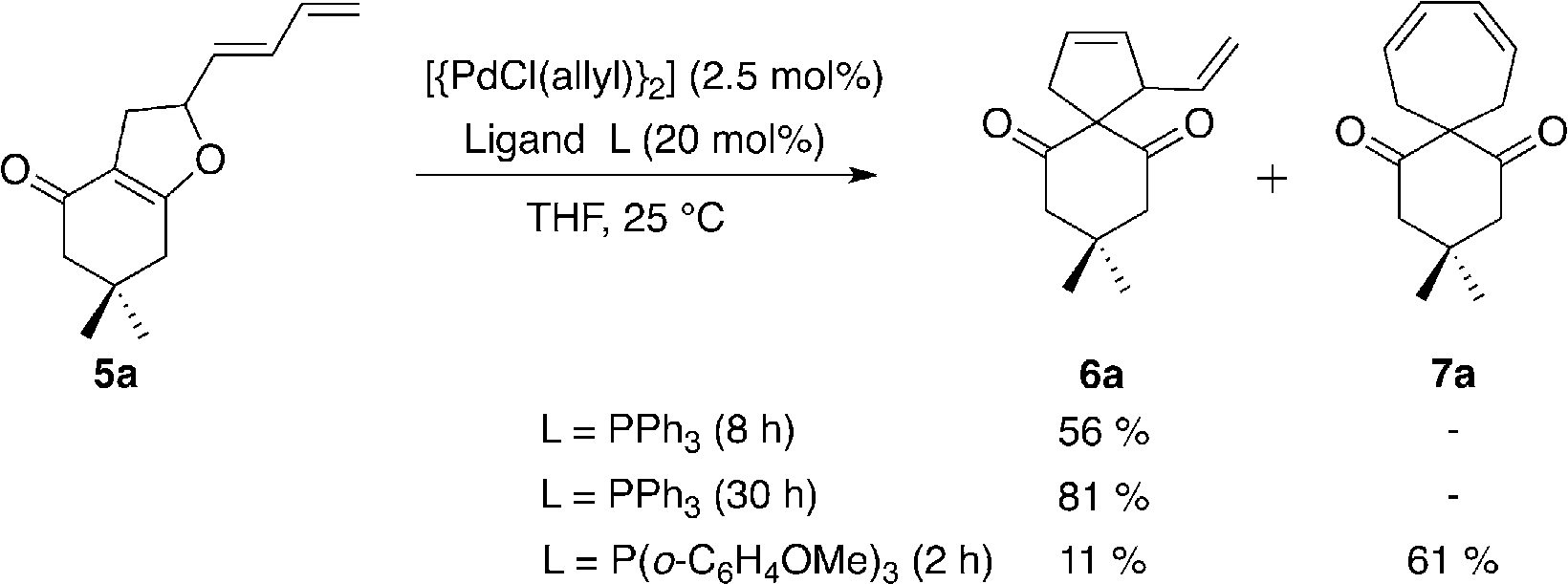
Conversion of dihydrofuran derivative 5a into carbocycles 6a and 7a.