Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 198821-22-6
Merimepodib (VX-497) is a novel noncompetitive inhibitor of IMPDH. Merimepodib is orally bioavailable and inhibits the proliferation of primary human, mouse, rat, and dog lymphocytes at concentrations of approximately 100 nM.
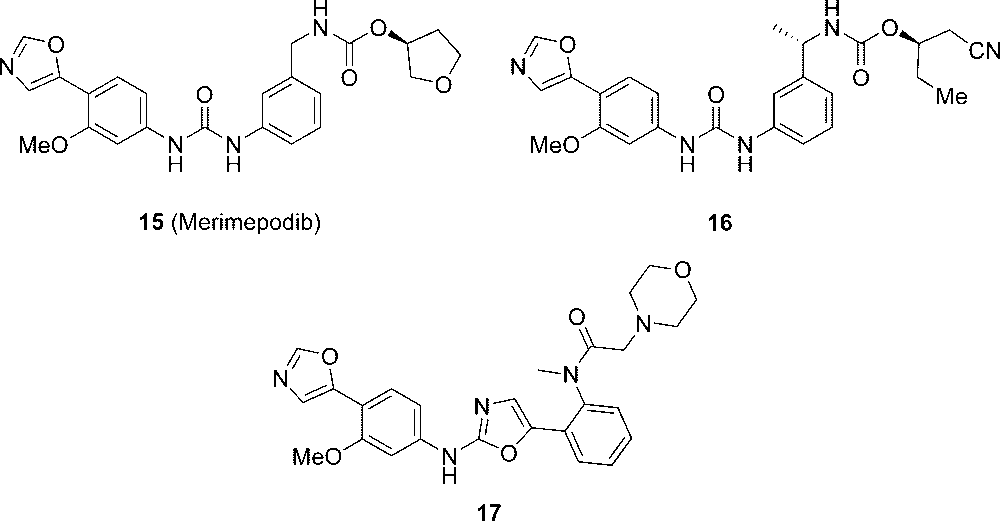
In a series of IMPDH inhibitors developed by Vertex and Bristol-Myers-Squibb such as (S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yl 3-(3-(3-methoxy-4-(oxazol-5-yl)phe-nyl)ureido)benzylcarbamate (15, merimepodib, Figure 5) and related inhibitors 16 and 17, the phenyloxazole moiety with an ortho methoxy group was introduced and found to bind at the nicotinamide subdomain of NAD-binding pocket of IMPDH.
CAS number: 199522-35-5
Nnc-26-9100 is an aminopyridine.
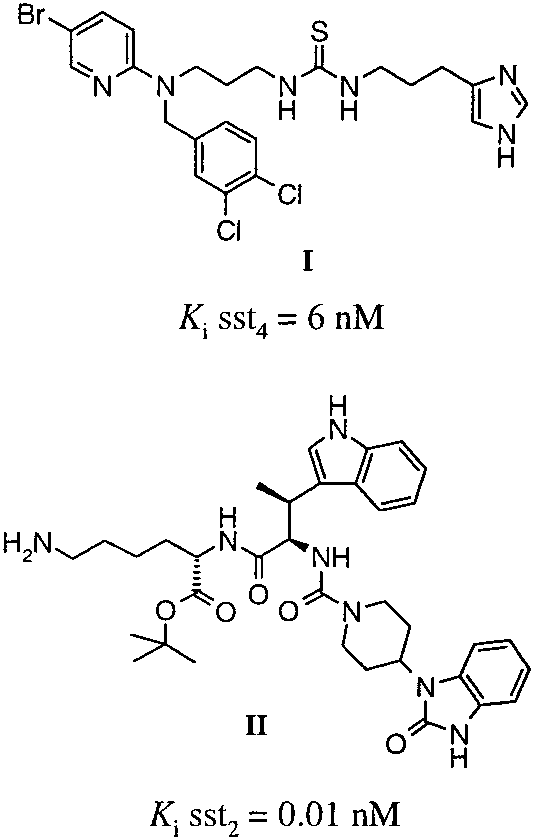
Chemical structures of I (NNC 26-9100) and II (L-054,522) and their inhibition constants (Ki) on somatostatin receptor subtypes.
CAS number: 201058-08-4
Wang Resin is a solid support used in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). It's particularly useful when working with Fmoc-protected amino acids, as the Wang resin linker is stable under basic conditions (like those used in Fmoc deprotection) but can be cleaved under acidic conditions to release the synthesized peptide.
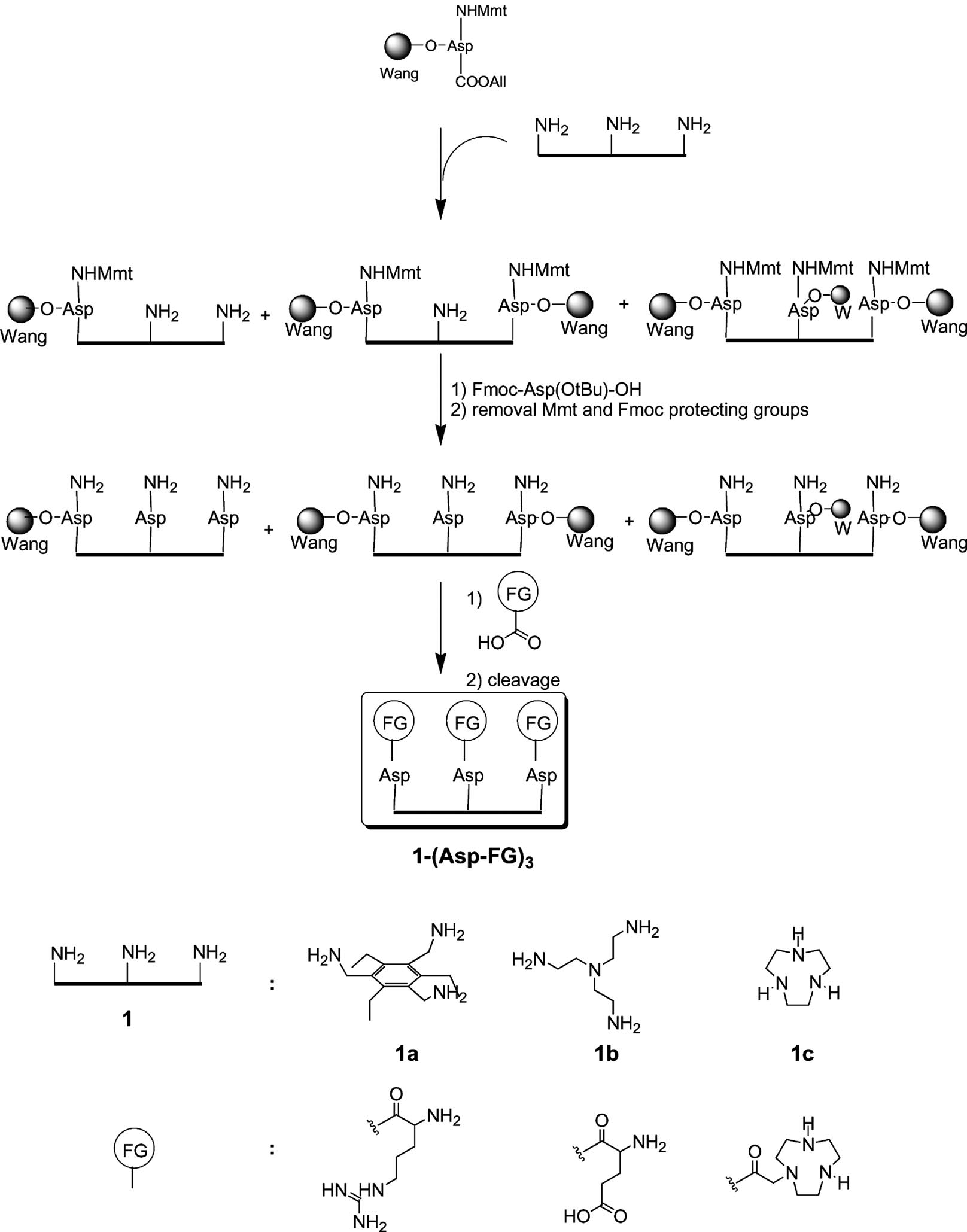
Schematic presentation of the protocol for the synthesis of compounds 1-(Asp-FG)3 on Wang resin
CAS number: 201338-44-5
(-)-Agelastatin C is a natural product, specifically a pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid, isolated from marine sponges. It's known for its complex tetracyclic structure and exhibits cytotoxic properties, meaning it can inhibit the growth of certain cells, including cancer cells. It was first isolated and characterized, along with (-)-Agelastatin D, from the sponge Cymbastela sp. from the Indian Ocean.
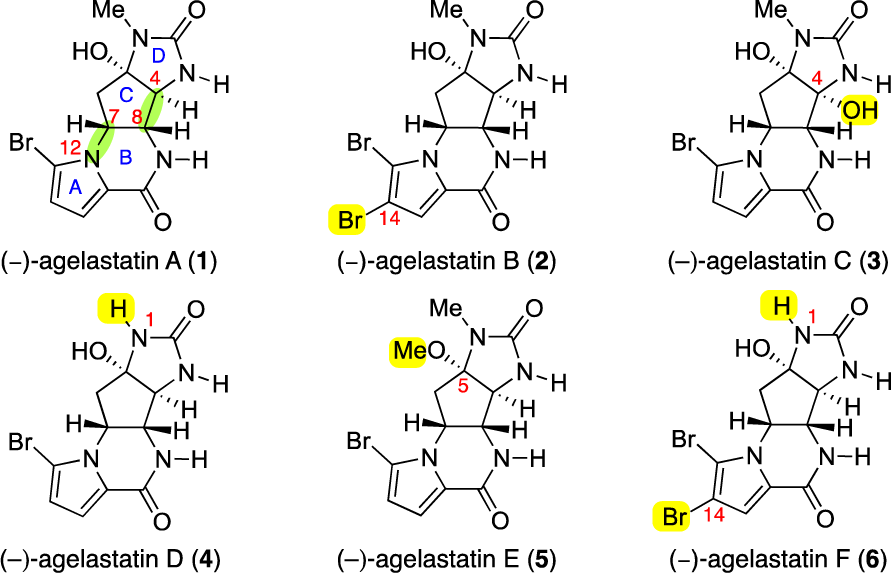
Structures of (−)-agelastatins A−F (1−6).
CAS number: 201338-45-6
Agelastatin D is a naturally occurring bromopyrrole alkaloid, specifically a derivative of agelastatin A, isolated from marine sponges like Cymbastela sp. It is structurally related to agelastatin A, but lacks an N-methyl group present in the latter.

Structures of (−)-agelastatins A−F (1−6).
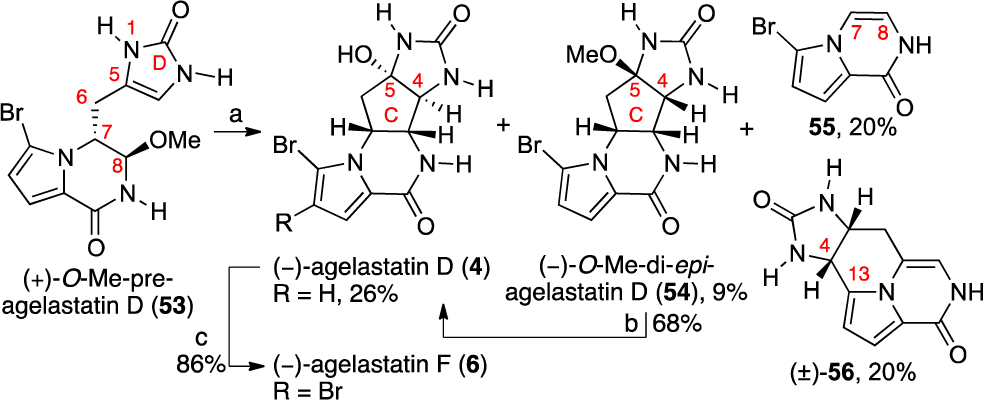
Total Synthesis of (−)-Agelastatin D (4) and the Formation of Byproducts 55 and 56
CAS number: 2022-85-7
Flucytosine is an antifungal prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of serious infections caused by certain strains of two types of fungi: Candida and Cryptococcus. For example, flucytosine may be used to treat cryptococcosis, which is an infection caused by Cryptococcus fungi.
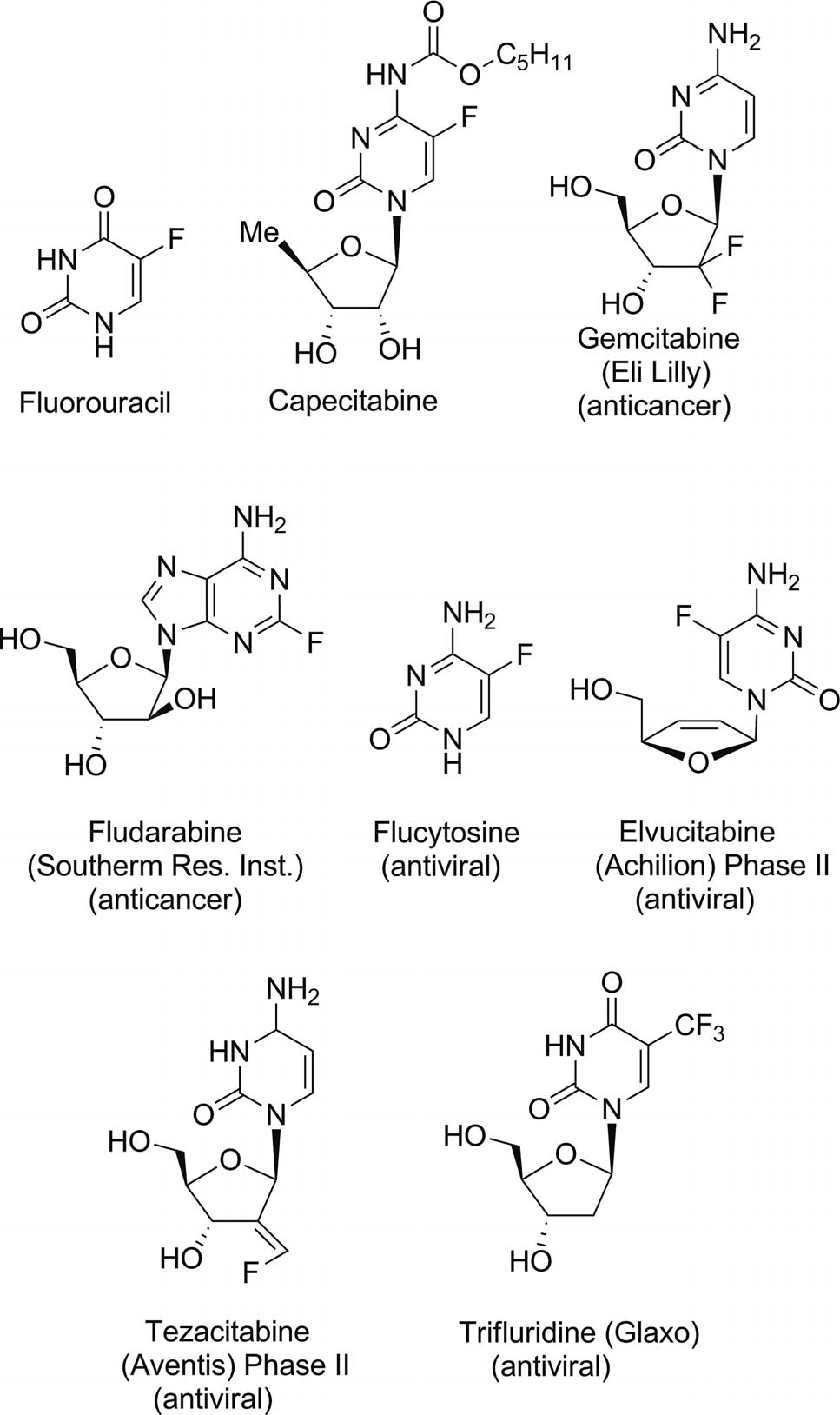
Fluorinated purine and pyrimidine antimetabolites clinically used for the treatment of numerous cancers and viral infections: Fluorouracil, capecitabine, gemcitabine, fludarabine, flucytosine, elvucitabine, tezacitabine, trifluridine.
CAS number: 202409-33-4
Etoricoxib is a new COX-2 selective inhibitor. Current therapeutic indications are: treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, chronic low back pain, acute pain and gout.
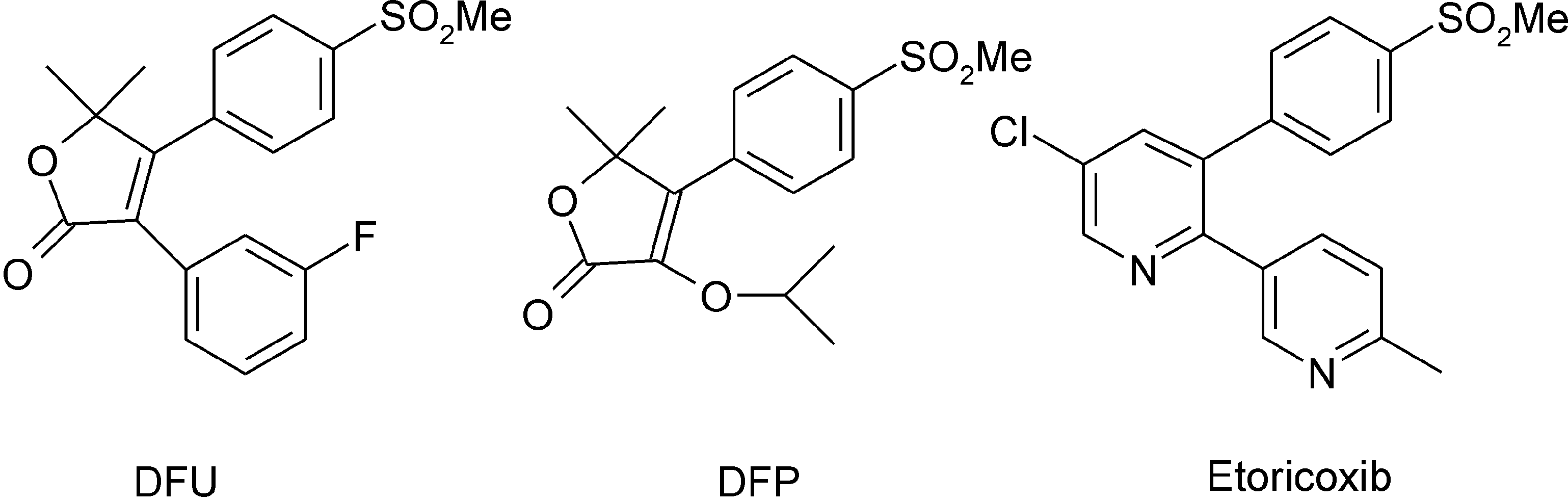
Chemical structures of DFU, DFP, and etoricoxib.
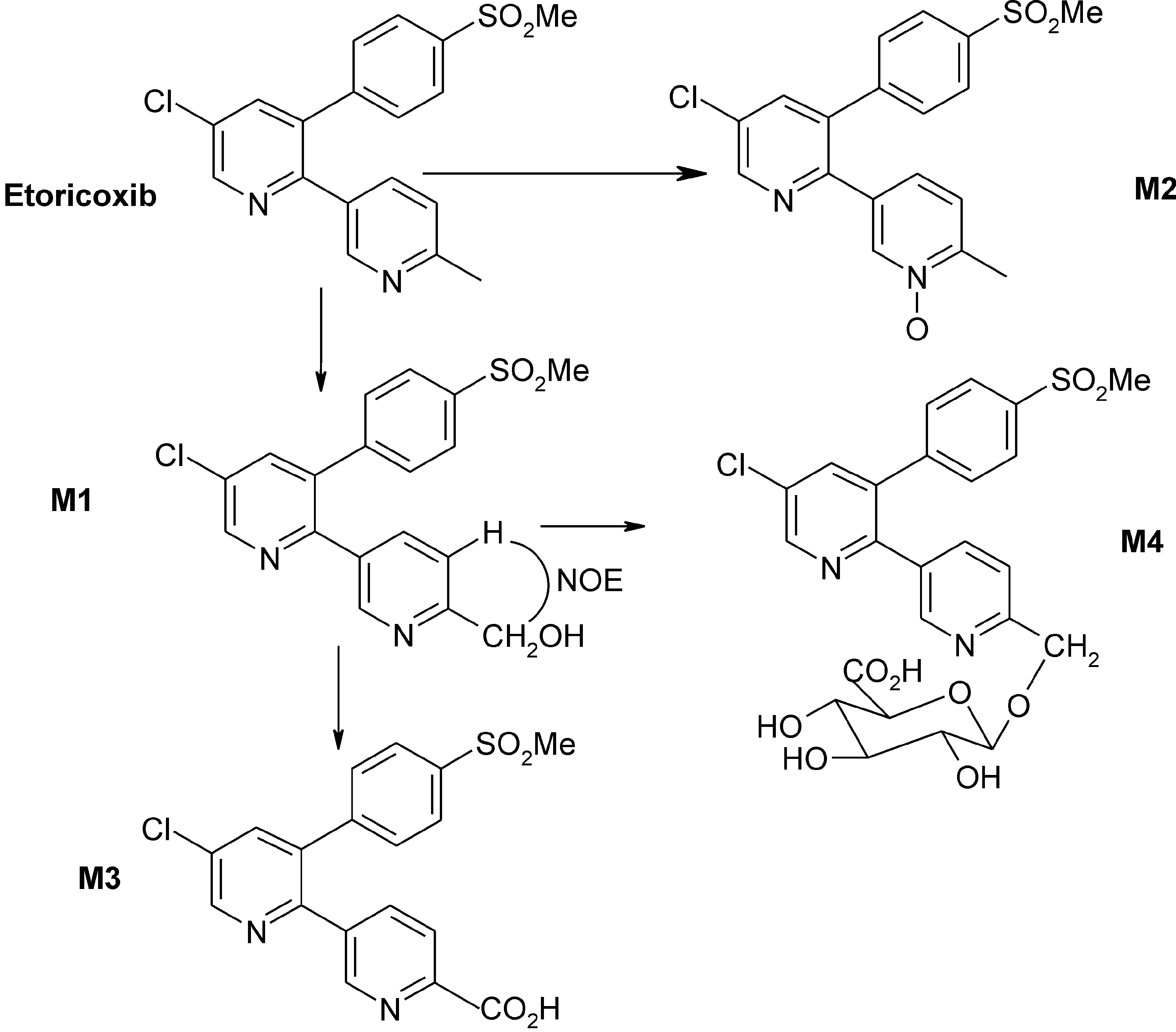
In vitro metabolic pathways of etoricoxib.
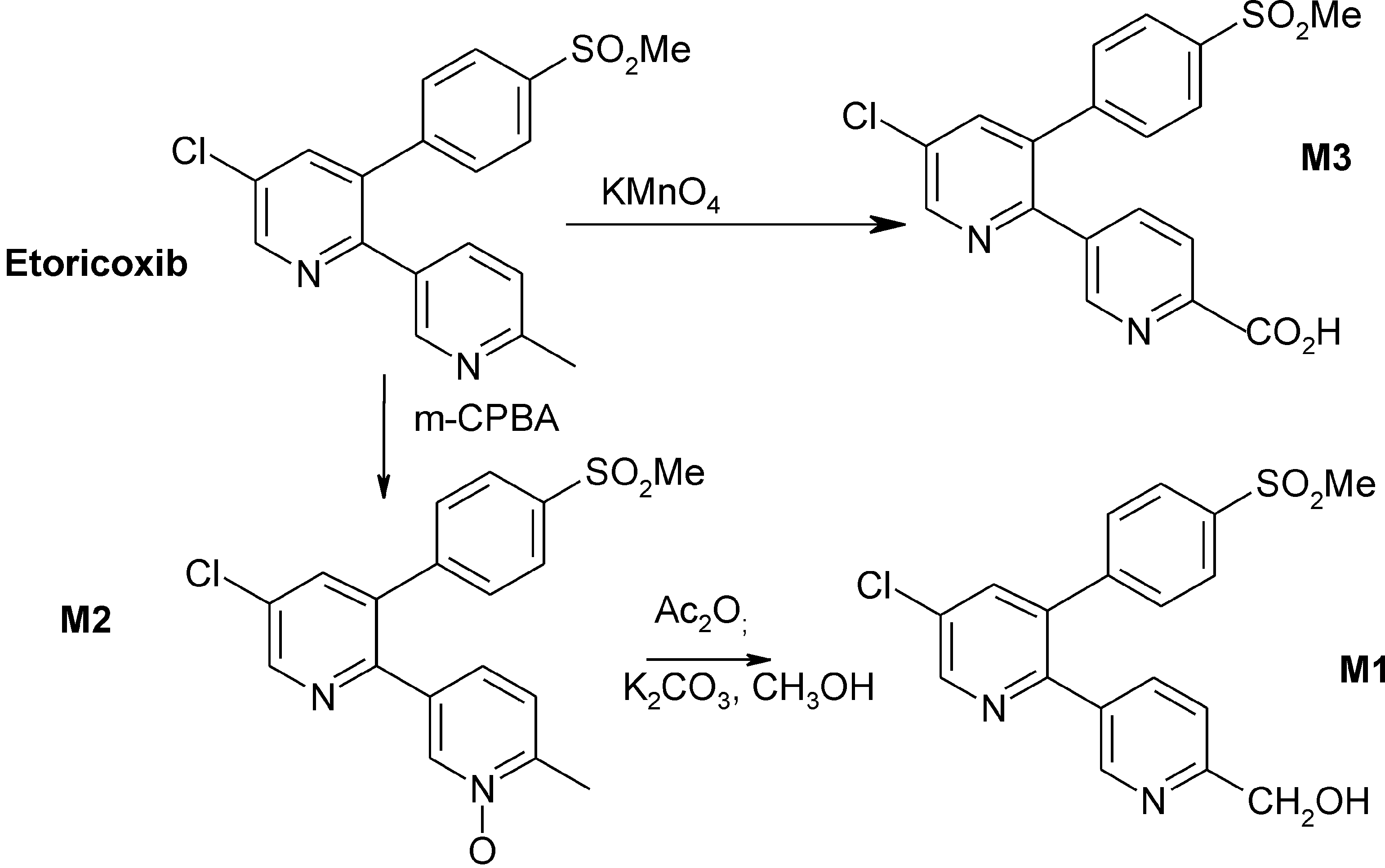
Synthesis of the oxidative metabolites of etoricoxib.
CAS number: 202533-71-9
Heliespirone A is a member of cyclohexenones.
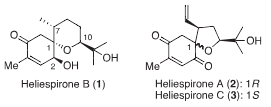
Structures of heliespirons: Heliespirone B, Heliespirone A, Heliespirone C.
CAS number: 20268-71-7
Hydroxymatairesinol (HMR) is a lignan, a type of phytoestrogen, found in Norway spruce (Picea abies). It's known for its potential anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties, and it acts as a precursor to enterolactone, a compound studied for its health benefits.
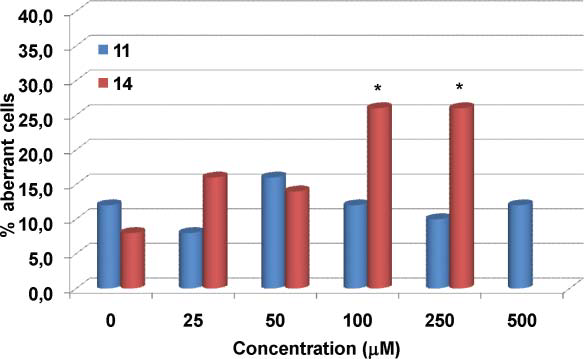
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the lignan 7-hydroxymatairesinol 11 and its catechol derivative 14 in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 205110-48-1
Cethromycin is a 3-keto (ketolide) derivative of erythromycin A with an 11,12-carbamate group and an O-6-linked aromatic ring system. Cethromycin represents a joint development effort by Abbott Laboratories, Taisho Pharmaceuticals, and Advanced Life Sciences, intended to be marketed under the trade name Restanza for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. However, after completing phase III clinical trials, it was deemed safe but not sufficiently efficacious by the FDA. Since this time, cethromycin has received FDA orphan drug designations for the prophylactic treatment of anthrax inhalation, plague due to Yersinia pestis, and tularemia due to Francisella tularensis. It has also been investigated, by itself or together with [zoliflodacin], for the treatment of gonorrhea, and was recently suggested as a possible treatment for liver-stage Plasmodium sporozoite infection.
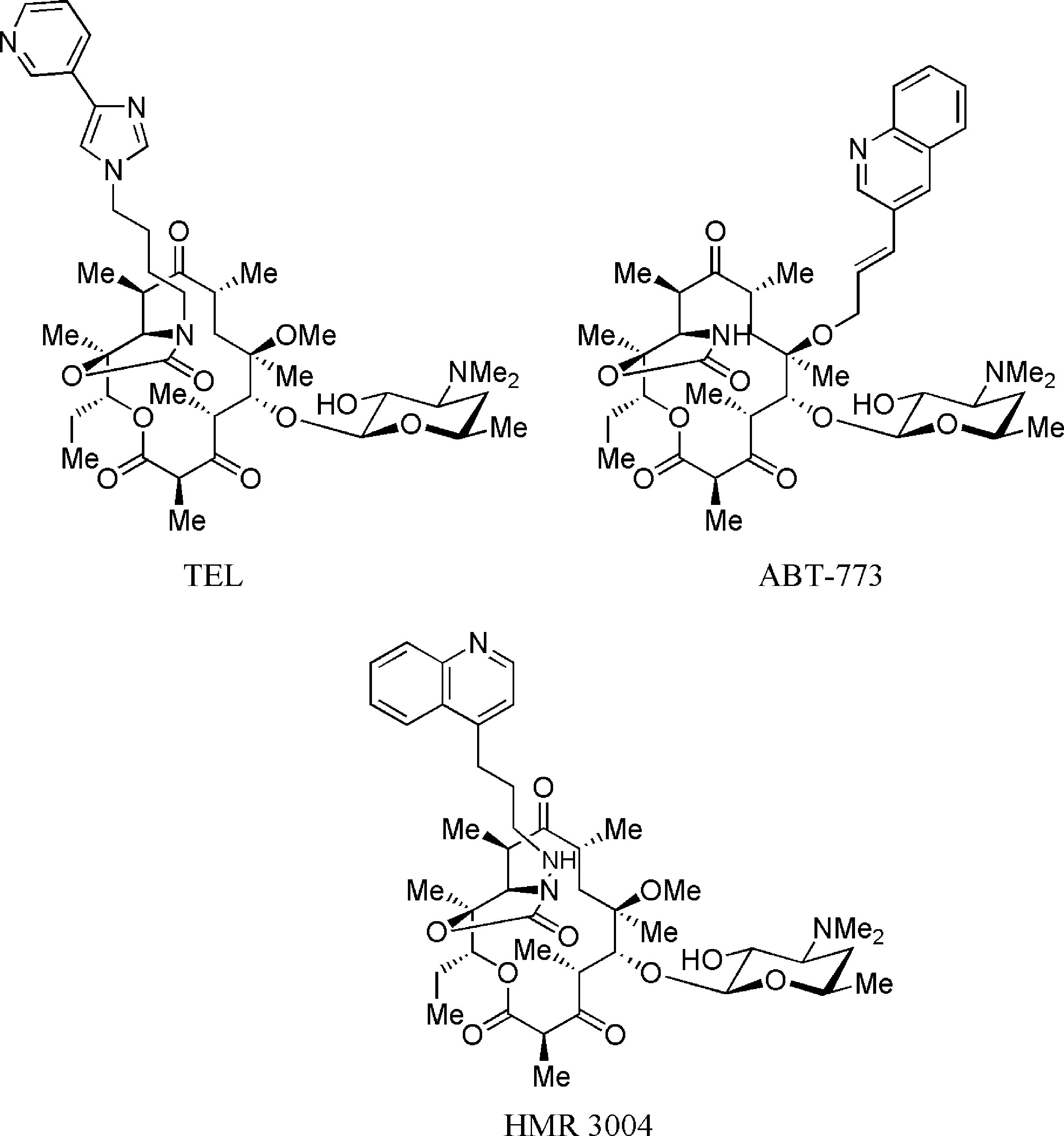
Structures of ketolides: Telithromycin, ABT-773, Hmr 3004.