Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 192703-06-3
SR 144528 is a secondary carboxamide resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 5-(4-chloro-3-methylphenyl)-1-(4-methylbenzyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid with the amino group of (1S,2S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine. A potent and selective cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2 receptor) inverse agonist (Ki = 0.6 nM). It has a role as a CB2 receptor antagonist and an EC 2.3.1.26 (sterol O-acyltransferase) inhibitor. It is a member of pyrazoles, a secondary carboxamide, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a bridged compound.
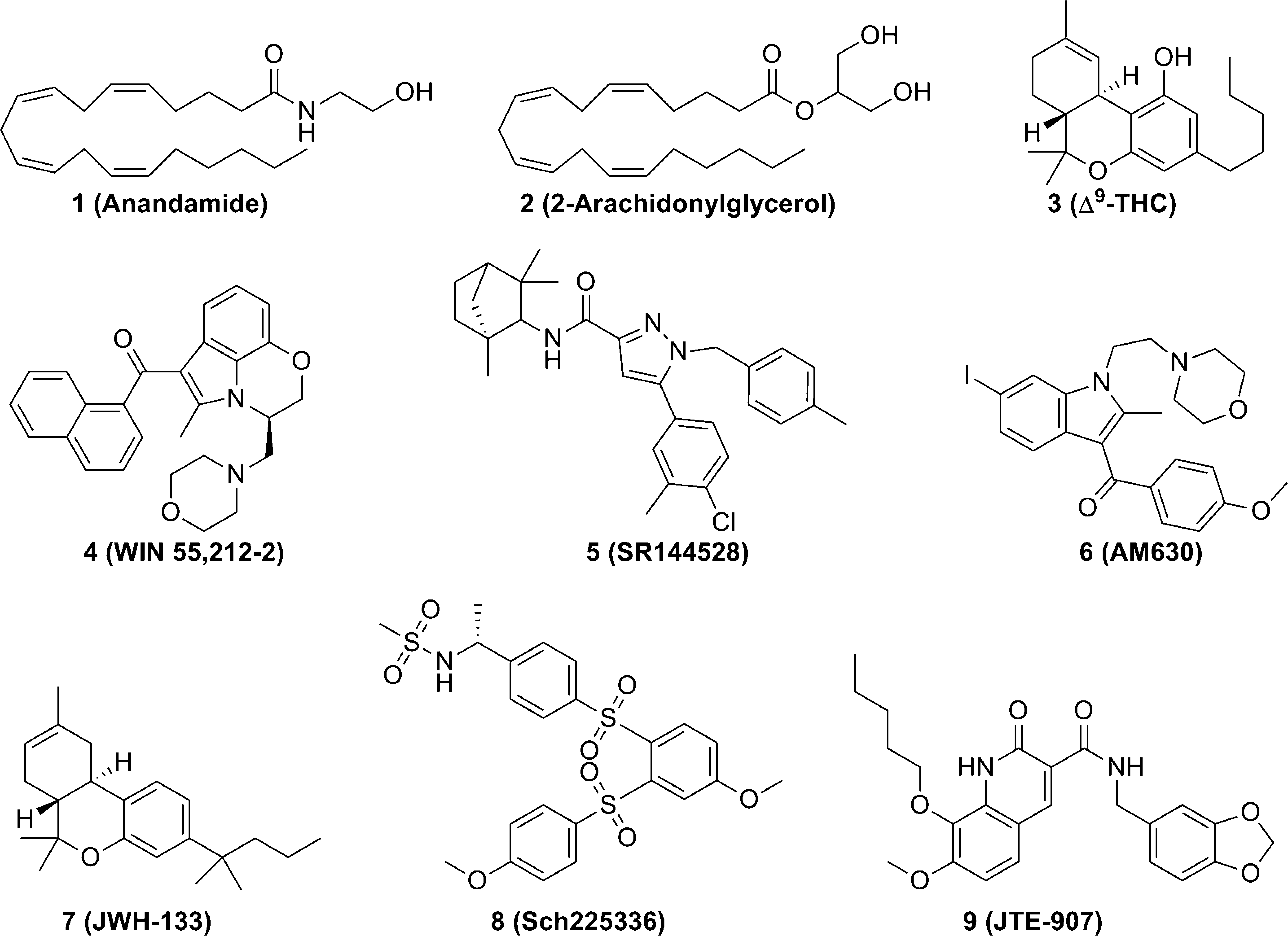
Representative cannabinoids with various chemical scaffolds: Anandamide, 2-Arachidonylglycerol, Win-55212-2, SR 144528, JWH-133, JTE-907.
CAS number: 1943604-24-7
Tubulysin A is a highly cytotoxic peptide with antimitotic activity that induces depletion of cell microtubules and triggers the apoptotic process. Treated cells accumulated in the G2/M phase.
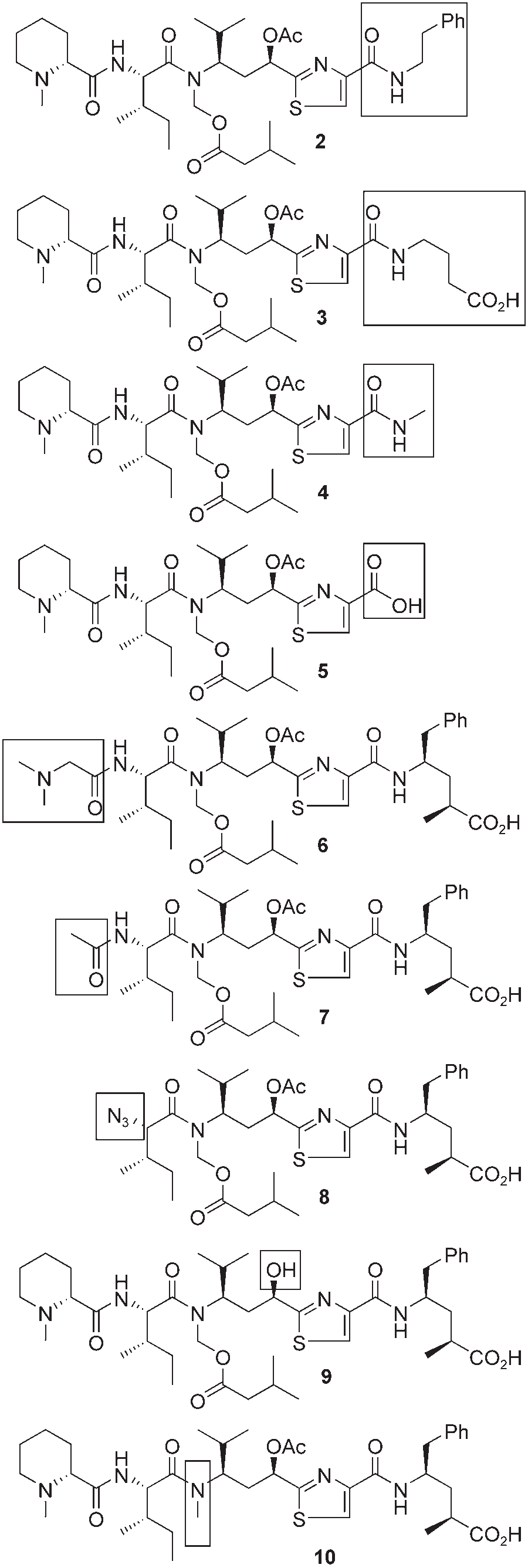
Tubulysin analogues 2–10.
CAS number: 195143-52-3
Argpyrimidine is a member of the class of hydroxypyrimidines obtained by cyclocondensation of L-arginine and methylglyoxal.
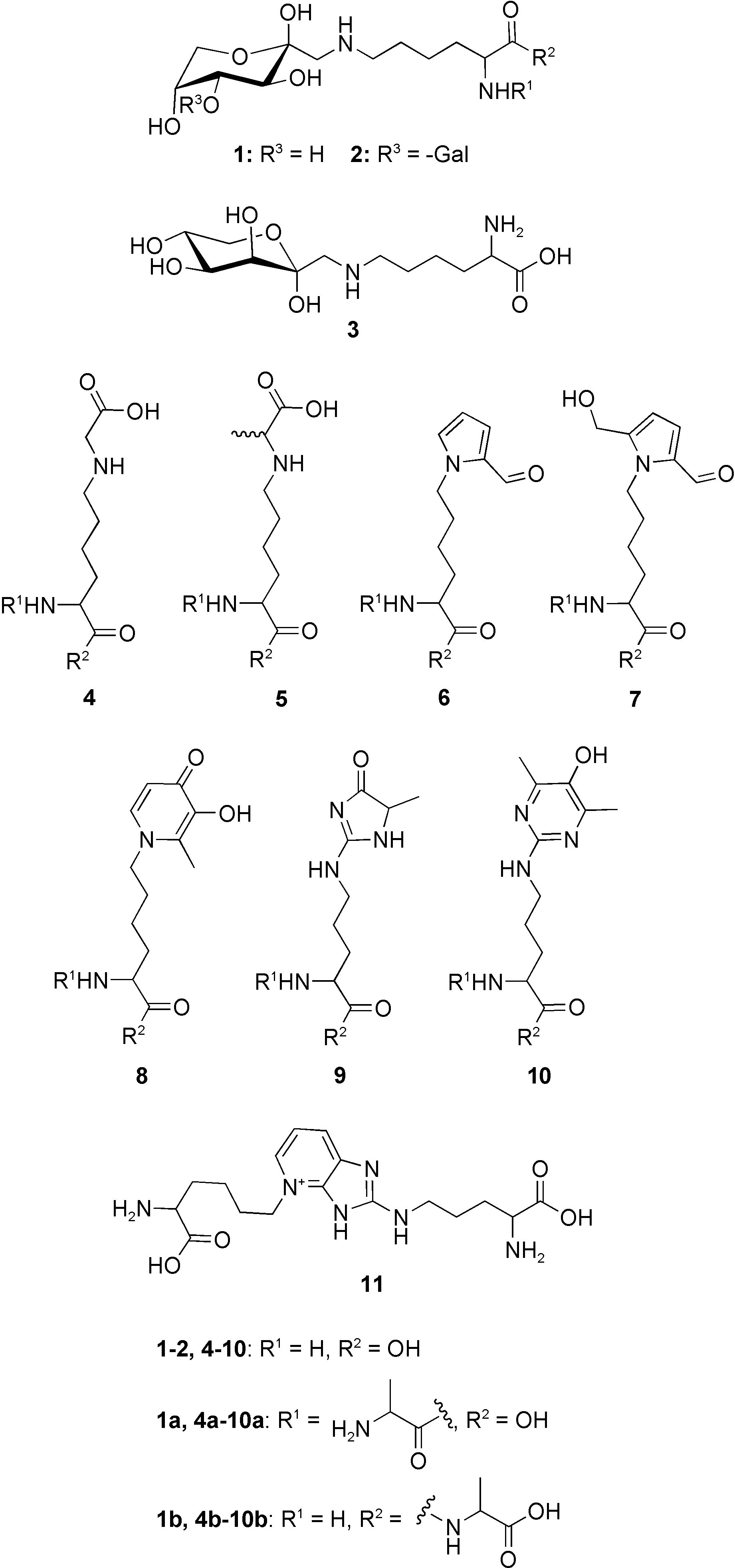
Chemical structures of the investigated Maillard reaction prod- ucts fructoselysine (1), lactuloselysine (2), tagatoselysine (3), CML (4), CEL (5), formyline (6), pyrraline (7), maltosine (8), MG-H1 (9), argpyrimidine (10), and pentosidine (11).
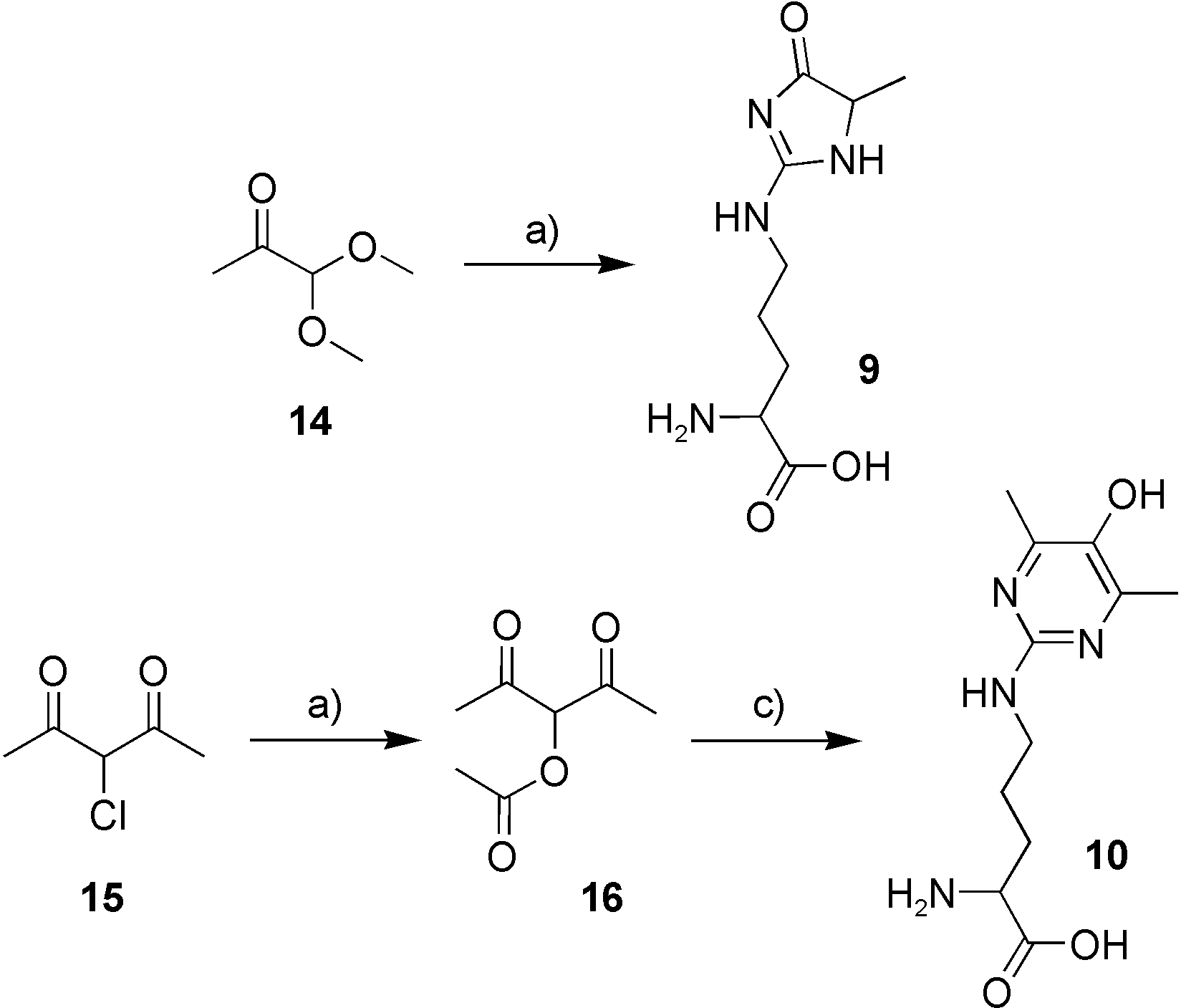
Syntheses of N5-(5-methyl-4-oxo-5-hydroimidazolon-2-yl)-l-ornithine (MG-H1, 9) and N5-(5-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-l-ornithine (argpyrimidine, Apy, 10). a) l-Arg, HCl (12n), RT, 8 h. b) DMSO, NaOAc, RT, 3 h. c) l-Arg, HCl (12n), RT, 20 h.
CAS number: 19545-26-7
Wortmannin is an organic heteropentacyclic compound, a delta-lactone, an acetate ester and a cyclic ketone. It has a role as an EC 2.7.1.137 (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) inhibitor, an anticoronaviral agent, a geroprotector, an autophagy inhibitor, a Penicillium metabolite, a radiosensitizing agent and an antineoplastic agent.
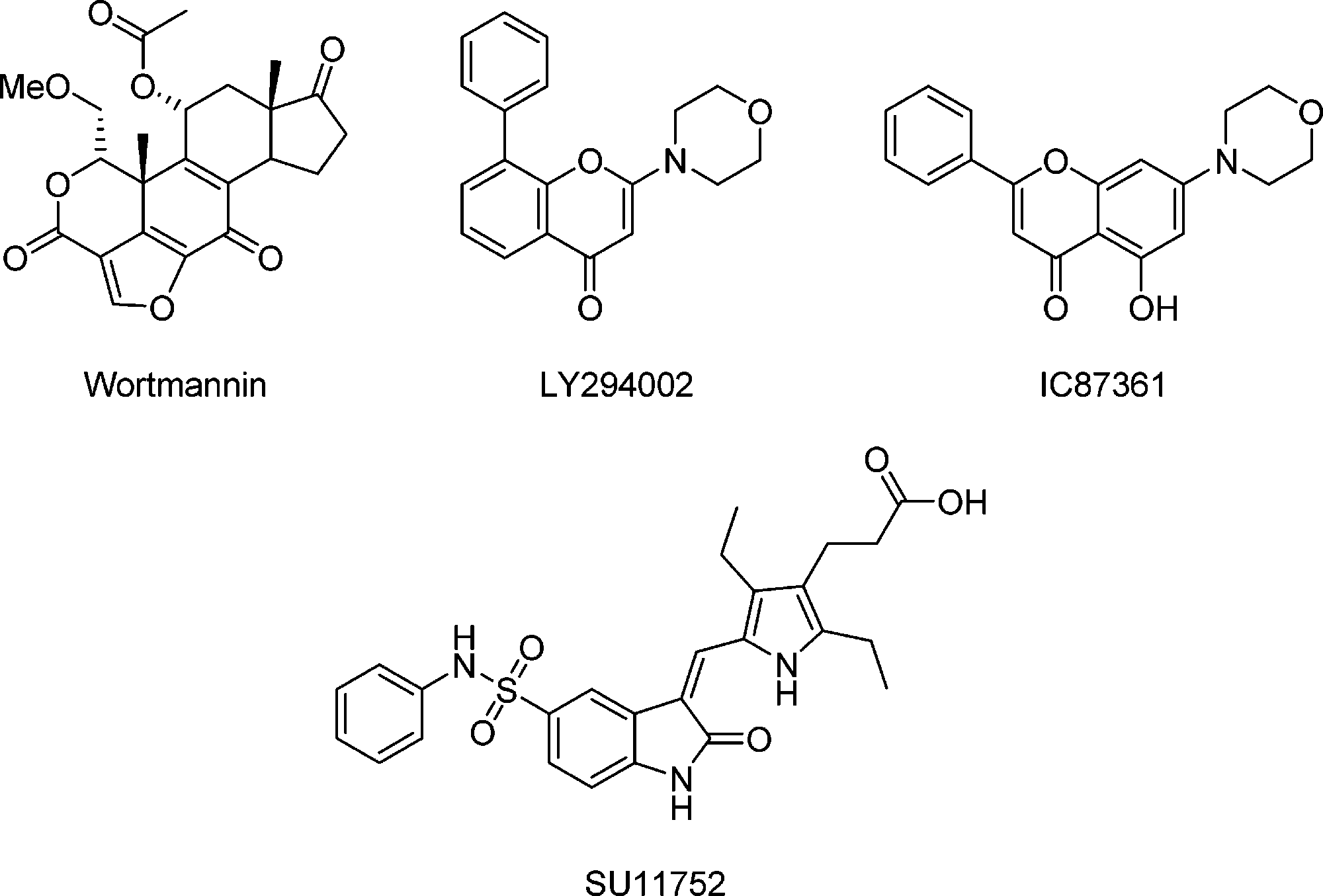
Structures of DNA-PK Inhibitors: wortmannin, LY294002, IC87361, SU11752.
CAS number: 196618-13-0
Oseltamivir is a cyclohexenecarboxylate ester that is the ethyl ester of oseltamivir acid. An antiviral prodrug (it is hydrolysed to the active free carboxylic acid in the liver), it is used to slow the spread of influenza.
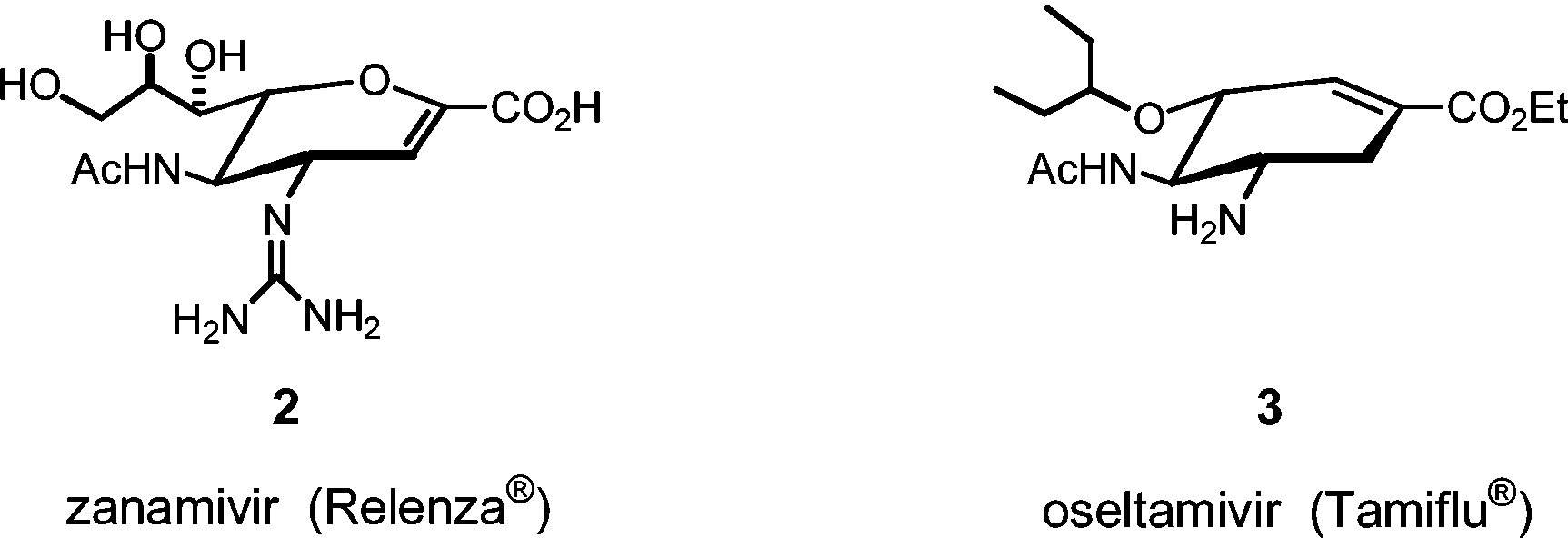
Commercially available neuraminidase inhibitors.
CAS number: 1968-28-1
1,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one is an imidazolinone.
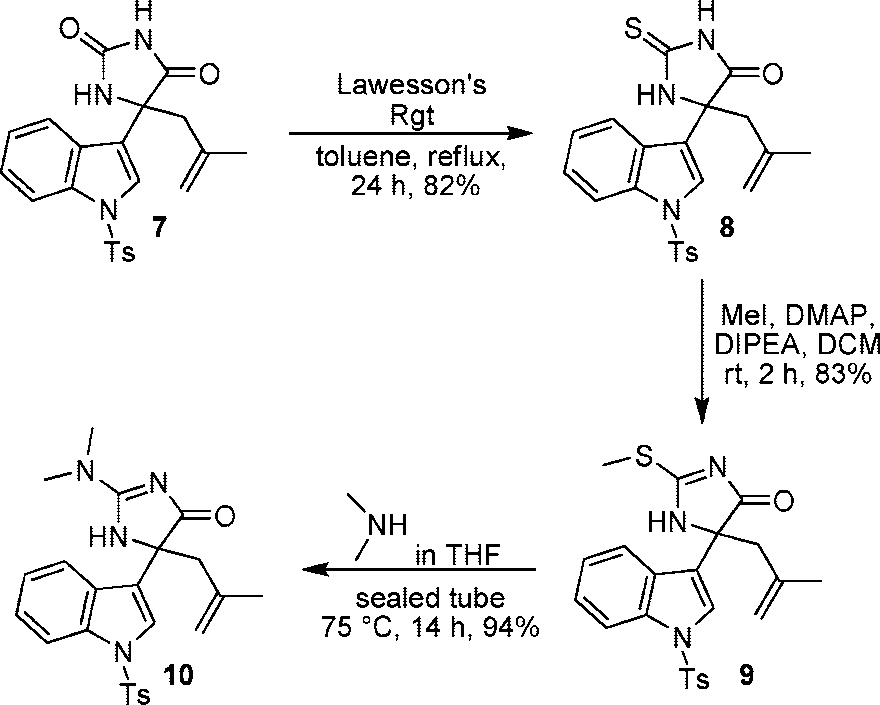
Synthesis of Alkaloid (1): Formation of Imidazolone (10)
CAS number: 1972-28-7
Diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH2O2CN=NCO2CH2CH3, commonly used as an activating reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in the Mitsunobu reaction. It is an orange-red liquid that can be dangerous, as it is thermally unstable and can explode when heated.
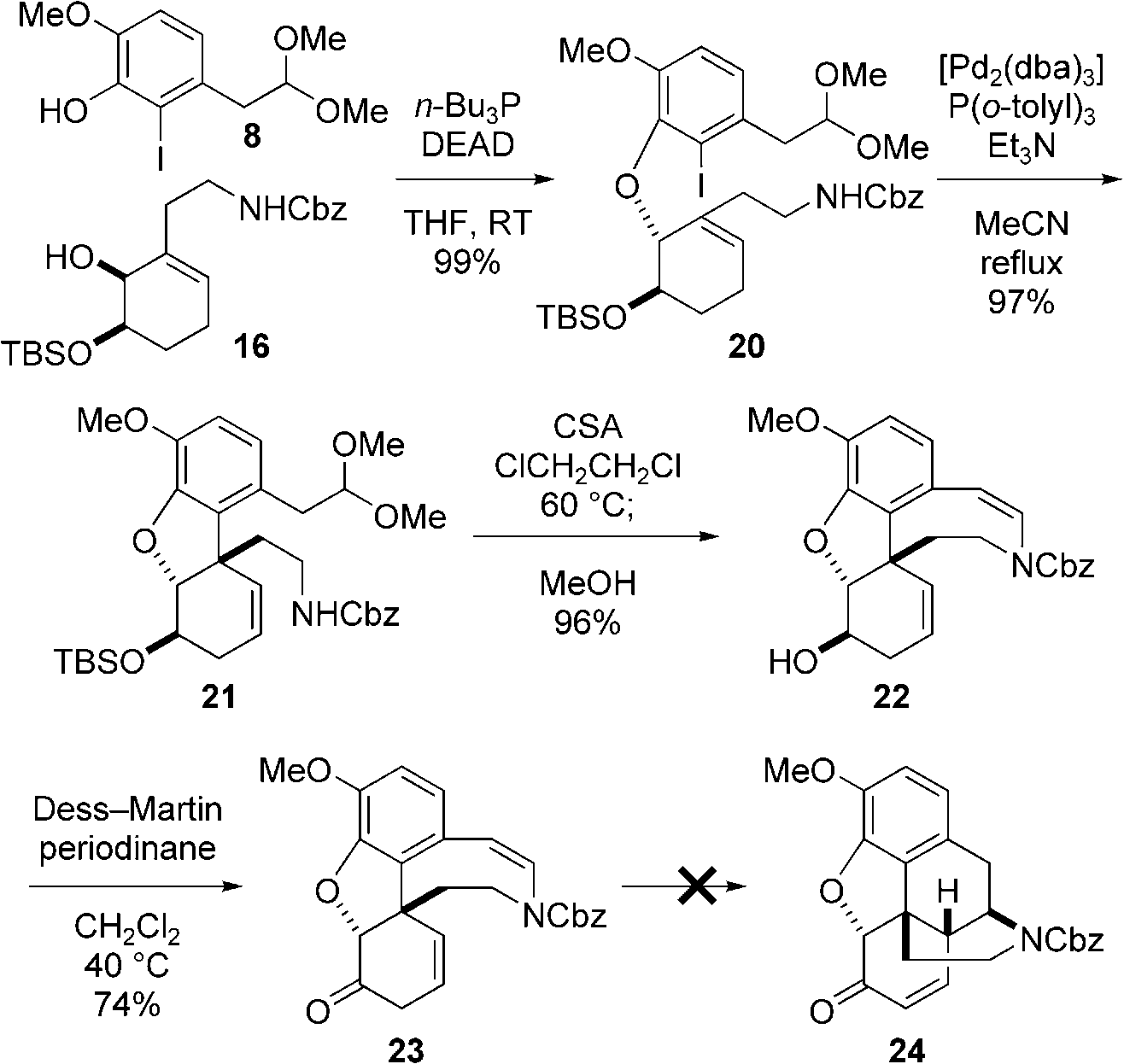
Attempted Mannich-type reaction. DEAD=diethyl azodicarboxylate, dba=(E,E)-dibenzylideneacetone, CSA=camphorsulfonic acid.
CAS number: 19794-93-5
Trazodone is triazolopyridine derivative from the serotonin receptor antagonists and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs) class of antidepressants. It is used in adults and has been shown to be comparable in efficacy to other drugs such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin-norepinephrine receptor inhibitor (SNRIs) in the treatment of depression. A unique feature of this drug is that it does not promote the anxiety symptoms, sexual symptoms, or insomnia, which are commonly associated with SSRI and SNRI therapy. Trazodone acts on various receptors, including certain histamine, serotonin, and adrenergic receptors, distinguishing it from other antidepressants that cover a narrow range of neurotransmitters. It was initially granted FDA approval in 1981.
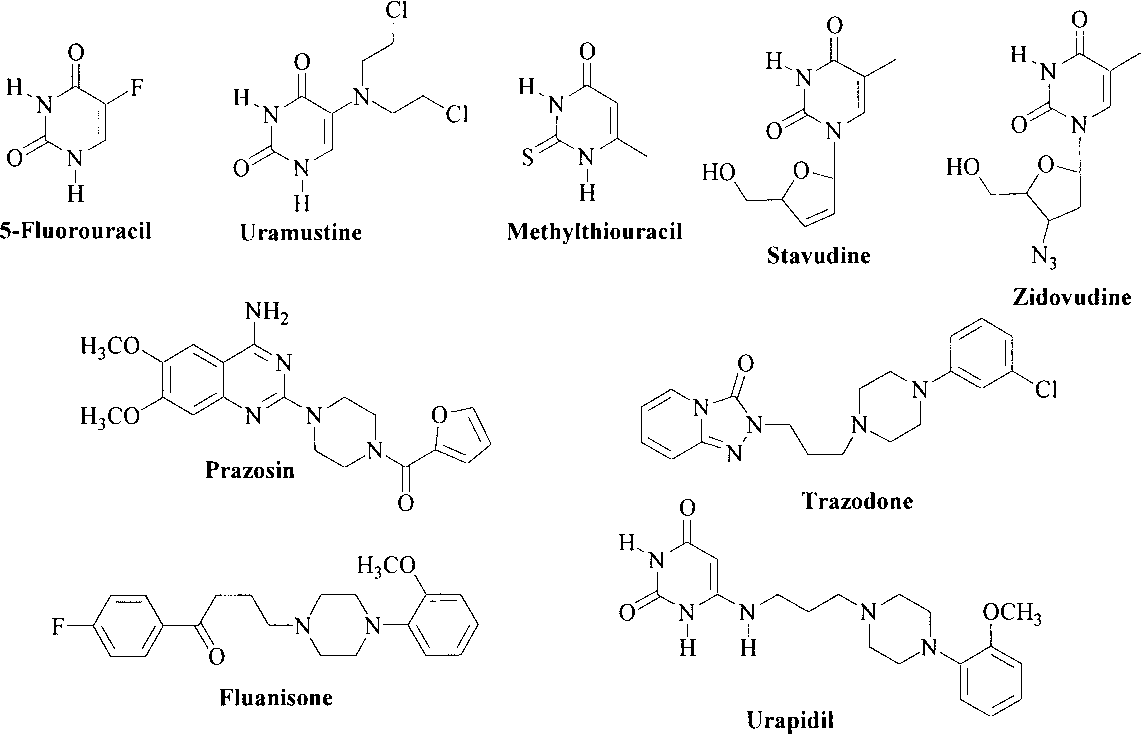
Several Pharmacologically Useful Agents Containing Uracil and Piperazine Moieties: 5-Fluorouracil, Uramustine, Methylthiouracil, stavudine, zidovudine, prazosin, trazodone, Fluanisone, urapidil.
CAS number: 198756-82-0
(S)-1-(2-Nitrophenyl)ethanamine is an organic chemical compound, specifically a chiral amine. It's also known as (1S)-1-(2-Nitrophenyl)ethylamine or, in some contexts, as (S)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethan-1-amine.
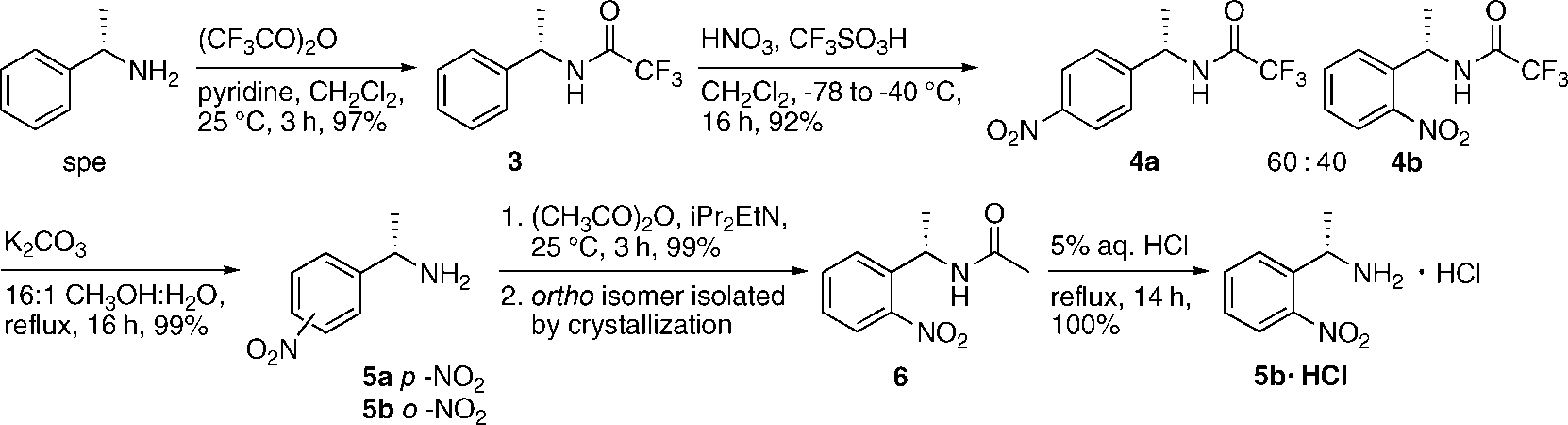
Synthesis of (S)-1-(2-Nitrophenyl)ethanamine (s2ne, 5b)