Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 7087-68-5
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) is a tertiary amino compound. It is a colorless liquid and is also known as Hunig's base.
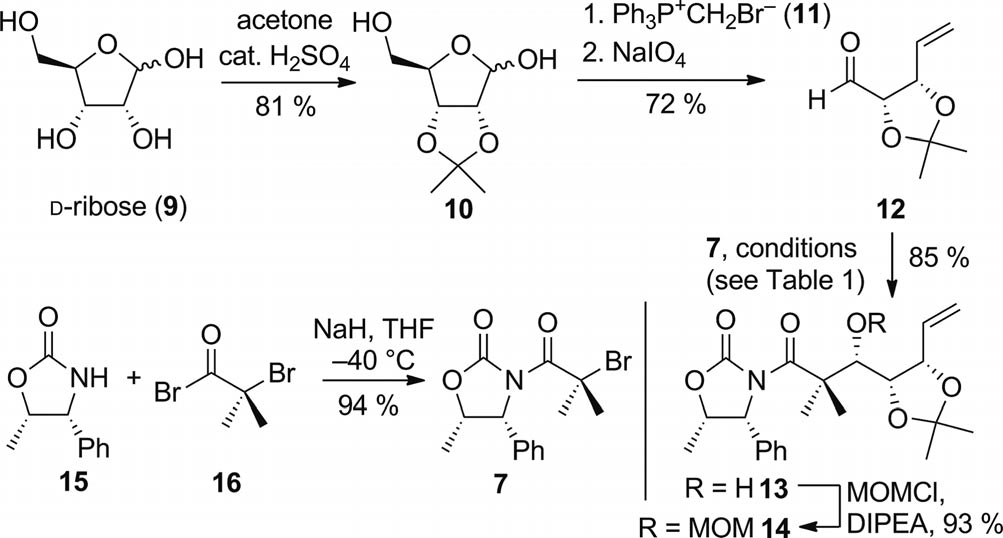
Preparation of alkene 14 (DIPEA = N,N-diisopropyl-ethylamine).
![Peptoid-synthesis-inspired modular assembly of azaxylylene precursors and their cyclizations. [a] Acetal hydrolysis step is required only in the a (i.e. benzaldehyde) series. [b] Major diastereomer is shown, the minor hydroxy epimer (not shown) is denoted with a prime, 16’a etc. Bn=benzyl, DIPEA=diisopropylethylamine, PTS=pyridinium para-tolue-nesulfonate.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3047941_09.png)
Peptoid-synthesis-inspired modular assembly of azaxylylene precursors and their cyclizations. [a] Acetal hydrolysis step is required only in the a (i.e. benzaldehyde) series. [b] Major diastereomer is shown, the minor hydroxy epimer (not shown) is denoted with a prime, 16’a etc. Bn=benzyl, DIPEA=diisopropylethylamine, PTS=pyridinium para-tolue-nesulfonate.
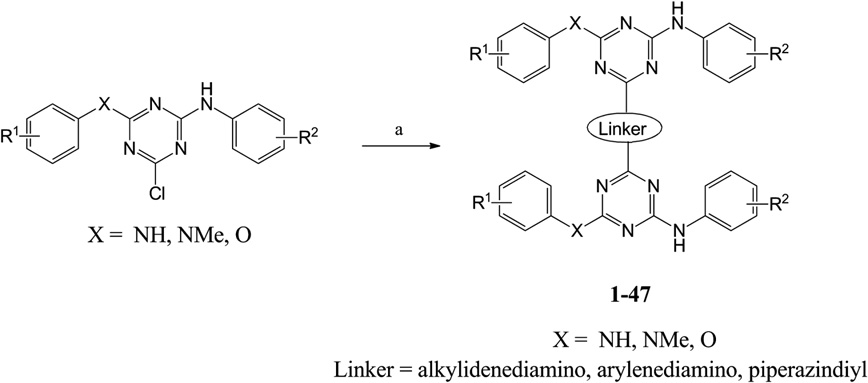
Synthesis of triazine dimers 1–47. Reagents and conditions: (a) diaminoalkanes/diaminobenzene/piperazine, DIPEA, dry dioxane, 110 °C.
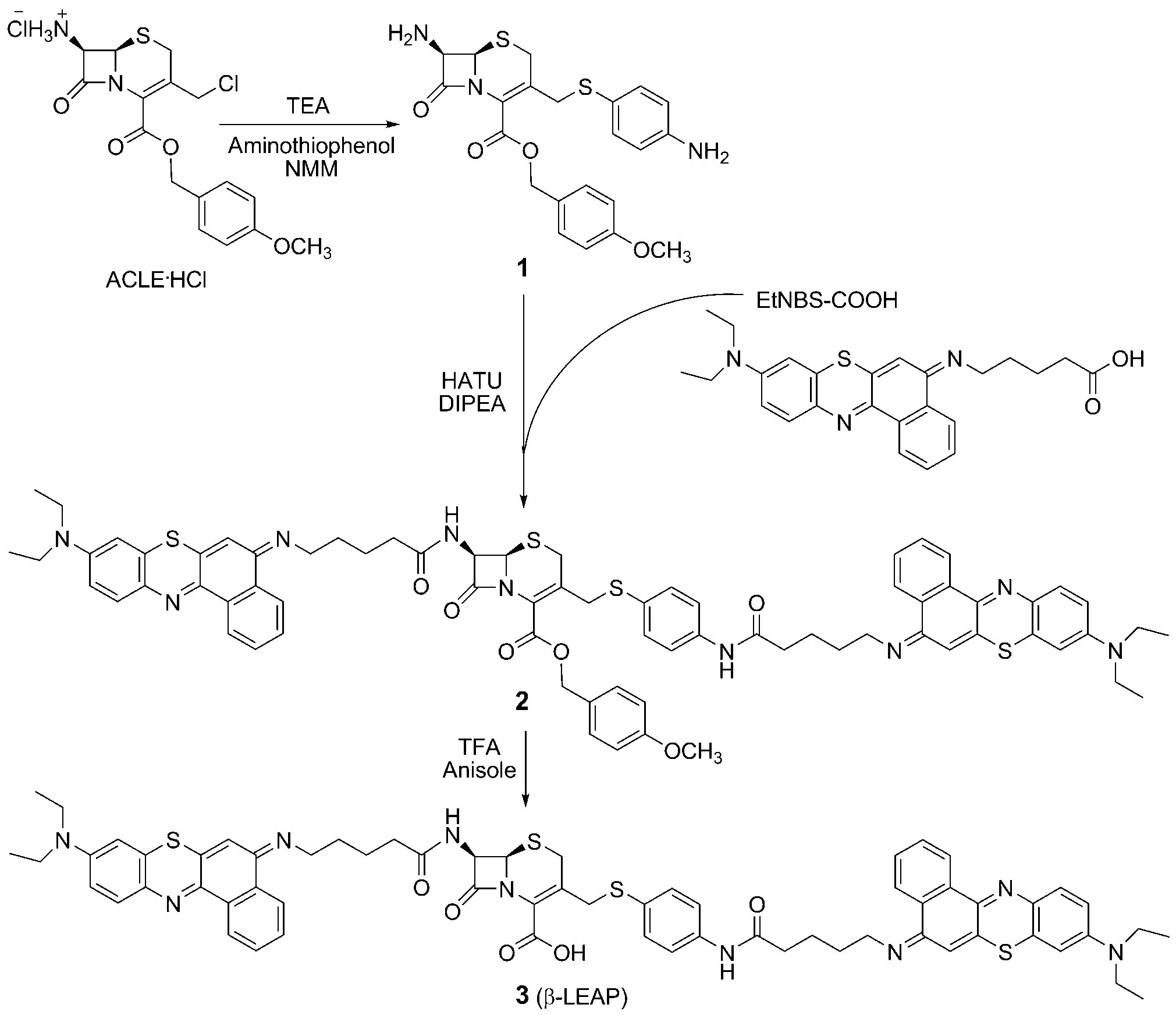
Synthesis of β-LEAP. DIPEA=N,N’-diisopropylethylamine, NMM=4-methylmorpholine, HATU=O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate, TEA=triethylamine, TFA=trifluoroacetic acid.
CAS number: 71-00-1
L-histidine is the L-enantiomer of the amino acid histidine. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a human metabolite, an algal metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a proteinogenic amino acid, a histidine and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a L-histidinium(1+). It is a conjugate acid of a L-histidinate(1-). It is an enantiomer of a D-histidine. It is a tautomer of a L-histidine zwitterion.
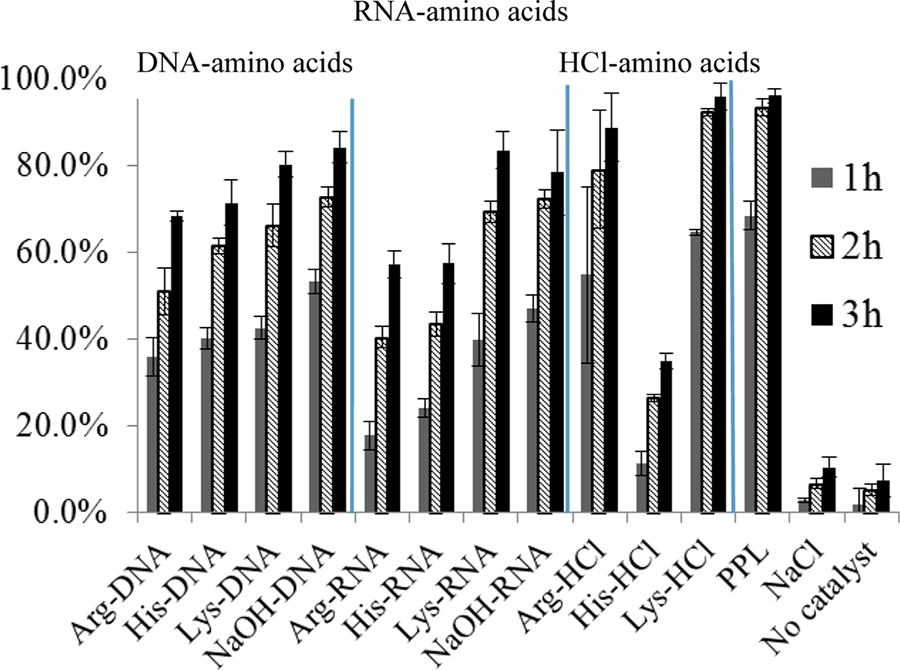
When the nucleotides were neutralized to pH 7.0 with NaOH or basic amino acids (L-lysine, L-arginine, or L-histidine), the reaction rate was significantly accelerated and the yield was comparable to that of porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL, one of the best enzymes for the Knoevenagel condensation reaction) as well as pH-neutral amino acid salts Arg•HCl and Lys•HCl.
CAS number: 71000-82-3
Cyanate is a pseudohalide anion and an organonitrogen compound. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a conjugate base of an isocyanic acid and a cyanic acid.
![Proposed reaction cycle for coordination complex [M] mediated isocyanate formation from CO, N2 and an electron source.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4525612_02.png)
Proposed reaction cycle for coordination complex [M] mediated isocyanate formation from CO, N2 and an electron source.
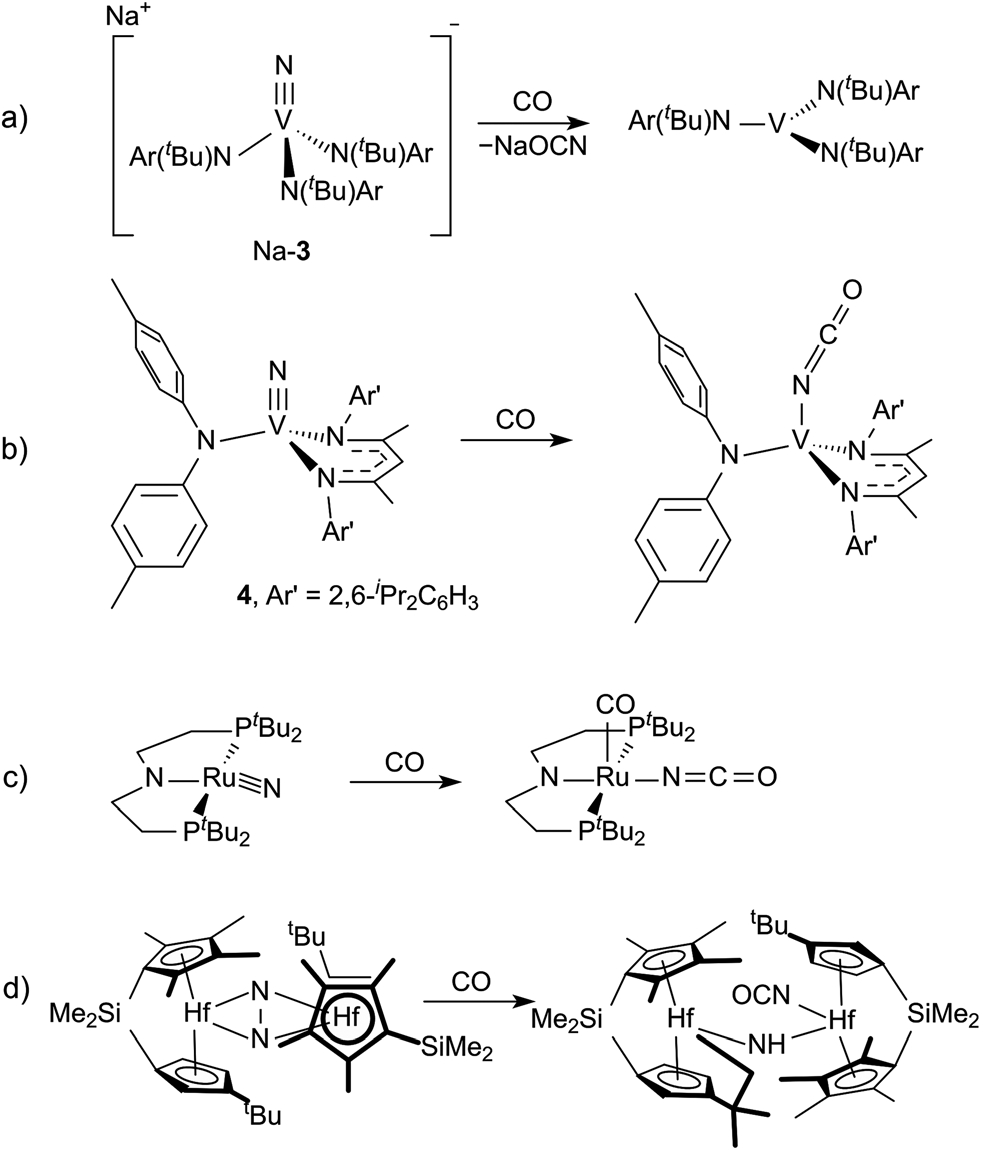
Examples of isocyanate formation from the reduction of N2-derived complexes by CO.
CAS number: 71239-64-0
Flustramine A is a marine-derived brominated alkaloid isolated from the bryozoan Flustra foliacea, classified as a pyrroloindoline with a specific structural arrangement of isoprenyl groups and a bromine atom. It serves as a template for developing compounds with potential applications, including anti-biofilm agents to disrupt bacterial signaling and AChE inhibitors for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
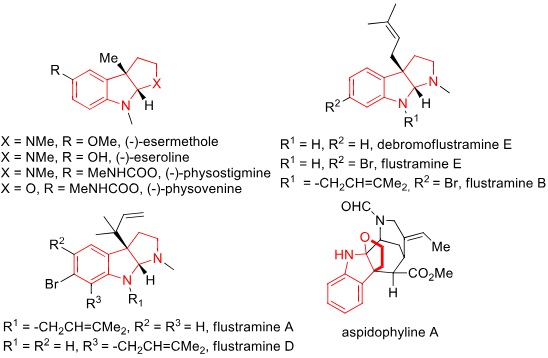
Indole Alkaloids Bearing FIH Skeletons: (-)-Esermethole, (-)-Eseroline, (-)-physostigmine, (-)-Physovenine, Flustramine E, Flustramine B, Flustramine A, Aspidophyline A.
CAS number: 71239-65-1
Flustramine B is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound isolated from the marine bryozoan (Flustra foliacea) and is known to exhibit a range of biological activities, including muscle relaxant and potential anti-cancer properties. It belongs to the family of pyrroloindoline alkaloids, which are complex polyindoline compounds found in various natural sources like amphibians, plants, and marine algae.

Indole Alkaloids Bearing FIH Skeletons: (-)-Esermethole, (-)-Eseroline, (-)-physostigmine, (-)-Physovenine, Flustramine E, Flustramine B, Flustramine A, Aspidophyline A.
CAS number: 71320-77-9
Moclobemide is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV (across all indications) that was first approved in 1990 and is indicated for major depressive disorder and depressive disorder and has 5 investigational indications.
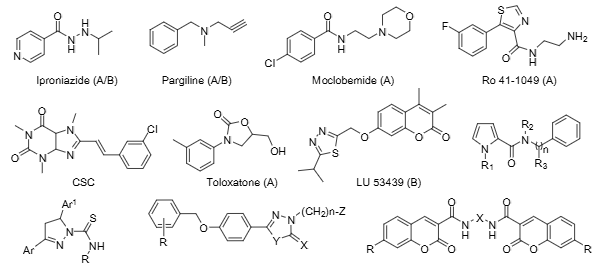
Some representative structures of MAO inhibitors used in research or clinical practice: Iproniazide, Pargiline, Moclobemide, Ro 41-1049, CSC, Toloxatone, LU-53439.
CAS number: 7144-08-3
Cholesteryl chloroformate is used in the preparation of hydrophobized chitosan oligosaccharide and can be used in the application as an efficient gene carrier.
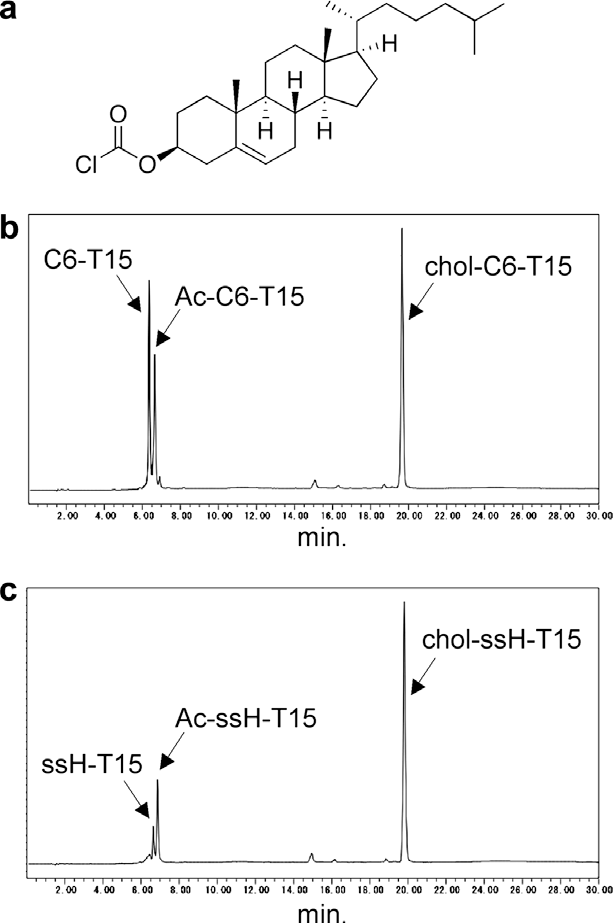
HPLC analyses of the conjugation reactions with cholesteryl chloroformate.
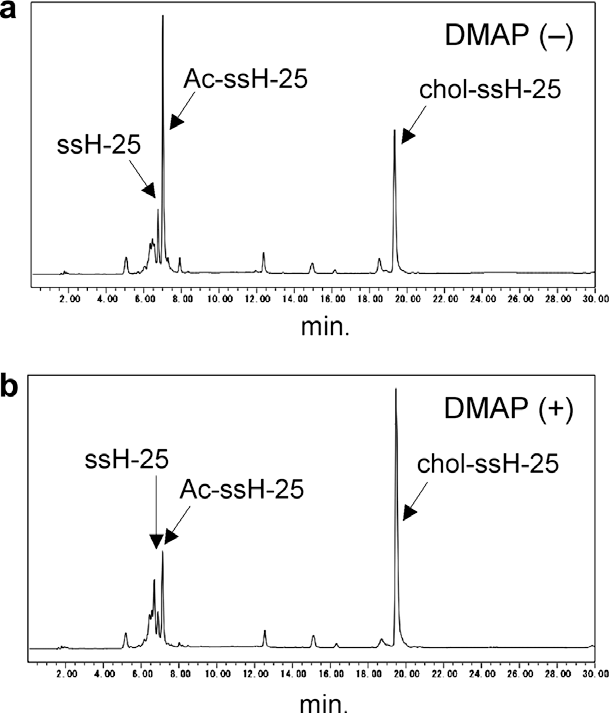
HPLC analyses of the conjugation reactions of ssH-25 with cholesteryl chloroformate.
CAS number: 71812-10-7
Neoxaline is a bioactive fungal alkaloid produced by the fungus Aspergillus japonicus.

Structures of neoxaline (1) and oxaline (2).
CAS number: 72-19-5
An essential amino acid occurring naturally in the L-form, which is the active form. It is found in eggs, milk, gelatin, and other proteins.

Retrosynthetic scheme of L-threonine: (a)–(c).
CAS number: 72-89-9
Acetyl-CoA is an acyl-CoA having acetyl as its S-acetyl component. It has a role as an effector, a coenzyme, an acyl donor and a fundamental metabolite. It is functionally related to an acetic acid and a coenzyme A. It is a conjugate acid of an acetyl-CoA(4-).
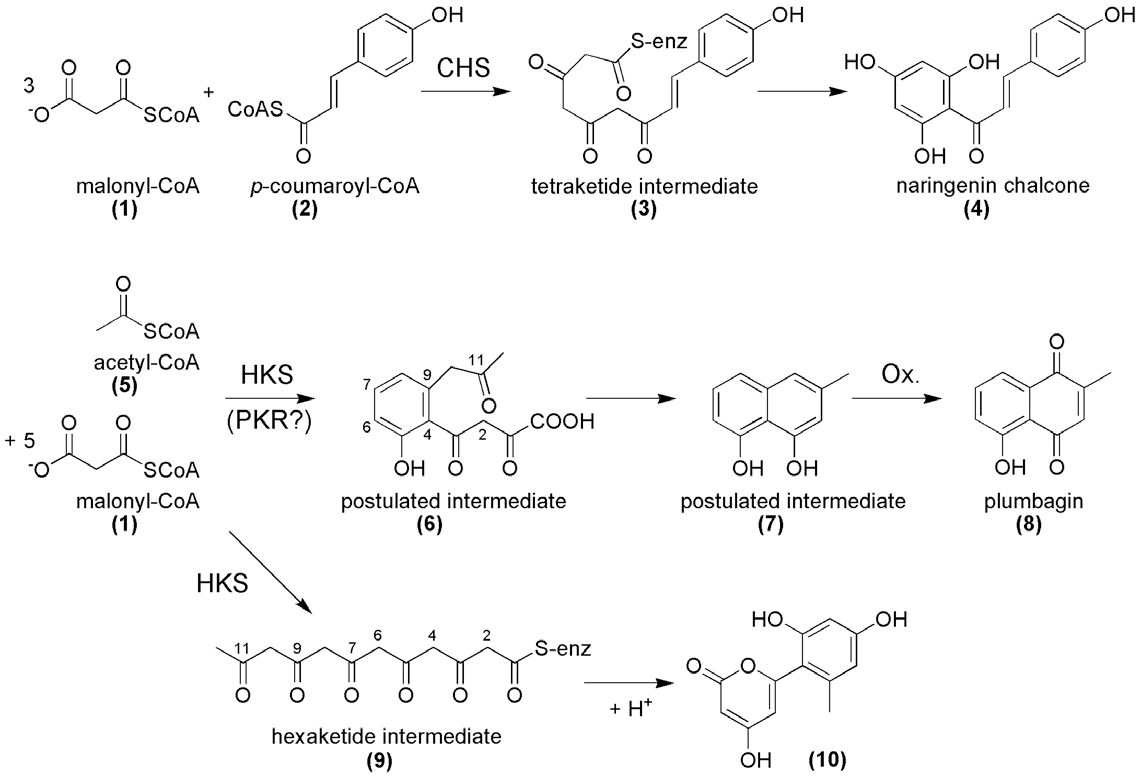
Postulated mechanism of plumbagin biosynthesis and comparison with the reaction of chalcone synthase (CHS). The PKS involved in plumbagin (8) biosynthesis presumably catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of acetyl-CoA (5) with five molecules of malonyl-CoA (1).