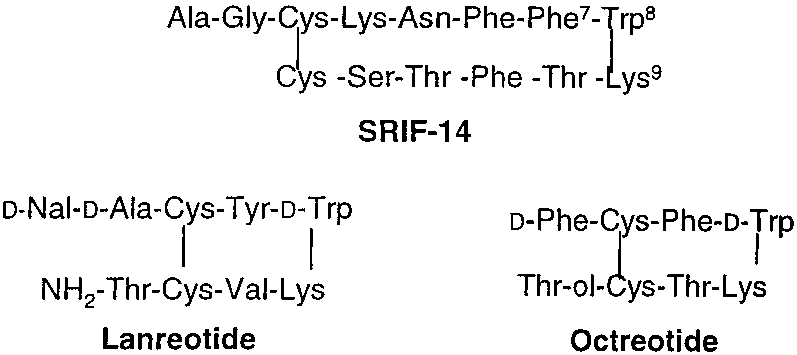
Lanreotide
CAS number: 108736-35-2
Lanreotide is a drug employed in the management of acromegaly (a hormonal condition caused by excess growth hormone) in addition to symptoms caused by neuroendocrine tumors, especially carcinoid syndrome.
Related images
Related Questions and Answers
A: Lanreotide treatment upregulated genes involved in T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, Ras signaling, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways in both responders and non-responders. However, the effects were more pronounced in responders, suggesting that lanreotide may enhance T cell activation and differentiation in these patients.
A: Genes such as TXNIP (thioredoxin-interacting protein), POU2F2 (Oct-2), and IGF1R were found to be differentially expressed in responders versus non-responders. TXNIP was lower in responders across all T cell subsets, while POU2F2 was lower in Th cells and IGF1R was higher in Treg cells of non-responders.
A: Lanreotide treatment significantly affected the expression of genes involved in cytokine signaling, ubiquitination, and proteasome degradation in T cells from responders compared to non-responders. These changes correlated with clinical response to lanreotide therapy.
A: Lanreotide did not significantly affect cytokine production (IL-2 and IFNg), apoptosis, or the activation of transcription factors (NFAT, NF-kB, and ERK1/2) in healthy donor T cells in vitro, even at clinically relevant concentrations.
A: Lanreotide primarily acts by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and hormone secretion through binding to SSTR2 and SSTR5. It also modulates immune function in NET patients, which correlates with clinical response.