Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 58-08-2
Caffeine is a drug of the methylxanthine class used for a variety of purposes, including certain respiratory conditions of the premature newborn, pain relief, and to combat drowsiness. Caffeine is similar in chemical structure to [Theophylline] and [Theobromine]. It can be sourced from coffee beans, but also occurs naturally in various teas and cacao beans, which are different than coffee beans. Caffeine is also used in a variety of cosmetic products and can be administered topically, orally, by inhalation, or by injection. The caffeine citrate injection, used for apnea of the premature newborn, was initially approved by the FDA in 1999. According to an article from 2017, more than 15 million babies are born prematurely worldwide. This correlates to about 1 in 10 births. Premature birth can lead to apnea and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, a condition that interferes with lung development and may eventually cause asthma or early onset emphysema in those born prematurely. Caffeine is beneficial in preventing and treating apnea and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in newborns, improving the quality of life of premature infants.
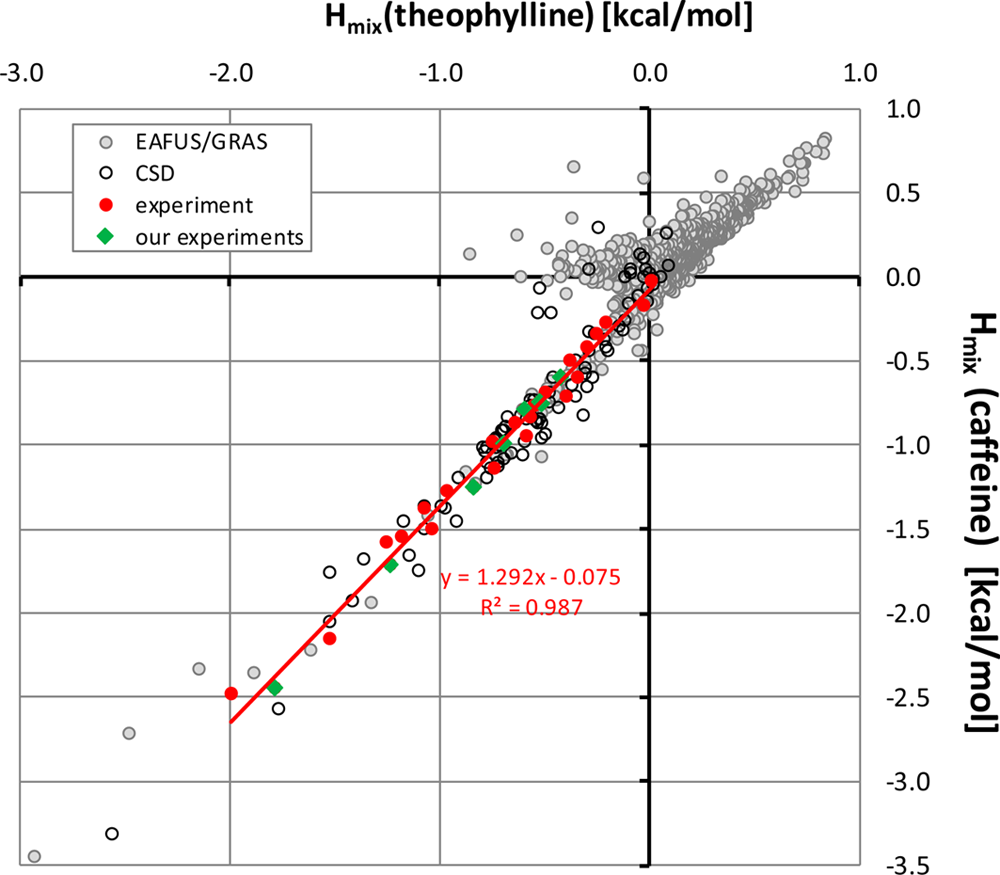
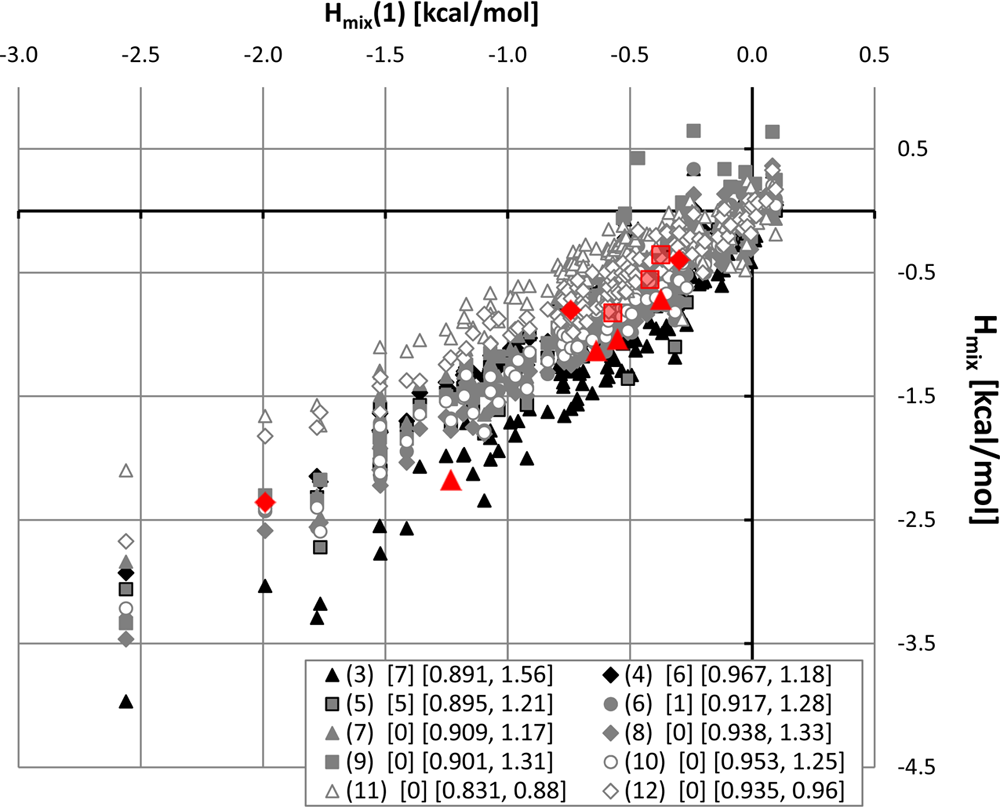
Correlation between mixing enthalpies of caffeine and theophylline. The four series corresponds to different sets of coformers mixed in the liquid state under supercooled conditions.
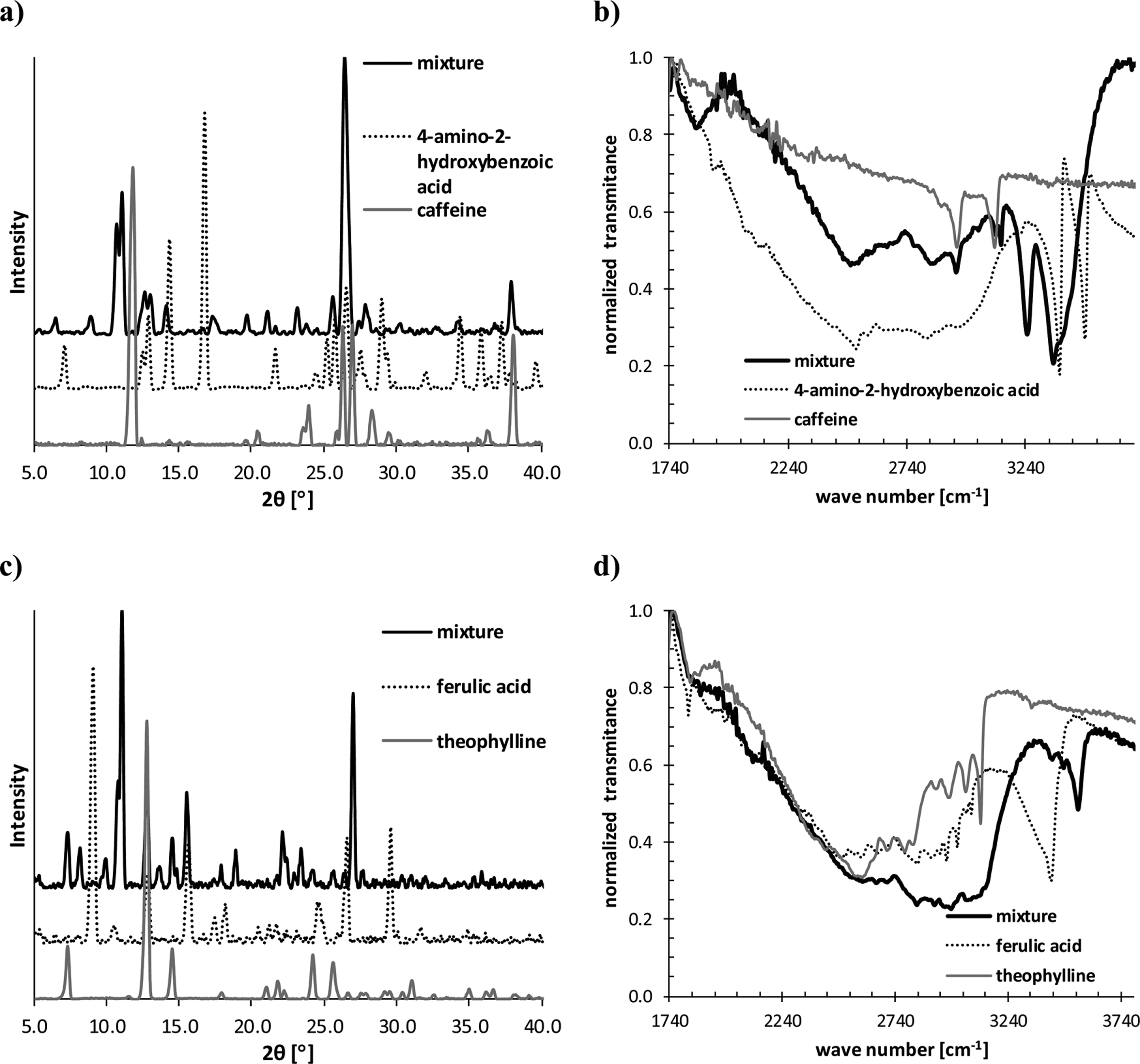
PXRD and FTIR spectra recorded for 1:1 caffeine/4-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid mixture (a, b) and 1:1 theophylline/ferulic acid mixture (c, d) obtained via liquid-assisted grinding.
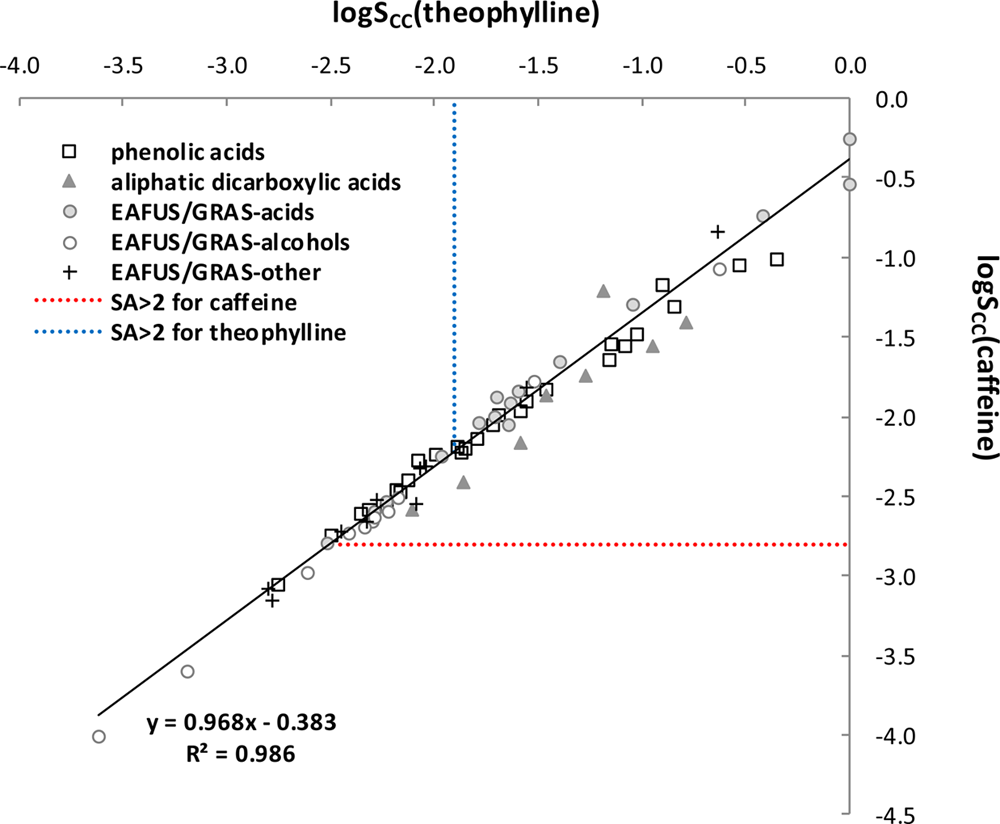
Correlation between estimated solubility values of caffeine and theophylline in the case of cocrystallization with the same coformers in a 1:1 stoichiometry.
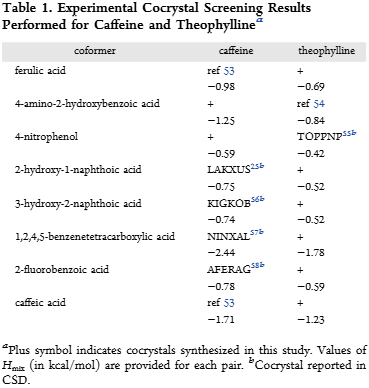
Experimental Cocrystal Screening Results Performed for Caffeine and Theophylline
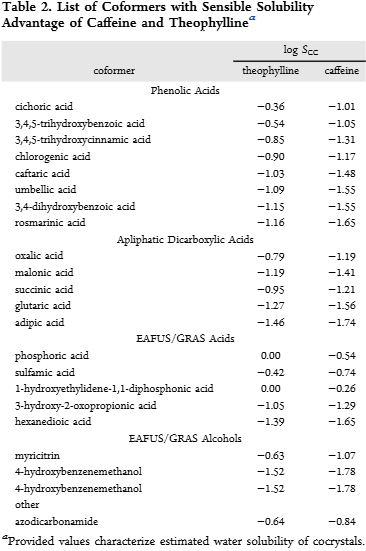
List of Coformers with Sensible Solubility Advantage of Caffeine and Theophylline
CAS number: 58-22-0
Testosterone is an androstanoid having 17beta-hydroxy and 3-oxo groups, together with unsaturation at C-4-C-5.. It has a role as an androgen, a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a 17beta-hydroxy steroid, an androstanoid, a C19-steroid and a 3-oxo-Delta(4) steroid.
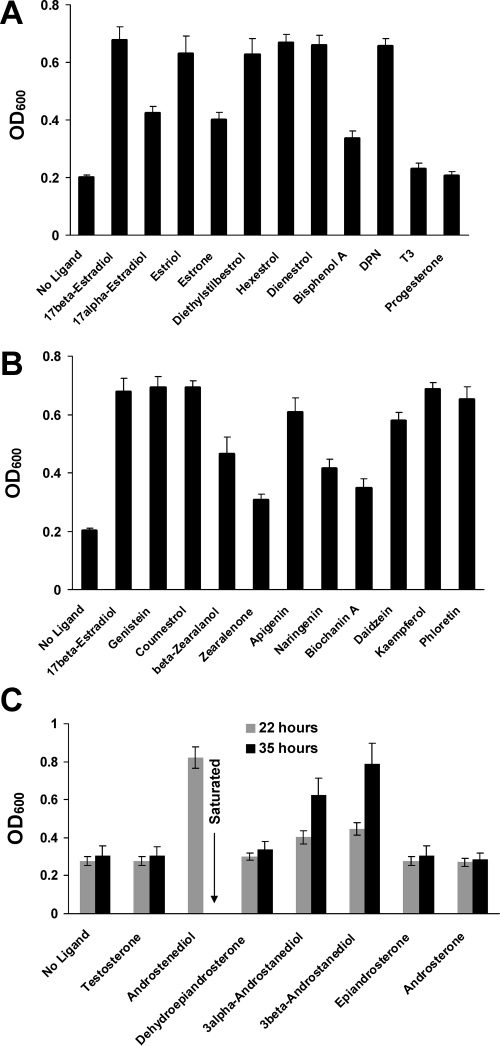
Reliable detection of estrogenic compounds: (A) synthetic estrogen analogues; (B) phytoestrogens; (C) testosterone and some of its metabolic precursors and metabolites.
CAS number: 58-54-8
A compound that inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic.
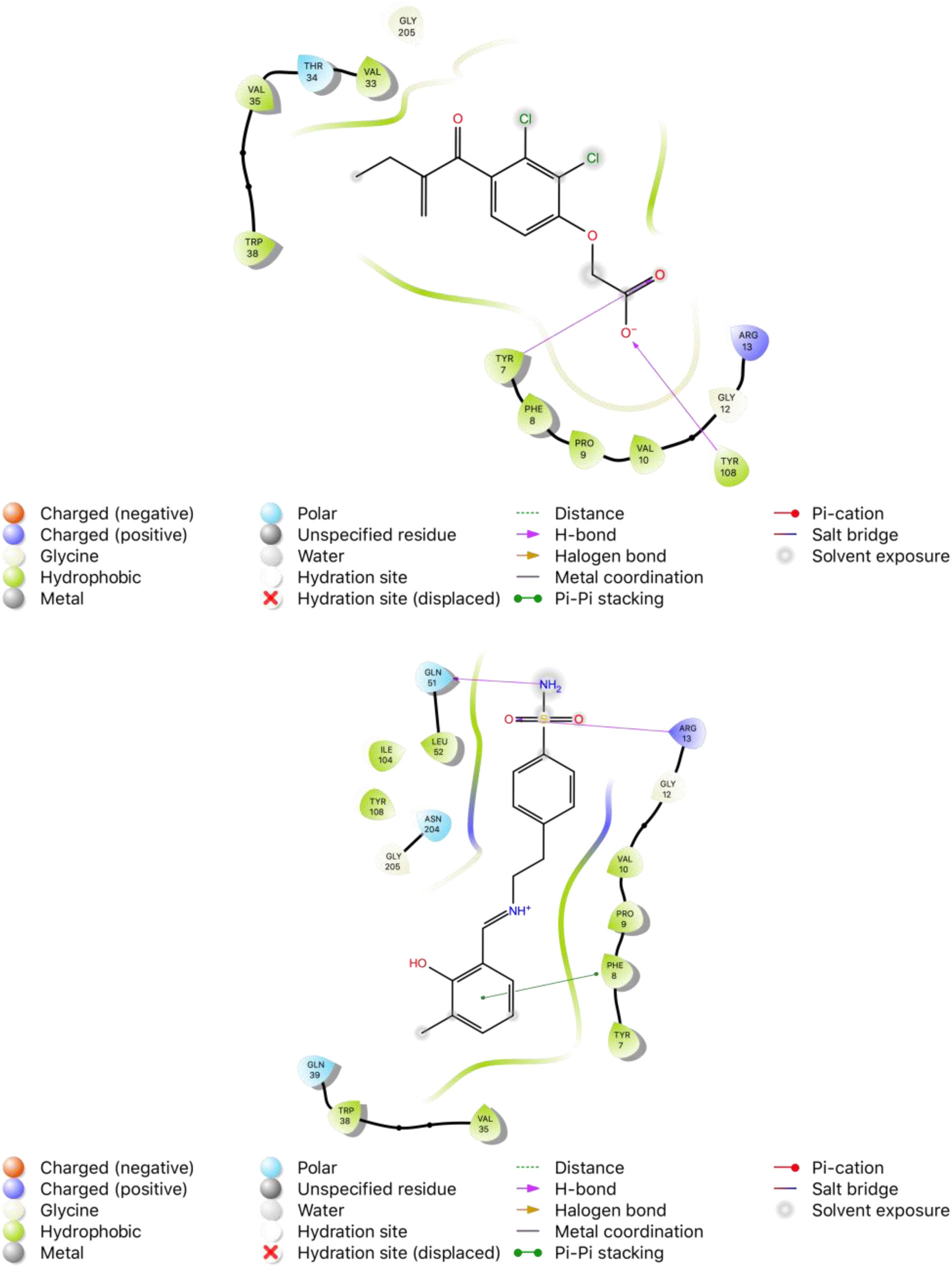
2D binding modes of native ligand ethacrynic acid (EAA) and compound 4 in the active site of GST (PDB ID: 2GSS), respectively.
CAS number: 58-55-9
Theophylline is a dimethylxanthine having the two methyl groups located at positions 1 and 3. It is structurally similar to caffeine and is found in green and black tea. It has a role as a vasodilator agent, a bronchodilator agent, a muscle relaxant, an EC 3.1.4.* (phosphoric diester hydrolase) inhibitor, an anti-asthmatic drug, an anti-inflammatory agent, an immunomodulator, an adenosine receptor antagonist, a drug metabolite, a fungal metabolite and a human blood serum metabolite.

Correlation between mixing enthalpies of caffeine and theophylline. The four series corresponds to different sets of coformers mixed in the liquid state under supercooled conditions.

PXRD and FTIR spectra recorded for 1:1 caffeine/4-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid mixture (a, b) and 1:1 theophylline/ferulic acid mixture (c, d) obtained via liquid-assisted grinding.
Relative values of mixing enthalpies of methylxanthines with respect to theophylline.

Correlation between estimated solubility values of caffeine and theophylline in the case of cocrystallization with the same coformers in a 1:1 stoichiometry.

Experimental Cocrystal Screening Results Performed for Caffeine and Theophylline

List of Coformers with Sensible Solubility Advantage of Caffeine and Theophylline
CAS number: 58-61-7
Adenosine is used for its antiarrhythmic properties in supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and can function as a diagnostic tool, depending on the type of SVT.
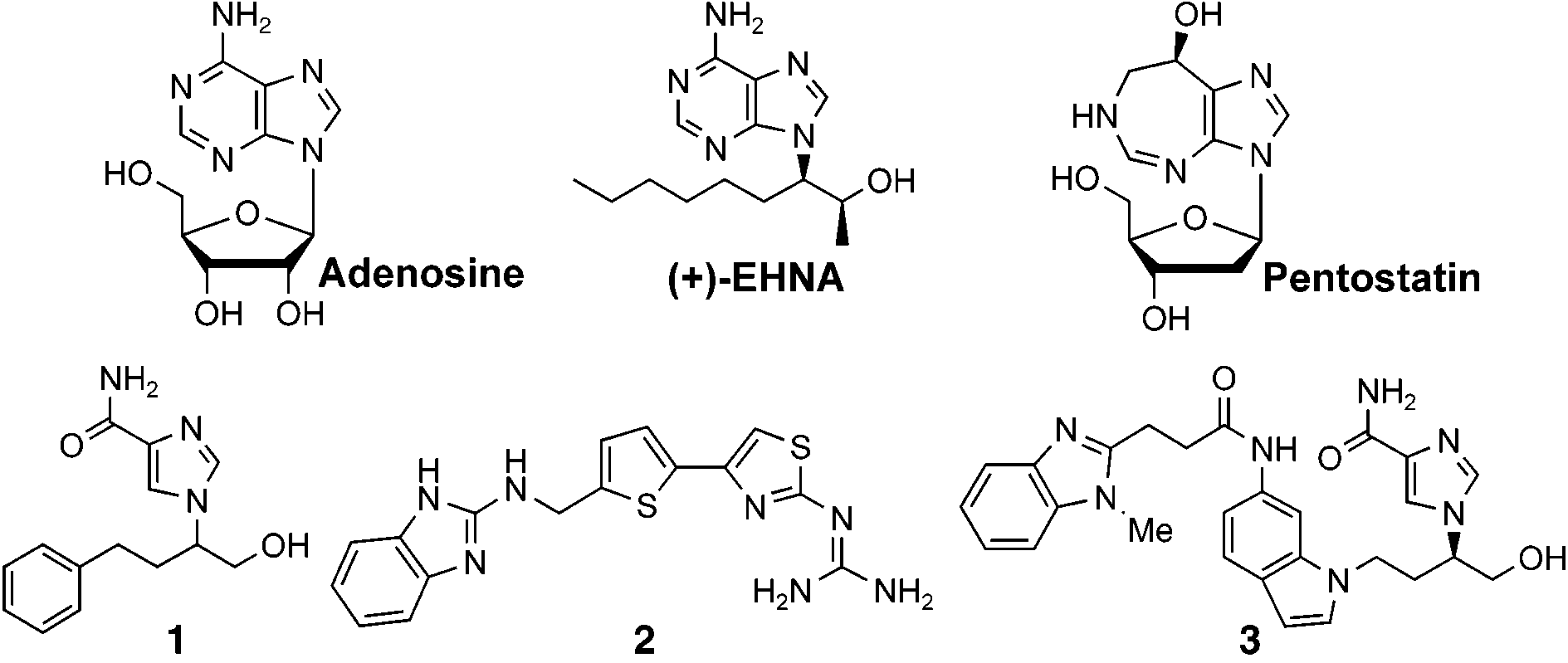
Chemical structures of adenosine and known ADA inhibitors.
CAS number: 58-85-5
Biotin is necessary for formation of fatty acids and glucose, which are used as fuels by the body.
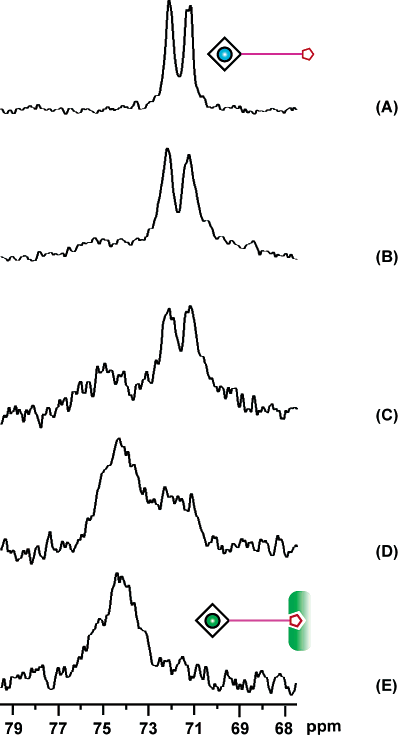
Biotin-avidin binding was detected using Xe NMR.
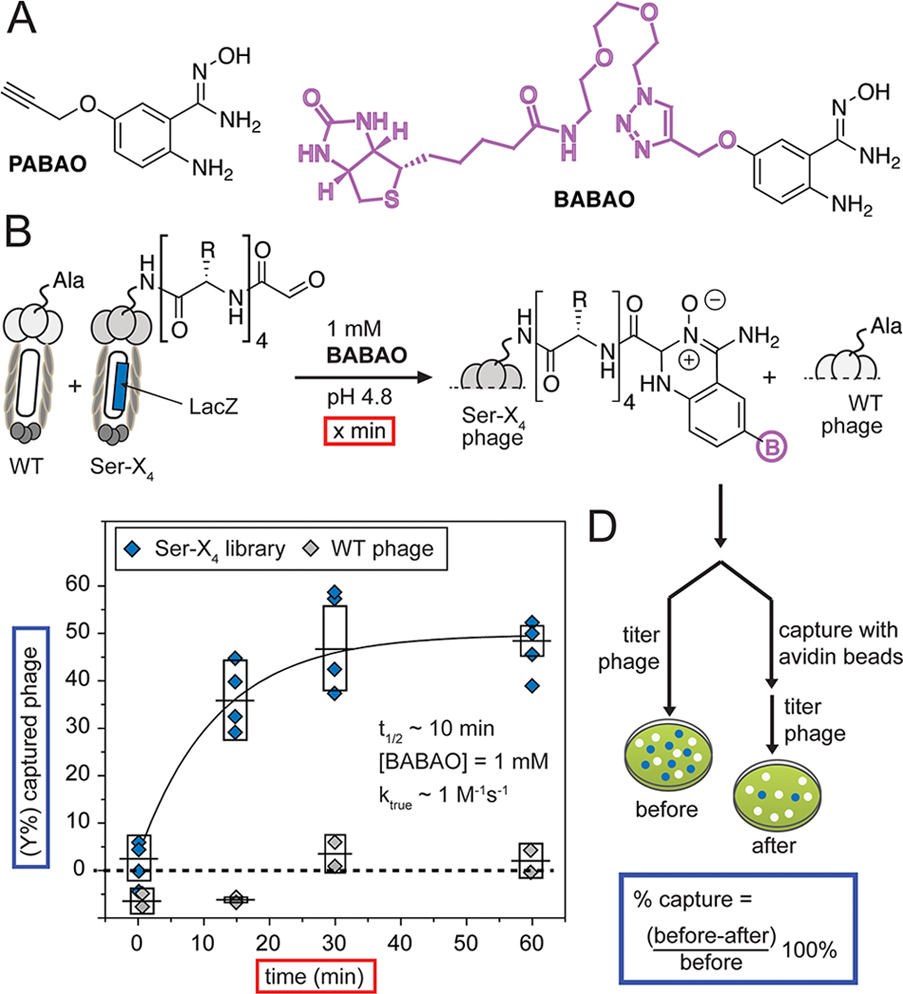
(A) Structures of ABAO derivatives that contain propargyloxy group and biotin. (B) Quantification of the reaction of BABAO with the M13 phage displaying a library of peptides with N-terminal glyoxal and wt phage displaying no aldehyde (1011 PFU/mL each). (C) Phage mixture was exposed to BABAO for the specified time. (D) To measure the reaction rate, we exposed the mixture of phage to 1 mM BABAO and measured biotinylation as a function of time by avidin capture. Error bars represent standard deviations from four independent kinetics experiments.
CAS number: 5821-51-2
Dibenzo[ghi,mno]fluoranthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). It's characterized by a structure of five fused benzene rings. This PAH is of interest due to its potential carcinogenic and mutagenic properties. It's found in the environment, often as a result of incomplete combustion, and is known for its low solubility in water.
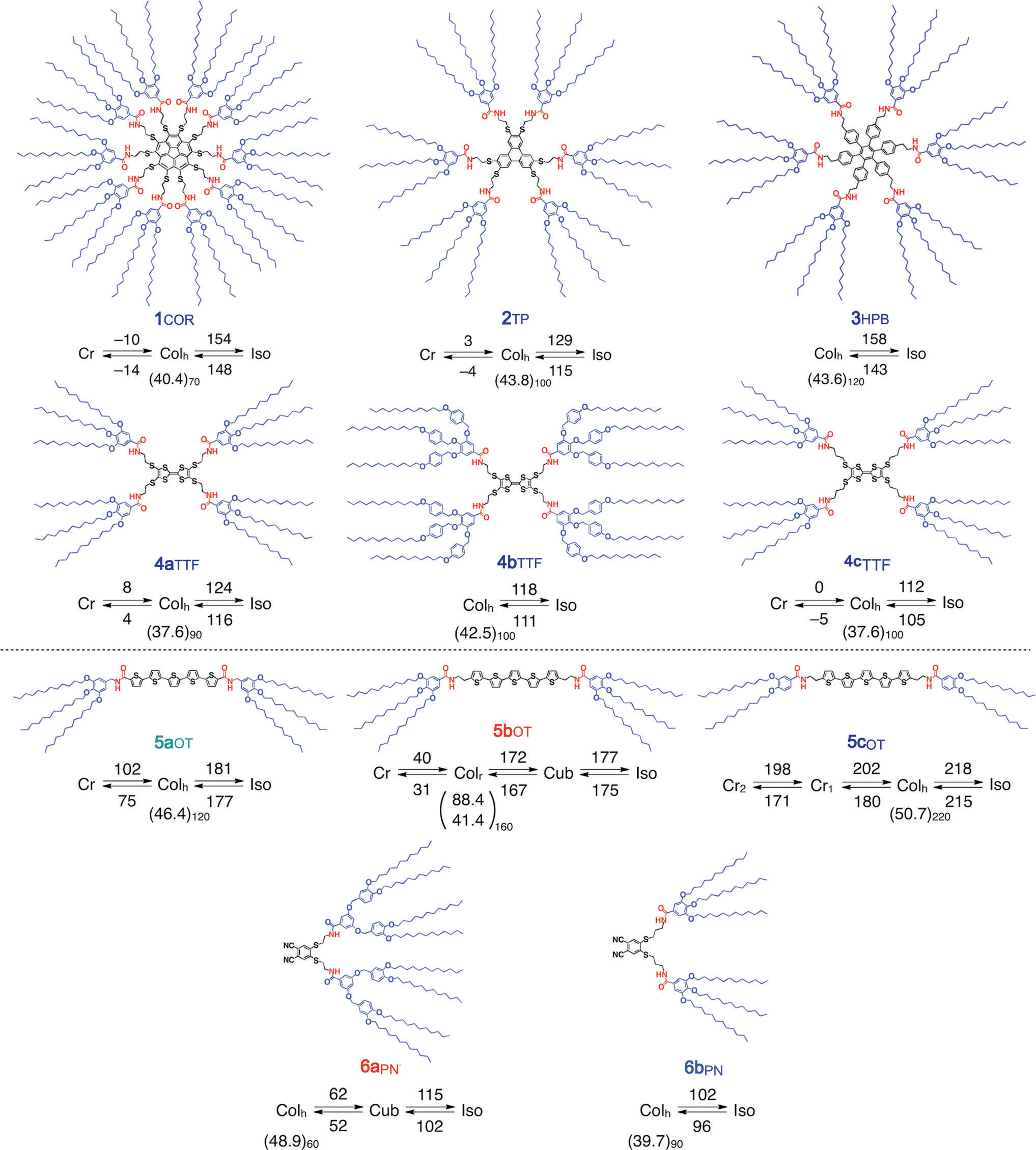
Structures and phase diagrams of LC compounds derived form corannulene (1COR), triphenylene (2TP), hexaphenylbenzene (3HPB), tetrathiafluvalene (4aTTF, 4bTTF, and 4cTTF), oligothiophene (5aOT, 5bOT, and 5cOT), and phthalonitrile (6aPN and 6bPN).
CAS number: 583-39-1
2-Thiobenzimidazole (2-TBI), also known as 2-mercaptobenzimidazole, is a chemical compound with the formula C7H6N2S that exists in both a thione (c=s) and a thiol (c-sh) form, which can tautomerize between each other. It is a versatile molecule used as a ligand in coordination chemistry, an antioxidant, an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other chemicals, and has shown significant biological activities including antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties. It is also a component in the rubber industry.
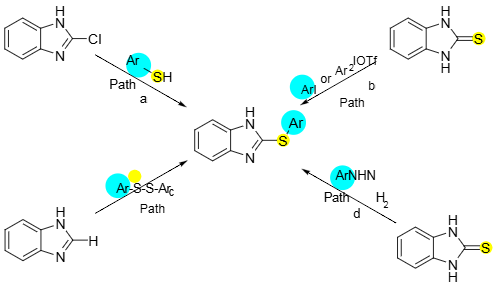
Existing synthetic strategies towards 2-thiobenzimidazoles.
CAS number: 583-63-1
1,2-benzoquinone is a benzoquinone resulting from the formal oxidation of catechol. It is a benzoquinone and a member of 1,2-benzoquinones.
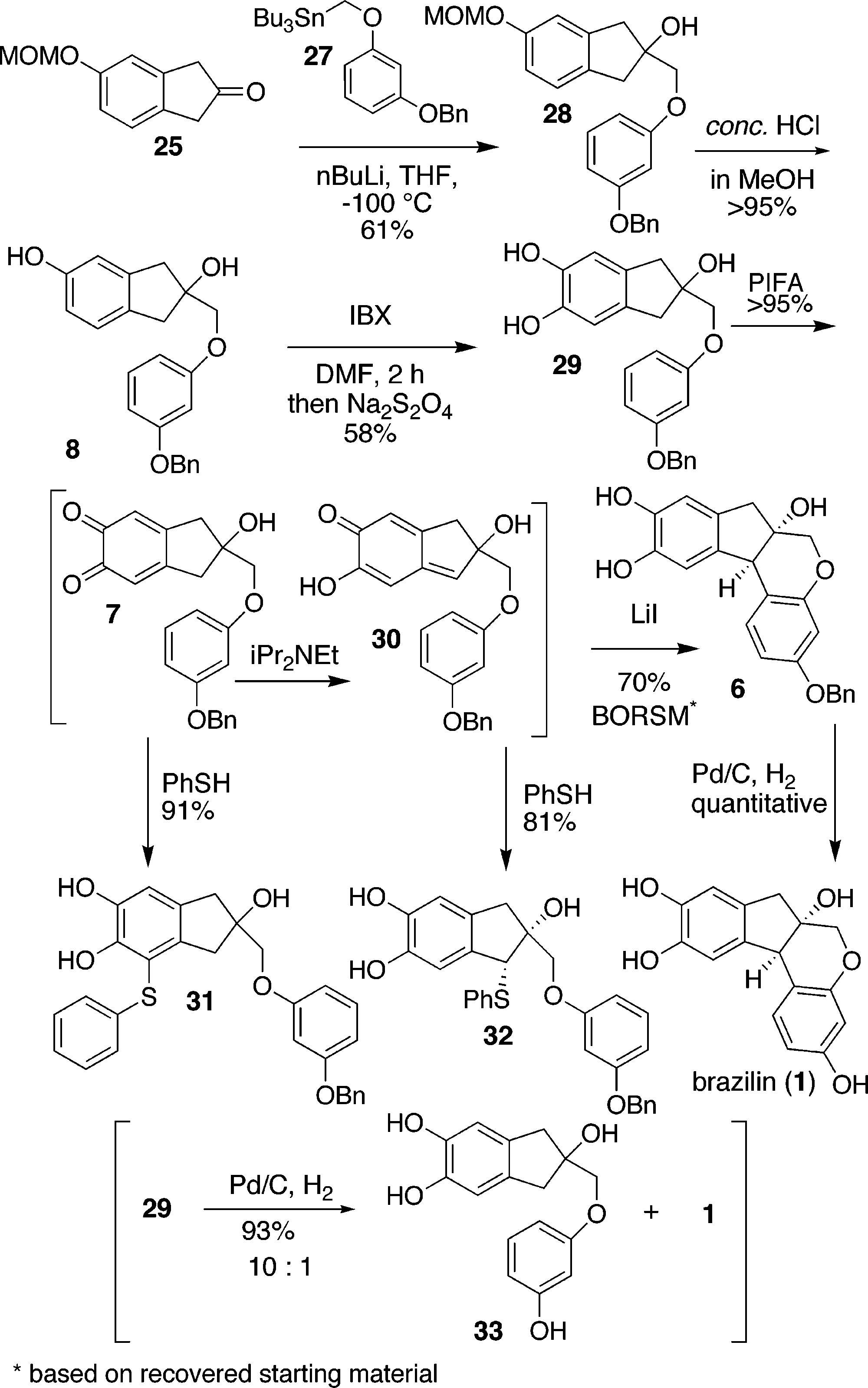
o-Quinone Formation, Reduction, Tautomerization, 1,4-Conjugate Addition, and Cyclization
CAS number: 58337-35-2
Elliptinium Acetate is acetate salt of elliptinium, a derivative of the alkaloid ellipticine isolated from species of the plant family Apocynaceae, including Bleekeria vitensis, a plant with anti-cancer properties. As a topoisomerase II inhibitor and intercalating agent, elliptinium stabilizes the cleavable complex of topoisomerase II and induces DNA breakages, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and RNA and protein synthesis.
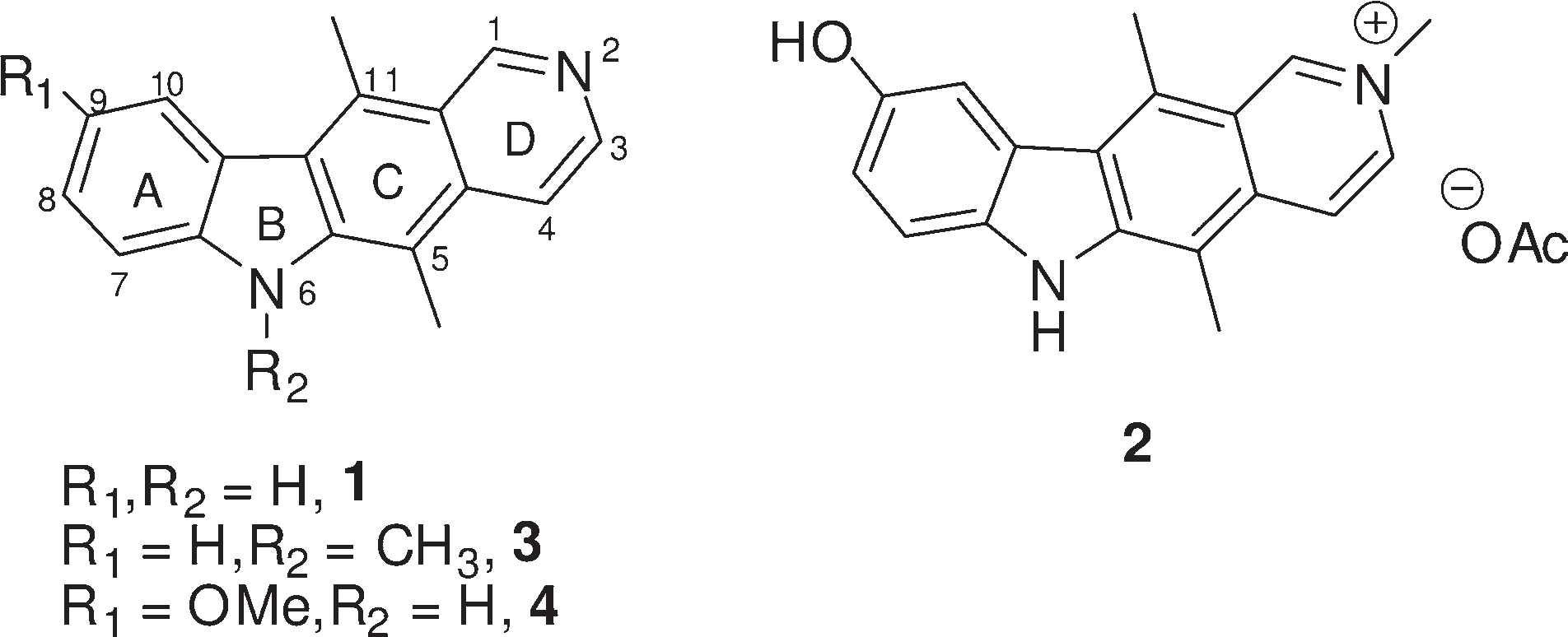
Structures of ellipticine and Celiptium.