Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 533-58-4
2-iodophenol is a 2-halophenol and an iodophenol.
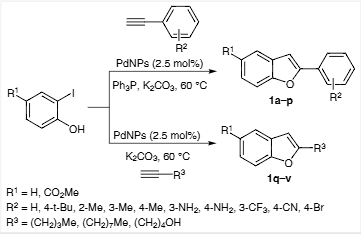
Palladium nanoparticles catalyzed synthesis of benzofurans by coupling of 2-iodophenols and terminal aryl- or alkylacetylenes
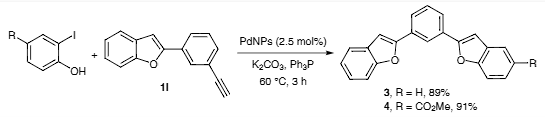
Coupling reactions between 2-(3-ethynylphenyl)benzofuran (1i) and iodophenols
CAS number: 53378-34-0
Dihydroquinazoline is a member of quinazolines.
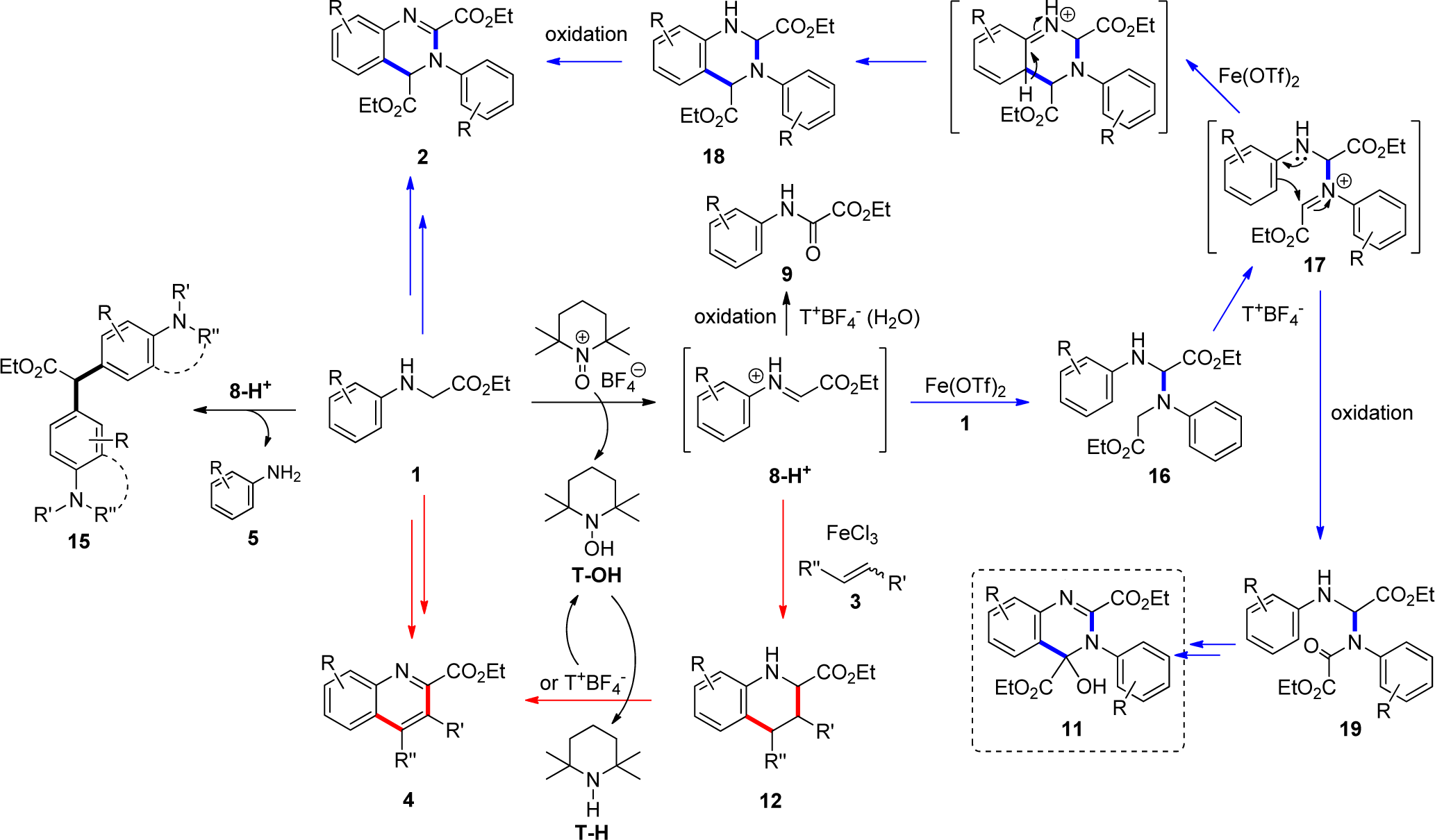
Proposed mechanism for the Synthesis of Dihydroquinazolines, Quinolines, and Diarylmethane Derivatives
CAS number: 5339-27-5
2-(Dimethylamino)benzeneethanol is also known as 2-(2-Dimethylaminoethyl)phenol or 2-(Dimethylamino)phenethyl alcohol. It features a benzene ring, an ethanolamine group (with a dimethylamino substituent), and is classified as a tertiary amine and a primary alcohol. It is also sometimes referred to as Deanol or DMAE.
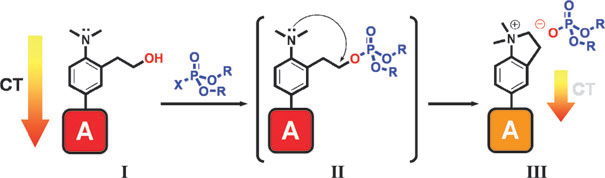
Colorimetric sensing protocol. A 2-(2-(dimethylamino)-phenyl)ethanol (DAPE) group acts as donor in charge-transfer dyes such as I containing an acceptor group (A). In III there is a drastic reduction of the donor ability of the amine group resulting in a remarkable weakening of the charge-transfer (CT) band.
CAS number: 5343-70-4
2-[2-(4-Chlorophenyl)ethenyl]pyridine is a chemical compound known as 2-(4-Chlorostyryl)pyridine. It is a heterocyclic organic chemical with a 4-chlorophenyl group attached to one side of an ethenyl (vinyl) group, which is in turn attached to a pyridine ring.
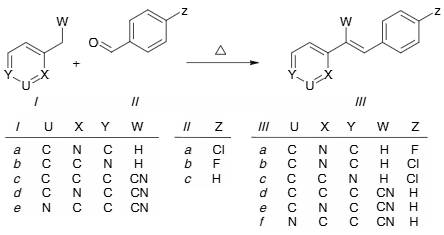
Synthesis of (E)-2-(4-fluorostyryl)pyridine IIIa, (E)-2-(4-chlorostyryl)pyridine IIIb, (E)-4-(4-chlorostyryl)pyridine IIIc, 2,3-diphenylacrylonitrile IIId, 3-phenyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)acrylonitrile IIIe, and 3-phenyl-2-(pyridin-3-yl)acrylonitrile IIIf.
CAS number: 536-74-3
Phenylacetylene (also known as Ethynylbenzene) is an alkyne hydrocarbon bonded to a benzene ring. It is an aromatic organic compound frequently employed in Sonogashira coupling reactions.
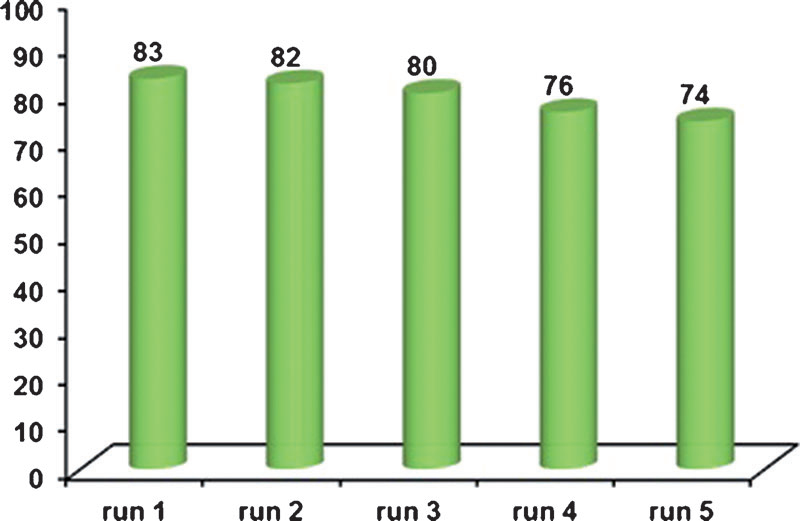
Recycling of catalyst for the reaction of iodobenzene with phenylacetylene.
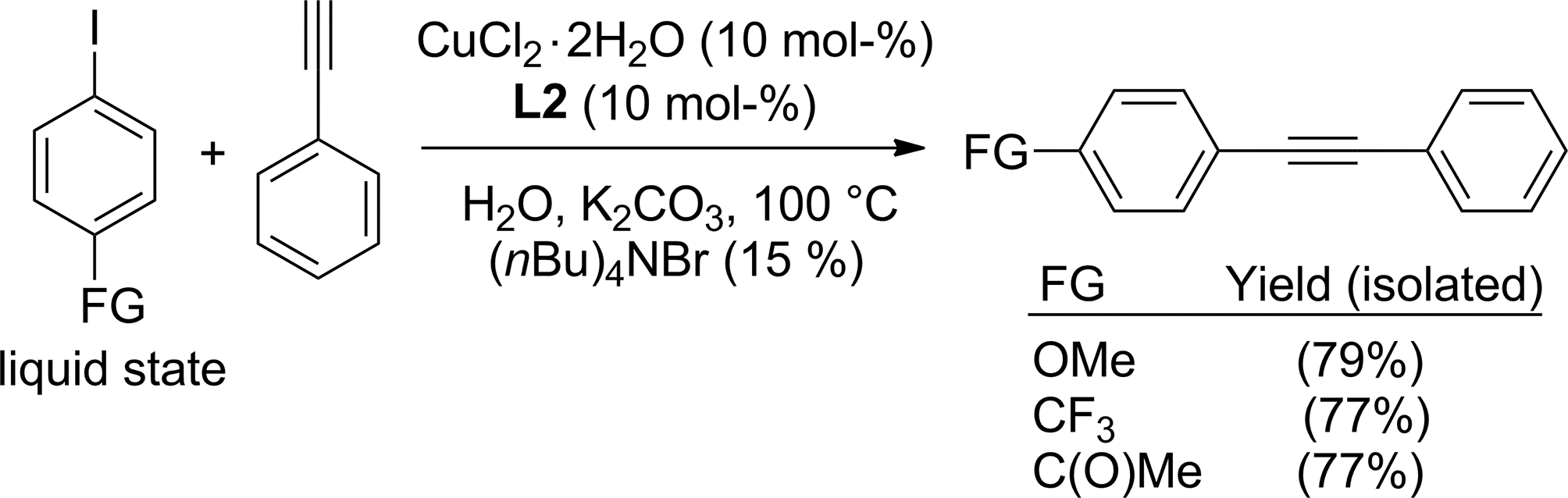
Coupling of liquid iodoarenes with phenylacetylene in water.
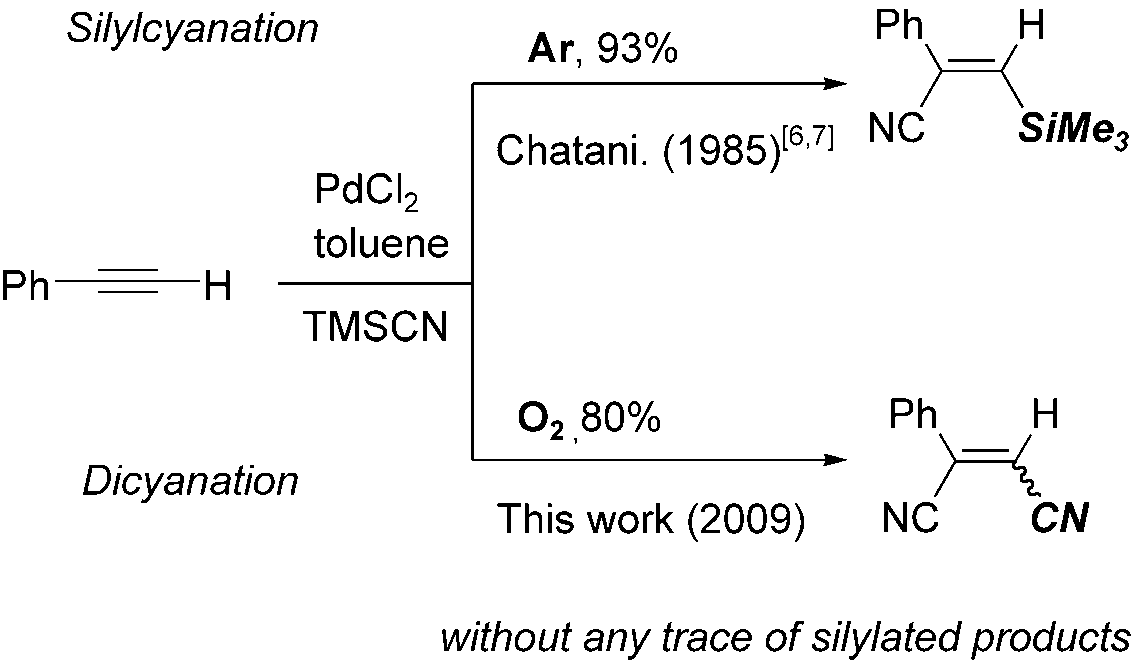
Pd-catalyzed cyanation of phenylacetylene with TMSCN.
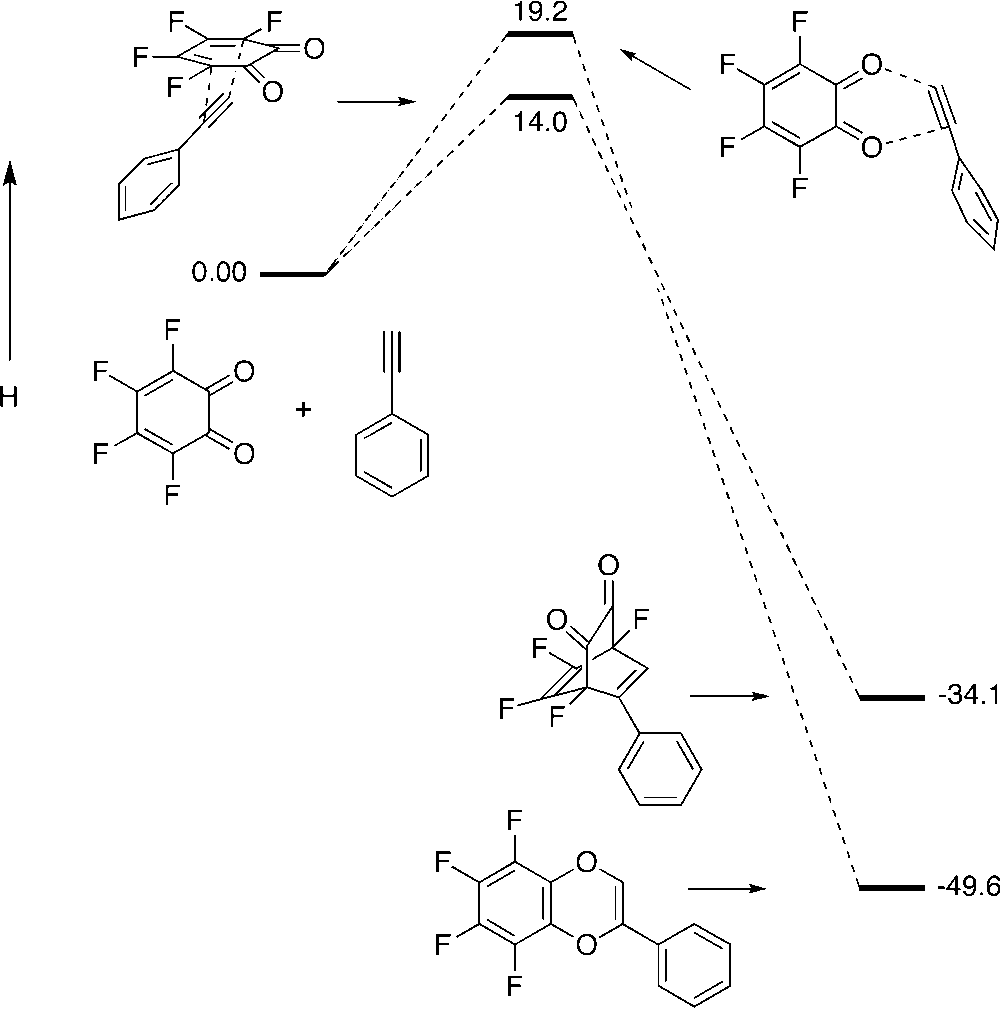
Reaction profiles for phenylacetylene/o-fluoranil cycloadditions, calculated at the B3LYP/6-31G/ level of theory.
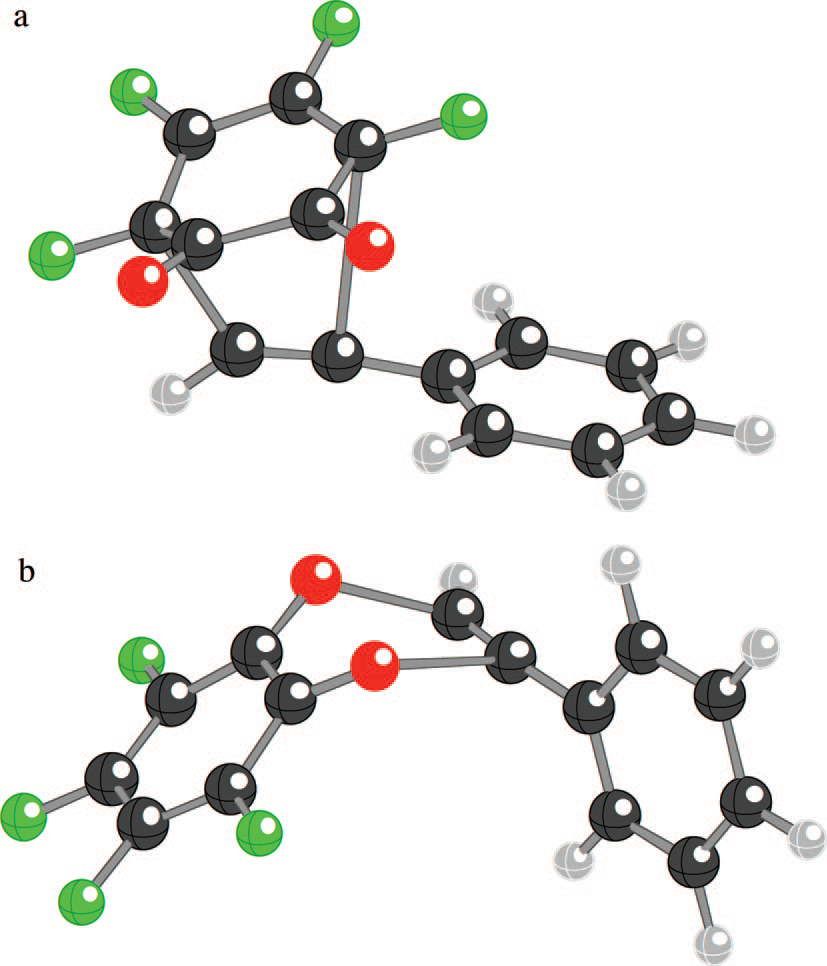
Transition states for reactions of phenylacetylene with o-fluoranil.
CAS number: 538-75-0
DCC (dicyclohexyl carbodiimide) is one of the most frequently used coupling agents, especially in organic synthesis applications.
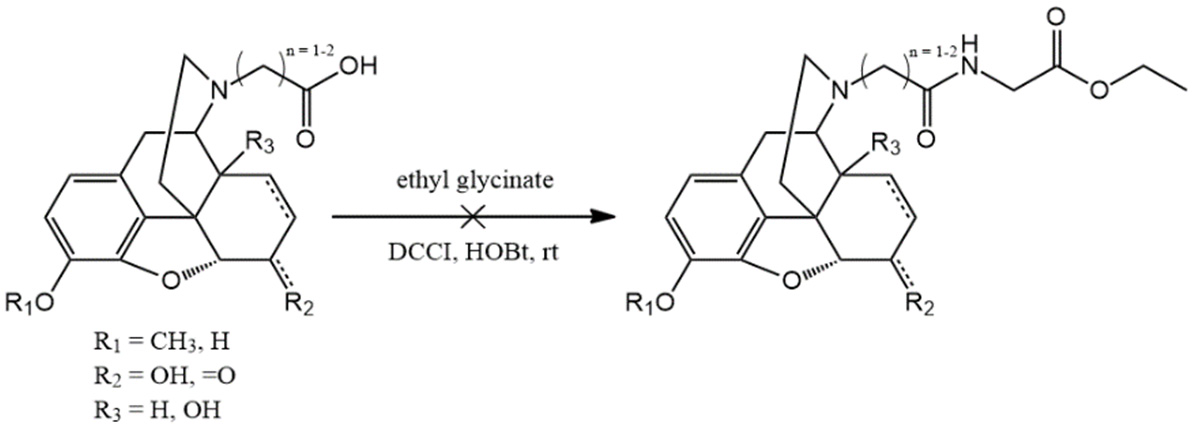
Attempted amino acid coupling: glycine ethyl ester, N,N'-dicyclohexyl carbodiimide (DCCI) or 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDAC), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt), water, room temperature.
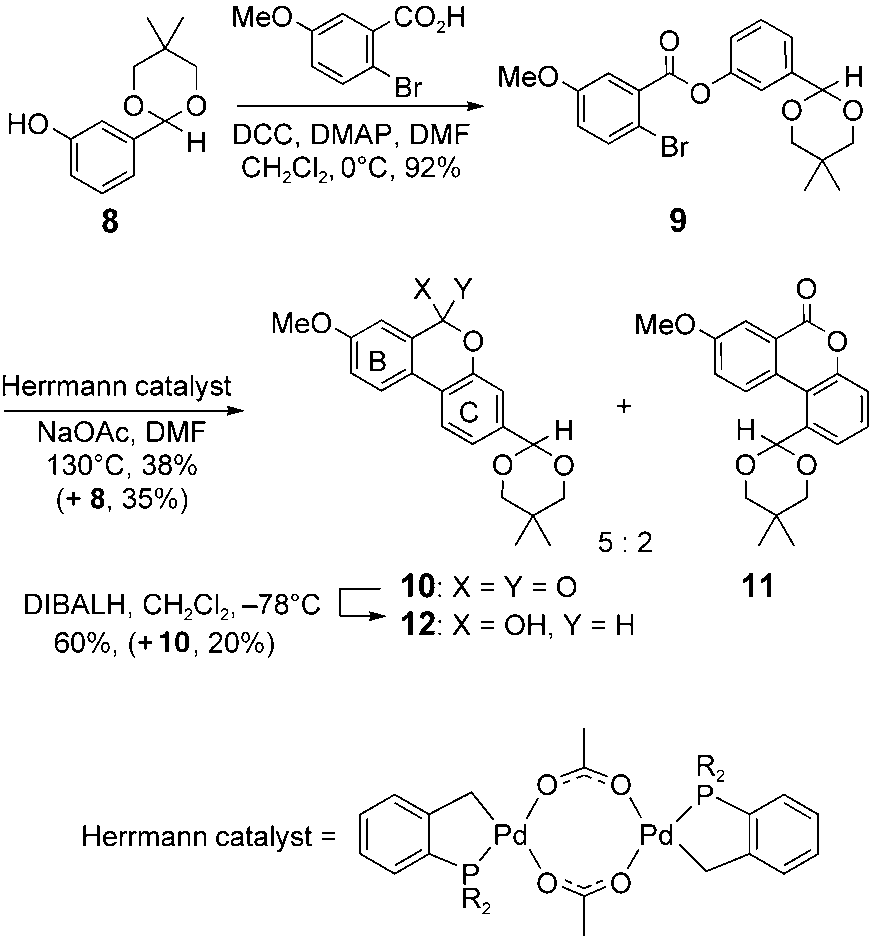
Synthesis of the BC ring system. DCC=dicyclohexylcarbo-diimide, DMAP=4-dimethylaminopyridine, DIBALH=diisobutylaluminum hydride, R=o-tolyl.
CAS number: 53847-30-6
2-arachidonoylglycerol is an endocannabinoid and an endogenous agonist of the cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2). It is an ester formed from omega-6-arachidonic acid and glycerol. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is an endocannabinoid and a 2-acylglycerol 20:4. It is functionally related to an arachidonic acid.
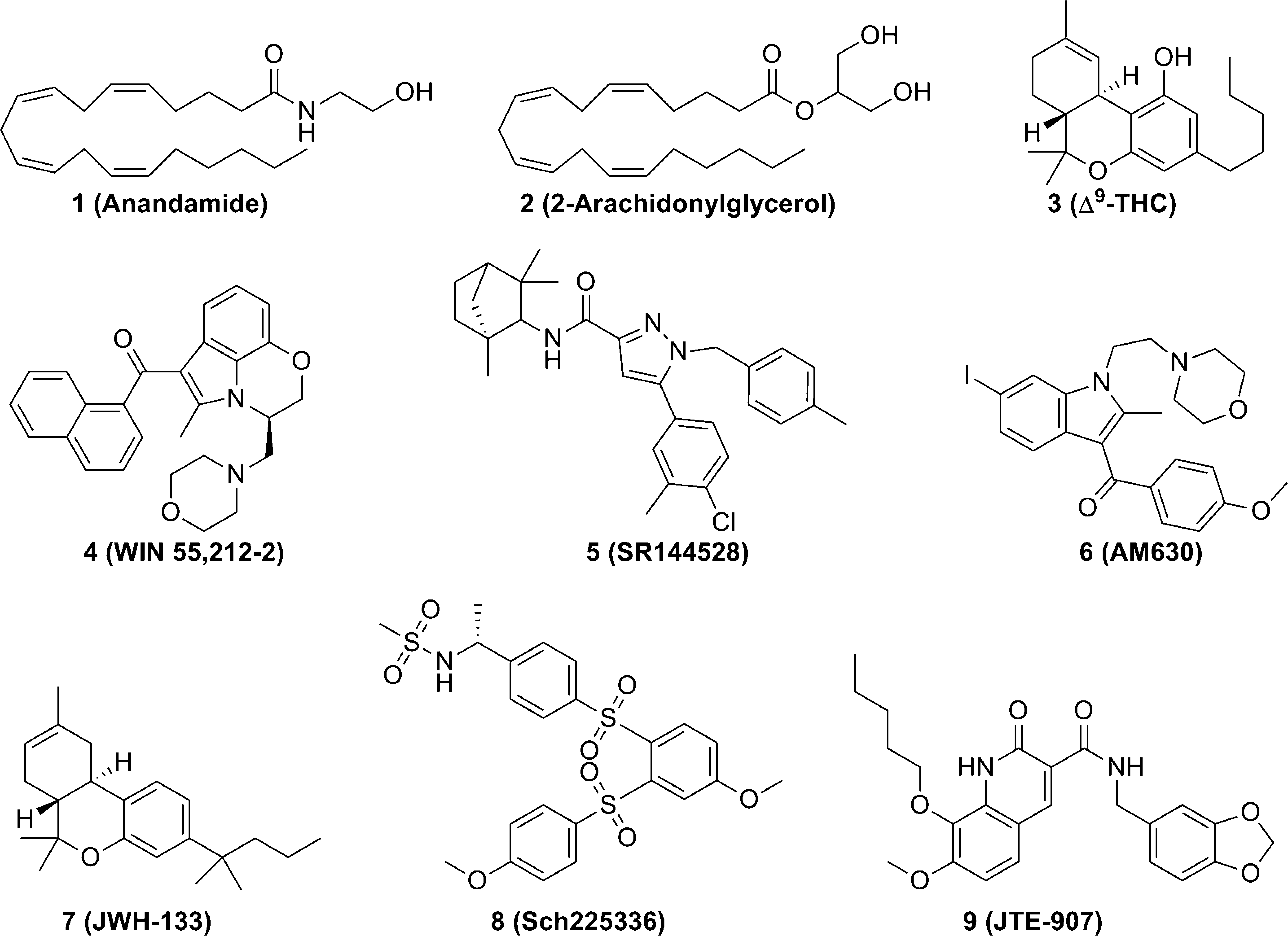
Representative cannabinoids with various chemical scaffolds: Anandamide, 2-Arachidonylglycerol, Win-55212-2, SR 144528, JWH-133, JTE-907.
CAS number: 54-05-7
Chloroquine is an aminoquinoline that is quinoline which is substituted at position 4 by a [5-(diethylamino)pentan-2-yl]amino group at at position 7 by chlorine. It is used for the treatment of malaria, hepatic amoebiasis, lupus erythematosus, light-sensitive skin eruptions, and rheumatoid arthritis.
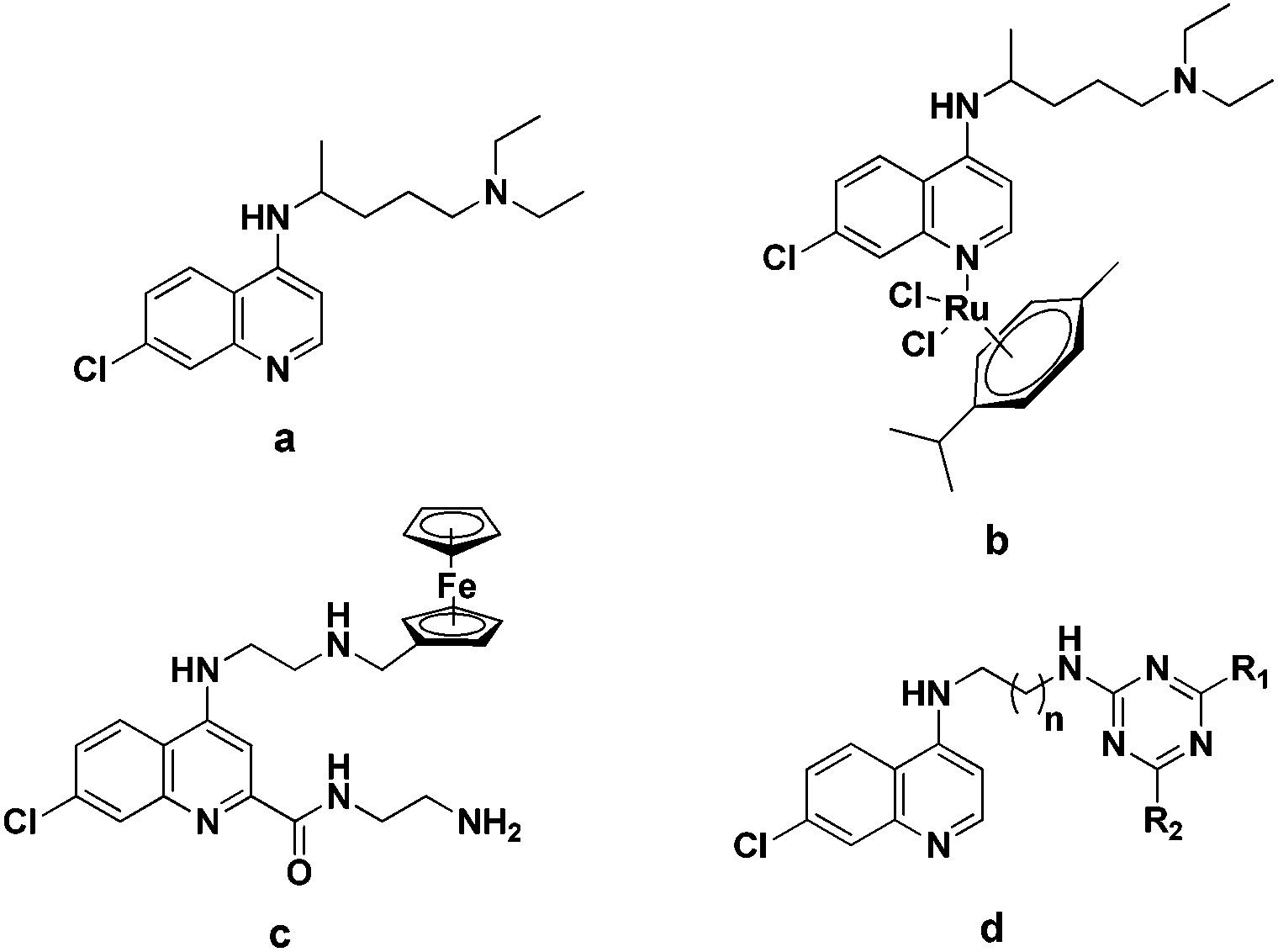
(a) Chloroquine (CQ); (b) ruthenium(II) complex of CQ; (c) fer-rocenyl-aminoquinoline-carboxamide based bio-organometallics; (d) general structure of 4-aminoquinoline-triazine based hybrids.
CAS number: 54-31-9
Furosemide is an odorless white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. A diuretic drug. Almost tasteless.
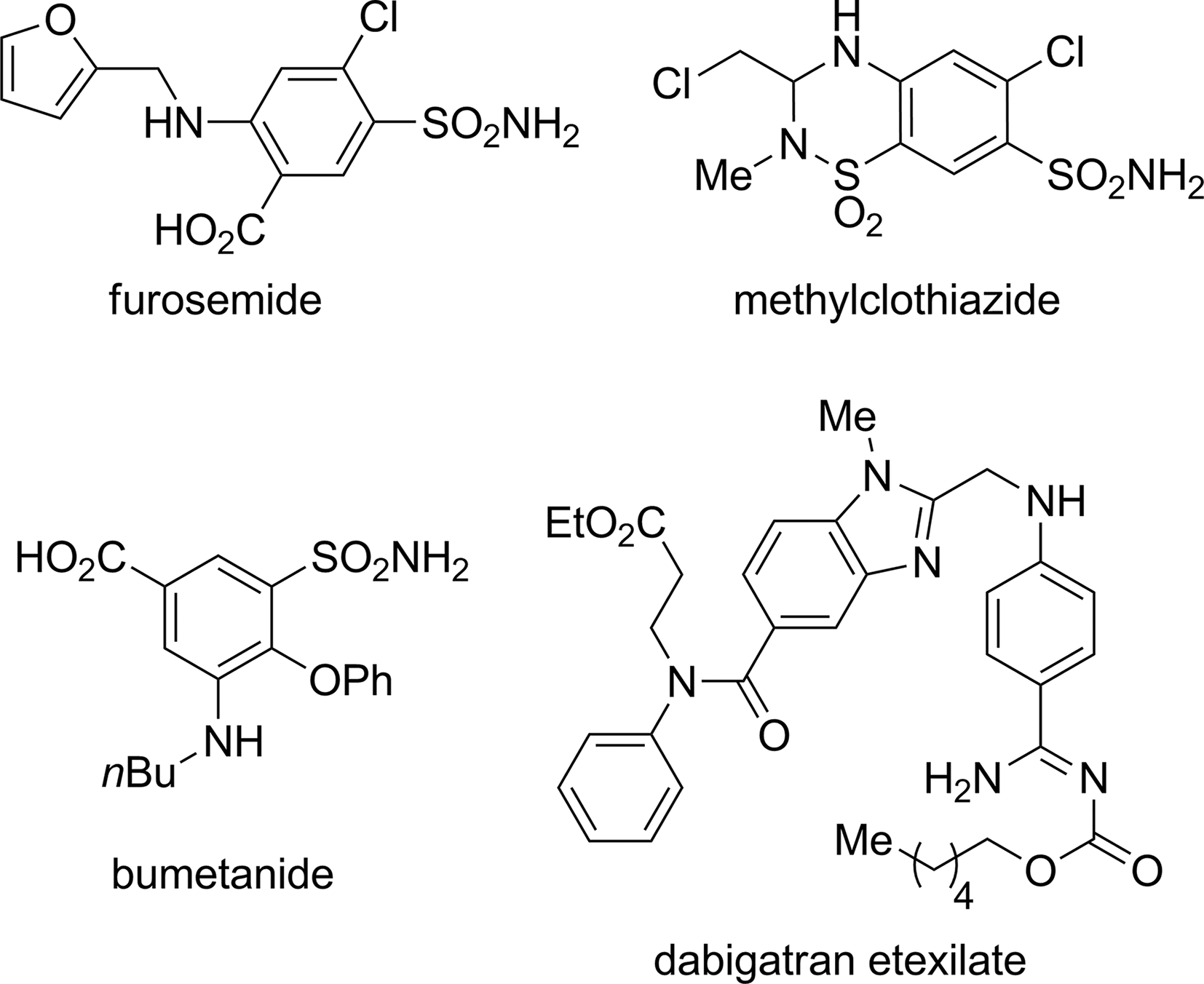
Some aniline-containing pharmaceuticals: furosemide, methylclothiazide, bumetanide
CAS number: 54-47-7
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is the monophosphate ester obtained by condensation of phosphoric acid with the primary hydroxy group of pyridoxal. It is a conjugate acid of a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-).
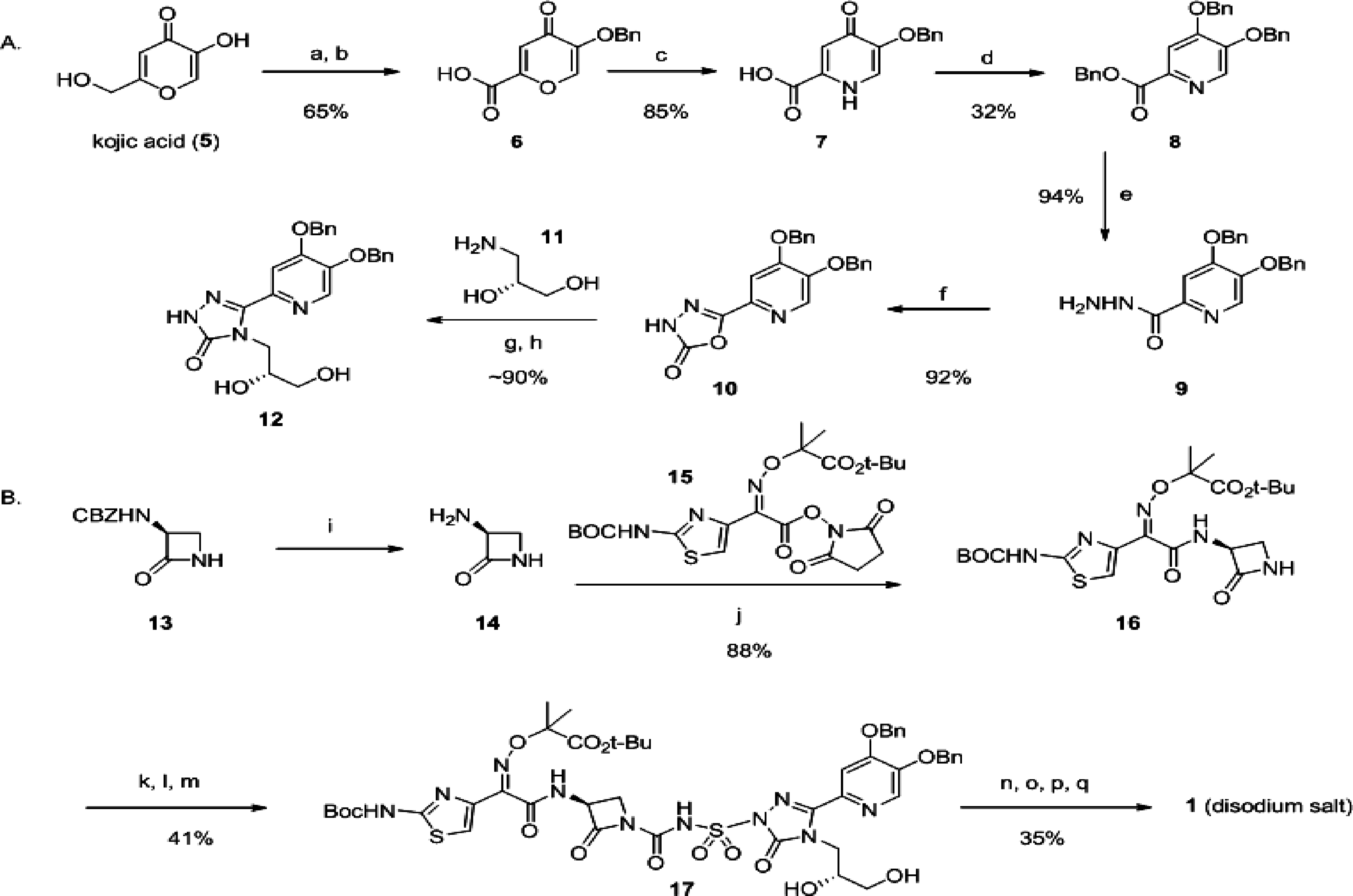
Representative Monocarbam Synthesis: Preparation of MC-1 (1)