Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 54-92-2
Iproniazid is a carbohydrazide and a member of pyridines.
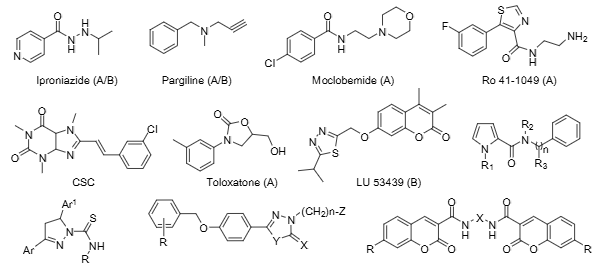
Some representative structures of MAO inhibitors used in research or clinical practice: Iproniazide, Pargiline, Moclobemide, Ro 41-1049, CSC, Toloxatone, LU-53439.
CAS number: 541-41-3
Ethyl chloroformate appears as a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point 66 °F. Very toxic by inhalation. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
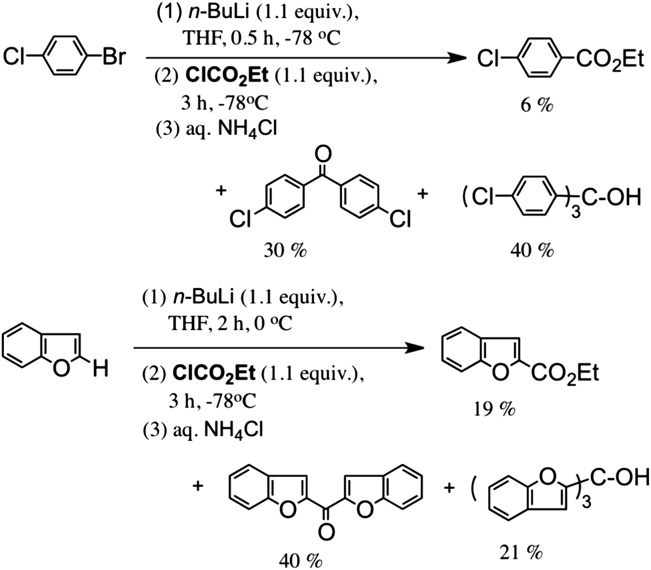
Introduction of ester group with ethyl chloroformate.
CAS number: 542-14-3
Aniline acetate is a chemical compound formed by the reaction of aniline (an aromatic amine) with acetic acid. It typically appears as white crystalline solids and is used in organic chemistry as a reagent or intermediate. Aniline acetate combines the properties of both aniline—an oily, slightly yellow liquid with a characteristic odor—and acetate, contributing to its solubility in water and alcohol.
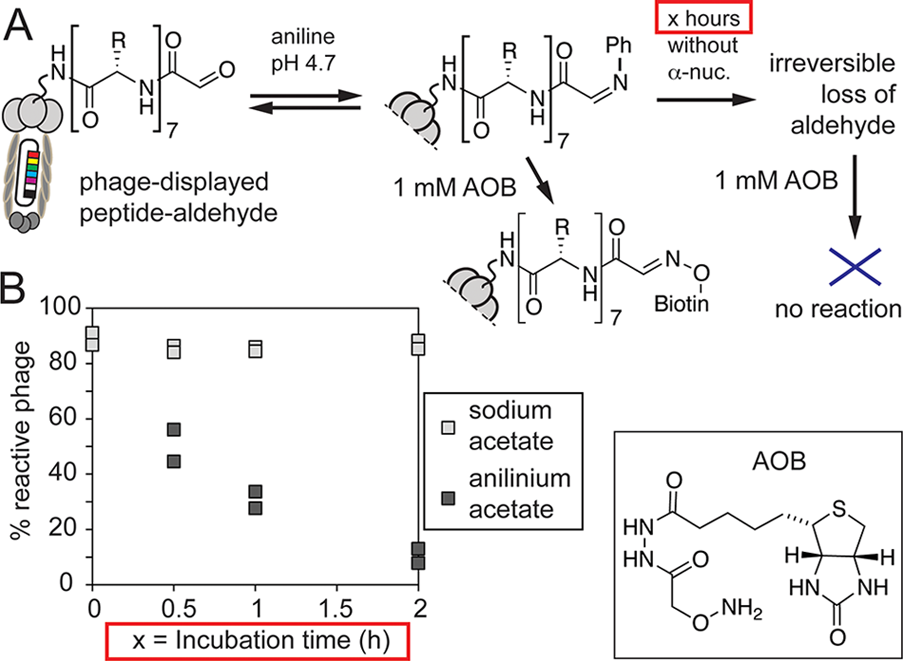
(A) Ligation of AOB to phage-displayed aldehydes is accelerated by aniline, but preincubation of phage with aniline in the absence of AOB leads to rapid loss of aldehyde and loss of reactivity toward AOB. (B) In anilinium acetate, pH 4.7, the aldehyde disappears with t1/2 ∼40 min; however, aldehydes alone are stable at the same pH in sodium acetate buffer.
CAS number: 542-92-7
Cyclopentadiene is a cycloalkadiene.
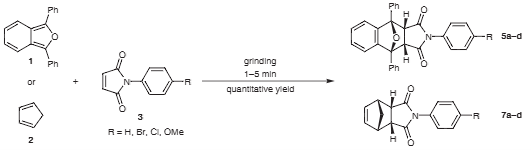
Diels–Alder reactions of 1,3-diphenyl-2-benzofuran or cyclopentadiene with various N-arylmaleimides
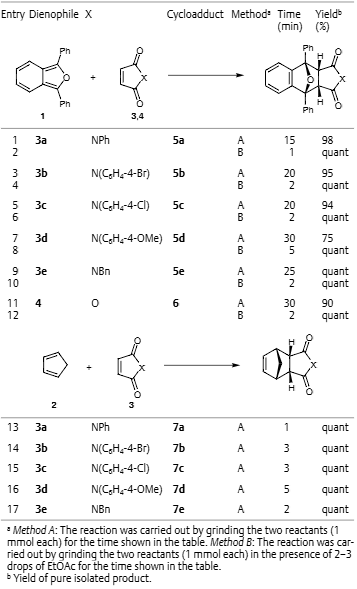
Diels–Alder Reactions of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-benzofuran or Cyclopentadiene with Various Dienophiles
CAS number: 5425-44-5
2-Phenyl-1,3-dithiane is a dithiane, a cyclic thioether containing a cyclohexane ring where two methylene bridges are replaced by sulfur atoms, specifically in the 1,3 positions. The phenyl group is attached to the central carbon of the dithiane ring.
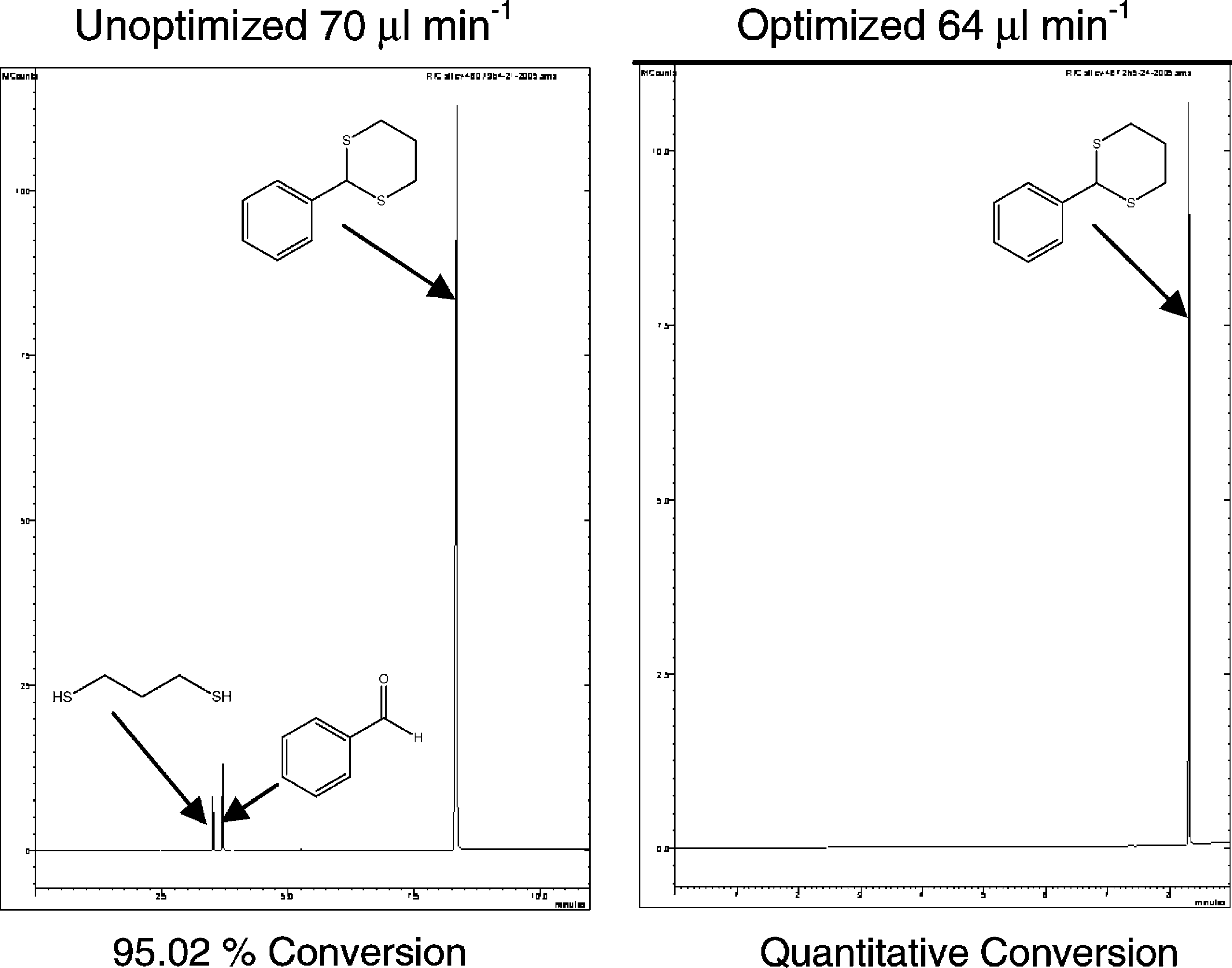
Gas chromatograms illustrating the difference between an optimized and an unoptimized system for the synthesis of 2-phenyl-1,3-dithiane 2, under continuous flow.
CAS number: 54350-48-0
Etretinate is a medication used to treat severe psoriasis. It is a synthetic aromatic retinoid. The mechanism of action of etretinate is still incompletely understood although, like retinoic acid, it is thought to interfere with the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes. It is thought to bind to the retinoic acid receptors.
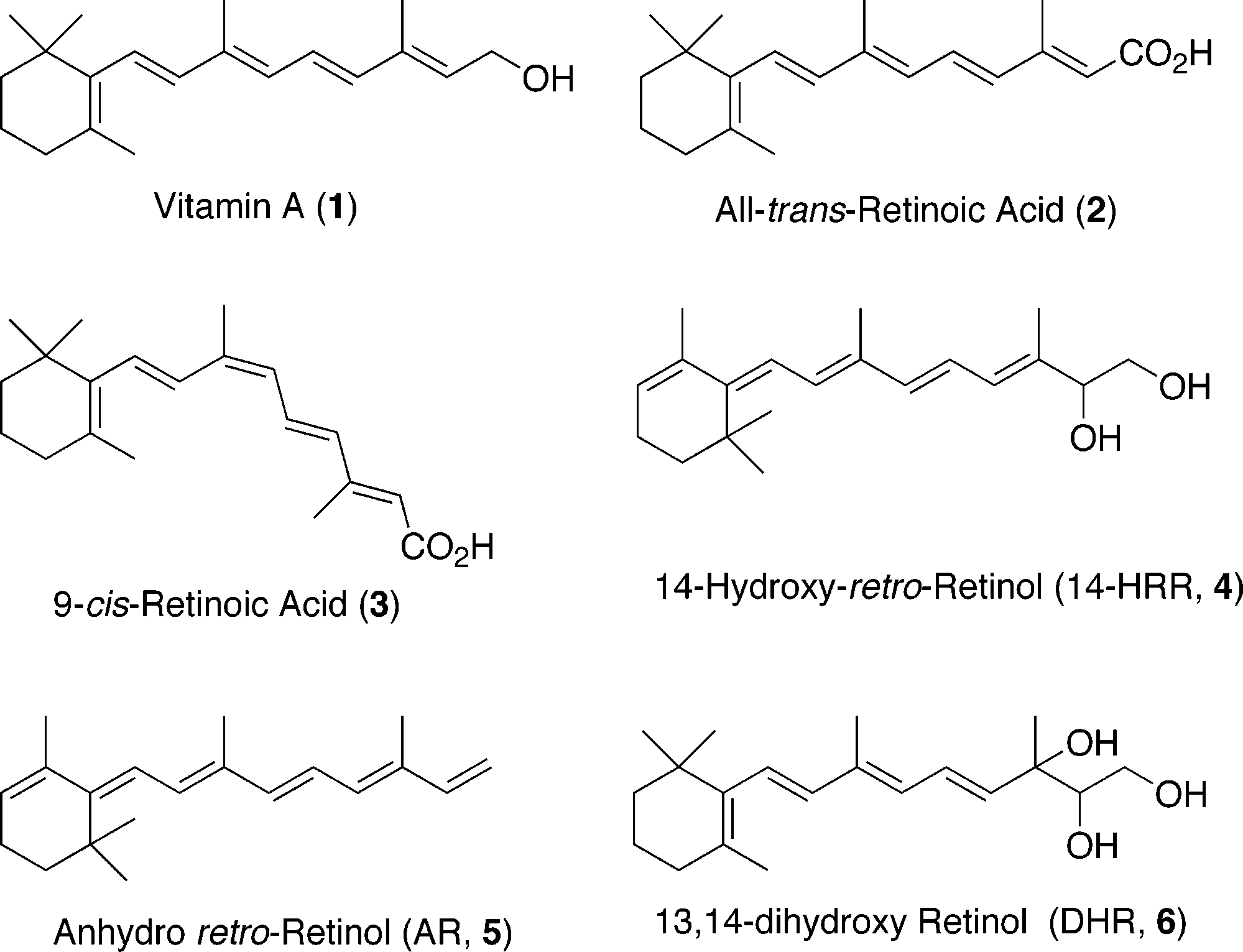
Natural retinoids and retro-retinoids
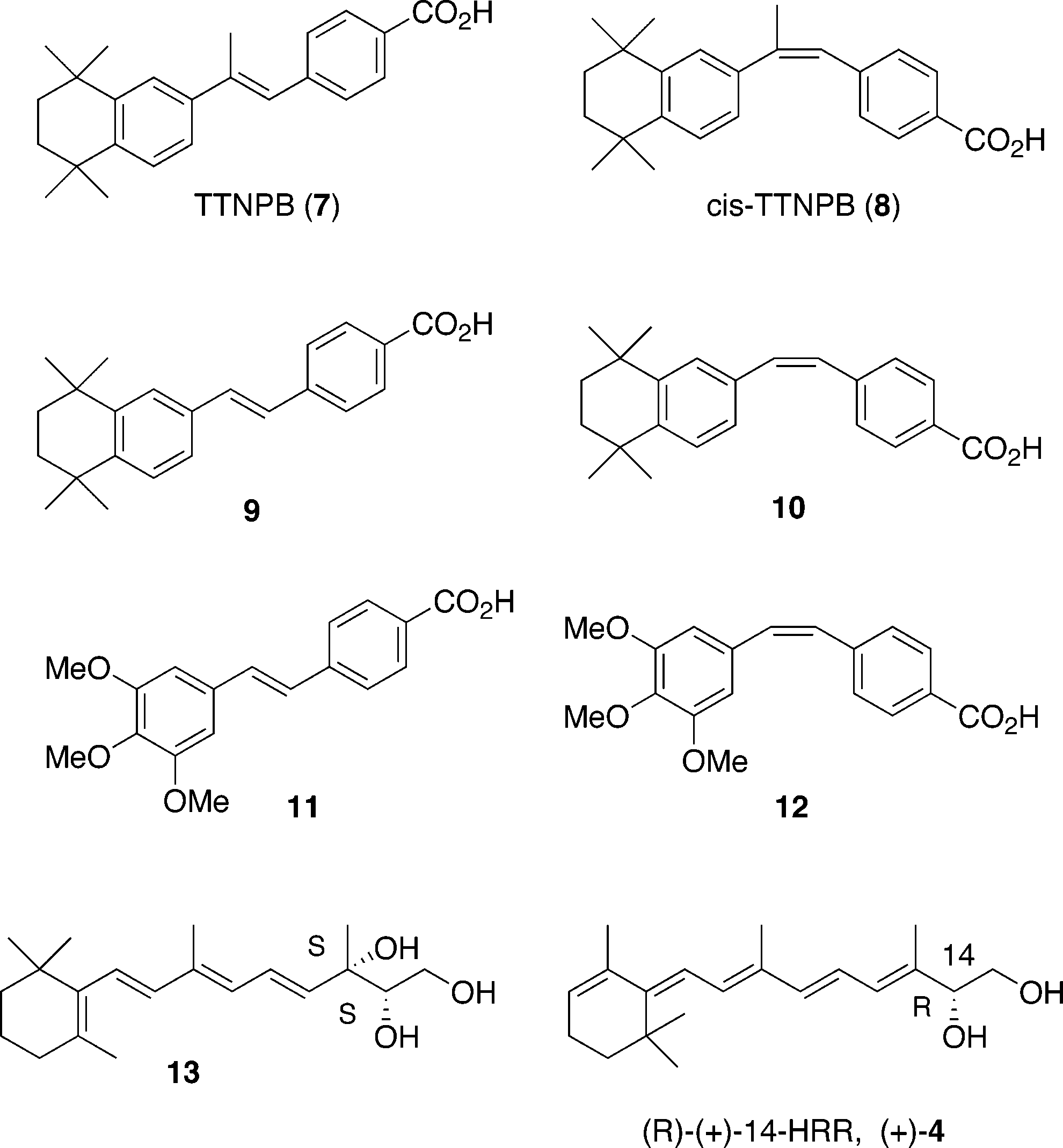
Synthesized retinoids and retro-retinoids.
CAS number: 5471-63-6
1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF) is a fluorescent probe used to detect various reactive species, particularly singlet oxygen, by undergoing a [4+2] cycloaddition reaction. This reaction results in 1,2-dibenzoylbenzene, a non-fluorescent product, and changes the fluorescence of DPBF, making it a valuable tool in chemical and biological research. It is also used as a model compound for singlet fission studies, in organic photovoltaic applications, and as a building block for synthesizing new polymers.

Diels–Alder reactions of 1,3-diphenyl-2-benzofuran or cyclopentadiene with various N-arylmaleimides

Diels–Alder Reactions of 1,3-Diphenyl-2-benzofuran or Cyclopentadiene with Various Dienophiles
CAS number: 54910-89-3
Fluoxetine is a type of antidepressant known as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).
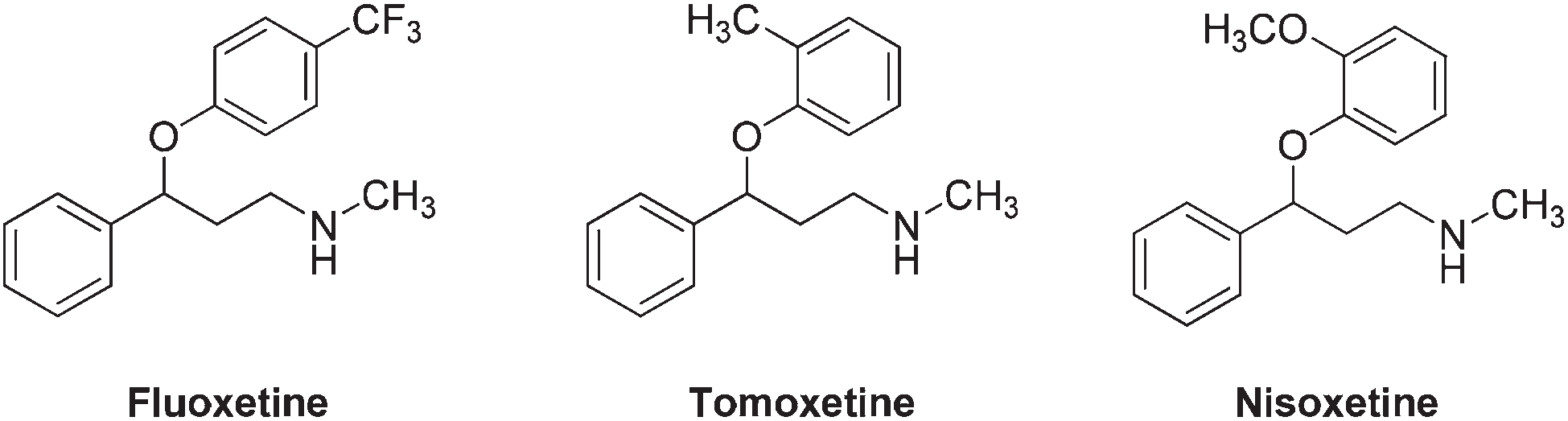
Structures of fluoxetine, atomoxetine, and nisoxetine.
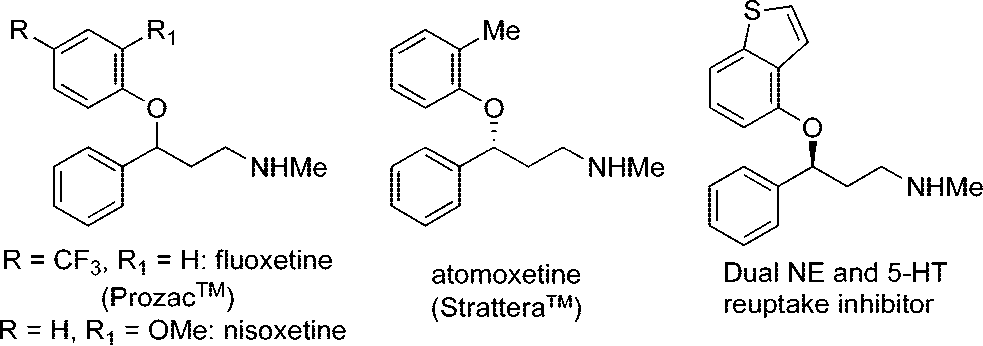
Examples of monoamine reuptake inhibitors containing a 3-aryl-3-phenoxypropylamine motif: fluoxetine, nisoxetine, atomoxetine
CAS number: 54990-68-0
Farnesiferol B is a terpene lactone. ChEBI. Farnesiferol B has been reported in Ferula assa-foetida and Ferula gummosa with data available. LOTUS - the natural products occurrence database. See also: Ferula assa-foetida resin (part of).
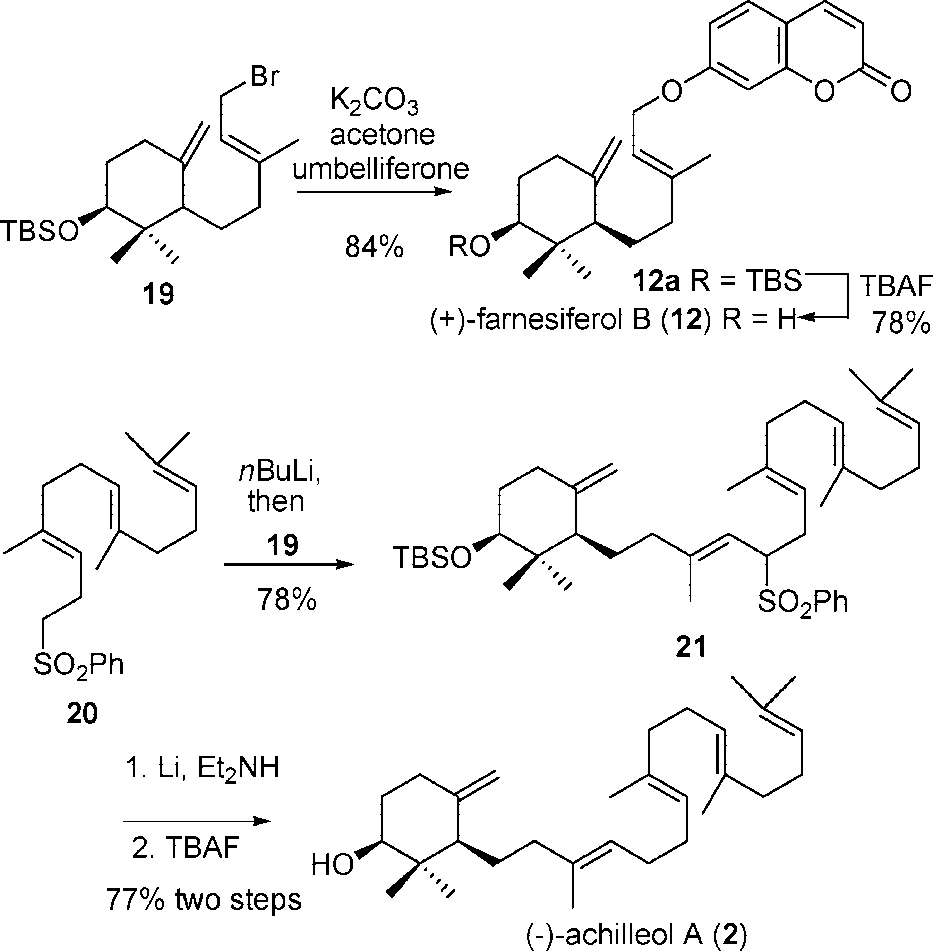
Enantioselective Synthesis of (-)-Achilleol A and (+)-Farnesiferol B
CAS number: 55-21-0
Benzamide is an aromatic amide that consists of benzene bearing a single carboxamido substituent. The parent of the class of benzamides.
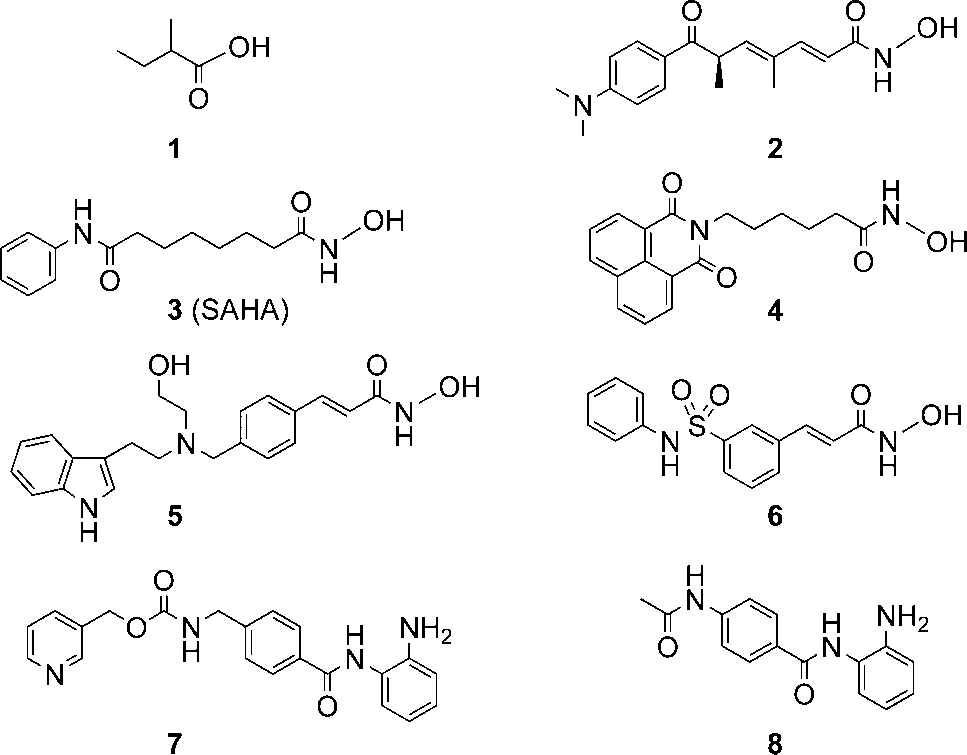
Chemically, the zinc-dependent HDACs inhibitors can be divided into several classes such as short-chain fatty acids (e.g., compound 1), hydroxamic acids 2–6, and benzamides 7 and 8 (Figure 3).