Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 475108-18-0
Tivozanib is a member of the class of quinolines that is 6,7-dimethoxyquinoline substituted by a 3-chloro-4-{[(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)carbamoyl]amino}phenoxy group at position 4. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases and was previously in clinical development for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. It has a role as a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist, an antineoplastic agent and an apoptosis inducer. It is an aromatic ether, a member of isoxazoles, a member of phenylureas, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a member of quinolines.
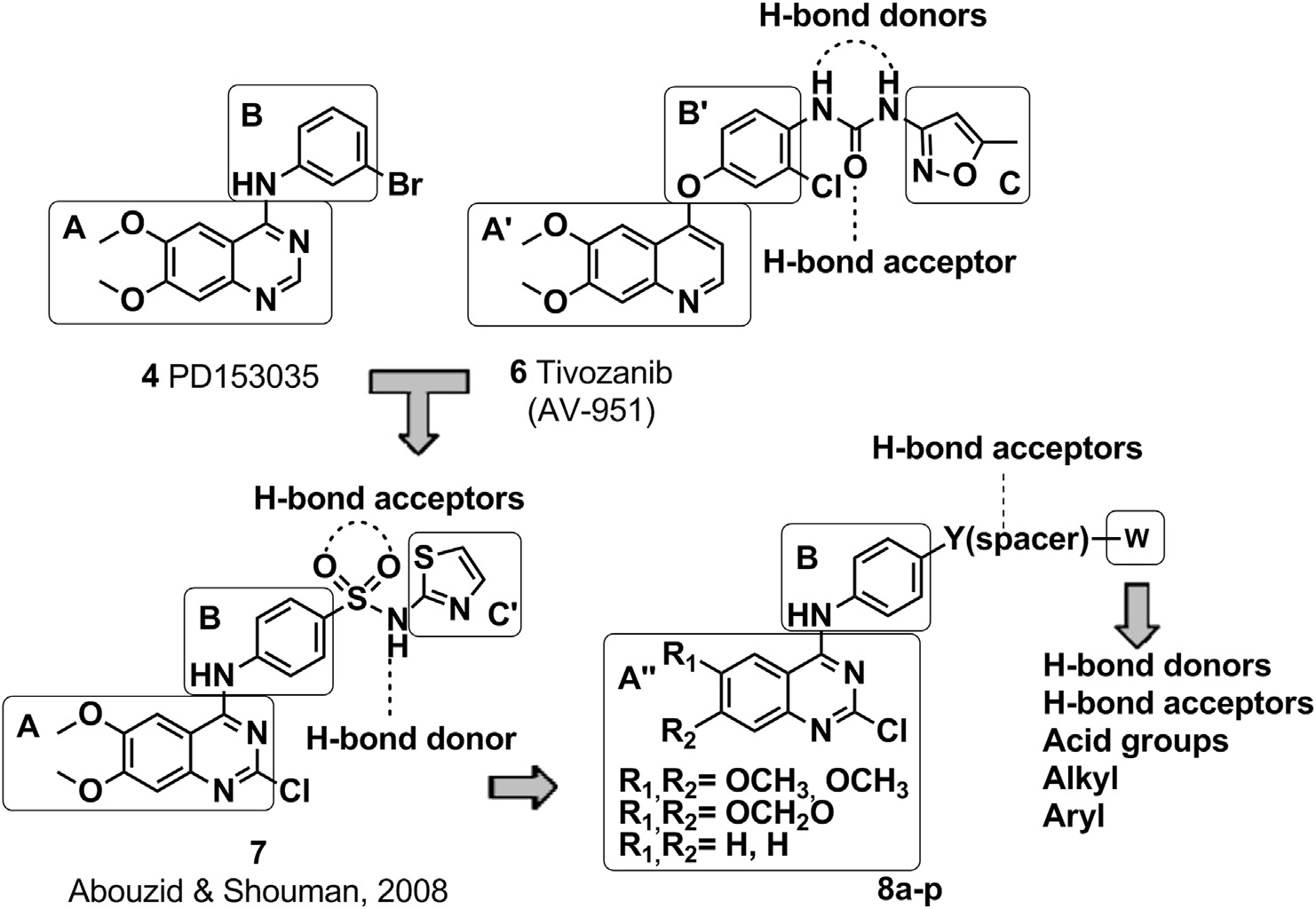
Structural design of the target 2-chloro-4-anilino-quinazoline derivatives 8aep.
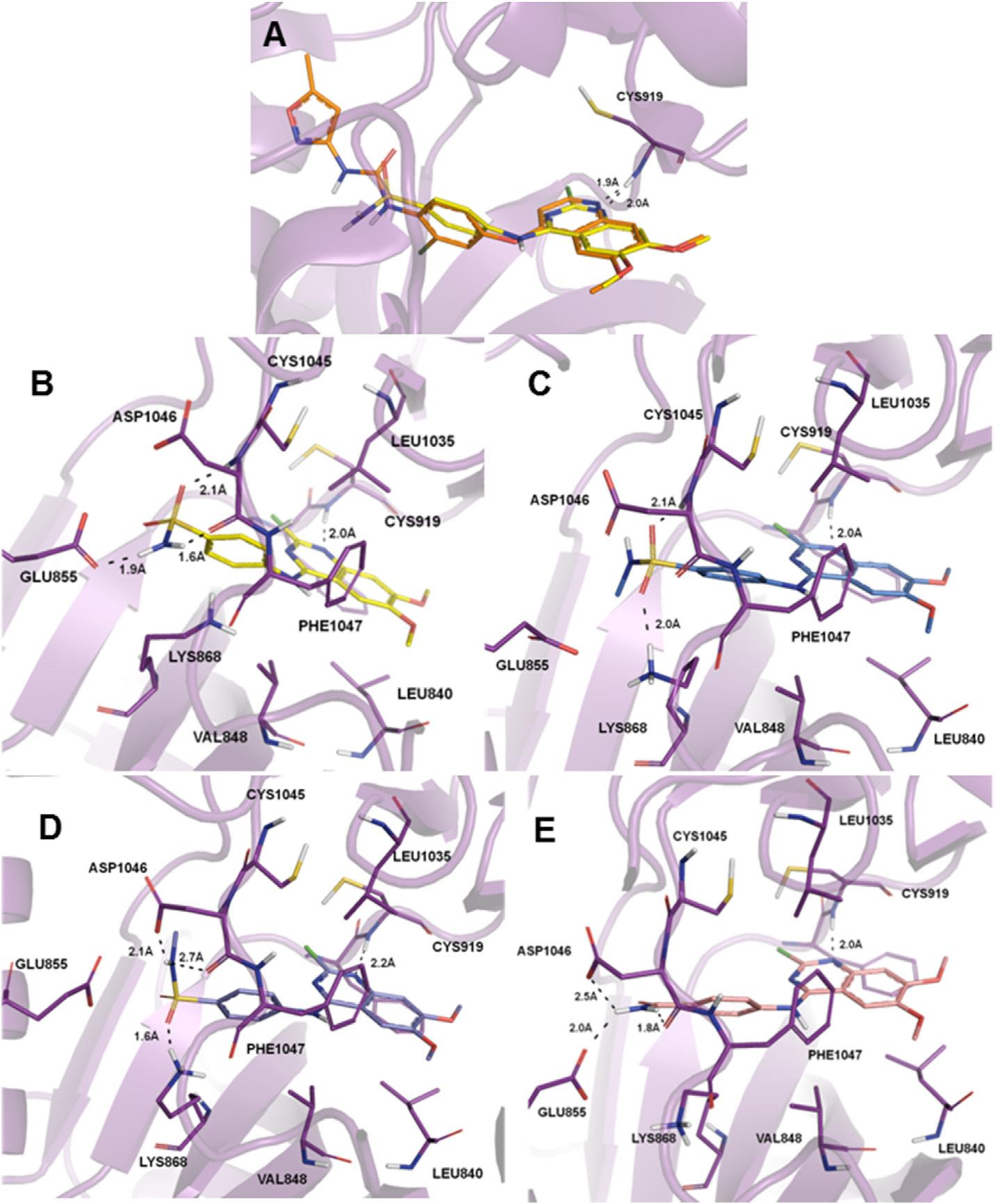
(A) Superposition of 8g (yellow) with tivozanib (6, orange) inside the VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase ATP binding site. (B) Binding interactions of 8g (yellow) with VEGFR-2. (C) Binding interactions of 8k (blue) with VEGFR-2 showing the best score value (Score: 71.82). (D) Binding interactions of 8k (blue) with VEGFR-2 showing the possibility of a hydrogen bond with the sulfonamide eNHe as a donor (Score: 69.29). (E) Binding interactions of 8o (light pink) with VEGFR-2.
CAS number: 478-88-6
Ergoline is a chemical compound that forms the core structure of a class of alkaloids found in ergot and other fungi. These alkaloids, including those found in ergot, have a range of uses, from treating migraines to inducing uterine contractions.
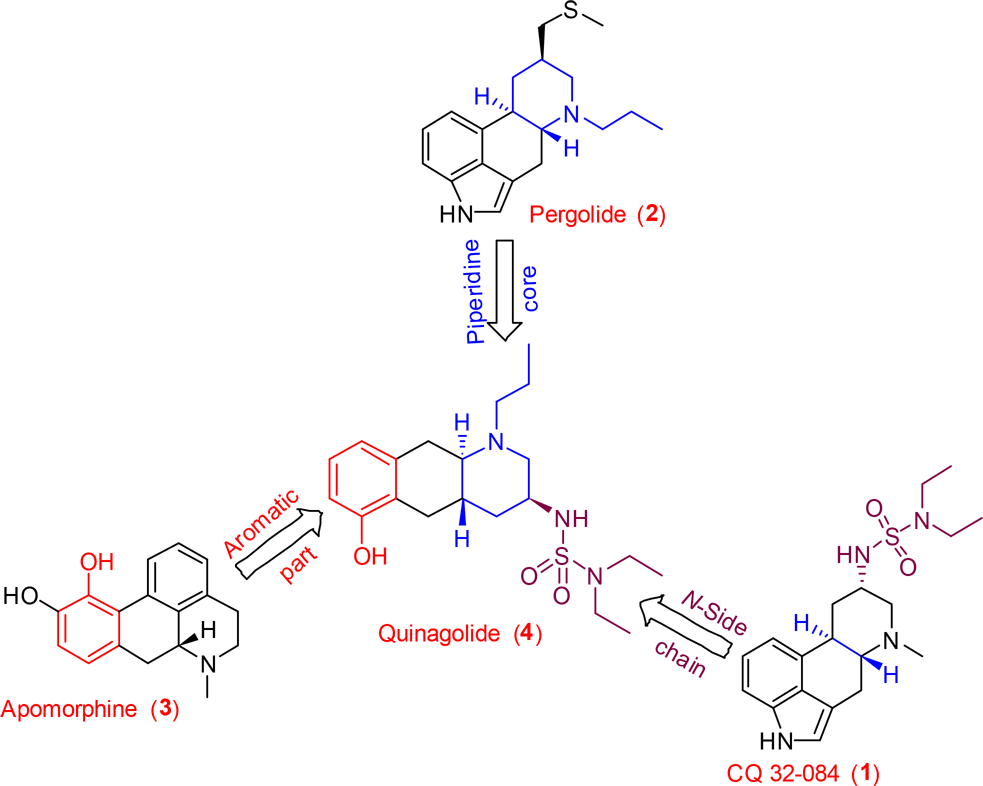
Quinolide (4) has structural features of both ergoline and apomorphine.
CAS number: 4782-75-6
Kondurite, also known as Conduritol D, is a naturally occurring organic compound classified as a cyclitol.
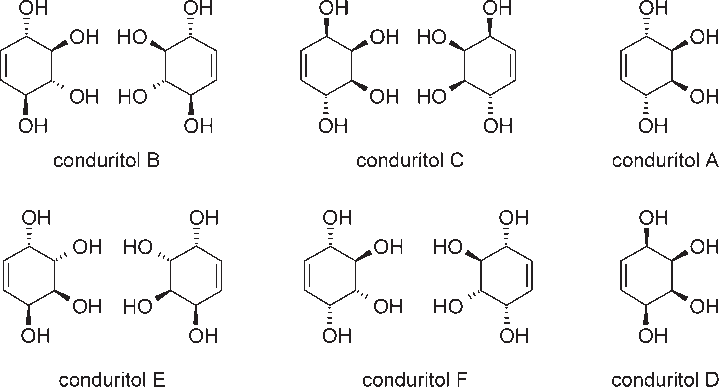
Structures of all conduritol isomers.
CAS number: 479-27-6
1,8-Diaminonaphthalene is a naphthalenediamine, specifically with the amino groups (NH₂) located at the 1 and 8 positions of the naphthalene ring. It's a colorless solid that darkens upon exposure to air due to oxidation.
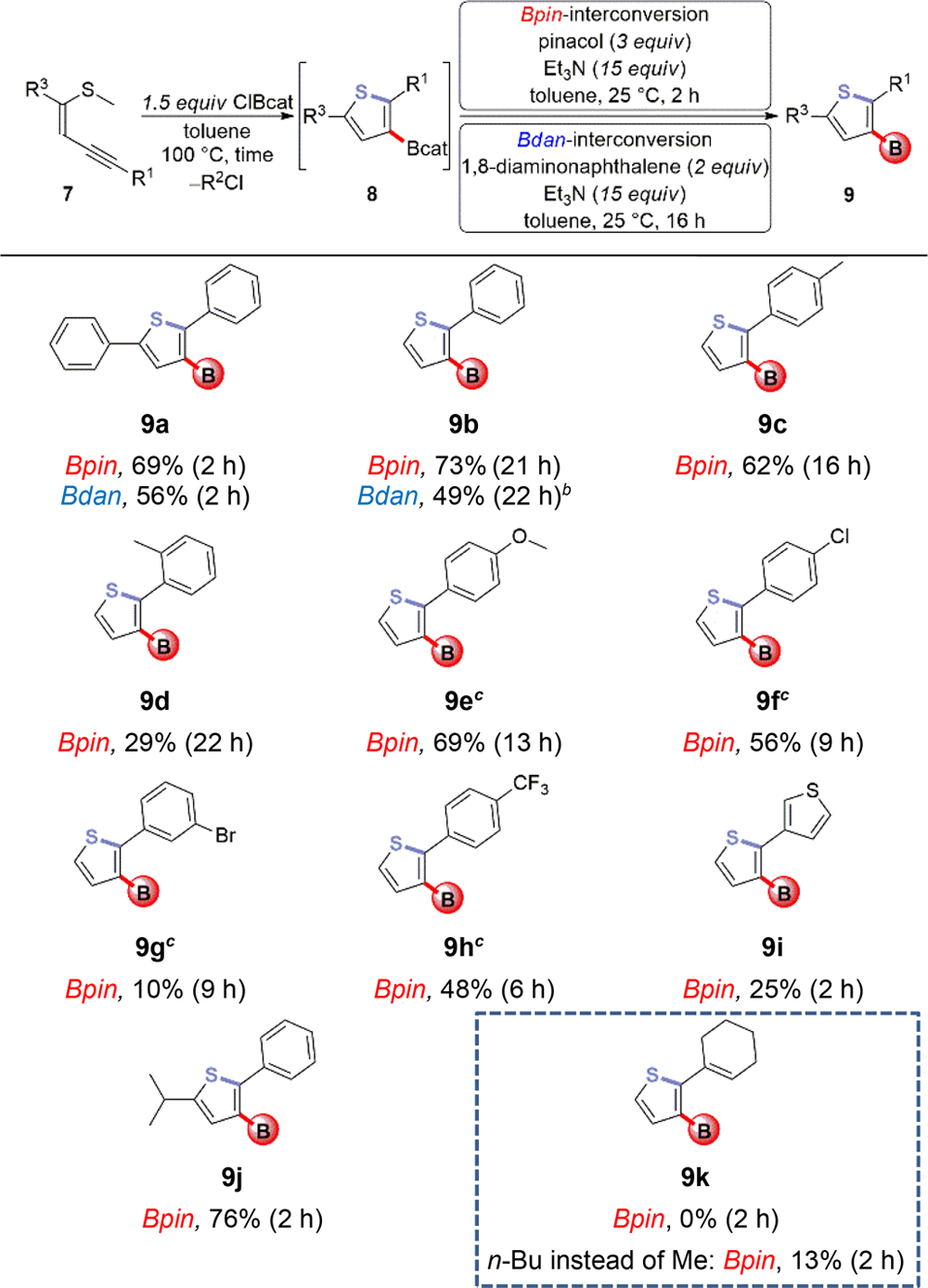
Regioselective Synthesis of 3-Borylated Thiophenes
CAS number: 480-41-1
(S)-naringenin is the (S)-enantiomer of naringenin. It has a role as an expectorant and a plant metabolite. It is a naringenin and a (2S)-flavan-4-one. It is a conjugate acid of a (S)-naringenin(1-). It is an enantiomer of a (R)-naringenin.
![Competition curves of naltrexone (◼) and compounds 8 (△), 9 (▼), 10 (+), 12 (▲), 15 (◇), 31 (○) and 32 (●) for [3H]-DAMGO binding to Wistar rat forebrain membranes.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/2127528_10.png)
Competition curves of naltrexone (◼) and compounds 8 (△), 9 (▼), 10 (+), 12 (▲), 15 (◇), 31 (○) and 32 (●) for [3H]-DAMGO binding to Wistar rat forebrain membranes.
CAS number: 480-90-0
1H-Inden-1-one, also known as 1-indanone, is a cyclic ketone with a benzene ring fused with a cyclopentenone ring.
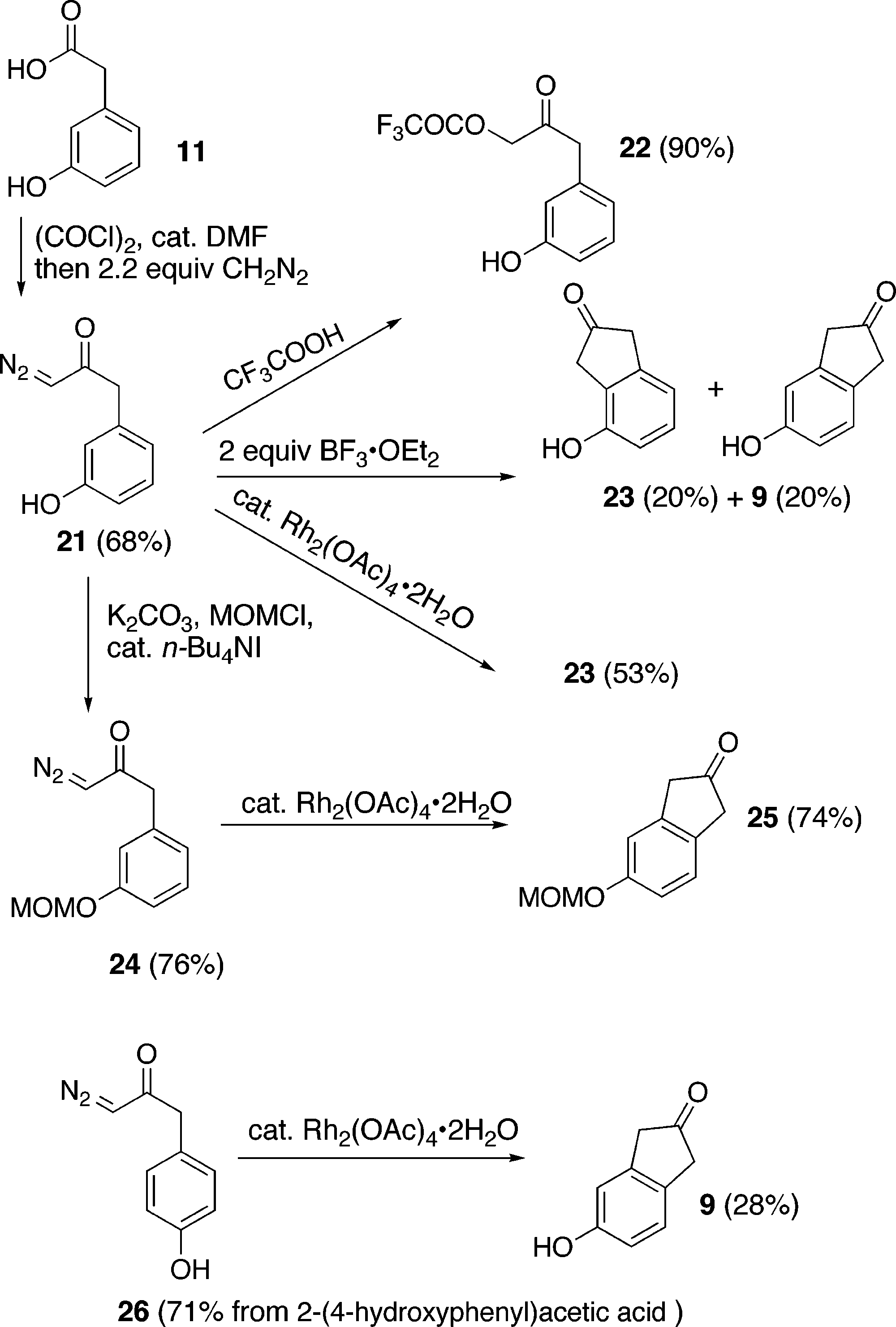
Synthesis of Indenones and Unusual Proximity Effects of Phenols; Comparison of H+- and Rh2+-Promoted Cyclizations
CAS number: 4803-27-4
Anthramycin is a member of the class of pyrrolobenzodiazepines that is (11aS)-5,10,11,11a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine substituted at positions 2, 5, 8, 9 and 11R by a (1E)-3-amino-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl, oxo, methyl, hydroxy and hydroxy groups, respectively.
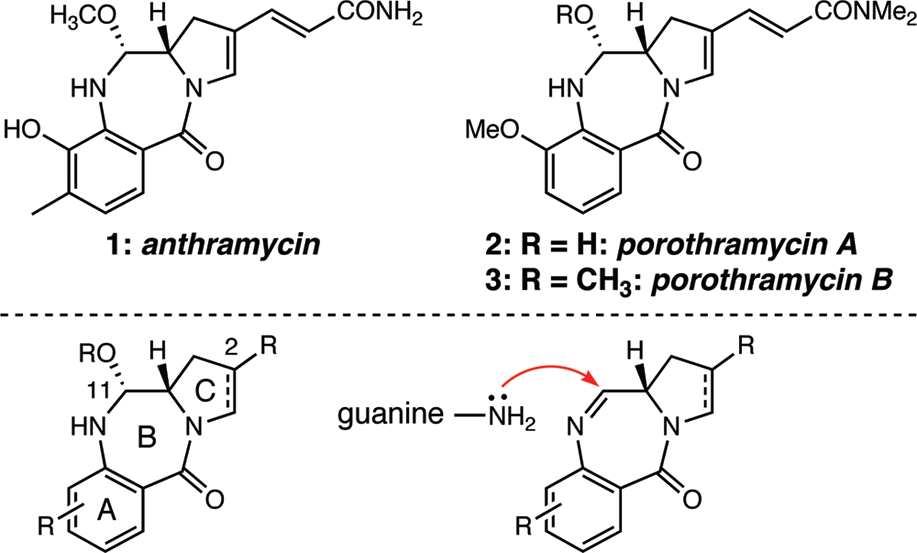
Structures of anthramycin and the porothramycins and the general scaffold of the pyrrolobenzodiazepinone antitumor antibiotics.
CAS number: 481-42-5
Plumbagin is a compound investigated for its anticancer activity. It has been found that it inactivates the Akt/NF-kB, MMP-9 and VEGF pathways.
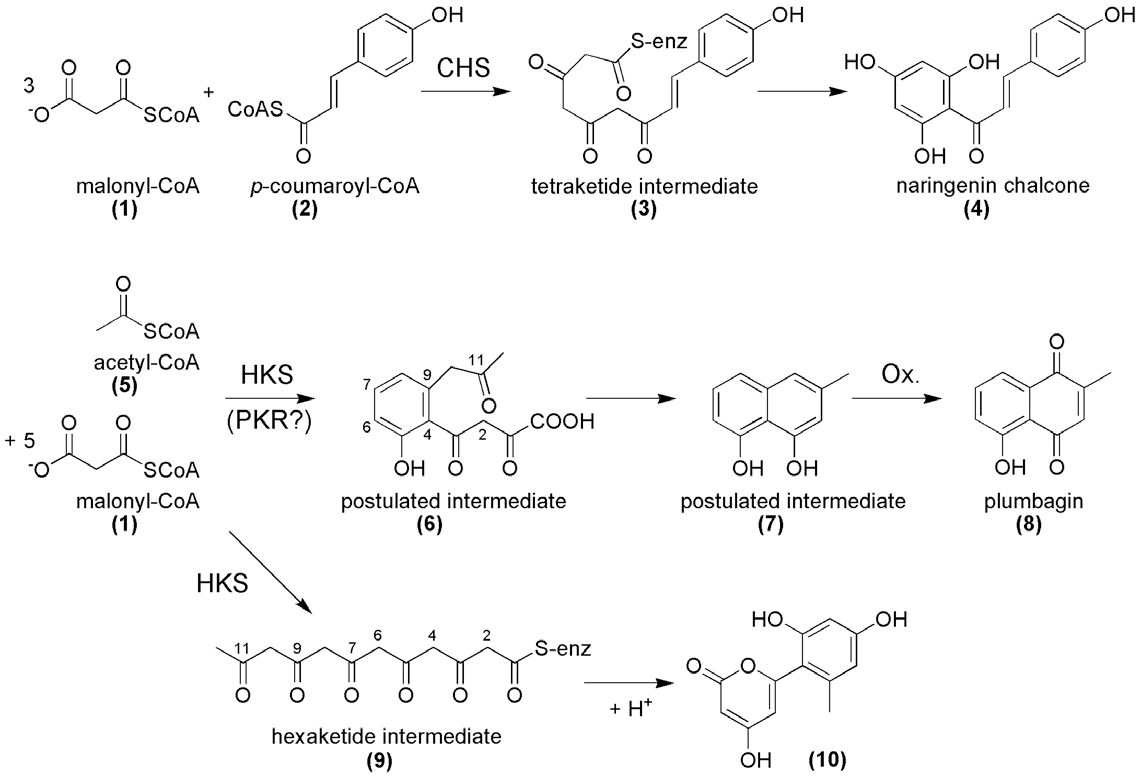
Postulated mechanism of plumbagin biosynthesis and comparison with the reaction of chalcone synthase (CHS). The PKS involved in plumbagin (8) biosynthesis presumably catalyzes the decarboxylative condensation of acetyl-CoA (5) with five molecules of malonyl-CoA (1).
CAS number: 481-82-3
Betti's base is a compound that is produced by the Betti reaction, a multicomponent condensation between 2-naphthol, aryl aldehydes, and ammonia or amines.
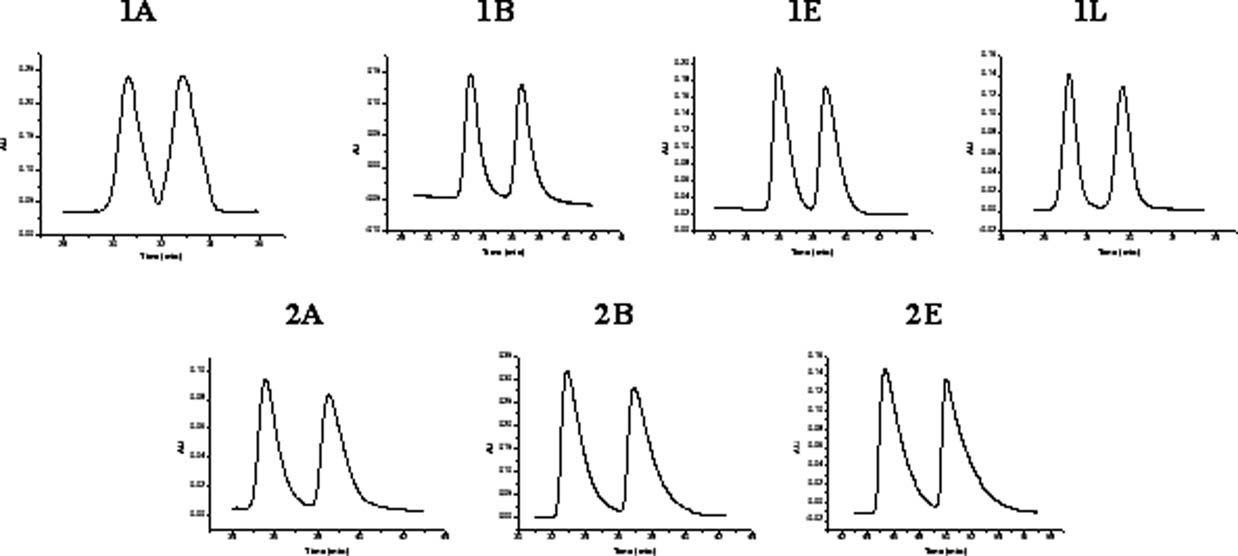
Selected chromatograms of Betti base analogs.
CAS number: 484-51-5
Khellinone, a naturally occurring compound derived from the plant Ammi visnaga, is classified as a benzofuran derivative.
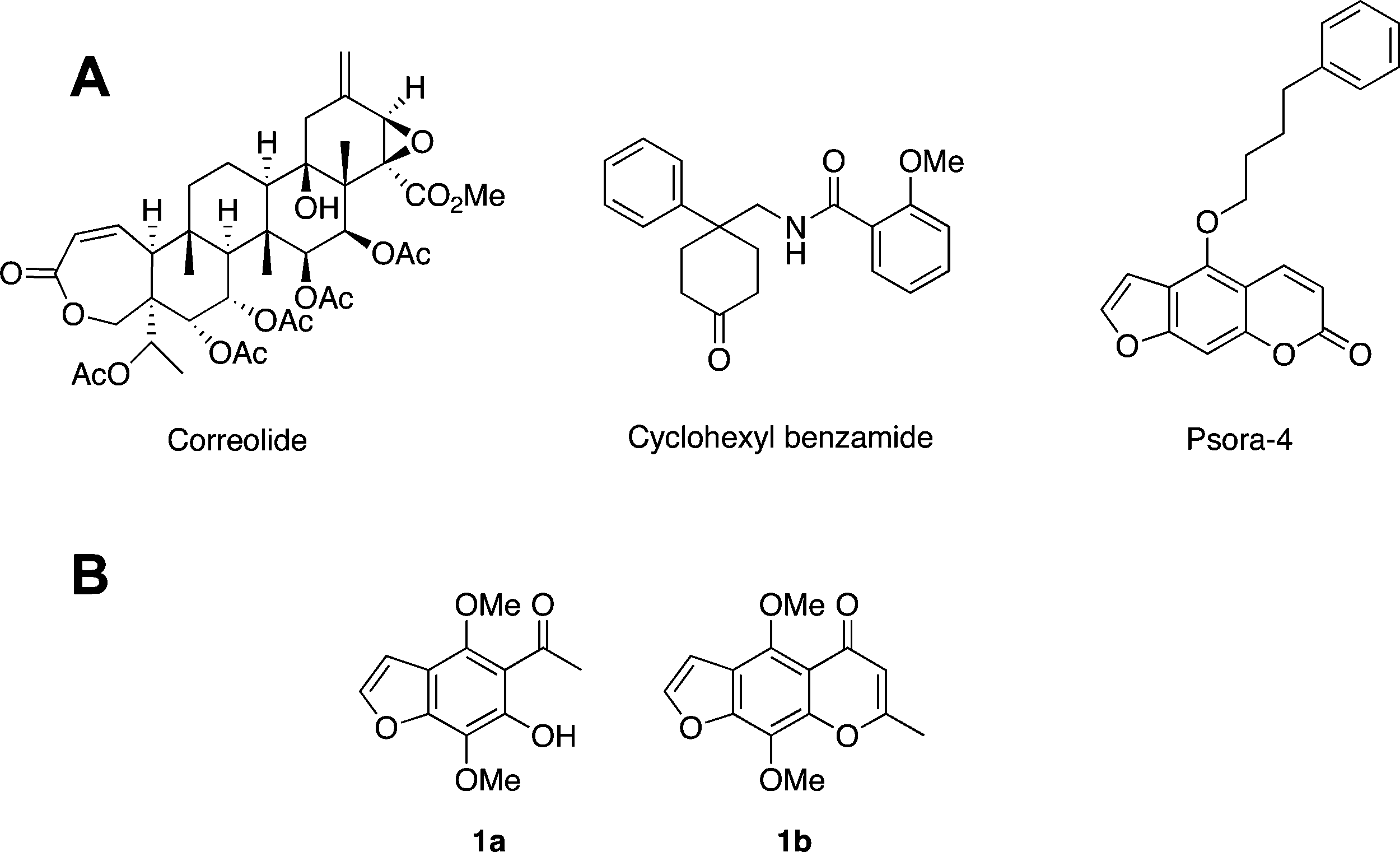
Figure 1. (A) Structures of correolide, a representative cyclohexyl benzamide and the 5-phenylalokoxypsoralen Psora-4. (B) Structures of khellinone 1a and khellin 1b. The 7-position in khellinone corresponds to the 9-position in khellin as indicated in Table 1.
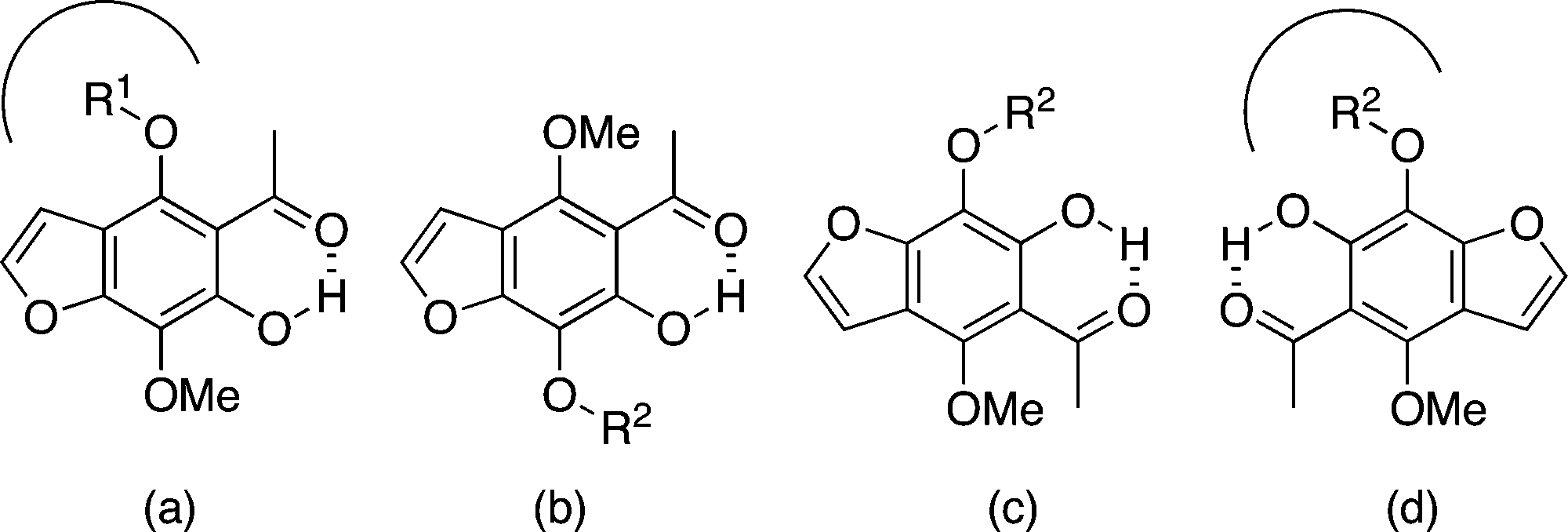
Pseudo-symmetry in the khellinone analogues.