Tivozanib
CAS number: 475108-18-0
Tivozanib is a member of the class of quinolines that is 6,7-dimethoxyquinoline substituted by a 3-chloro-4-{[(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)carbamoyl]amino}phenoxy group at position 4. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases and was previously in clinical development for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. It has a role as a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist, an antineoplastic agent and an apoptosis inducer. It is an aromatic ether, a member of isoxazoles, a member of phenylureas, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a member of quinolines.
Related images
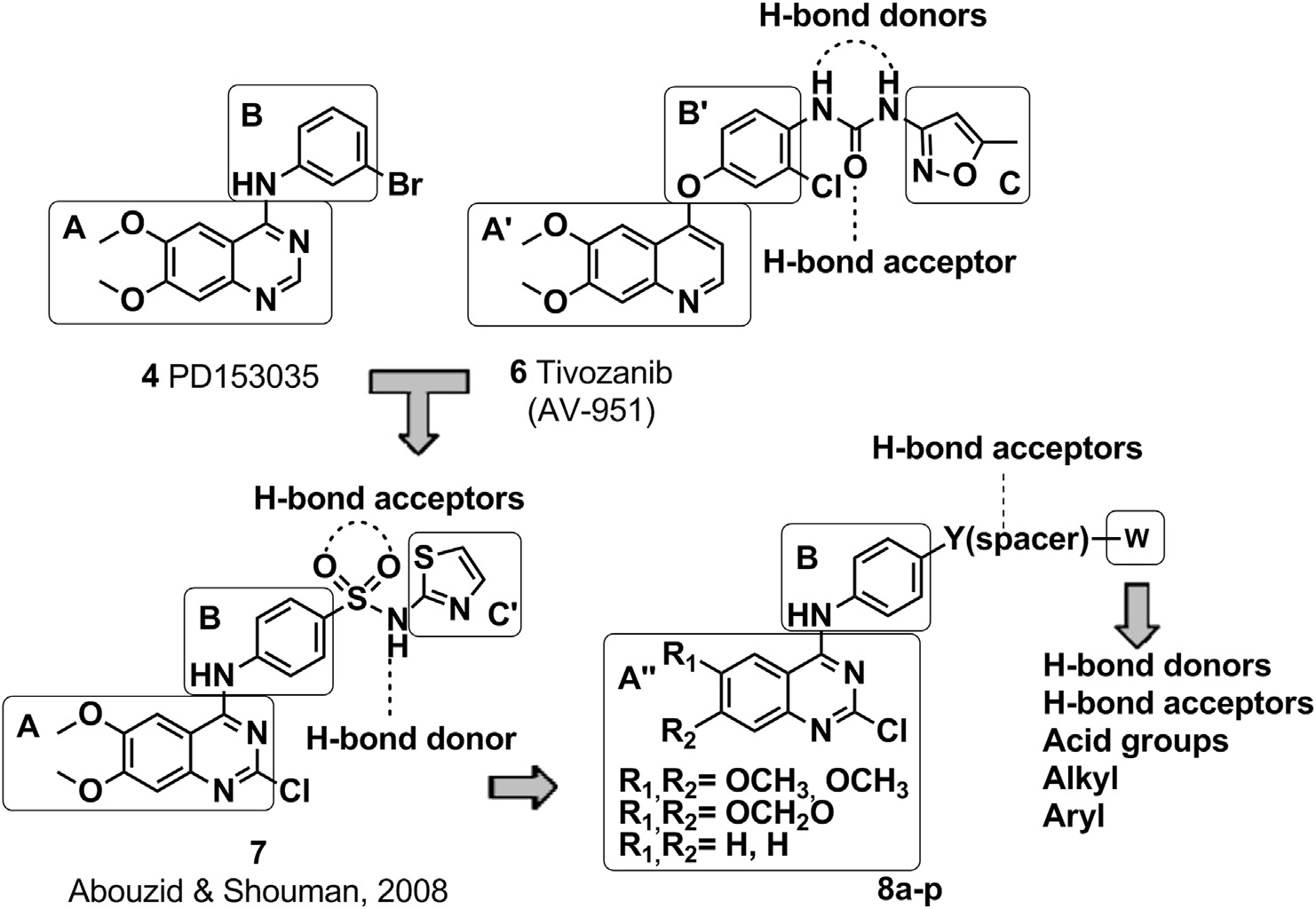
Structural design of the target 2-chloro-4-anilino-quinazoline derivatives 8aep.
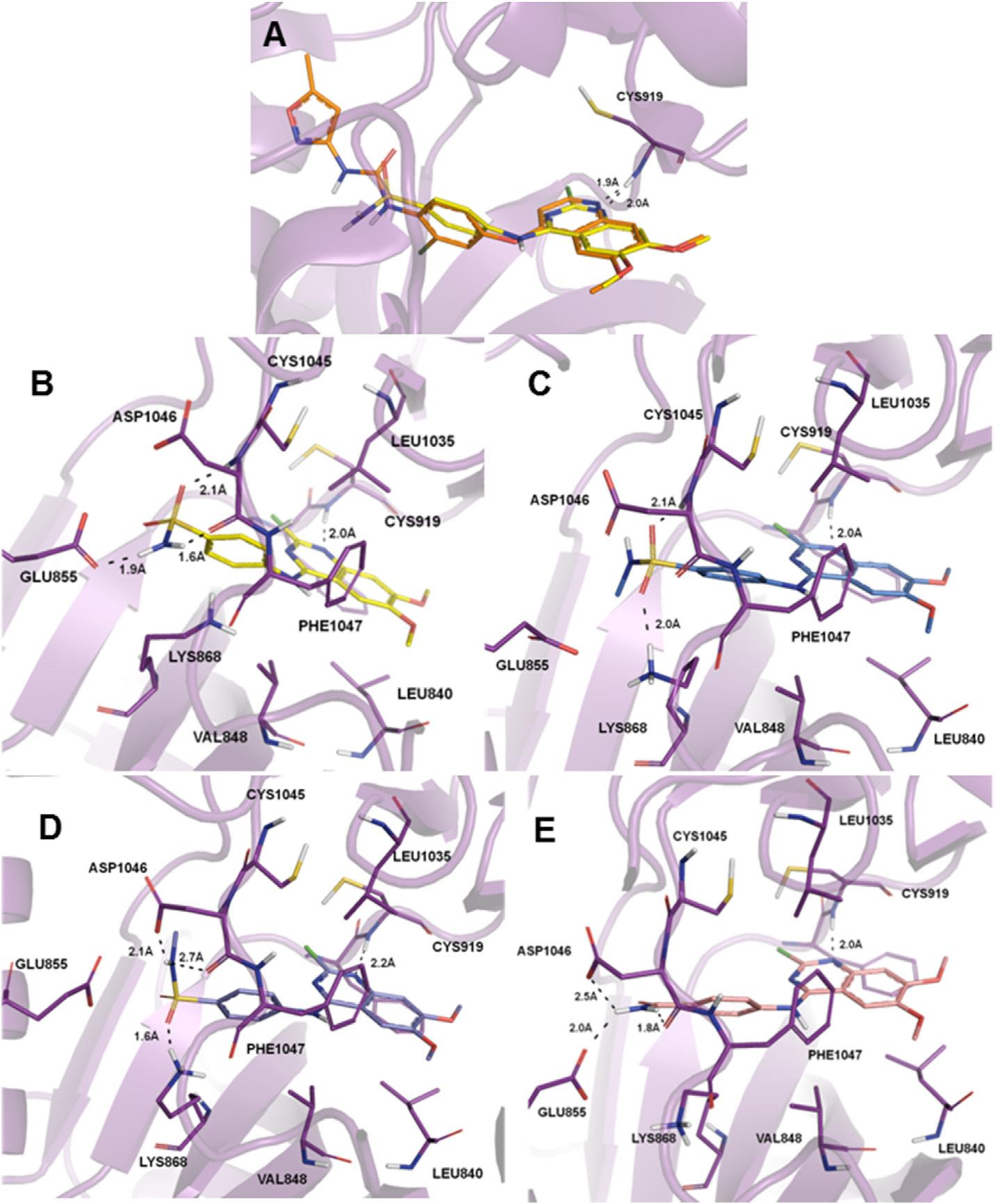
(A) Superposition of 8g (yellow) with tivozanib (6, orange) inside the VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase ATP binding site. (B) Binding interactions of 8g (yellow) with VEGFR-2. (C) Binding interactions of 8k (blue) with VEGFR-2 showing the best score value (Score: 71.82). (D) Binding interactions of 8k (blue) with VEGFR-2 showing the possibility of a hydrogen bond with the sulfonamide eNHe as a donor (Score: 69.29). (E) Binding interactions of 8o (light pink) with VEGFR-2.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet