Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 3812-32-6
Carbonate is a carbon oxoanion. It is a conjugate base of a hydrogencarbonate.
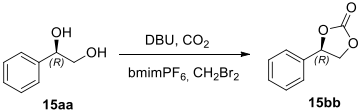
Synthesis of cyclic carbonate.
CAS number: 3843-74-1
Methyl caffeate is an alkyl caffeate ester formed by the formal condensation of caffeic acid with methyl alcohol. It is an alkyl caffeate ester and a methyl ester.
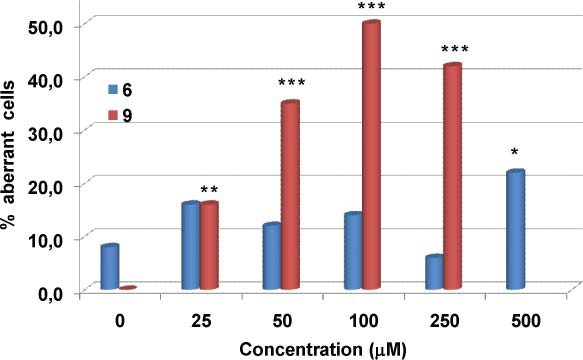
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the monolignol methyl ferulate 6 and its catechol derivative methyl caffeate 9 in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 38480-28-3
2-Bromopyrrole is a brominated derivative of pyrrole, a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring with one nitrogen atom. Specifically, it is a bromine-substituted pyrrole, with the bromine atom attached to the second carbon atom of the pyrrole ring.
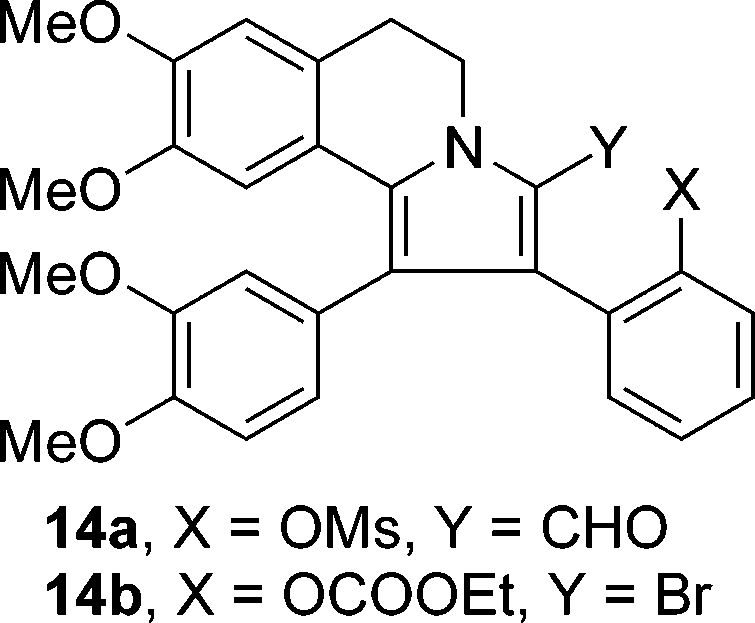
Structure of 2-formylpyrrole 14a and 2-bromopyrrole 14b.
CAS number: 3902-71-4
Trioxsalen (trimethylpsoralen, trioxysalen or trisoralen) is a furanocoumarin and a psoralen derivative obtained from several plants, mainly Psoralea corylifolia. Like other psoralens it causes photosensitization of the skin. It is administered either topically or orally in conjunction with UV-A (the least damaging form of ultraviolet light) for phototherapy treatment of vitiligo and hand eczema. The photoactivated form produces interstrand linkages in DNA resulting in cell apoptosis.
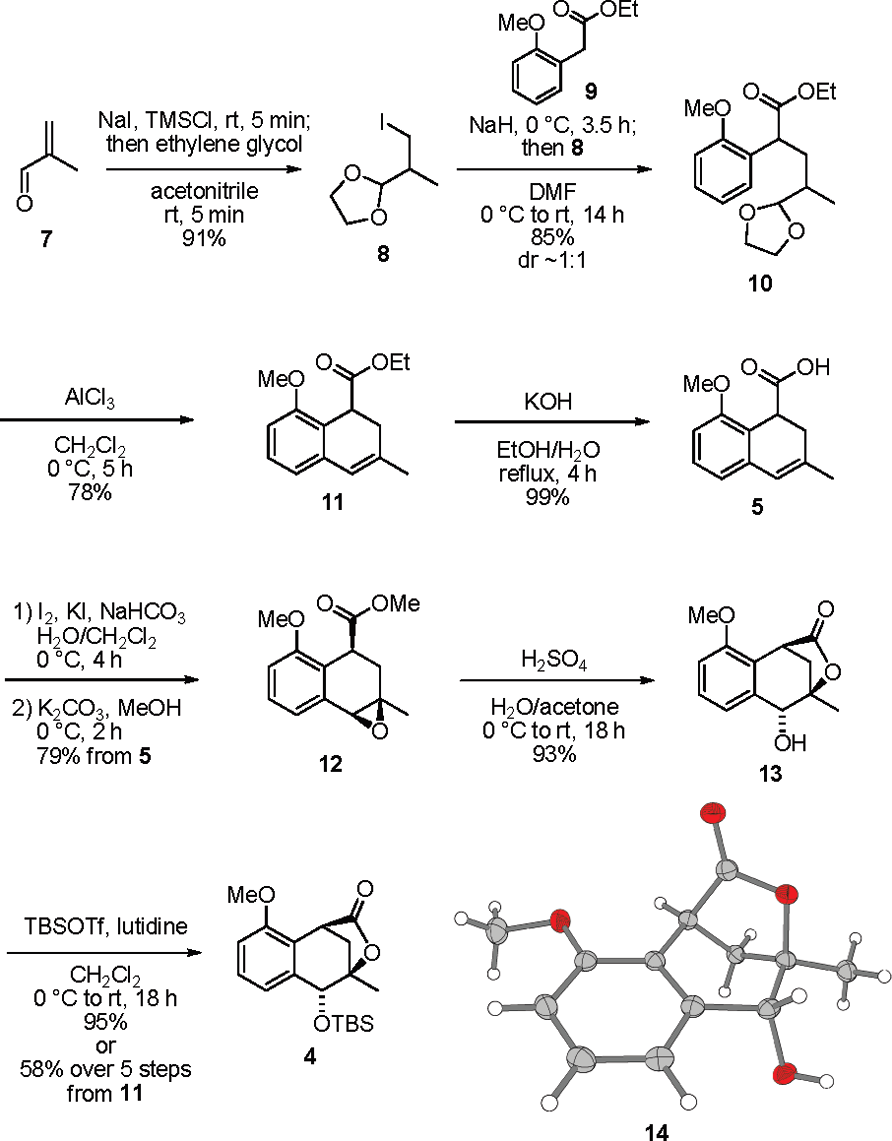
Synthesis of the Lactone 4
CAS number: 3907-06-0
3,3-Dimethylcyclopropene is a chemical compound with a three-membered ring and two methyl groups attached to the same carbon atom.
![M06-2X/6-31G(d)-optimized transition-state structures for the cycloadditions of 1,3- and 3,3-dimethylcyclopropene [Cp(1,3) and Cp(3,3)] with diphenyl-substituted nitrile imine (NI) and tetrazine (Tz). M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p)//6-31G(d)-computed energies and relative rate constants (distances in Å, energies in kcal/mol, krel based on Gwater at 298 K) are also shown.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4119092_03.png)
M06-2X/6-31G(d)-optimized transition-state structures for the cycloadditions of 1,3- and 3,3-dimethylcyclopropene [Cp(1,3) and Cp(3,3)] with diphenyl-substituted nitrile imine (NI) and tetrazine (Tz). M06-2X/6-311+G(d,p)//6-31G(d)-computed energies and relative rate constants (distances in Å, energies in kcal/mol, krel based on Gwater at 298 K) are also shown.
CAS number: 390817-85-3
4-methoxy-N-(7-methyl-3-(2-pyridinyl)-1-isoquinolinyl)benzamide is a specific organic compound. It's an amide, specifically a benzamide derivative, where the benzamide is substituted with a 4-methoxy group and then linked to a 7-methyl-3-(2-pyridinyl)-1-isoquinolinyl group.
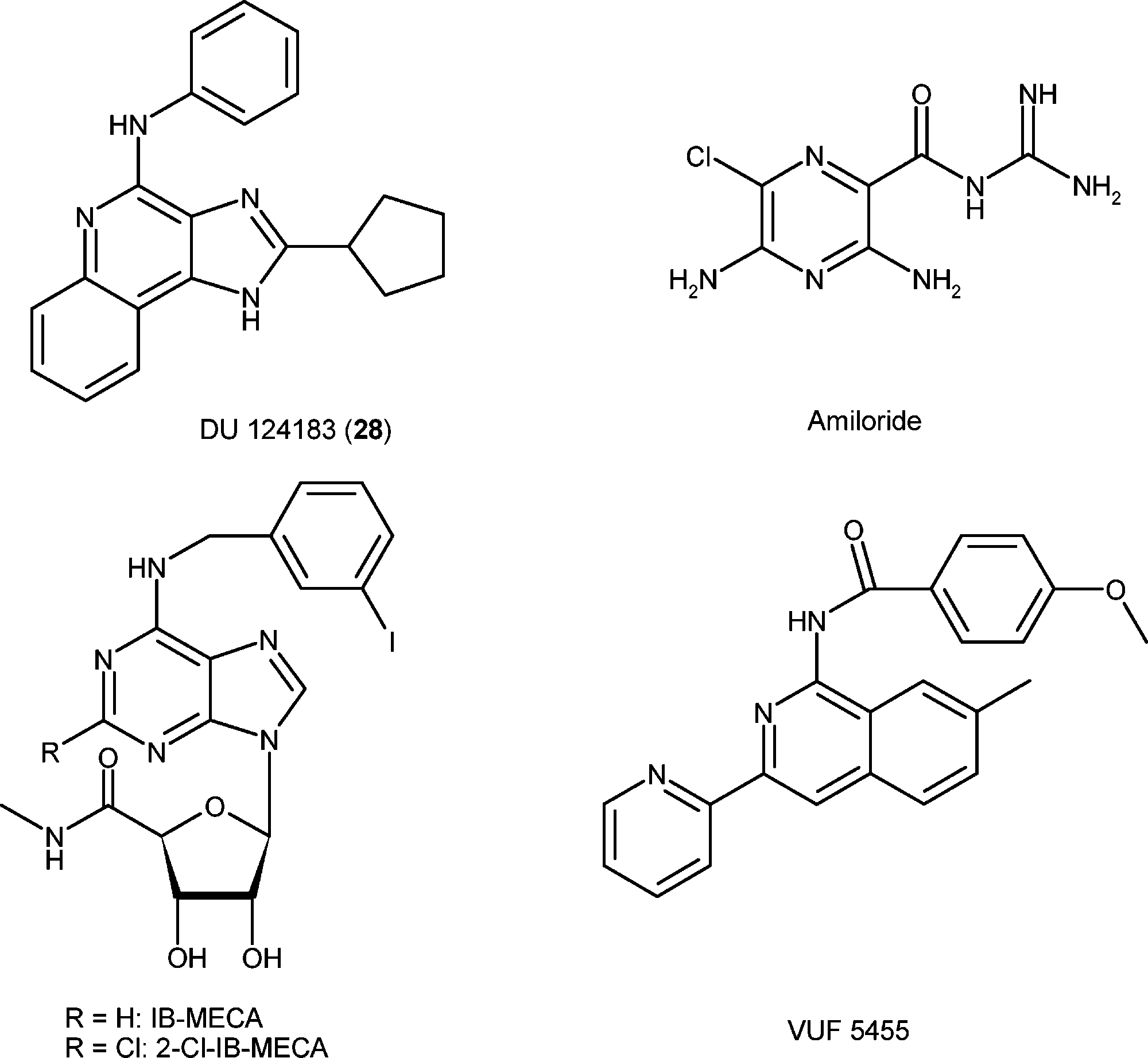
Structures of reference agonists (IB-MECA and 2-Cl-IB-MECA) and allosteric modulators (DU 124183, amiloride, and VUF5455) of the A3AR.
CAS number: 3943-74-6
Methyl vanillate is a benzoate ester that is the methyl ester of vanillic acid. It has a role as an antioxidant and a plant metabolite. It is a benzoate ester, a member of phenols and an aromatic ether. It is functionally related to a vanillic acid.
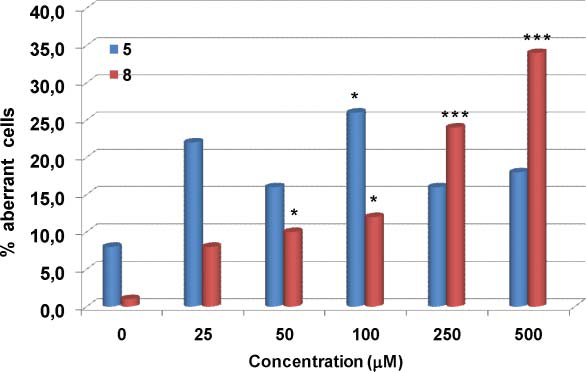
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the monolignol methyl vanillate 5 and its catechol derivative methyl protocatechuate 8 in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 39922-09-3
Cyclohexylidene refers to a cyclic substituent group derived from cyclohexane where a double bond is present within the ring. It's a structural component, not a molecule itself, and is often found as a substituent on another molecule.
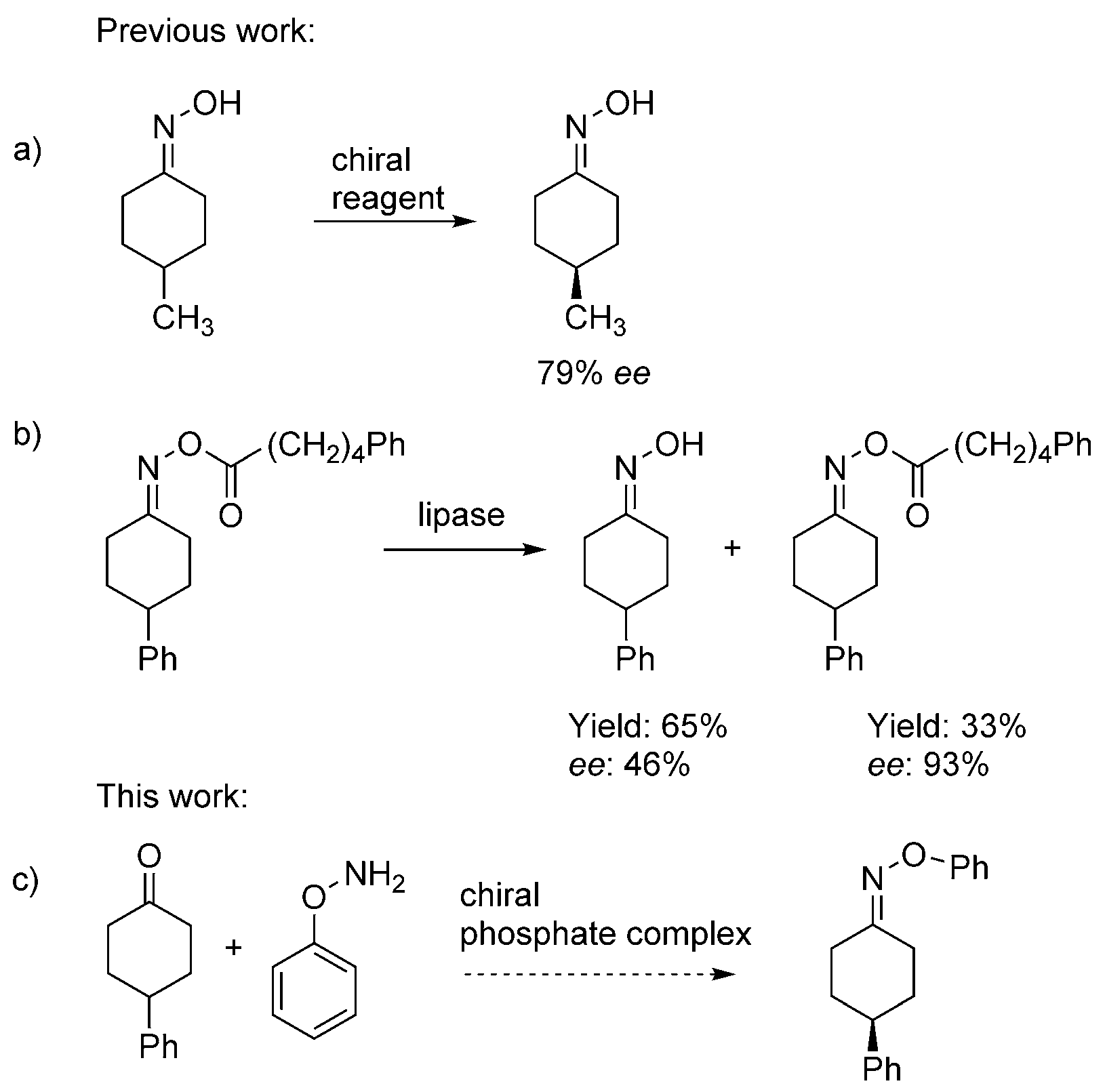
Synthesis of chiral cyclohexylidene oximes.
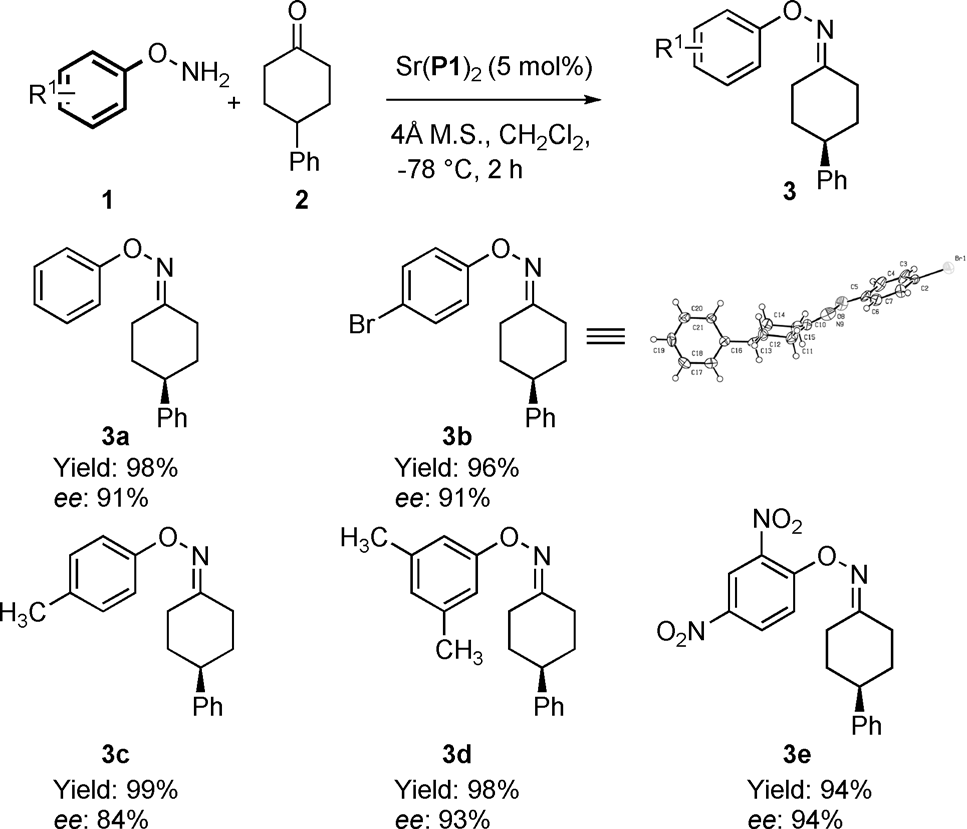
Substrate scope for the synthesis of chiral cyclohexylidene oximes.
CAS number: 4005-51-0
Aminothiadiazole is a synthetic derivative of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). Aminothiadiazole competitively inhibits inosine 5-monophosphate dehydrogenase, thereby disrupting the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation in a number of cells. This agent is also a selective human adenosine A3 receptor antagonist. (NCI04)
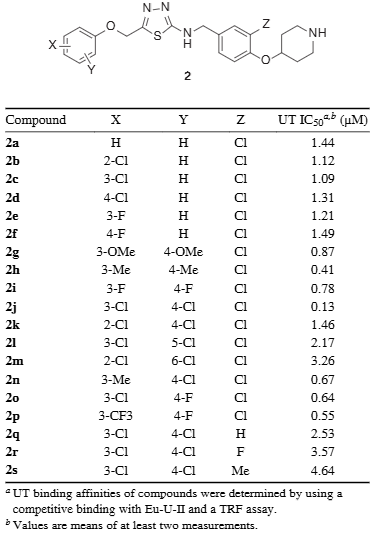
Substituents effects on the UT binding affinity of 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amines.
(5-methyl-2-methylidenehexyl) (Z,2R)-2-hydroxy-6-[(1R,4E,6E,9S,11S,12R,13R,14Z,16E,21S,23S,24S)-11-hydroxy-24-(hydroxymethyl)-12,15,24-trimethyl-3-oxo-2,22,26-trioxatricyclo[19.3.1.19,13]hexacosa-4,6,14,16,19-pentaen-23-yl]hex-4-enoate is a chemical substance used in research.
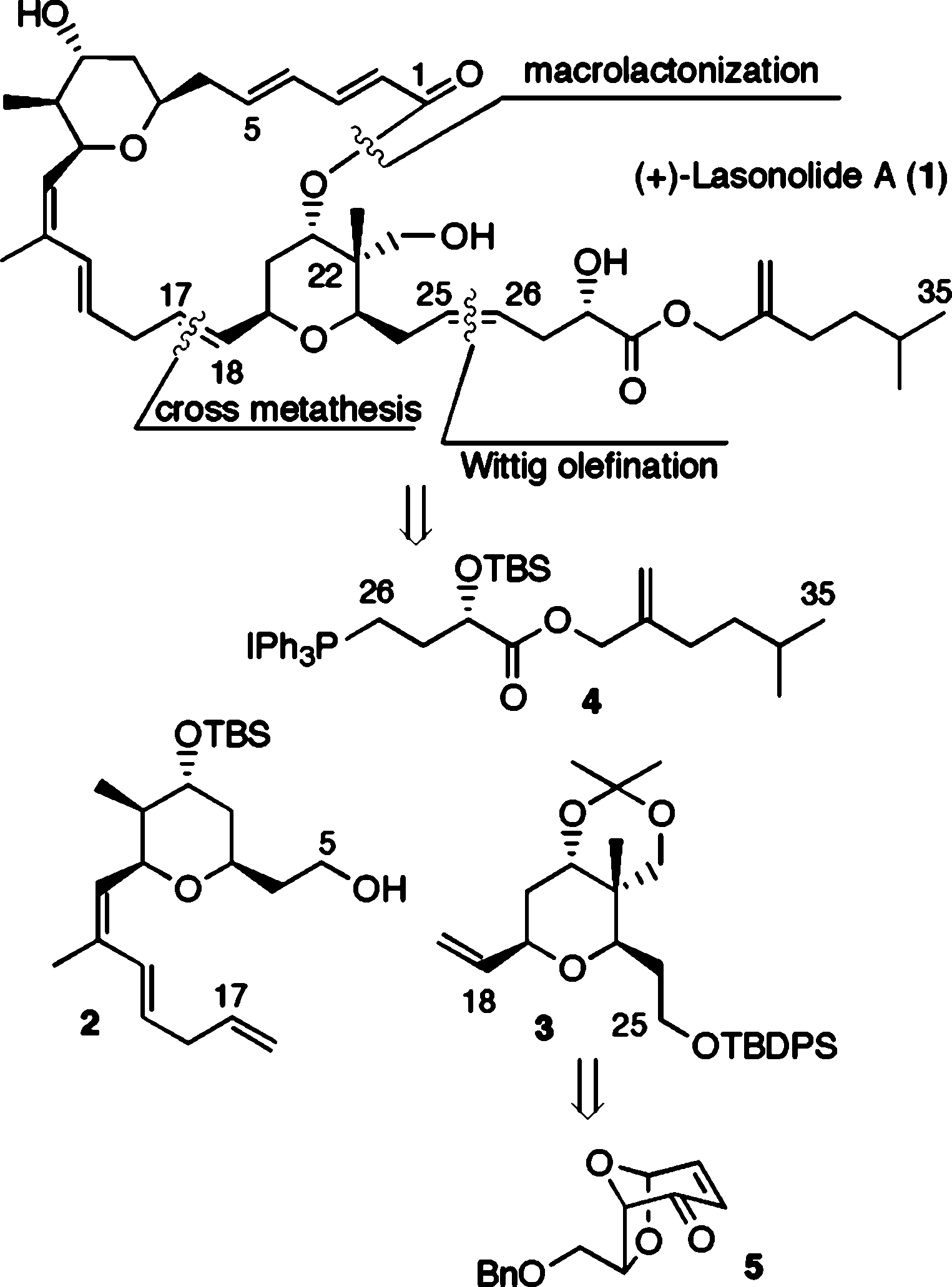
Structure of (+)-lasonolide A and retrosynthetic analysis.
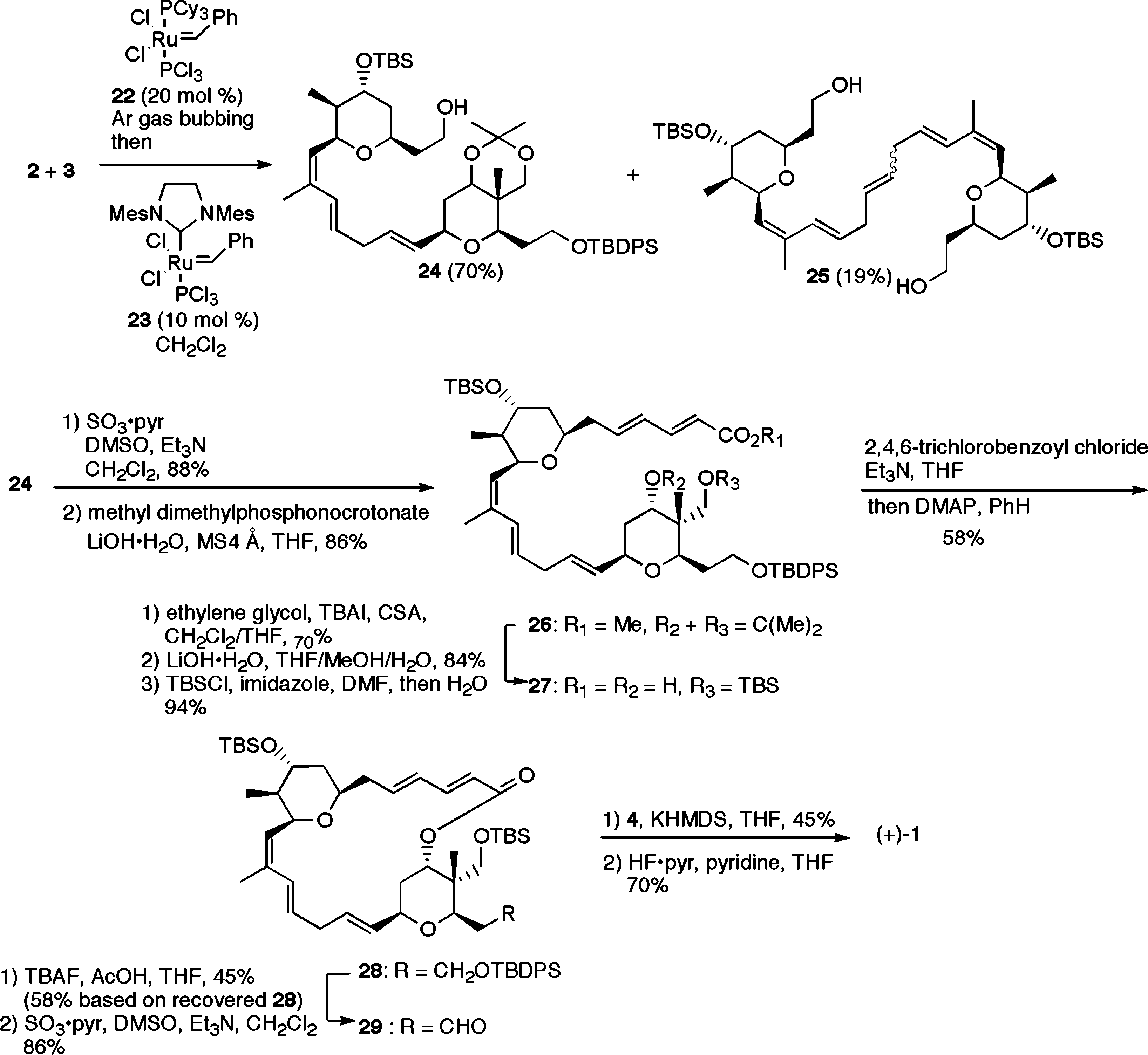
Total Synthesis of (+)-Lasonolide A