Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 25348-64-5
Conduritol is a tetrol that is cyclohexene in which a hydrogen attached to each of the carbons at positions 3, 4, 5, and 6 is replaced by a hydroxy group. The group consists of six possible diastereoisomers, known as conduritols A to F, some of which can exist as two distinct enantiomers. It is a tetrol, a secondary alcohol and a cyclitol. It derives from a hydride of a cyclohexene.
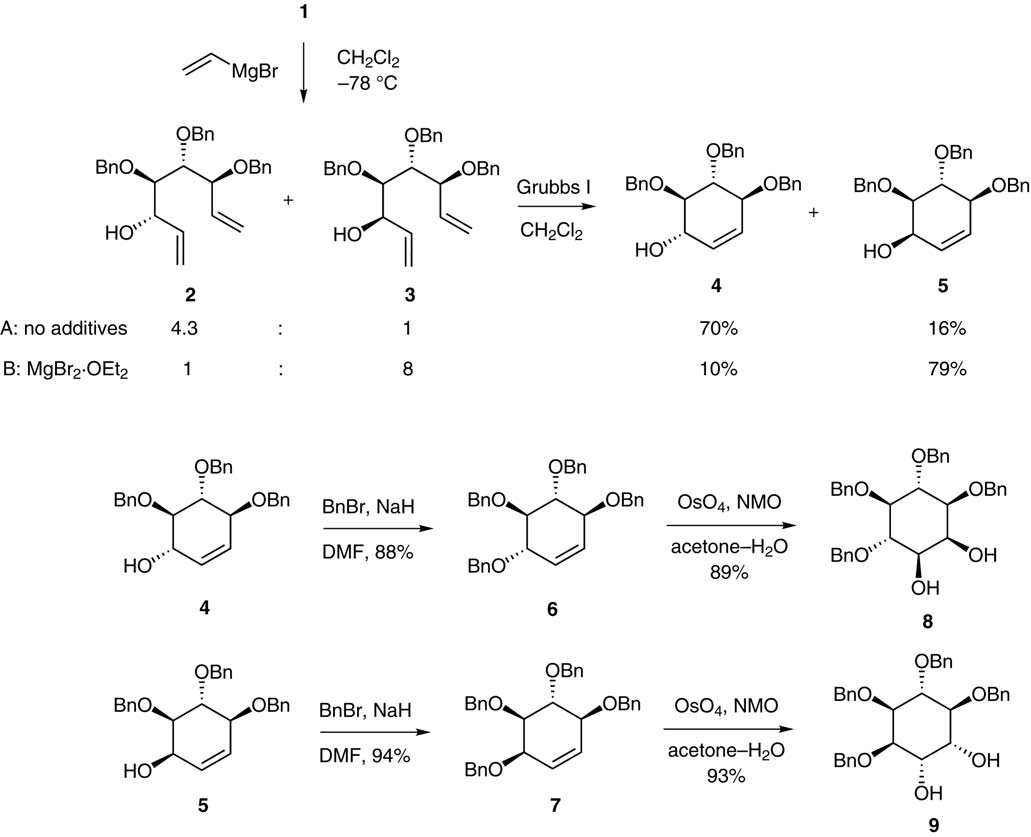
Syntheses of benzylated derivatives of conduritol B, conduritol F, myo-inositol, and chiro-inositol.
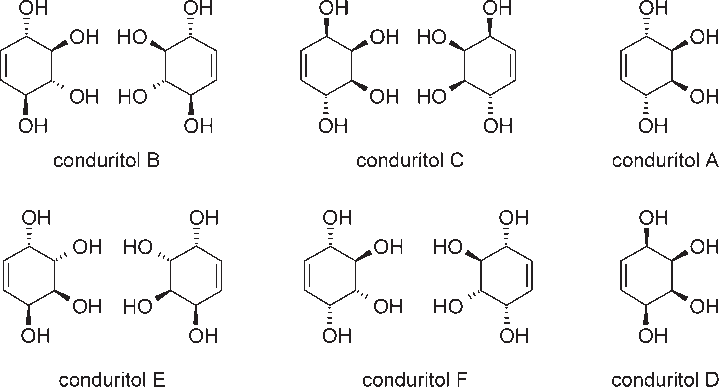
Structures of all conduritol isomers.
CAS number: 2537-36-2
Tetramethylammonium perchlorate (TMAP) consists of a tetramethylammonium cation and a perchlorate anion. It's a white crystalline solid, highly soluble in polar solvents like water and methanol. TMAP is used as an intermediate in organic and chemical synthesis, as a mobile phase in high performance liquid chromatography, and as a supporting electrolyte in electrochemistry.
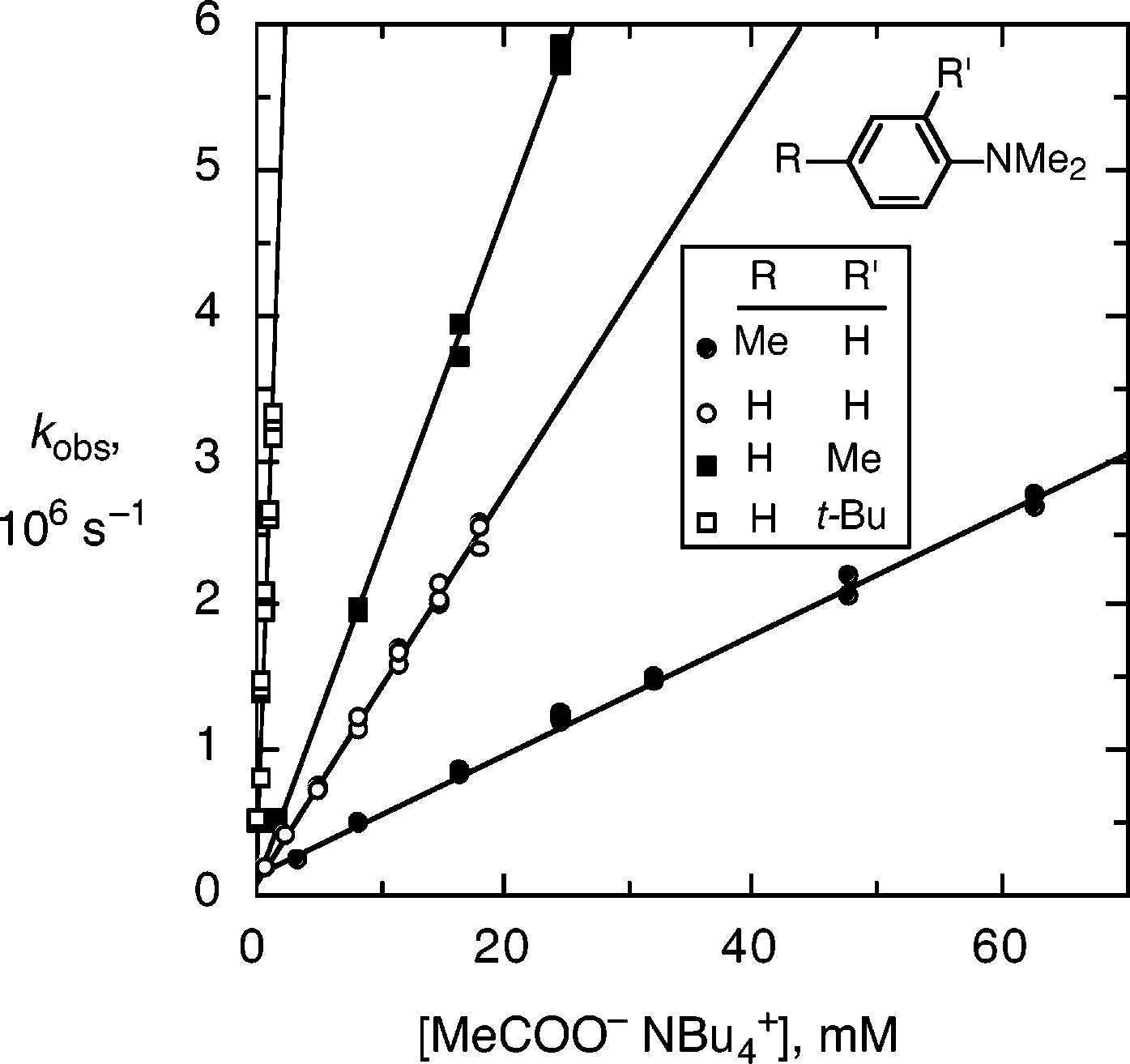
Plots of observed rate of pseudo-first-order decay, kobs, versus concentration of tetrabutylammonium acetate for deprotonation of the radical cations of (open circles) N,N-dimethylaniline, 1c, and N,N,-dimethylaniline with (filled circles) a 4-methyl substituent, 1b, (filled squares) a 2-methyl substituent, 2, and (open squares) a 2-tert-butyl substituent, 3, in acetonitrile with 0.5 m water and 0.5 m tetramethylammonium perchlorate, at room temperature.
CAS number: 254-03-5
4H-chromene is a simplest member of the class of chromene in which the heterocyclic pyran ring has a double bond between positions 2 and 3. It is a chromene and an organic heterobicyclic compound. It is a tautomer of a 2H-chromene.
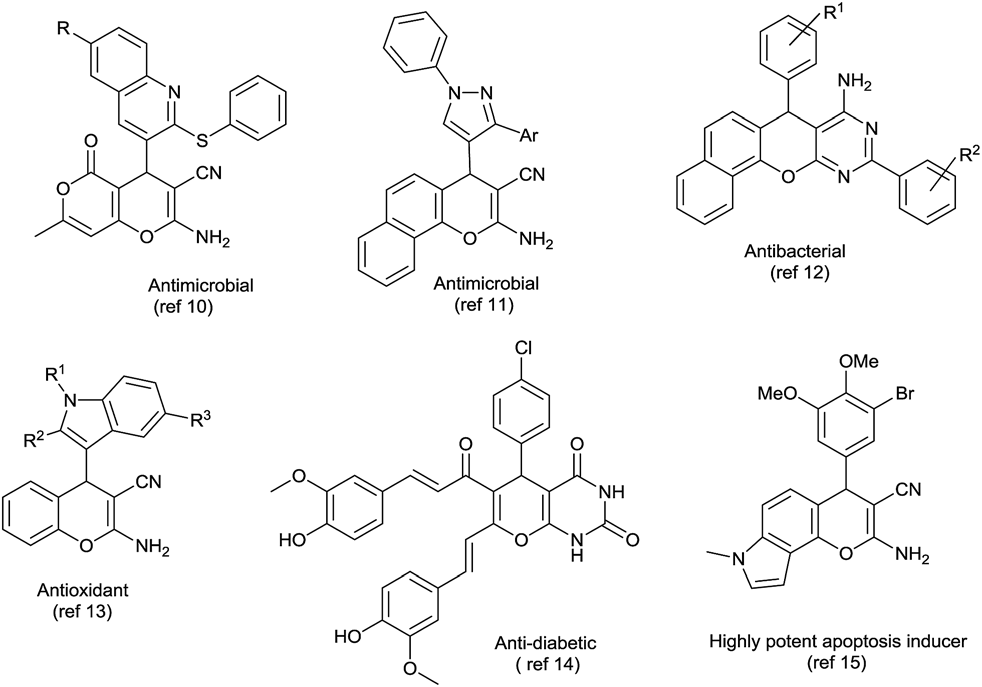
Bioactive 4H-chromene and pyrimidine-fused heterocycles.
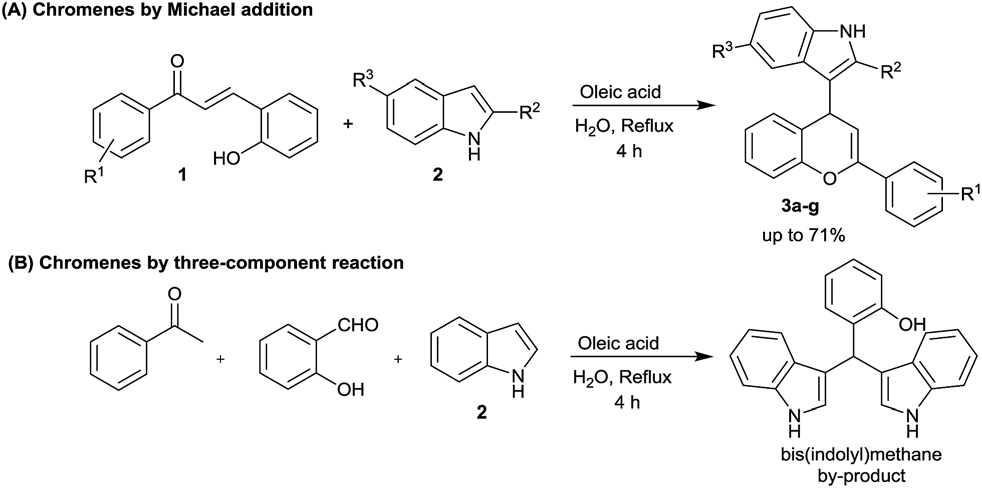
Oleic acid catalysed 4H-chromene synthesis.
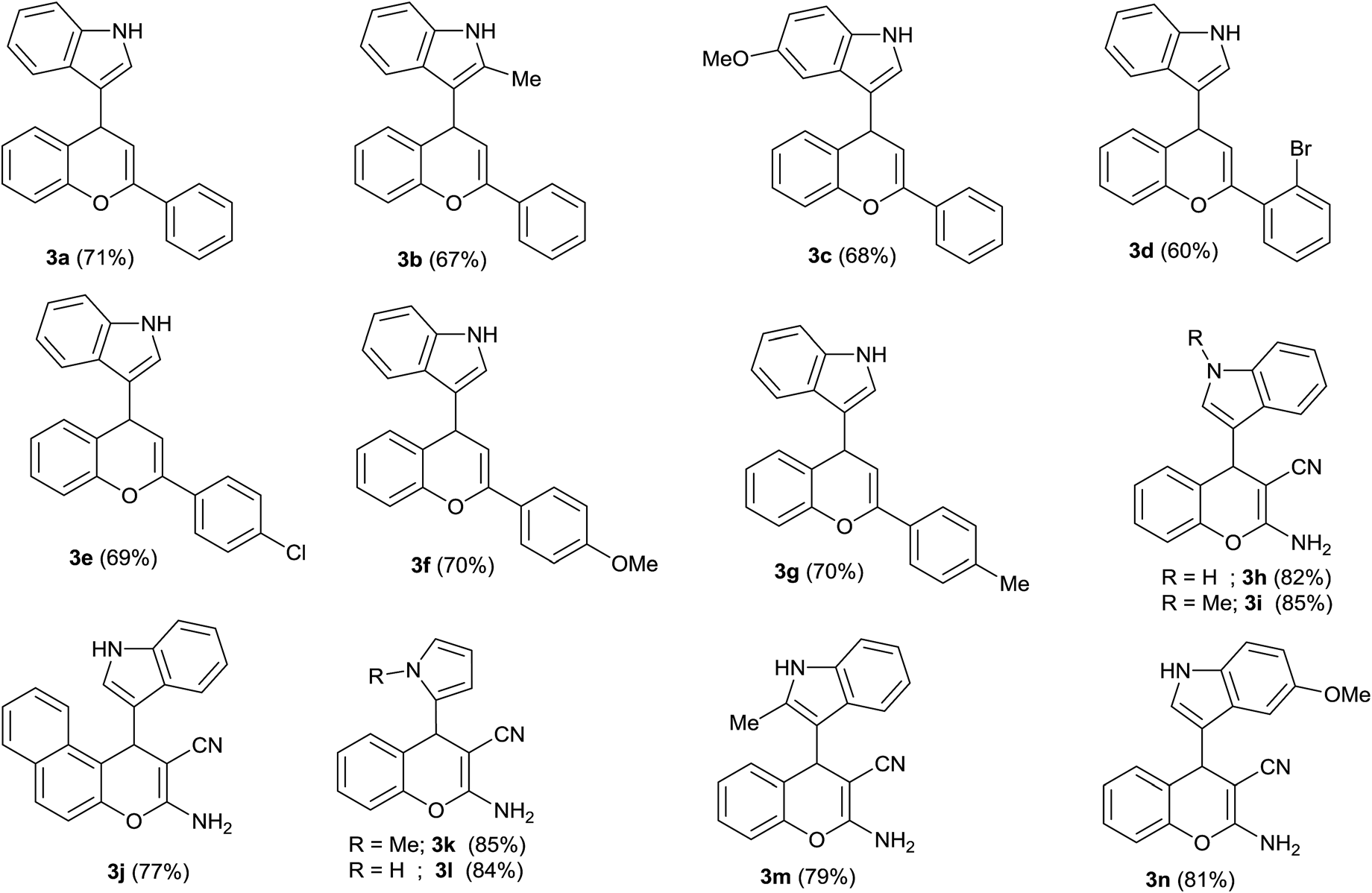
Synthesized 4H-chromene derivatives.
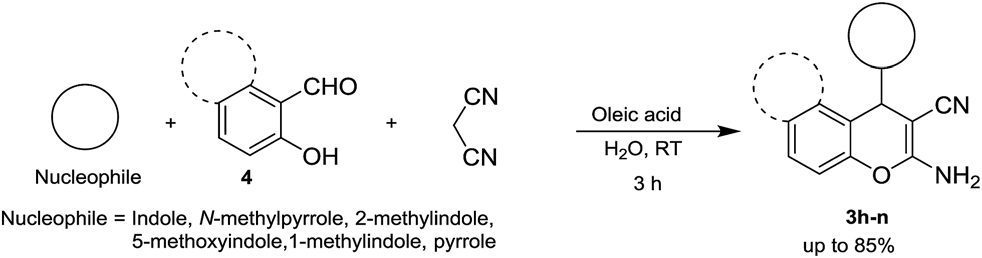
Oleic acid catalysed 4H-chromene synthesis by three-component reaction.
CAS number: 254-04-6
2H-chromene is a simplest member of the class of chromene in which the heterocyclic pyran ring has a double bond between positions 3 and 4. It is a chromene and an organic heterobicyclic compound. It is a tautomer of a 4H-chromene.
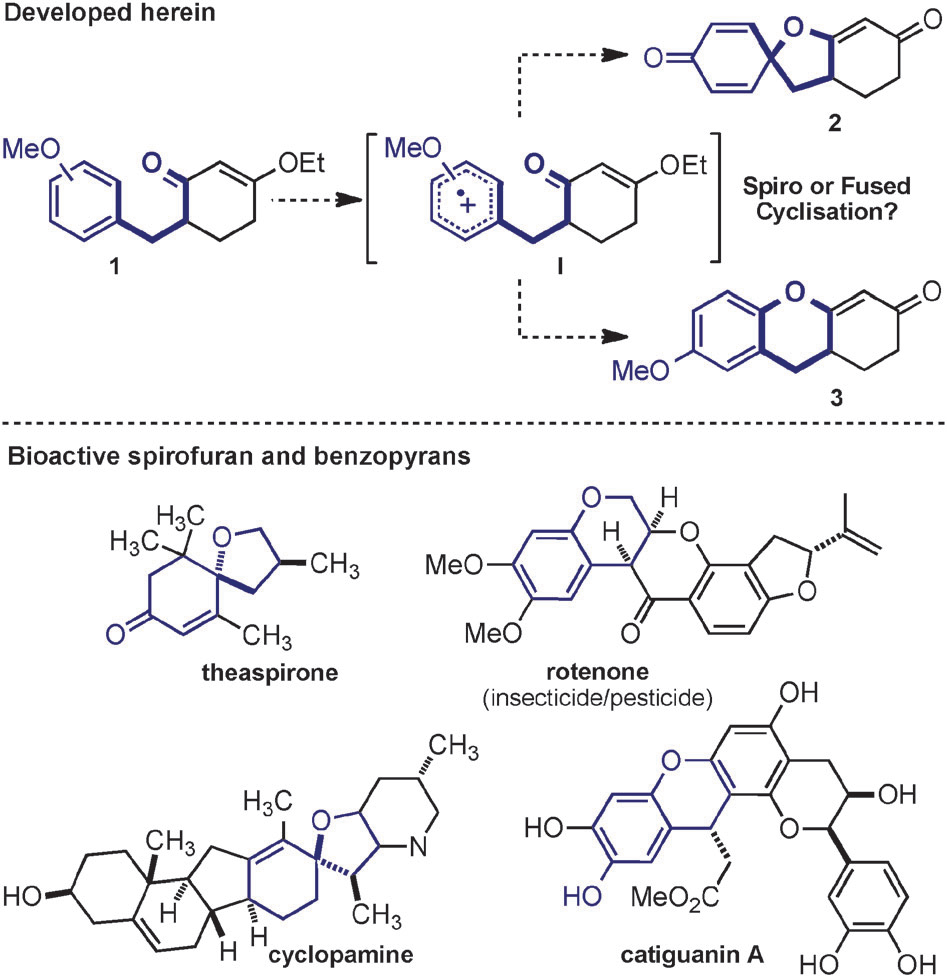
Proposed studies and spirofuran and benzopyran heterocycles.
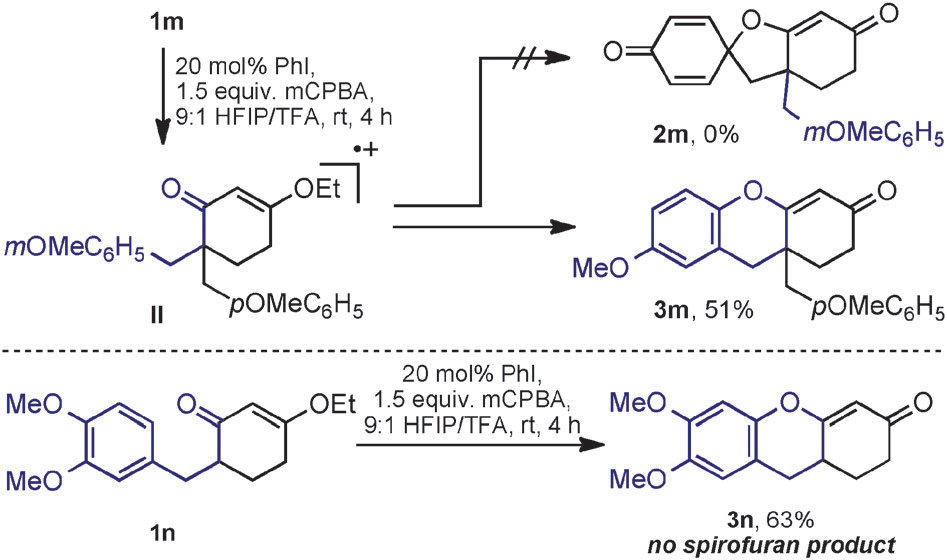
Preferential benzopyran formation.
CAS number: 254-82-0
Pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine is a bicyclic heterocycle composed of fused pyrimidine and pyrimidine rings. It is a biologically important molecule with diverse pharmacological applications, particularly as a core structure for various drug candidates.
![The formation of the pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine 6 can be envisaged through the mechanism described in Scheme 2.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/4296070_04.png)
The formation of the pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine 6 can be envisaged through the mechanism described in Scheme 2.
CAS number: 25409-10-3
3-Propyl-3-buten-2-one is also known as 3-methylene-2-hexanone. It is an unsaturated ketone, characterized by a double bond (alkene) and a ketone functional group.
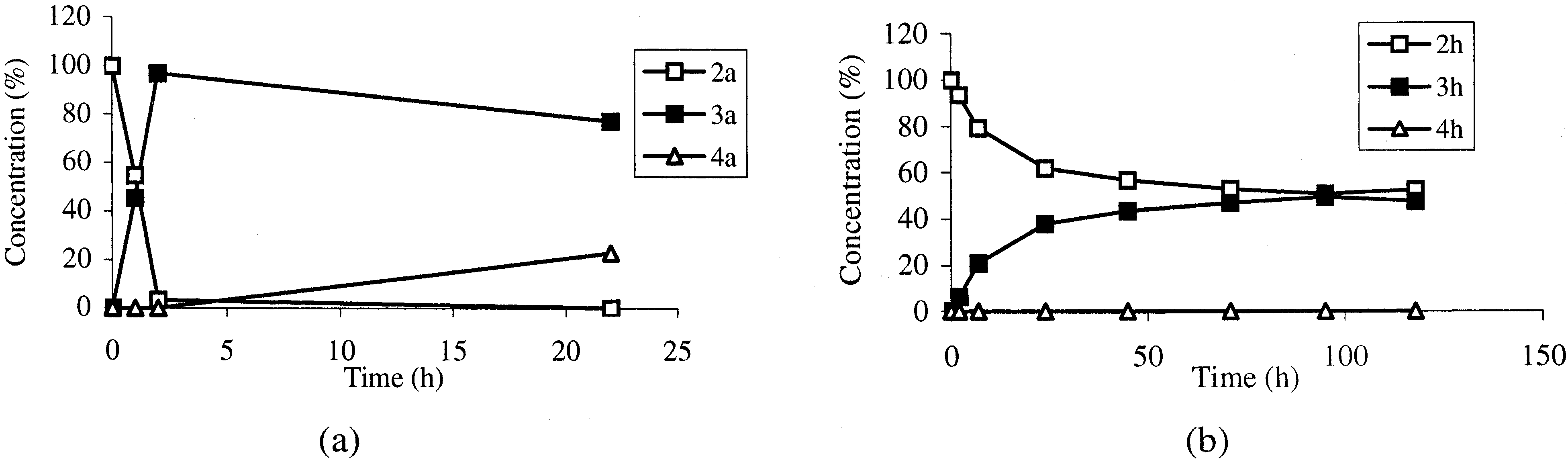
Profile of baker’s yeast reduction of: (a) 3-propyl-3-buten-2-one 2a; (b) 1-phenyl-2-propyl-2-propen-1-one 2h.
CAS number: 25448-04-8
Tetrahydroquinoline is an organic compound and a bicyclic molecule derived from quinoline by hydrogenation of the aromatic ring. It's a colorless oil that is a semi-hydrogenated derivative of quinoline.
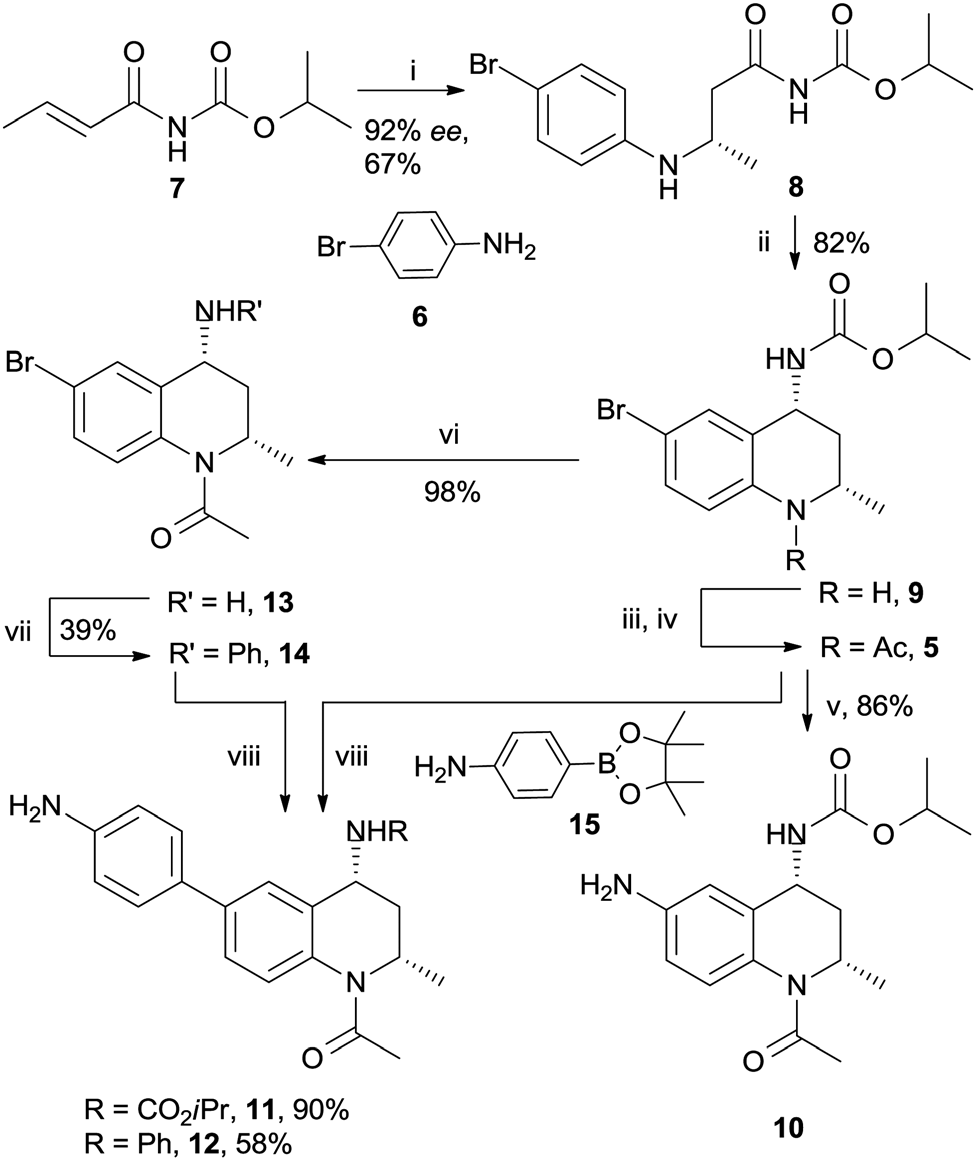
Preparation of THQ cores 10, 11 and 12.
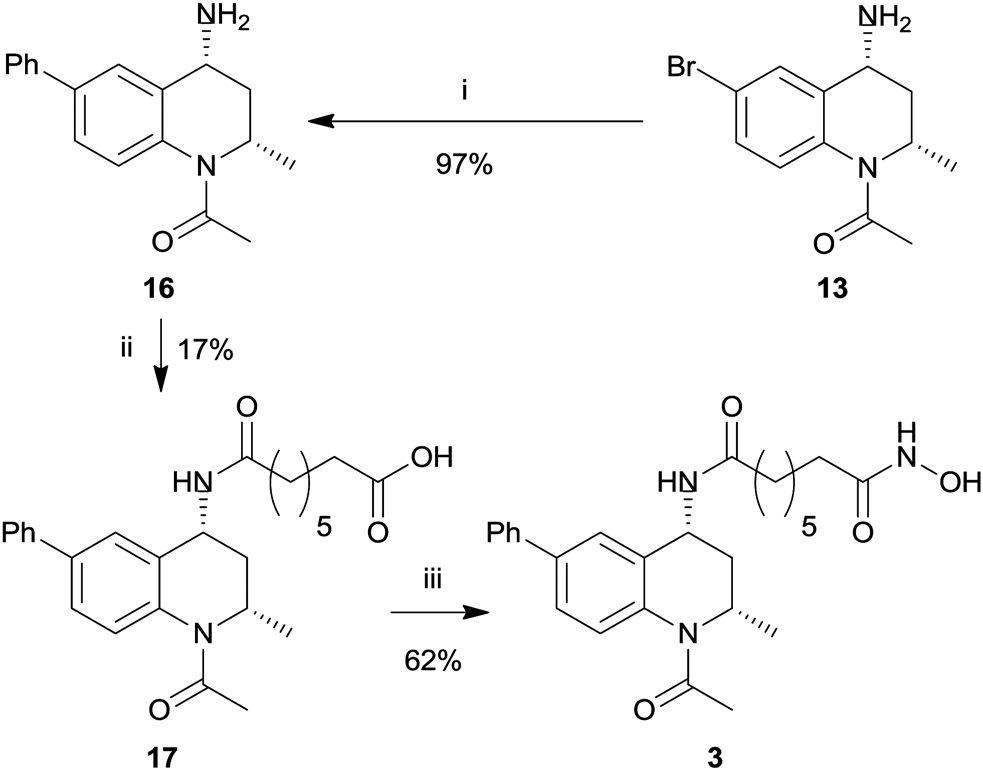
Attachment of HDAC Pharmacophore to the THQ 4-position.
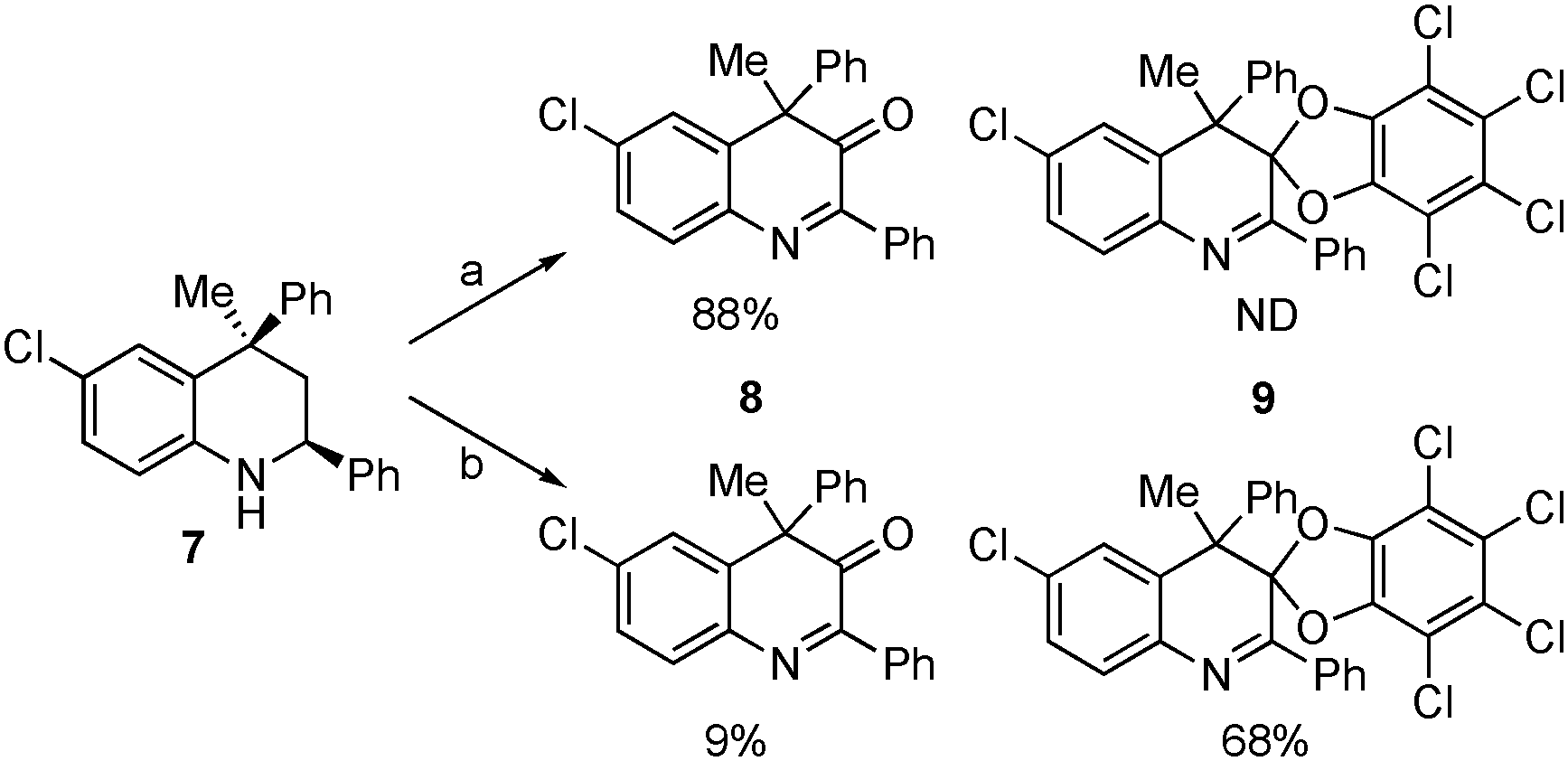
Comparison between a catalytic amount and a stoichiometric amount of o-chloranil in the oxidation of tetrahydroquinoline derivative.
CAS number: 25512-63-4
Cyclohexen-1-ol is a cyclic alcohol with a double bond, specifically it is a cyclohexene molecule with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the ring.

Preparation of cyclohexenol 16. DMAP=4-(dimethylamino)-pyridine, Cbz=benzyloxycarbonyl, THF=tetrahydrofuran, TBS=tert-butyldimethylsilyl, dppf=1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene.
CAS number: 2552-55-8
Ibotenic acid is a non-proteinogenic alpha-amino acid. It has a role as a neurotoxin.
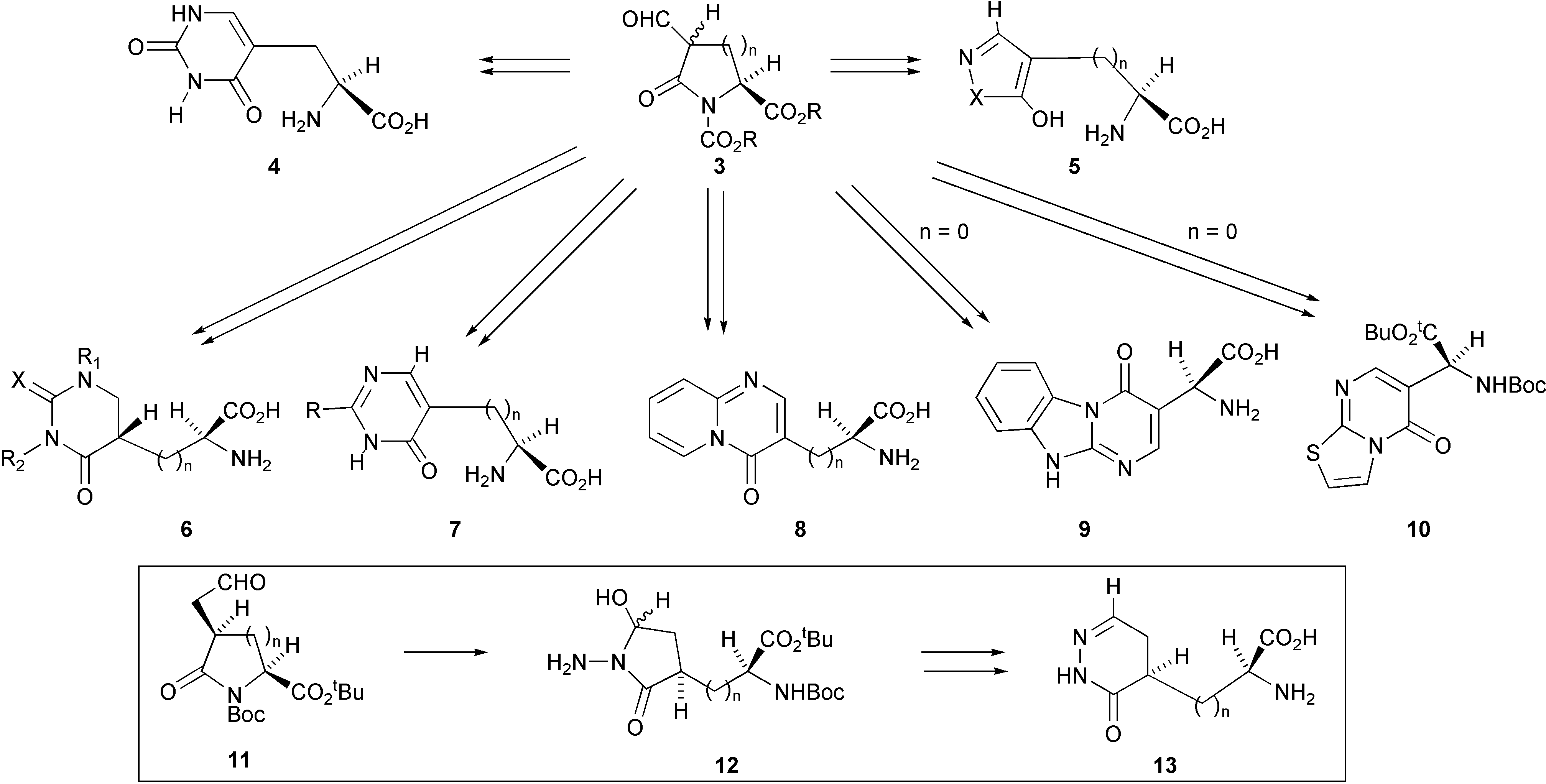
We have discovered a versatile and economical synthesis for the preparation of a large variety of homochiral compounds in which a heterocyclic ring system is fused to the β-carbon atom of L-alanine. This methodology has recently been extended to encompass the preparation of analogues of the lower homologue, ibotenic acid. The synthesis, shown in Scheme 1, involves reaction of bisnucleophiles with an aldehyde of a pyroglutamic acid derivative 3 (n = 1) or an aldehyde of a β-lactam 3 (n = 0) or with their homologues 11.
CAS number: 25535-16-4
Propidium Iodide is a fluorescent nucleic acid dye which binds only to double-stranded nucleic acids. It is commonly used to determine the DNA content of a cell or to discriminate viable from non-viable cells.
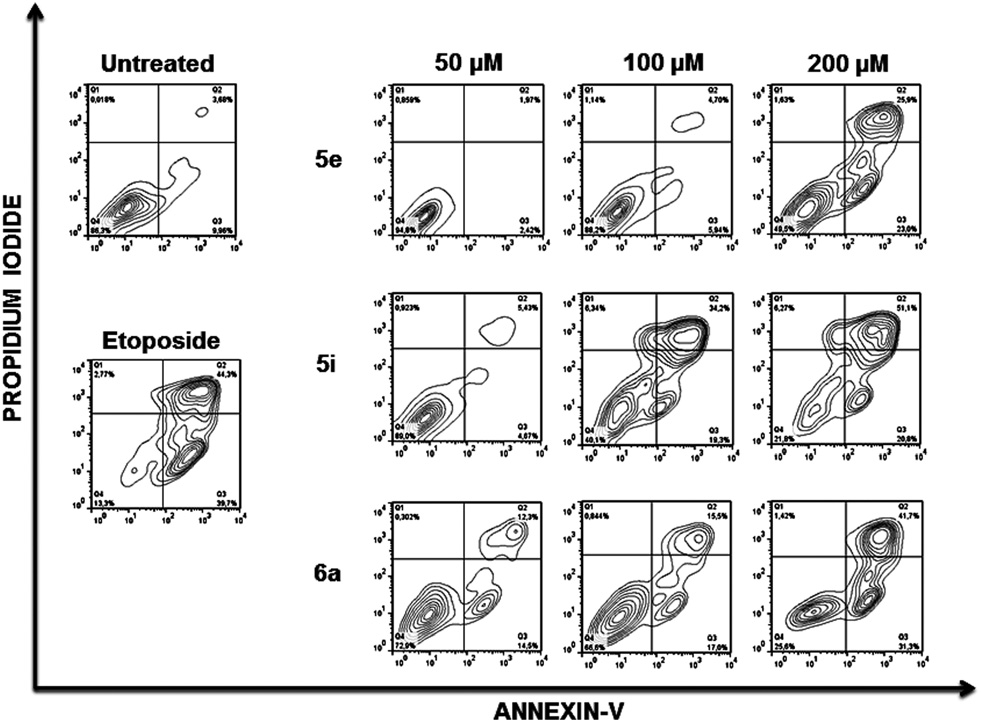
Membrane phosphatidylserine expression after treatment of Jurkat cells with compounds 5e, 5i and 6a. Jurkat cells were treated for 48 h with the indicated compounds and doses and the percentages of apoptotic cells was measured by flow cytometry after double staining with propidium iodide and Annexin-V-Fluos.
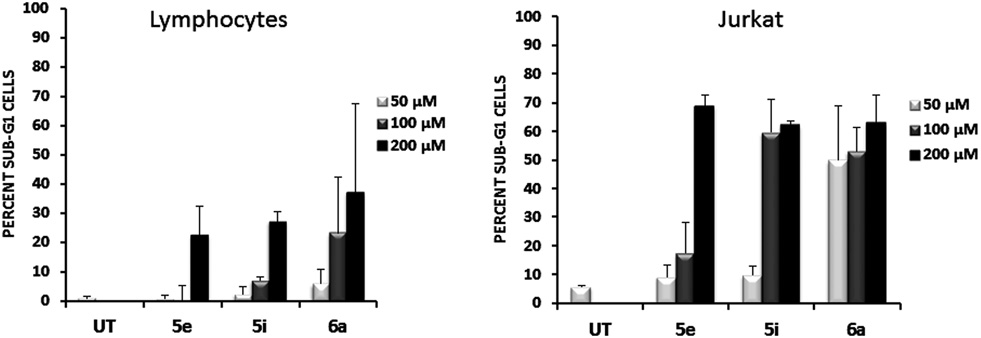
Effect of indicated compounds on primary lymphocytes and Jurkat cells. Primary cell line N1 and Jurkat cells were treated for 48 h at the indicated doses of compounds 5e, 5i and 6a and cell cycles were analysed by flow cytometry after staining with propidium Iodide.