Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 17881-88-8
Methoxydimethylphenylsilane, also known as Silane, methoxydimethylphenyl-, is an organosilicon compound featuring a phenyl group (C6H5) attached to a silicon atom, which is also bonded to two methyl groups (CH3) and a methoxy group (OCH3). This colorless to pale yellow liquid is used as a reagent in organic synthesis and materials science, particularly in surface modification, silane coupling applications, and as a precursor in the production of silicones or functionalized silanes. Its structure allows for reactivity with hydroxyl groups, making it useful in adhesion promotion, coatings, and polymer cross-linking.
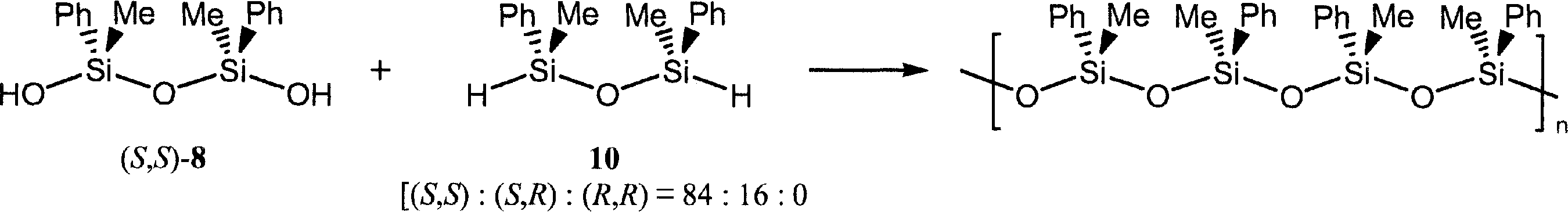
Synthesis of syndiotactic poly(methylphenylsiloxane) (PMPS).
CAS number: 179324-69-7
Bortezomib is l-Phenylalaninamide substituted at the amide nitrogen by a 1-(dihydroxyboranyl)-3-methylbutyl group and at N(alpha) by a pyrazin-2-ylcarbonyl group. Bortezomib was first synthesized in 1995. In May 2003, bortezomib became the first anticancer proteasome inhibitor that was approved by the FDA under the trade name VELCADE. Phase I, II, III, and IV clinical trials are undergoing to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of bortezomib in leukemia, myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and solid tumours.
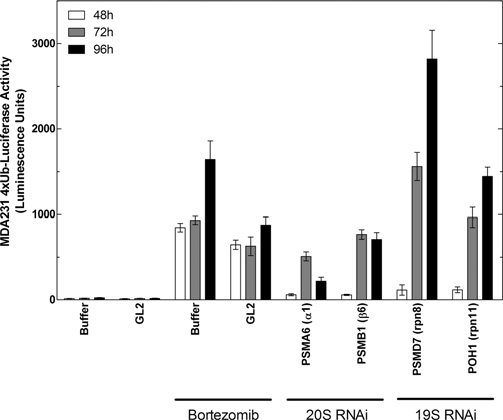
Effects of bortezomib and depletion of 26S subunits by RNAi on accumulation of 4xUb-Luc in cells
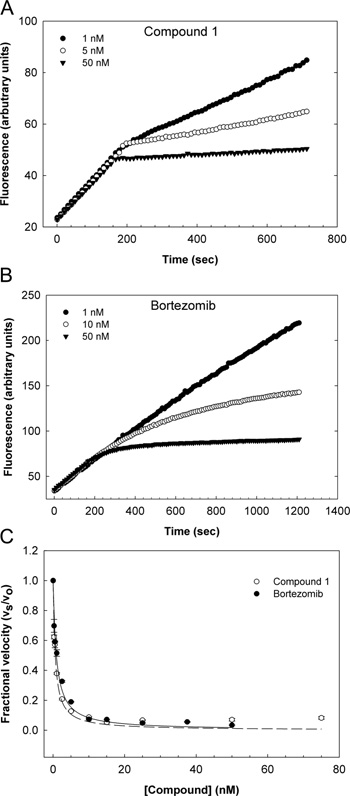
Kinetics of proteasome inhibition by compound 1 and bortezomib
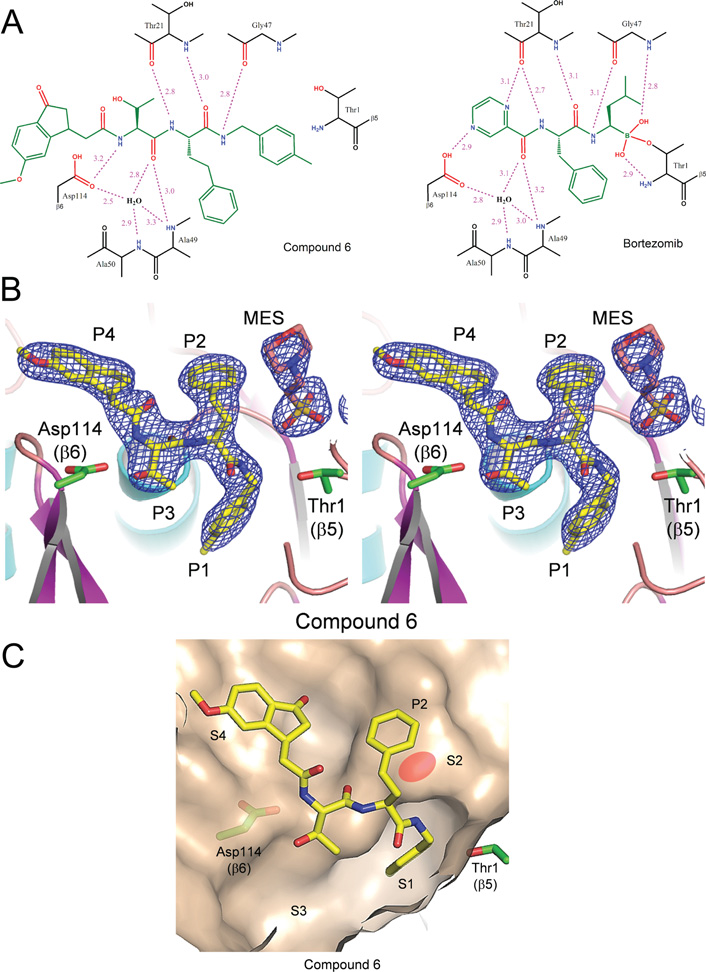
Hydrogen-bonding interactions and crystal structure of compound 6 bound to the chymotrypsin-like site of the 20S proteasome with reference to bortezomib
CAS number: 17933-03-8
3-Tolylboronic acid is a boronic acid derivative, specifically featuring a methyl group attached to the third carbon of a phenyl ring, which is further linked to a boronic acid group. This compound is a white solid and is primarily used as a reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions.
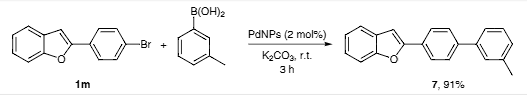
Suzuki coupling of 2-(4-bromophenyl)benzofuran (1m) and 3-tolylboronic acid
CAS number: 179936-52-8
Tryprostatin B is a cyclic dipeptide that is brevianamide F (cyclo-L-Trp-L-Pro) substituted at position 2 on the indole ring by a prenyl group. It is a dipeptide, a member of indoles, a pyrrolopyrazine and an indole alkaloid. It is functionally related to a brevianamide F.
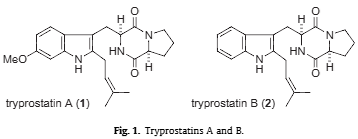
Tryprostatins A and B.
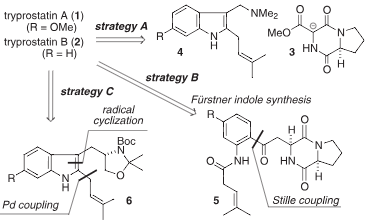
Retrosynthetic analysis for tryprostatins A and B.
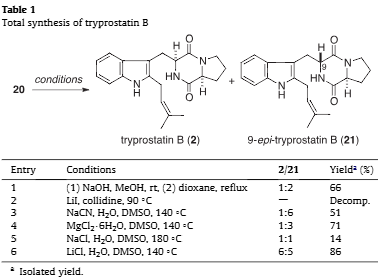
Total synthesis of tryprostatin B
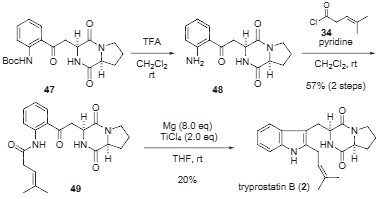
Total synthesis of tryprostatin B.
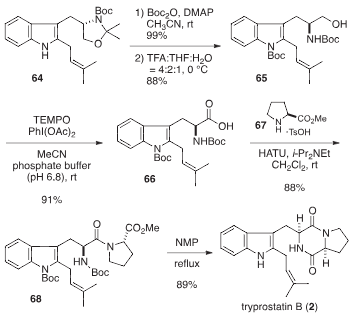
Total synthesis of tryprostatin B.
CAS number: 18039-42-4
5-Phenyl-1H-tetrazole is a heterocyclic compound characterized by a phenyl group attached to a tetrazole ring. It's a white to light beige powder.
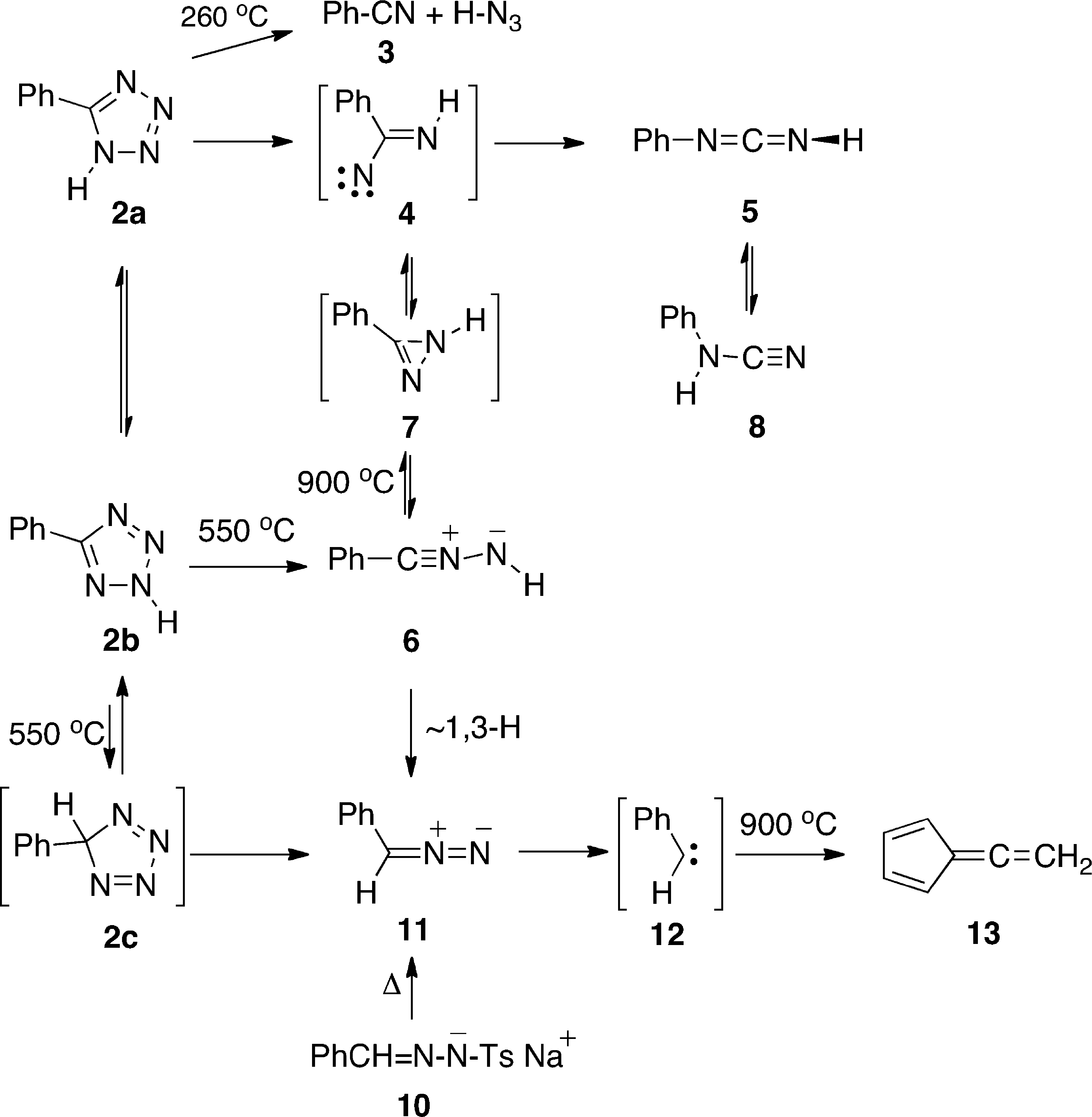
Thermolysis of 5-Phenyltetrazole
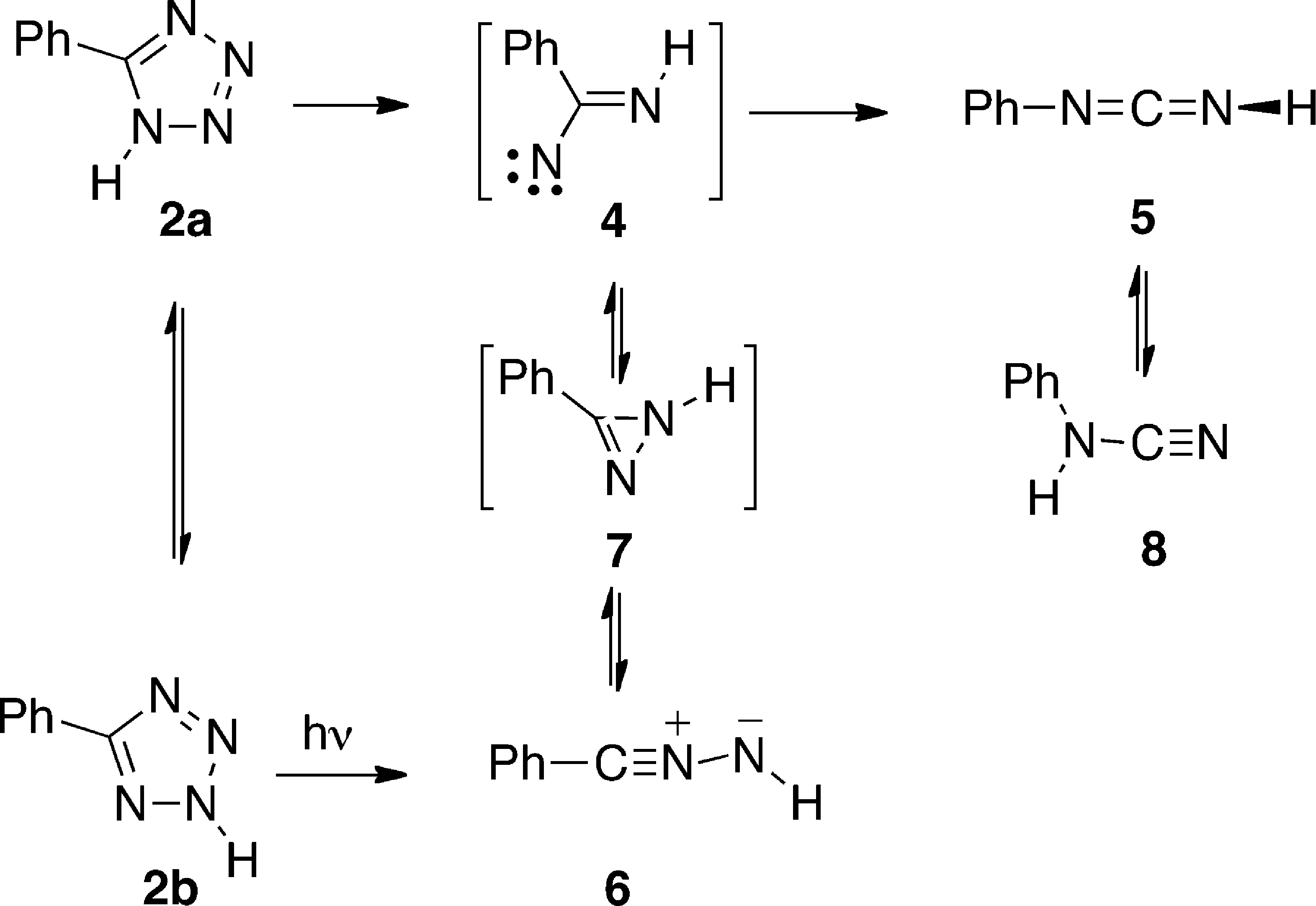
Photolysis of 5-Phenyltetrazole 2
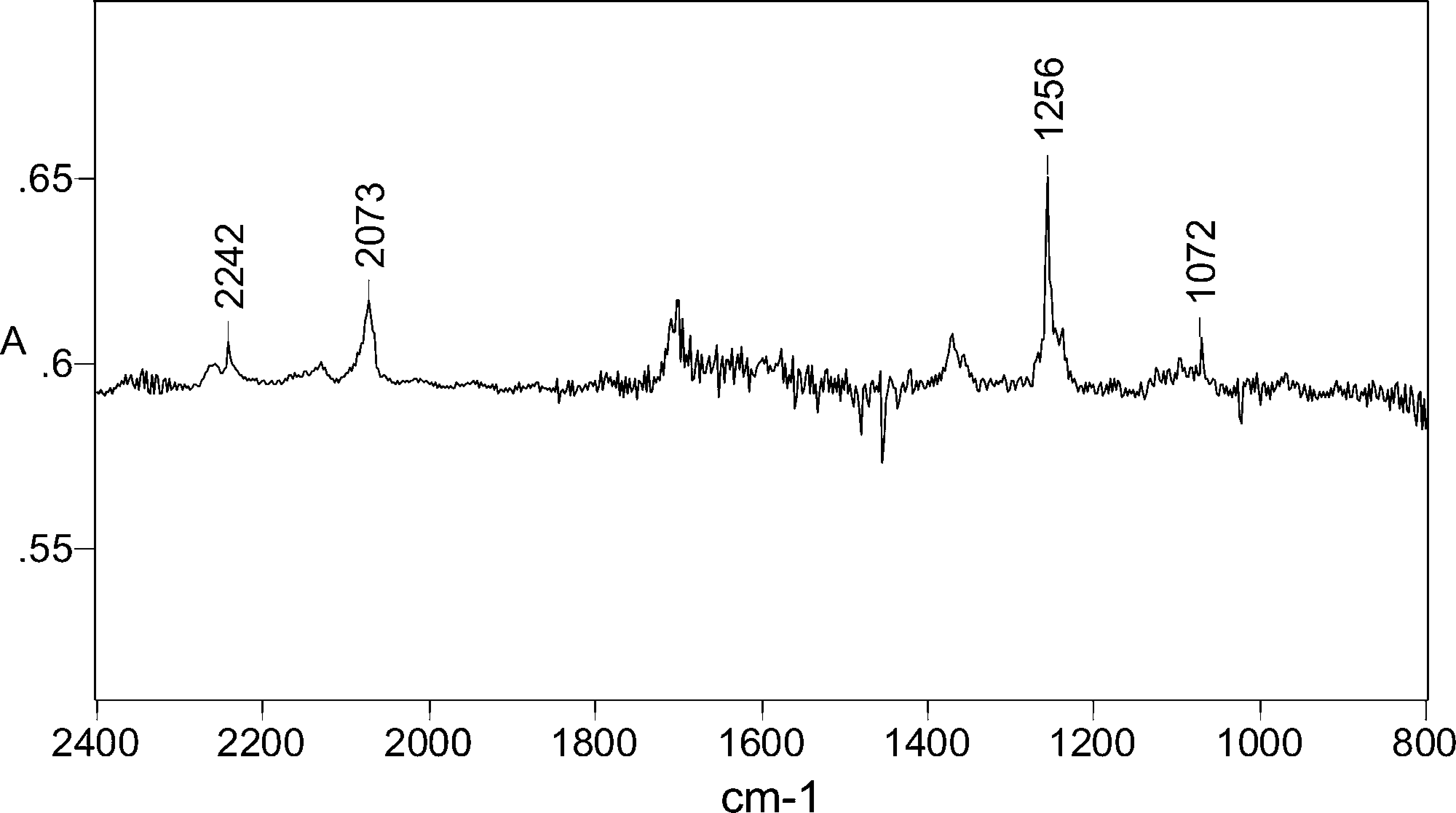
IR difference spectrum after 1 min photolysis (254 nm) of 5-phenyltetrazole 2 in Ar matrix at 12 K. Positive peaks: photolysis products, largely benzonitrile imine 6; the peak near 1700 cm−1 is due to an impurity on the deposition window. Negative peaks: reacted tetrazole 2.
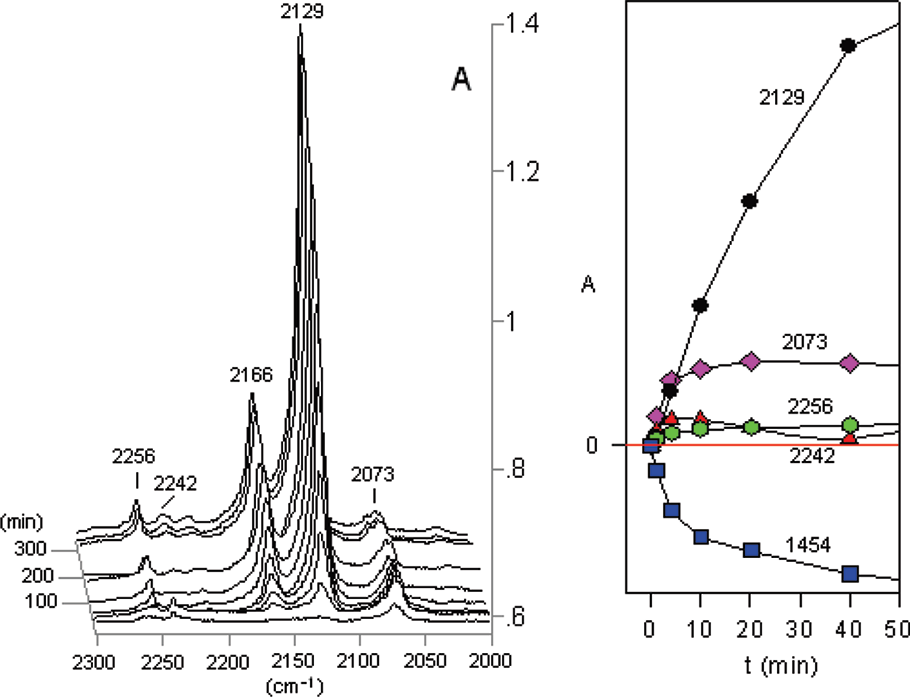
(Left) Partial IR difference spectra of 5-phenyltetrazole 2 at 12 K in Ar matrix at different photolysis times, showing peaks due to the photolysis products. Peaks at 2129 and 2166 cm−1 are due to PhN=C=NH 5. The peak at 2073 cm−1 is assigned to PhCNNH 6. Ordinate in absorbance units. (Right) Plots of IR absorbances at different wavelengths versus photolysis time. Ordinate in relative absorbance units.
CAS number: 180509-18-6
2'-alpha-mannosyl-L-tryptophan is a C-glycosyl compound that is L-tryptophan in which the hydrogen at position 2 on the indole protion has been replaced by an alpha-mannosyl residue. It is a L-tryptophan derivative and a C-glycosyl compound. It is functionally related to an alpha-D-mannose. It is a tautomer of a 2'-alpha-mannosyl-L-tryptophan zwitterion.
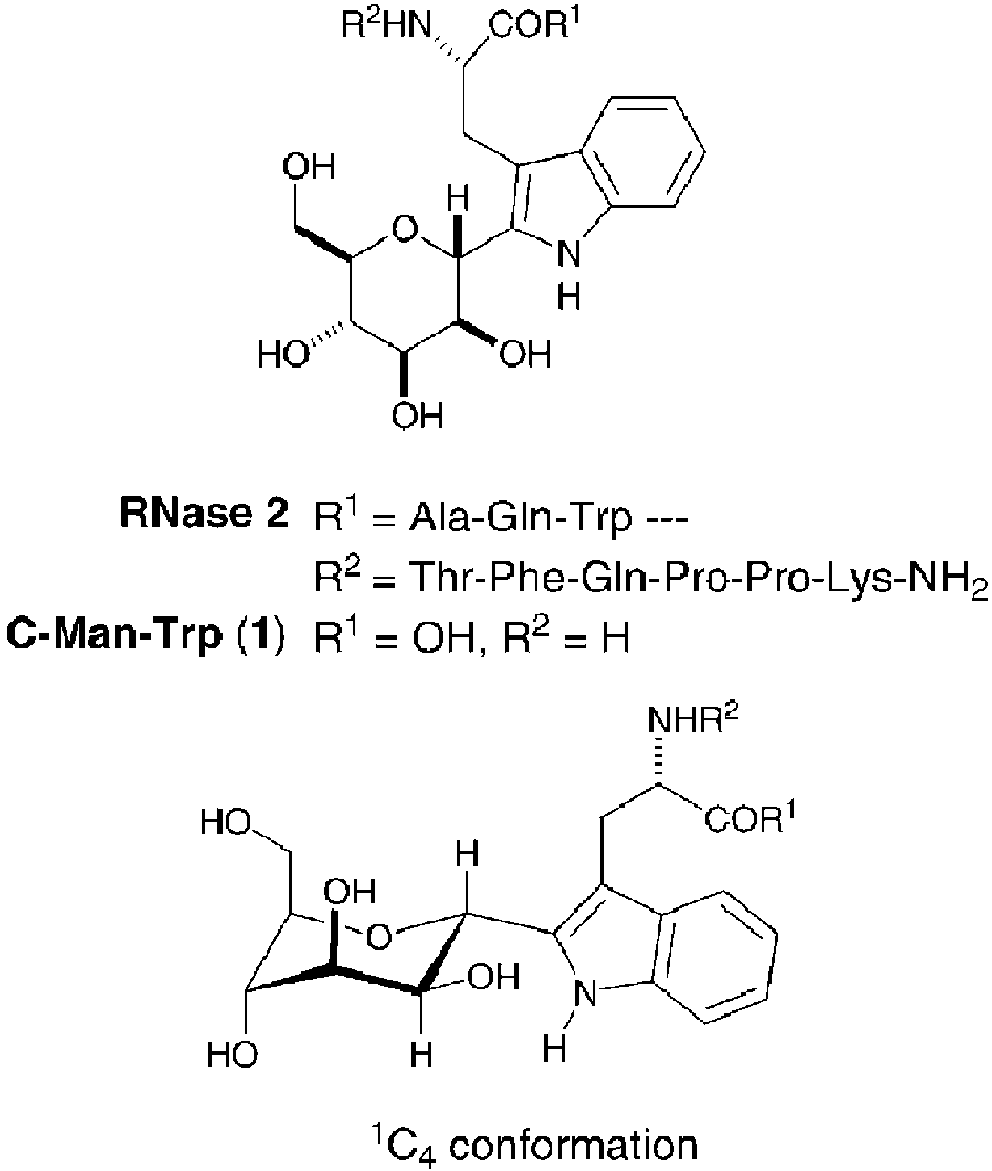
Structure of α-C-mannosyltryptophan.
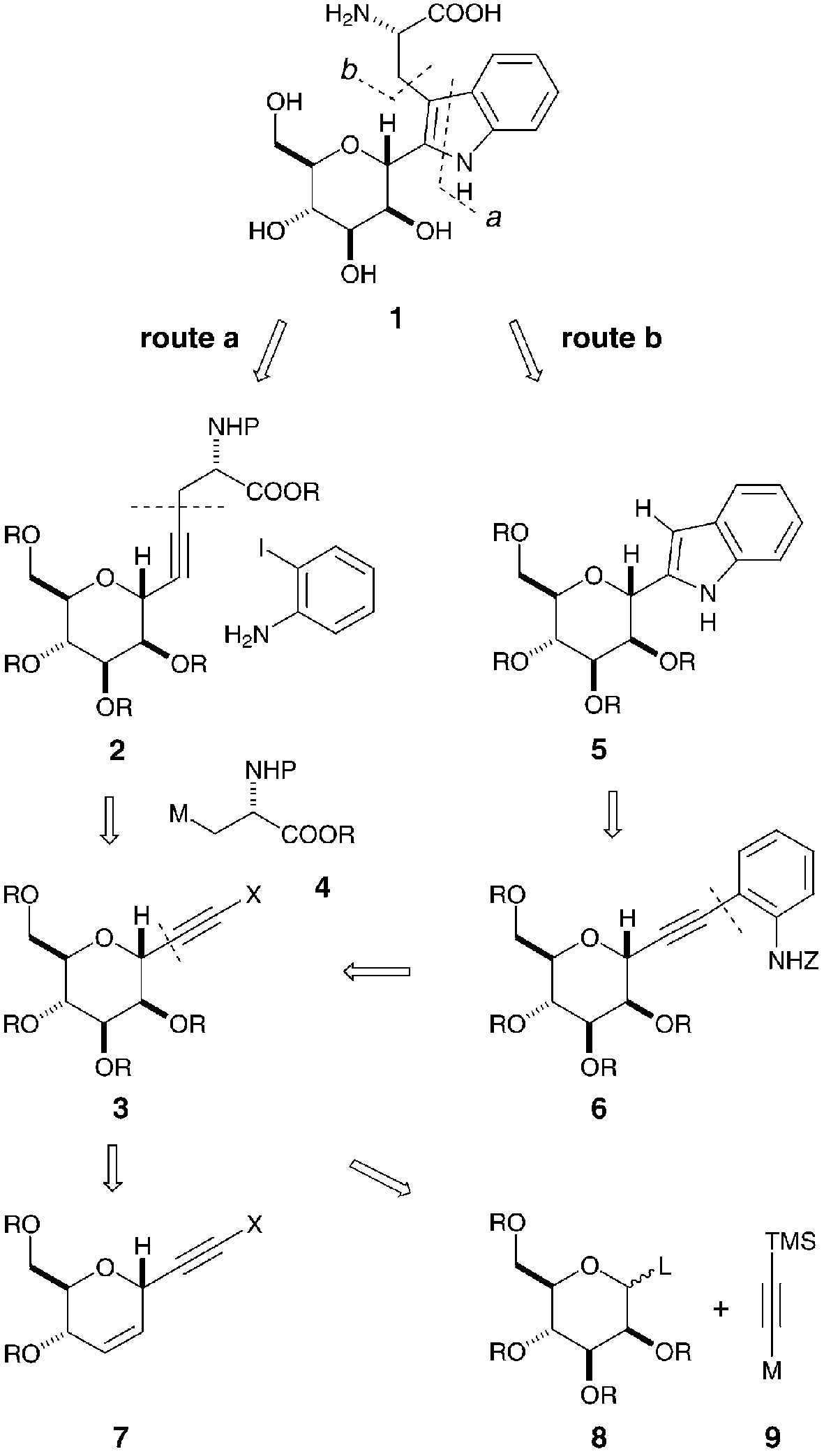
Synthetic plan of α-C-glycosyltryptophan exemplified by C-man-Trp (1).
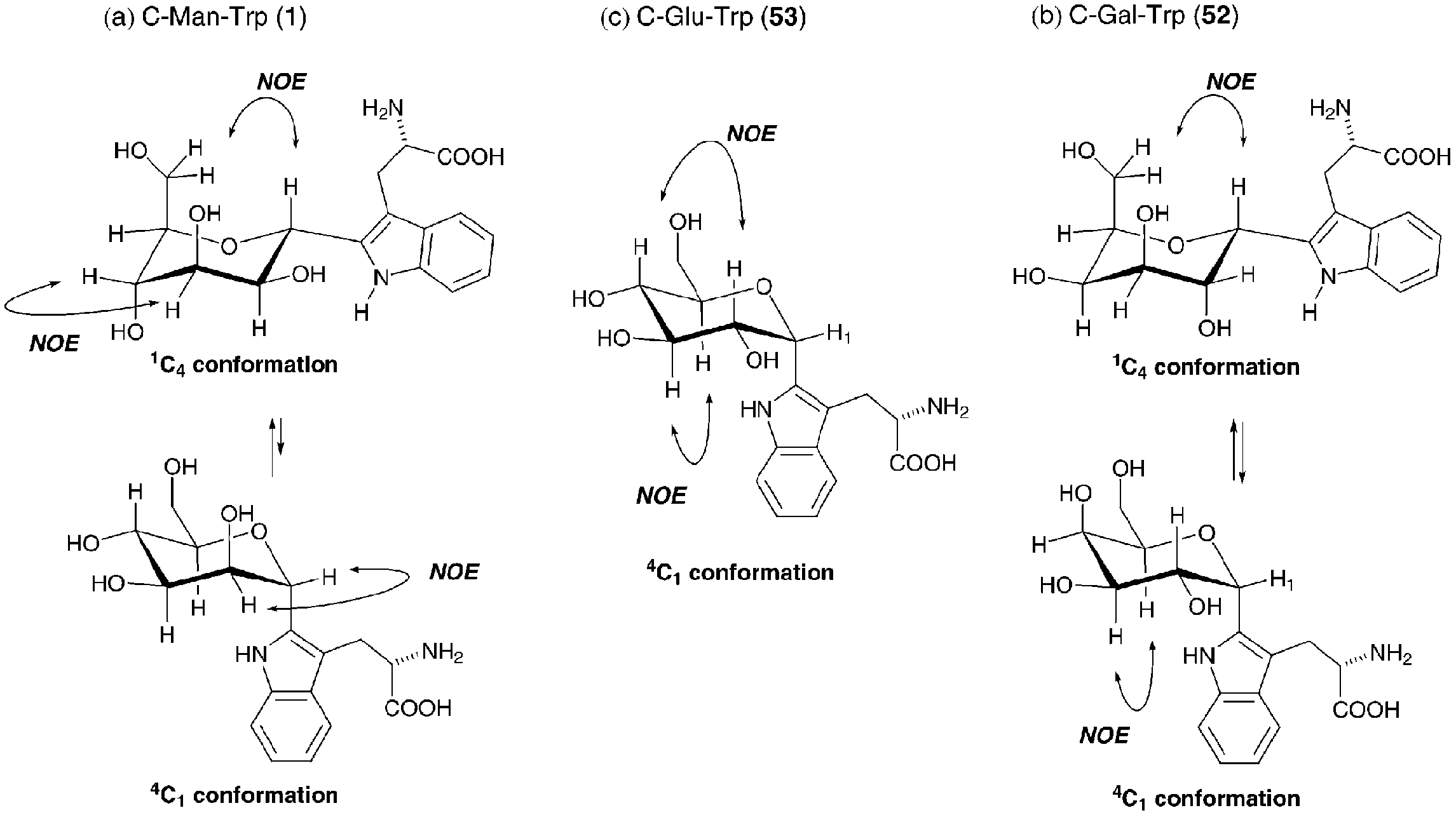
Conformation of α-C-glycosyltryptophan and the observed NOESY correlations.
CAS number: 18155-21-0
Sulfonium is a sulfur hydride, a sulfonium compound and an onium cation. It is a conjugate acid of a hydrogen sulfide.
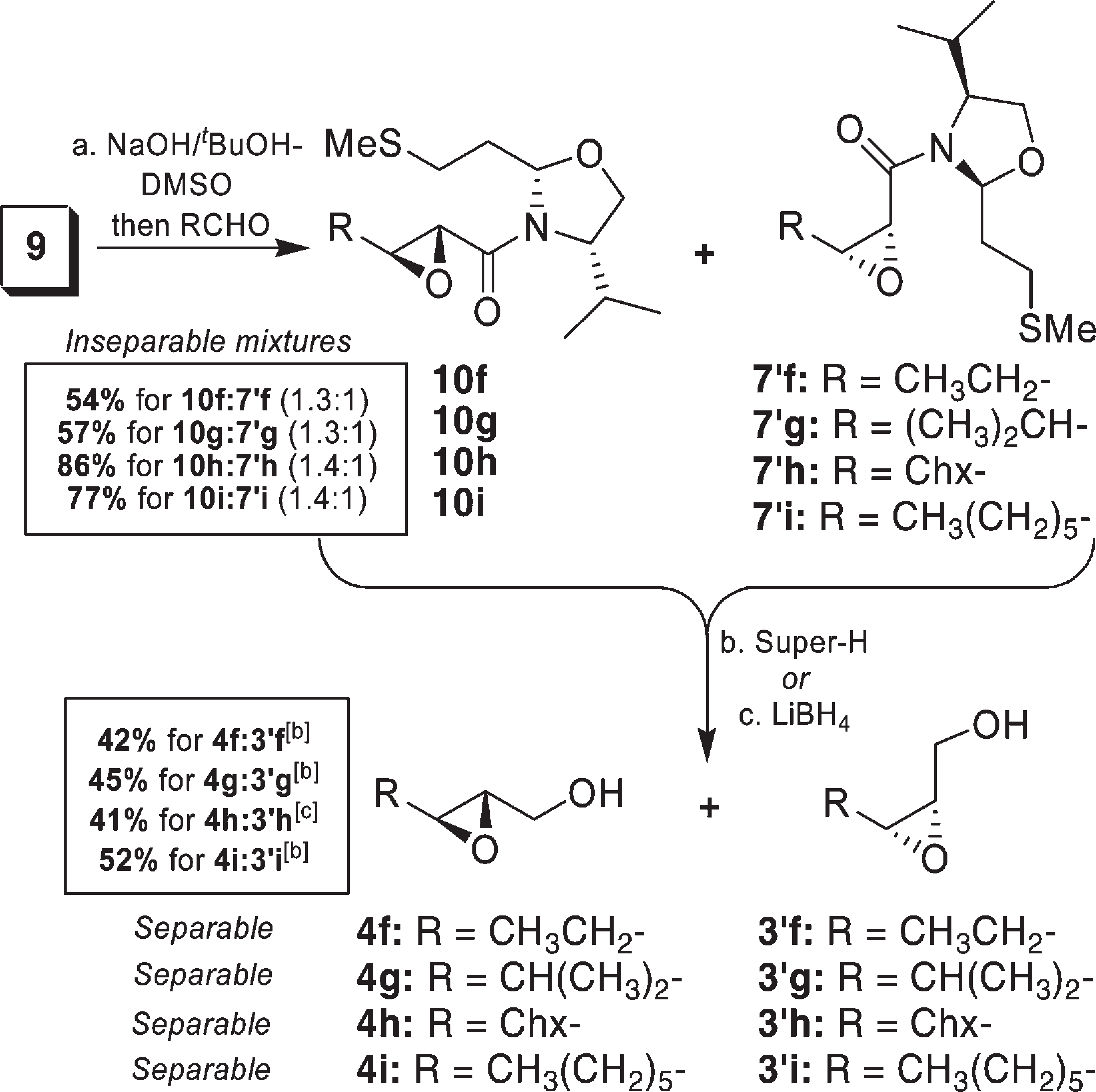
Reaction of Sulfur Ylide Derived from Sulfonium Salt 9 with Aliphatic Aldehydes
CAS number: 181695-72-7
Valdecoxib is a sulfonamide derivative and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities. Valdecoxib selectively binds to and inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, thereby preventing the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, which are involved in the regulation of pain, inflammation, and fever. This NSAID does not inhibit COX-1 at therapeutic concentrations and therefore does not interfere with blood coagulation.
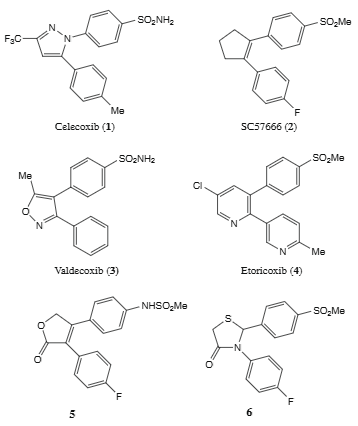
Representative examples of selective COX-2 inhibitors: Celecoxib, SC57666, Valdecoxib, Etoricoxib.
CAS number: 18172-67-3
(-)-beta-pinene is the (1S,5S)-enantiomer of beta-pinene. It is an enantiomer of a (+)-beta-pinene.
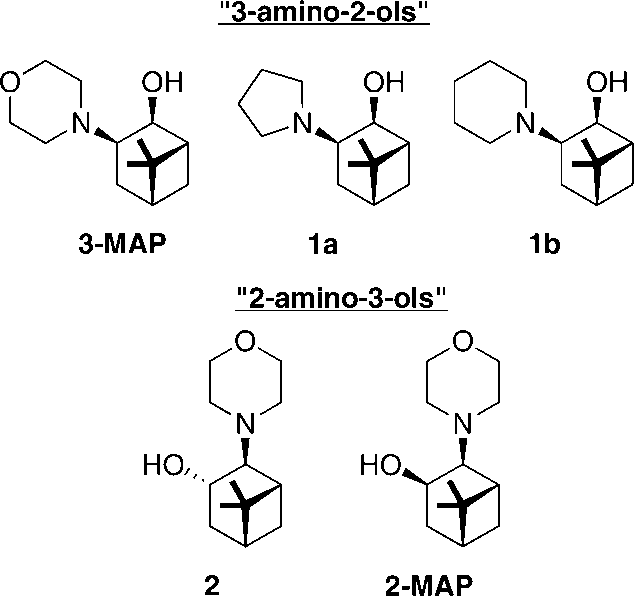
Amino alcohols synthesized from (-)-β-pinene.
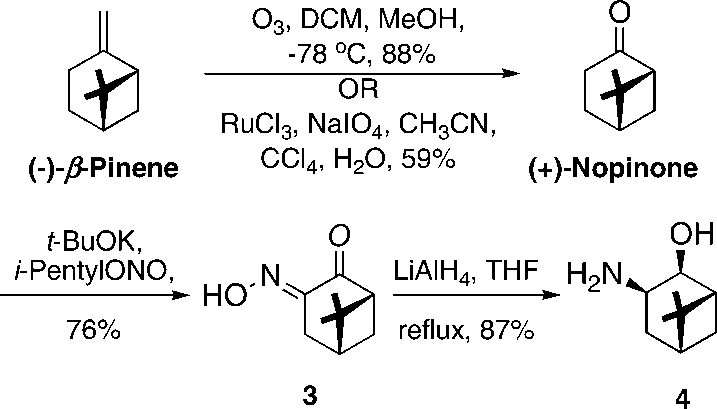
Synthesis of Primary 3-Amino-2-ol from (-)-β-Pinene
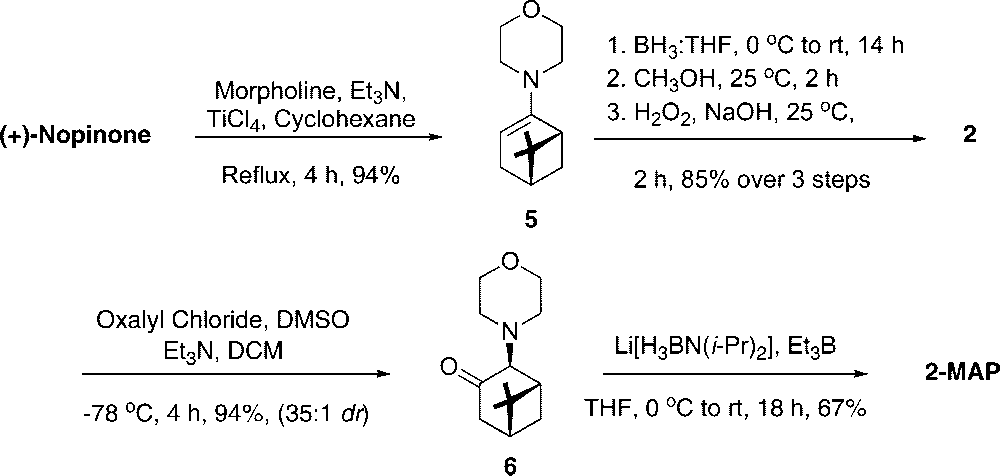
Synthesis of Chiral Auxiliary 2-MAP
CAS number: 182133-25-1
Arzoxifene is a synthetic, aromatic derivative with anti-estrogenic properties. Similar to the agent raloxifene, arzoxifene binds to and interacts with estrogen receptors as a mixed estrogen agonist/antagonist. This agent exhibits greater bioavailability and higher anti-estrogenic potency in the breast than does raloxifene; it exhibits reduced estrogenicity in the uterus compared with either tamoxifen or raloxifene. Arzoxifene may have beneficial effects on bone and the cardiovascular system (NCI04)
![Pharmaceuticals containing the benzo[b]thiophene core structure: raloxifene, arzoxifene, zileuton, SB-271046, sertaconazole](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/1580751_02.png)
Pharmaceuticals containing the benzo[b]thiophene core structure: raloxifene, arzoxifene, zileuton, SB-271046, sertaconazole