Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 17309-53-4
Cerium nitrate is a chemical compound, specifically a salt of cerium and nitric acid.
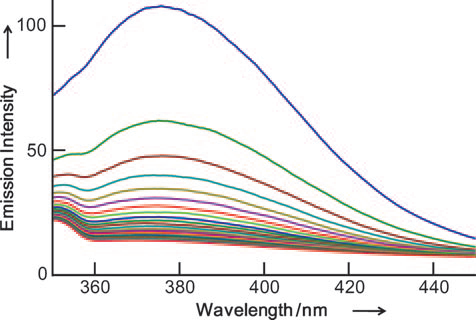
Changes in the emission spectrum of Ce(NO3)3 and EDTP mixture incubated in air at pH 7.0 and 508C
CAS number: 17350-84-4
Alpha-Methyl-D-phenylalanine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid, meaning it's not incorporated into proteins during translation. It is a derivative of phenylalanine with a methyl group (CH3) attached to the alpha carbon, and it has the D-configuration.
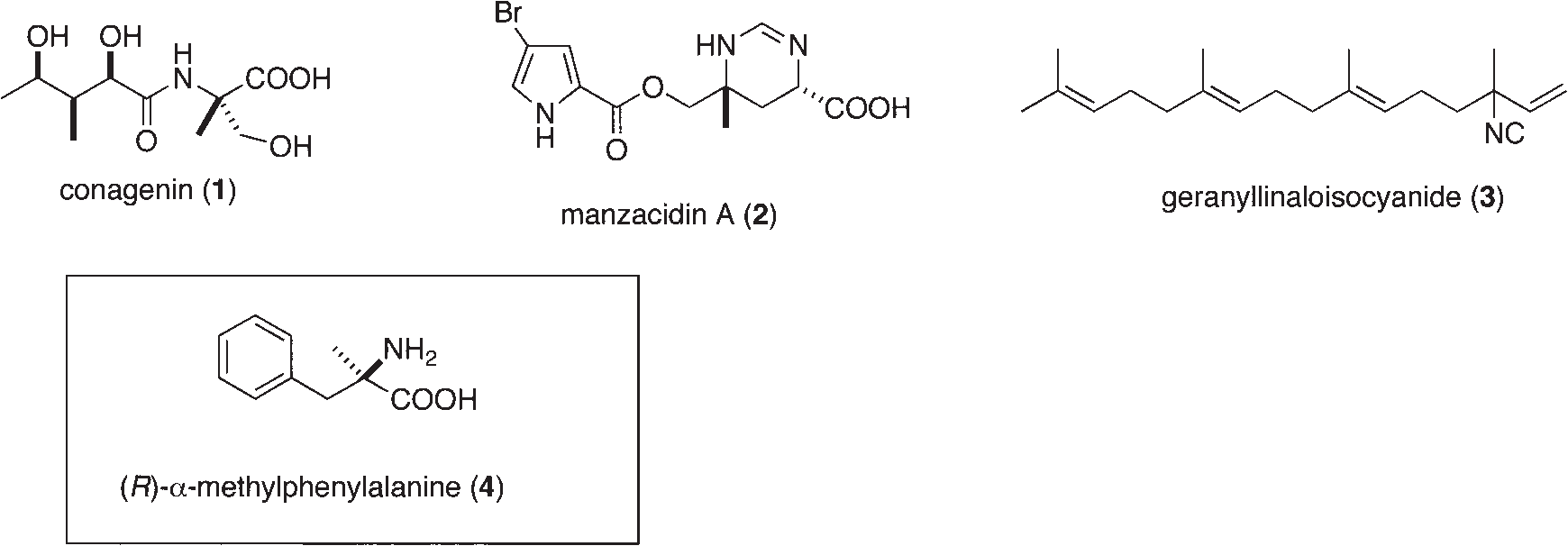
Representative Natural Products and α-Alkyl Amino Acid Containing Quaternary Stereocenter with Nitrogen Substituent: Conagenin, manzacidin A, geranyllinaloisocyanide, alpha-methyl-D-phenylalanine
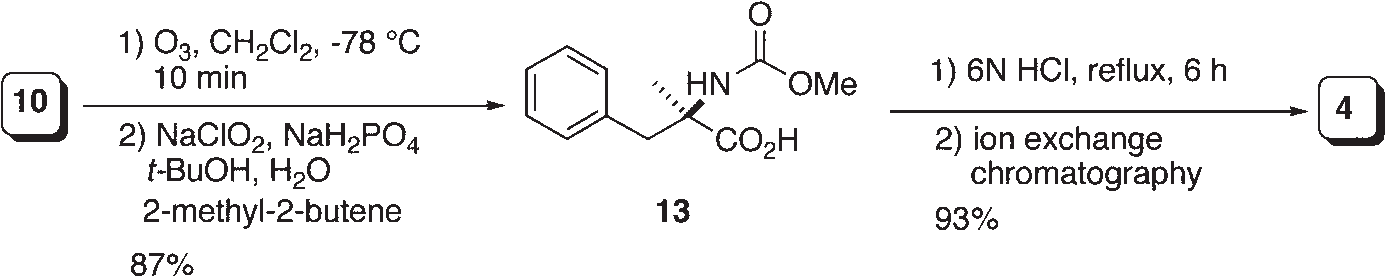
Synthesis of (R)-α-methylphenylalanine.
CAS number: 17372-87-1
A versatile red dye used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, etc., and as tissue stain, vital stain, and counterstain with HEMATOXYLIN. It is also used in special culture media.
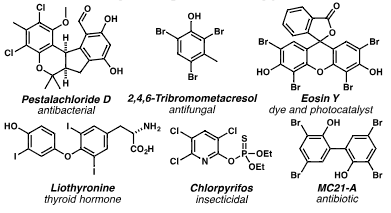
Selected haloarenes: Pestalachloride D, 2,4,6-Tribromo-m-cresol, Eosine Y, Liothyronine, Chlorpyrifos, mC21-A.
CAS number: 17388-17-9
Nandinine, (A+-)-, is a berberine derivative with potential anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties. It has been shown to inhibit inflammation in adipocytes (fat cells) and improve insulin sensitivity, potentially offering benefits in treating type 2 diabetes.
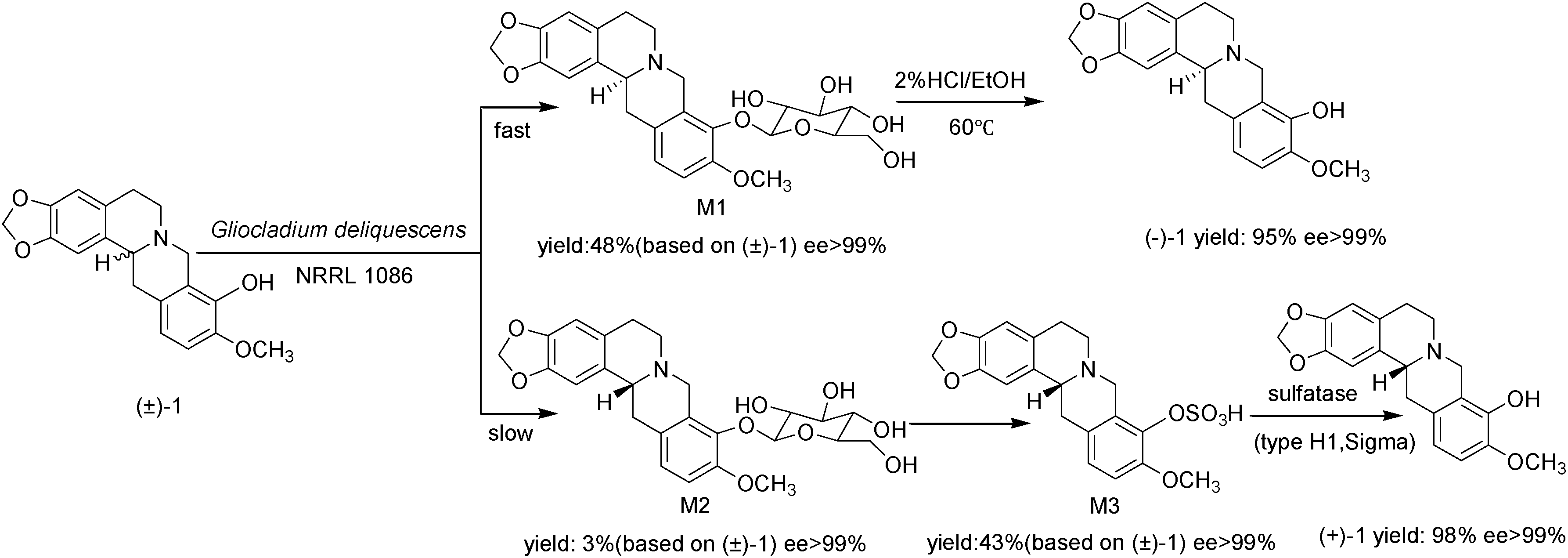
Biotransformation and hydrolytic pathway of tetrahydroberberrubine (+-)-1.
CAS number: 1740-19-8
Dehydroabietic acid is an abietane diterpenoid that is abieta-8,11,13-triene substituted at position 18 by a carboxy group. It has a role as a metabolite and an allergen. It is an abietane diterpenoid, a monocarboxylic acid and a carbotricyclic compound. It is functionally related to an abietic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a dehydroabietate.
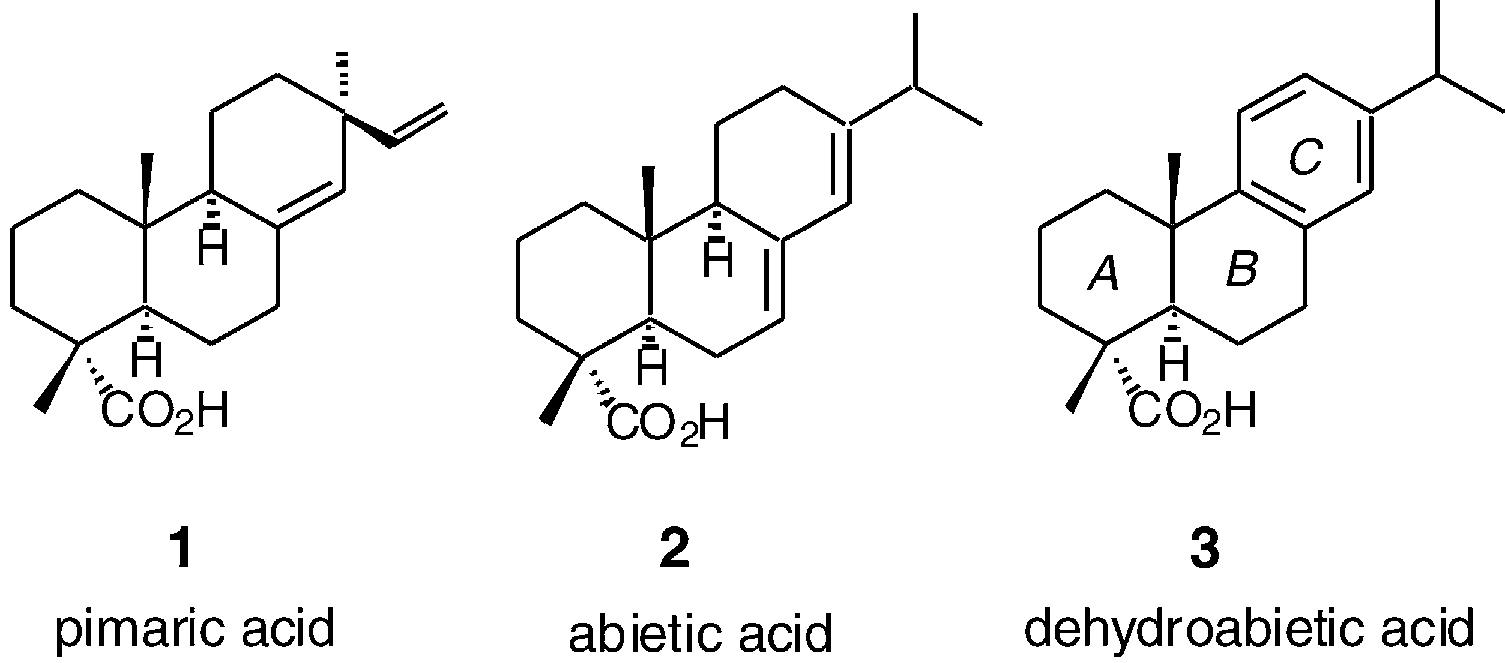
Scaffolds for BK channel modulators in this study.
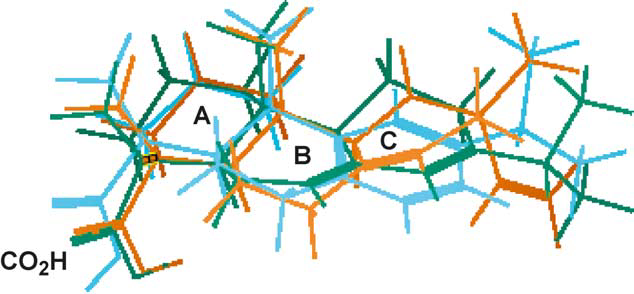
Superimposed structures of pimaric acid (1, green), abietic acid (2, brown) and dehydroabietic acid (3, blue).
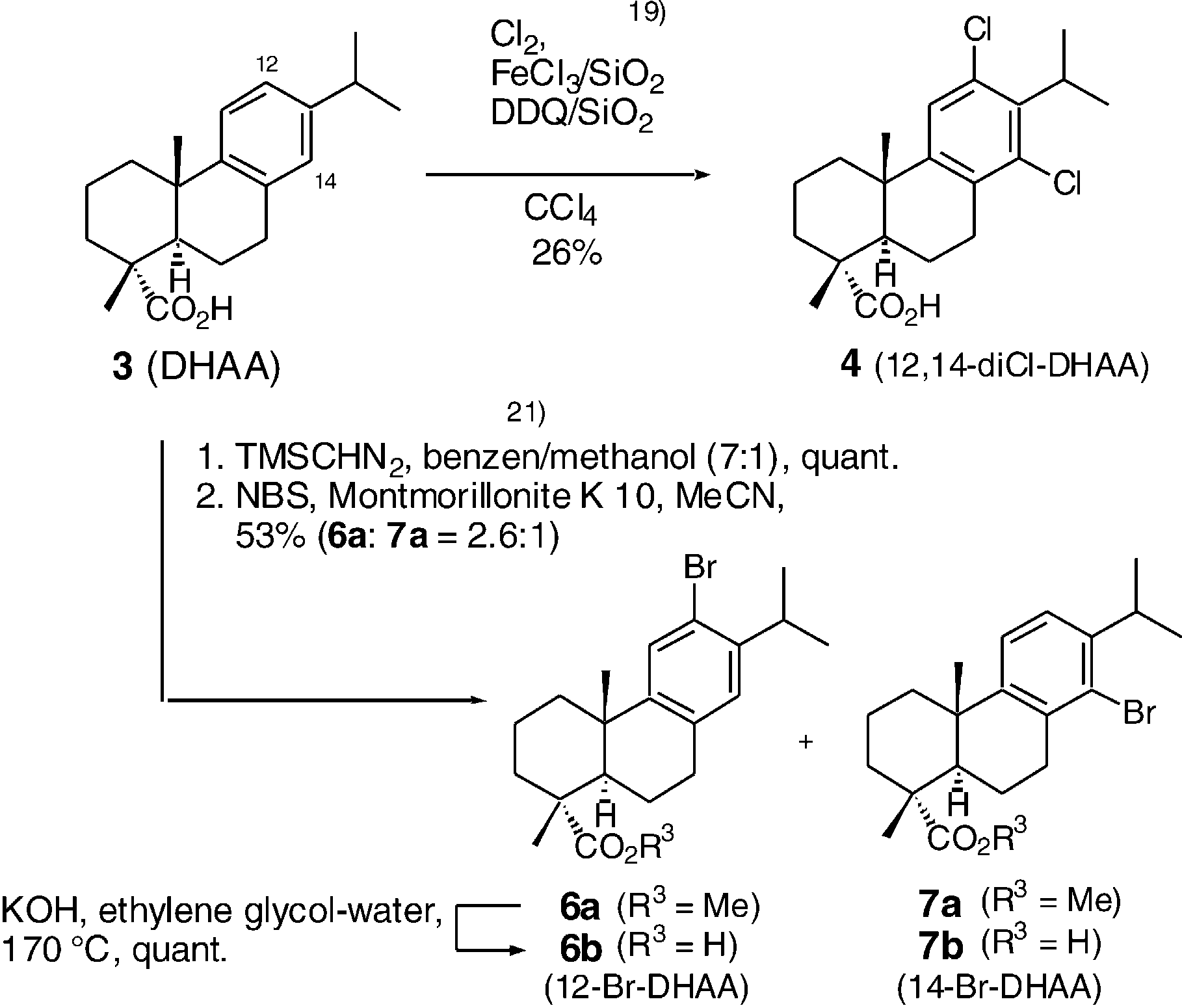
Synthesis of halogenated dehydroabietic acid derivatives.
CAS number: 17455-13-9
18-crown-6 is a crown ether that is cyclooctadecane in which the carbon atoms at positions 1, 4, 7, 10, 13 and 16 have been replaced by oxygen atoms. It has a role as a phase-transfer catalyst. It is a crown ether and a saturated organic heteromonocyclic parent.
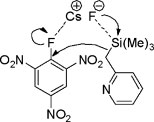
Proposed six membered transition state mechanism
CAS number: 17673-25-5
Phorbol esters are a class of tetracyclic diterpenoids which are primarily known for their tumor-promoting activity.
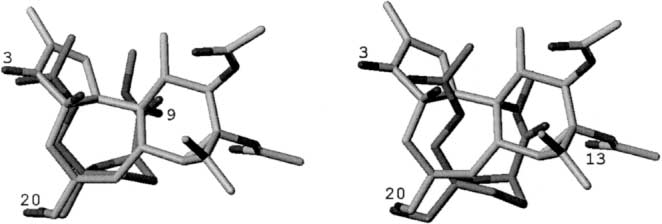
Superimposition of IV-cis on three pharmacophores of phorbol 12,13-diacetate (matched with C3, C20, C9 (left) or C3, C20, C13 (right)).
CAS number: 1769-41-1
Isonitrosoacetanilide is characterized by the presence of a hydroxyimino group (-NOH) and an acetamide moiety (NH-CO-CH3). It is a solid, crystalline substance with potential applications in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry.
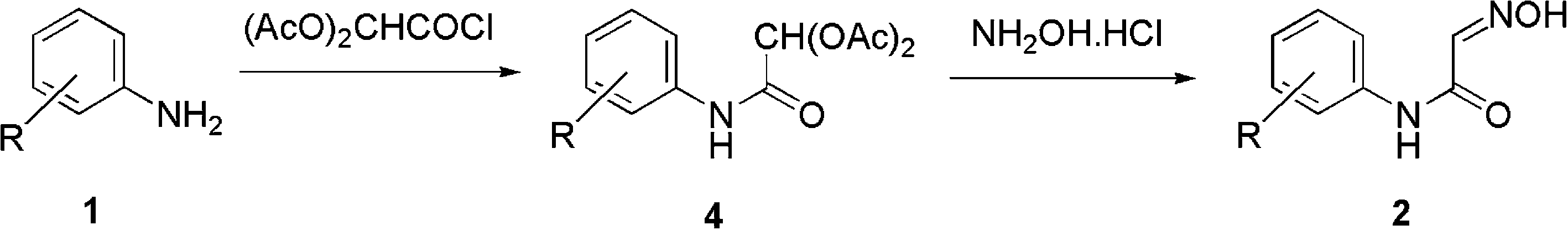
Two-step synthesis of isonitrosoacetanilides.
CAS number: 178734-41-3
Cavicularin is a complex natural product isolated from the liverwort Cavicularia densa. It belongs to the class of macrocyclic bis(bibenzyl) compounds and features a unique, strained 14-membered macrocyclic ether ring incorporating two ethano bridges and multiple hydroxyl groups.
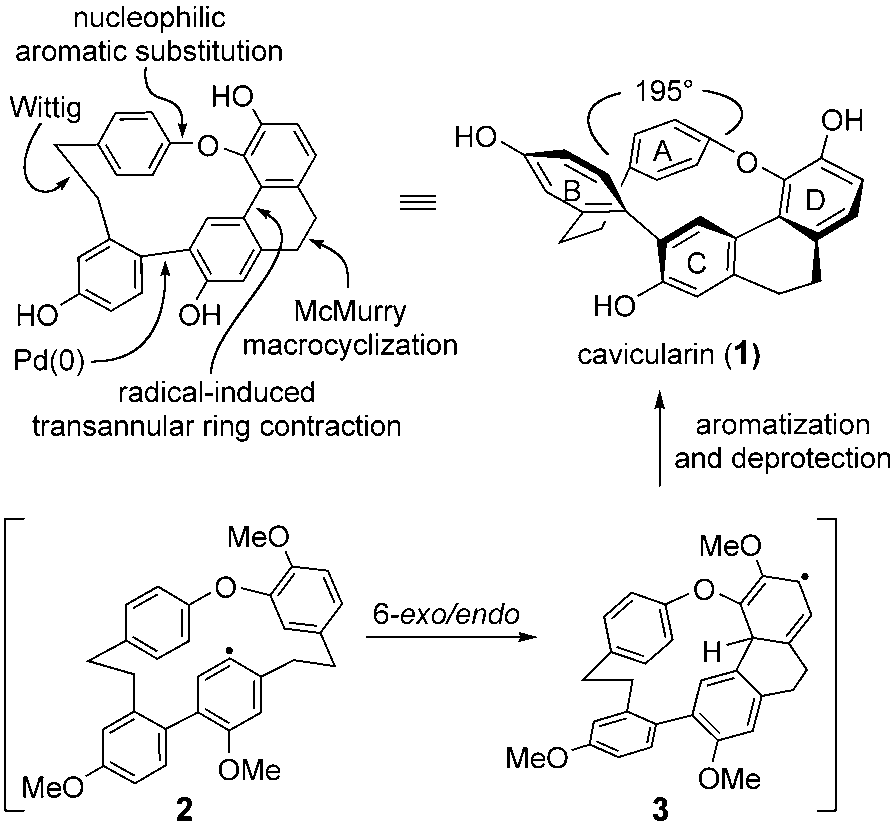
Synthetic strategy to cavicularin (1).
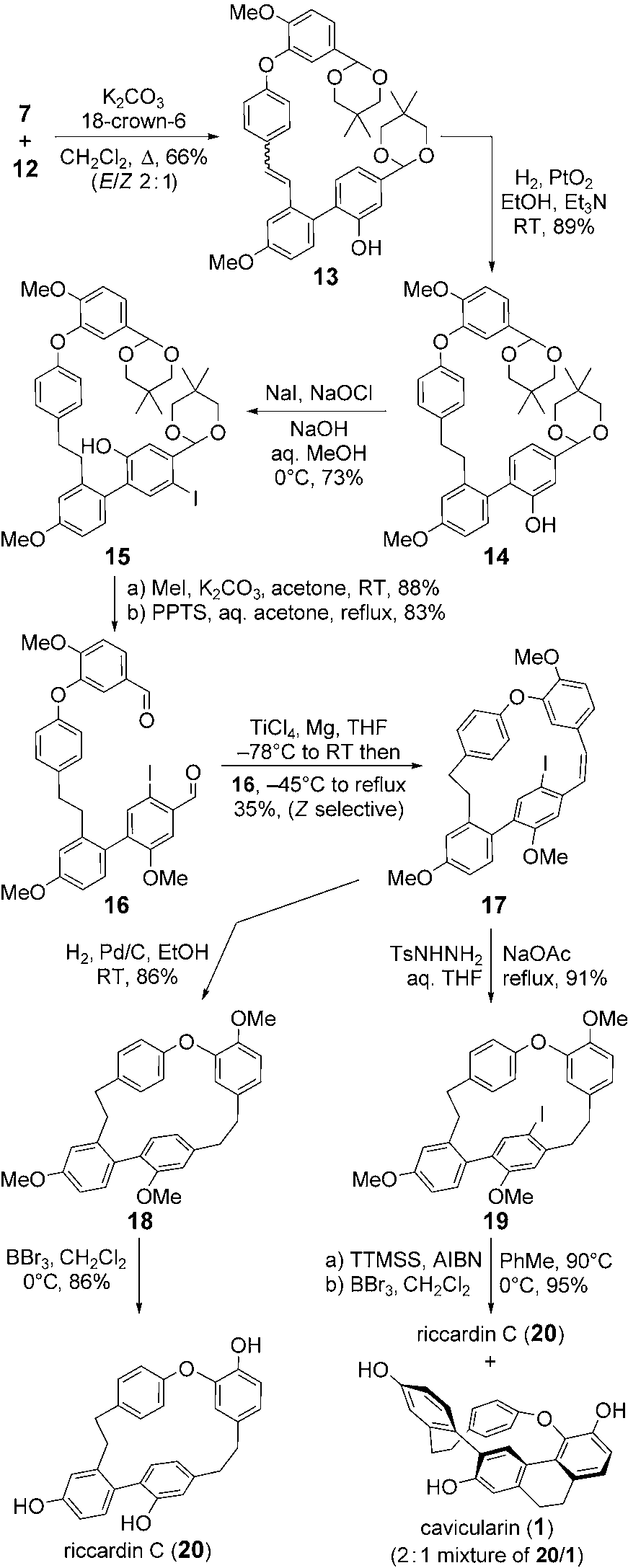
Total synthesis of cavicularin (1) and riccardin C (20). Ts =p-toluenesulfonyl, TTMSS=tris(trimethylsilyl)silane, AIBN=azo-bis(isobutyronitrile).
CAS number: 17881-80-0
2-Trimethylsilylmethylpyridine, also known as Pyridine, 2-[(trimethylsilyl)methyl]-, is an organosilicon compound featuring a pyridine ring substituted at the 2-position with a trimethylsilylmethyl group.

Proposed six membered transition state mechanism