Ferulic Acid
CAS number: 1135-24-6
Ferulic acid is a member of the class of ferulic acids that is cinnamic acid substituted by a methoxy and a hydroxy group at positions 3 and 4 of the phenyl ring. It has a role as a neuroprotective agent, a plant metabolite and an antioxidant.
Related images
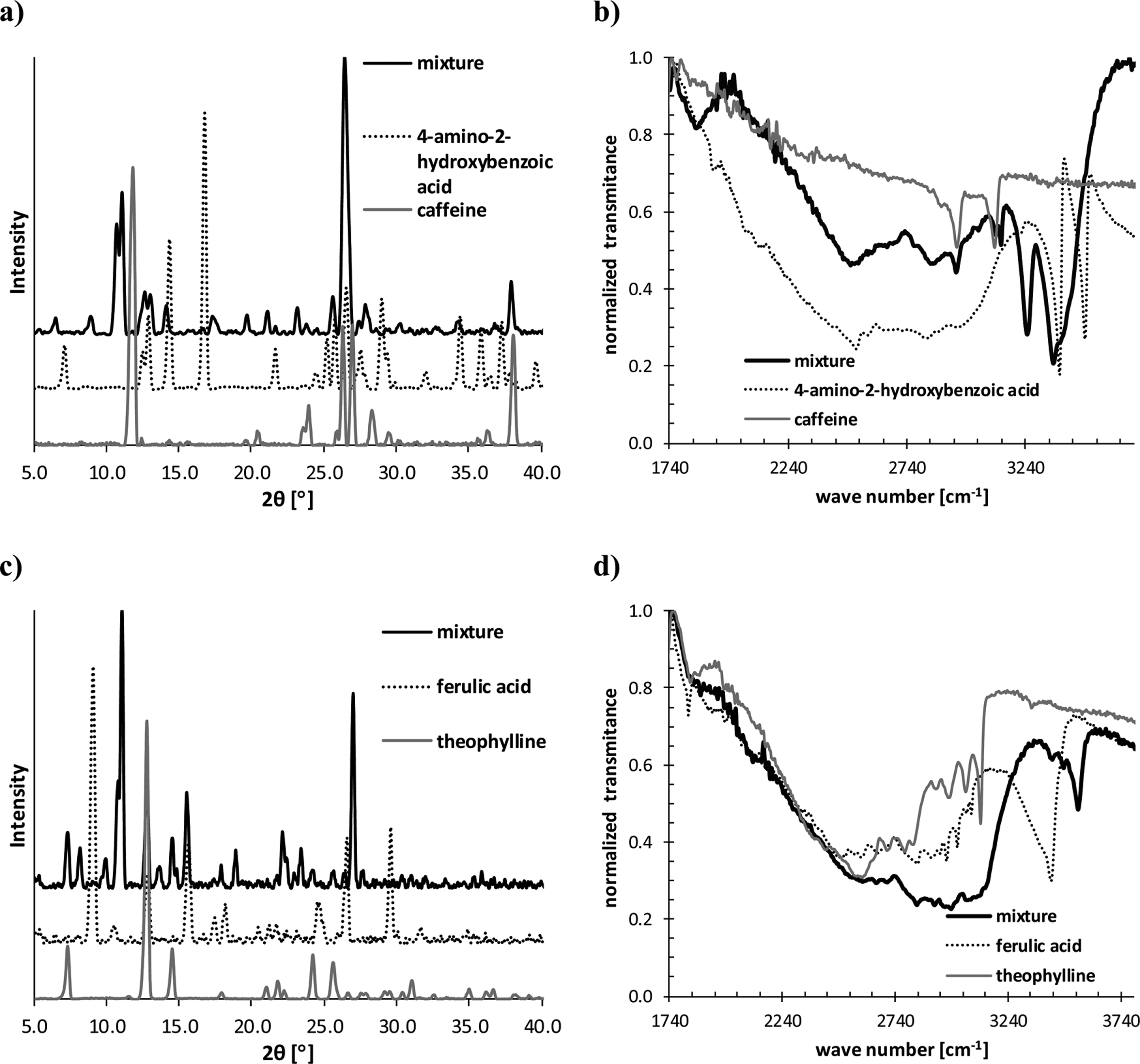
PXRD and FTIR spectra recorded for 1:1 caffeine/4-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid mixture (a, b) and 1:1 theophylline/ferulic acid mixture (c, d) obtained via liquid-assisted grinding.
Related Questions and Answers
A: FA exhibits significant synergistic antibacterial effects when combined with fosfomycin sodium, ceftriaxone, gentamicin, and tetracycline. The most pronounced synergistic effect is observed with fosfomycin sodium. This combination therapy can potentially reduce the required concentration of antibiotics, making FA a promising candidate for combination therapy against drug-resistant E. coli infections.
A: FA significantly downregulates the expression of csgD (43.32% reduction), flhC (23.14%), flhD (45.36%), motA (14.62%), and fimA (63.24%), while upregulating the transcription of pdeR (569.10% increase), pdeA (45.35%), and dosP (26.02%). This suggests that FA inhibits biofilm formation by suppressing the expression of genes involved in bacterial adhesion and motility and by promoting the degradation of c-di-GMP, which is crucial for biofilm development.
Q: What is the role of Ferulic Acid (FA) in inhibiting biofilm formation by Escherichia coli (E. coli)?
A: FA significantly inhibits biofilm formation by E. coli without affecting bacterial growth or metabolic activity. It reduces the production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and weakens bacterial motility. The study also shows that FA downregulates the expression of biofilm-related genes, such as csgD, flhC, flhD, motA, and fimA, while upregulating the transcription of c-di-GMP-related genes (pdeR, pdeA, and dosP). This dual mechanism of action makes FA a promising candidate for treating E. coli infections.