Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 594-65-0
Trichloroacetamide appears as a white, crystalline solid and is known for its strong odor. It's primarily used in organic synthesis, particularly as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
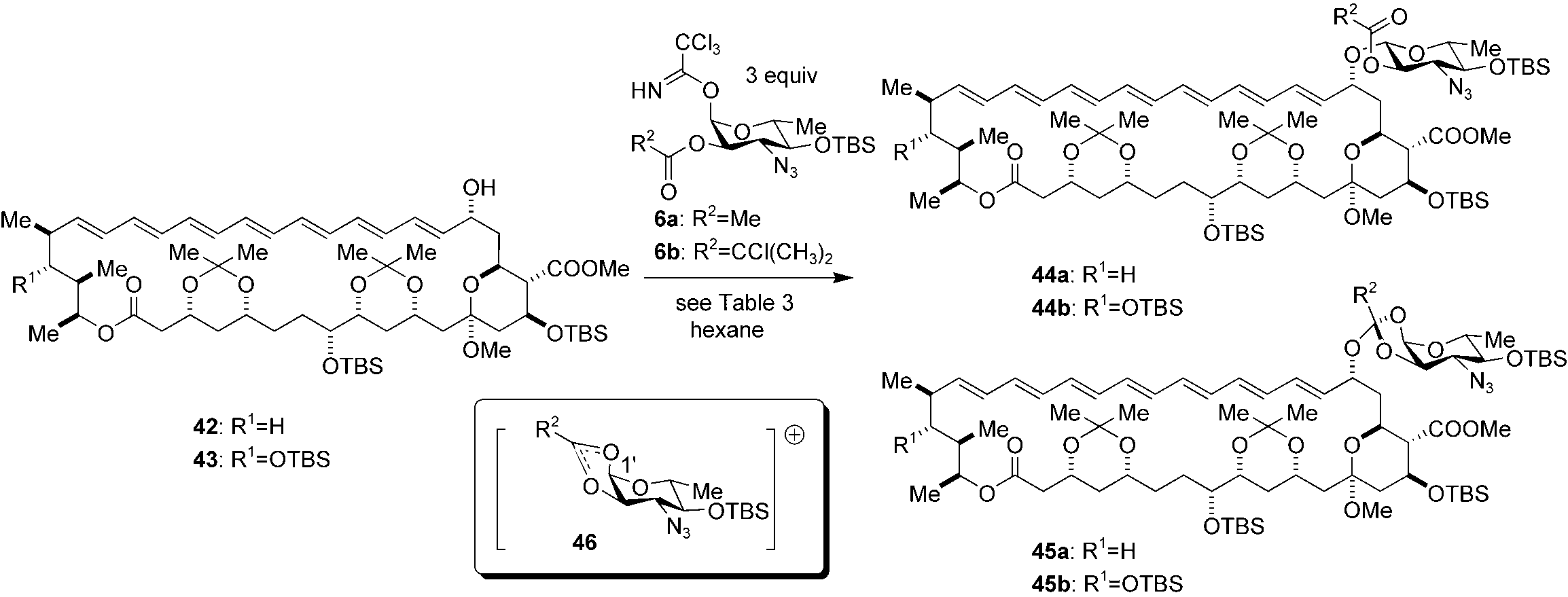
Glycosidation of amphoteronolide 43 and 35-deoxy amphoteronolide 42 with trichloroacetimidates 6 (see Table 3).
CAS number: 5961-85-3
TCEP is a tertiary phosphine in which phosphane is substituted with three 2-carboxyethyl groups. It is a commonly used reducing agent. It has a role as a reducing agent. It is a tricarboxylic acid and a phosphine derivative.
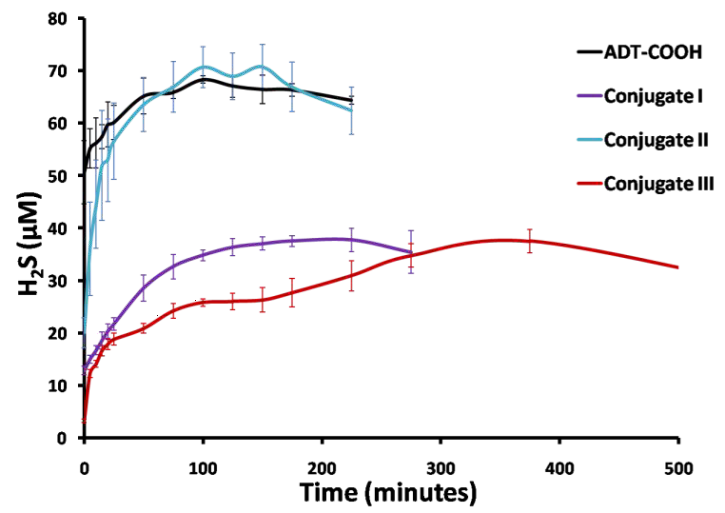
In vitro H2S release from ADT-COOH, conjugates I, II and III (100 µM) on incubation with tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP, 1mM) at 37 °C.
CAS number: 598-42-5
2-hydroxyacetamide is a member of acetamides.
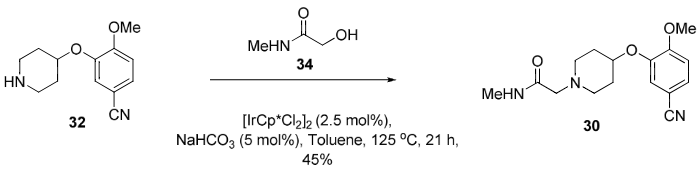
Amination of Glycolic Amide 34
CAS number: 60-24-2
2-Mercaptoethanol is one of the most common agents used for disulfide reduction.
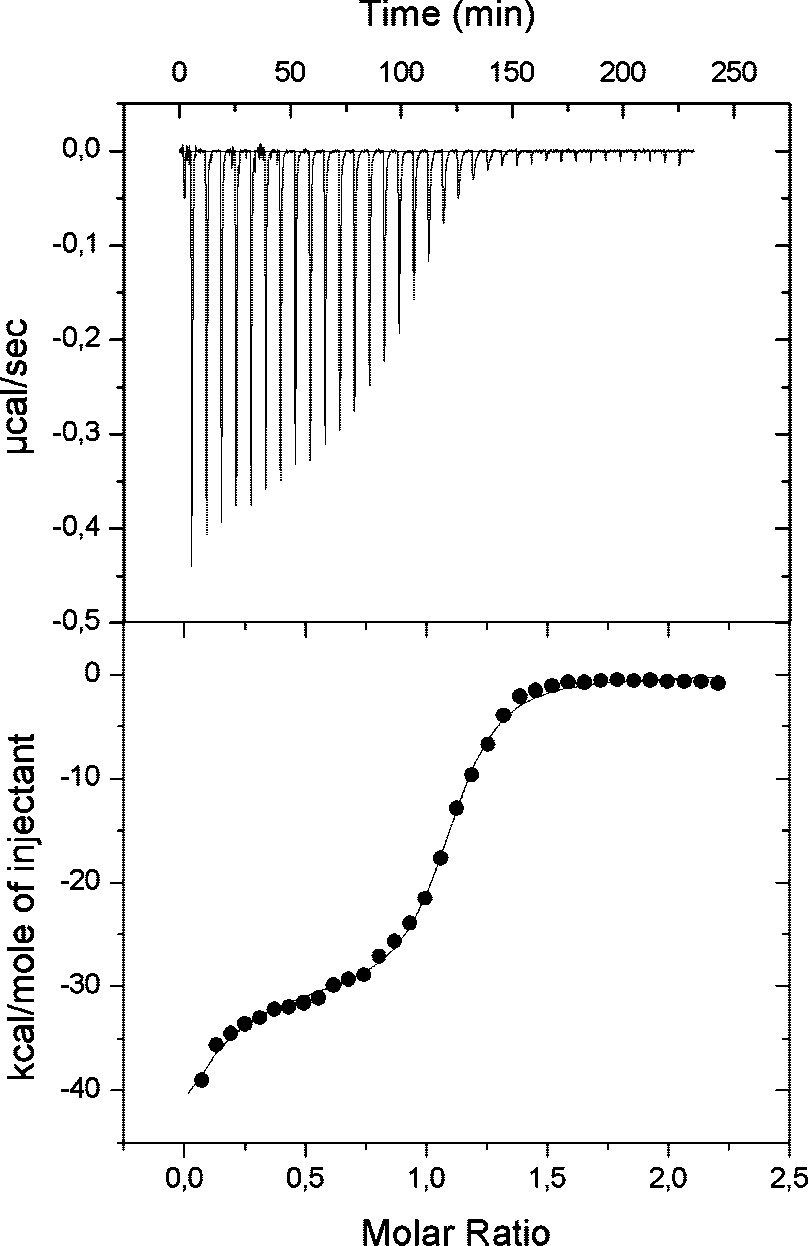
Isothermal titration of inhibitor 21 with BHMT. Titration was performed at 25°C in 50 mM HEPES/NaOH, pH 7.5, containing 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol. Upper panel: experimental data.
CAS number: 60-29-7
Diethyl ether is an ether in which the oxygen atom is linked to two ethyl groups. It has a role as an inhalation anaesthetic, a non-polar solvent and a refrigerant. It is a volatile organic compound and an ether.
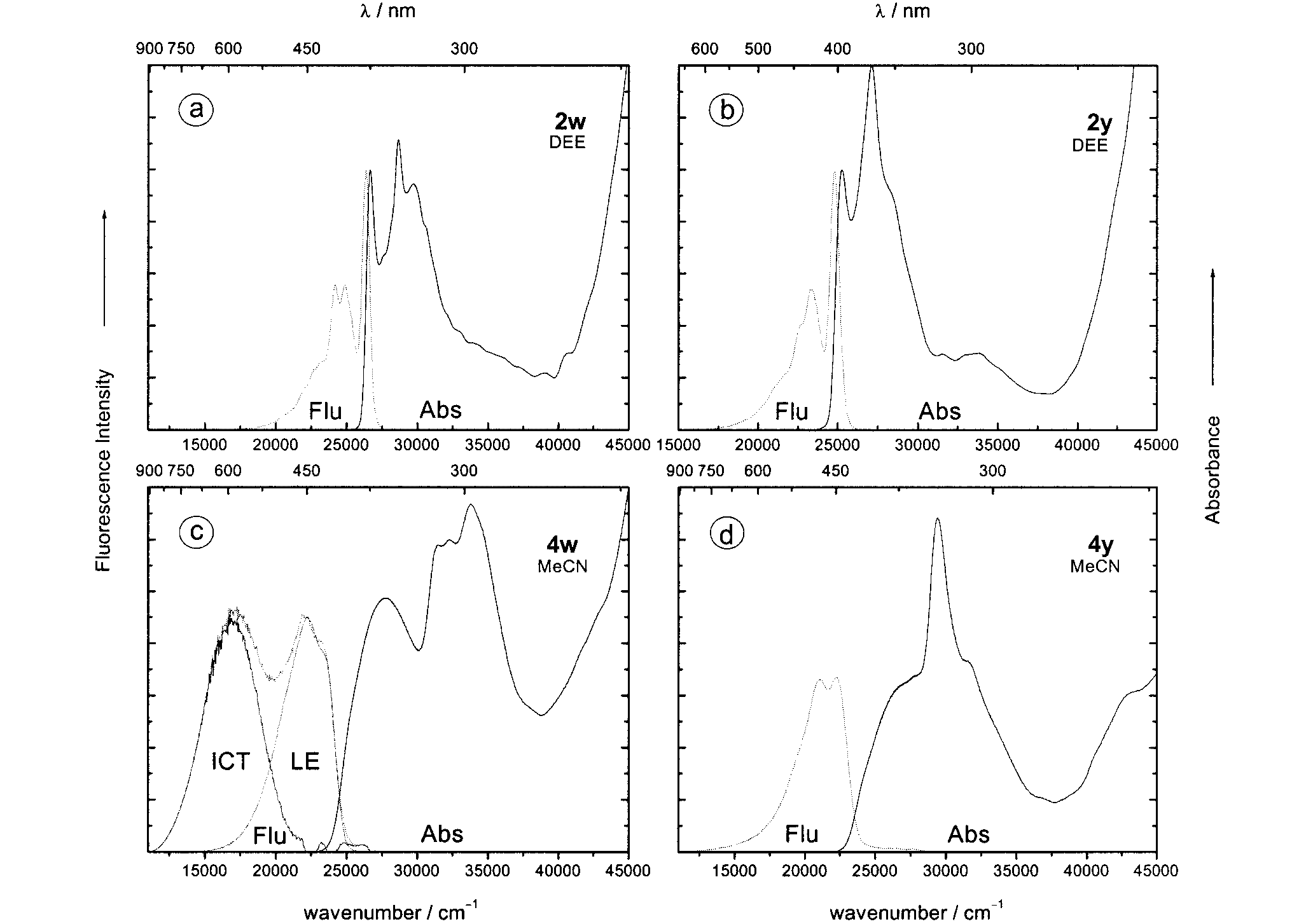
Absorption and fluorescence spectra (at 25 °C) of the alkynes 2w and 2y and their cycloadducts 4w and 4y in diethyl ether (DEE) and in acetonitrile (MeCN)
CAS number: 60-35-5
Acetamide is a member of the class of acetamides that results from the formal condensation of acetic acid with ammonia. It is a monocarboxylic acid amide, a N-acylammonia and a member of acetamides. It is a tautomer of an acetimidic acid.
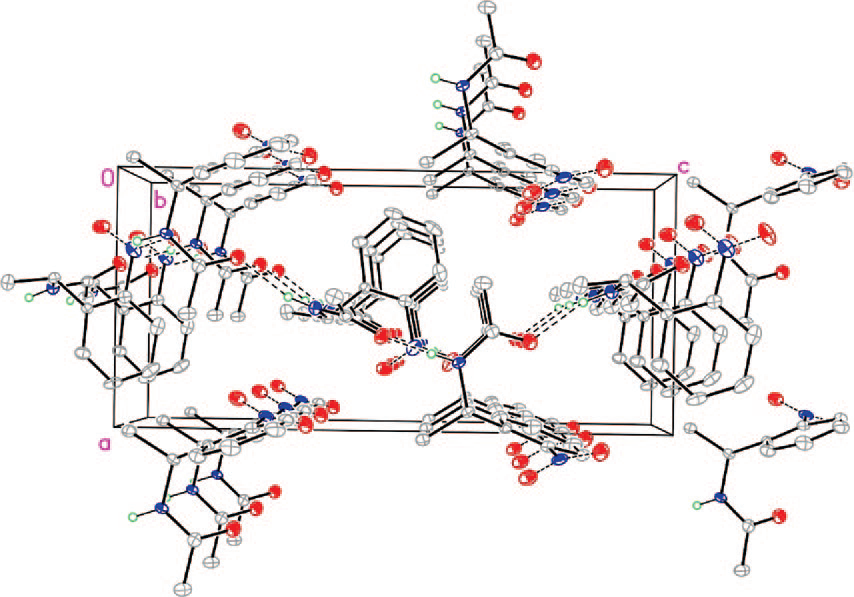
X-ray crystal structure of acetamide 6. The unit cell is indicated; intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown in dashed gray.
CAS number: 60118-28-7
Phosphonate(2-) is a divalent inorganic anion obtained by removal of both protons from phosphonic acid It is a phosphorus oxoanion and a divalent inorganic anion. It is a conjugate base of a phosphonate(1-).
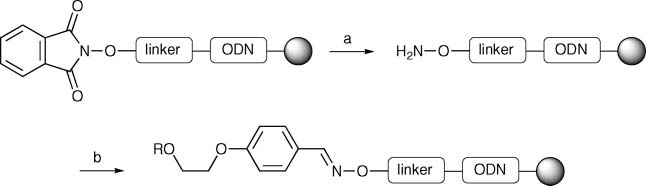
Coupling of the support-bound aminooxy-functionalized oligonucleotides with the phosphonate building blocks 3 and 4.
CAS number: 6027-13-0
L-Homocysteine, an amino acid, is a homocysteine that has L configuration. Homocysteine is an essential intermediate in normal mammalian metabolism of methionine.
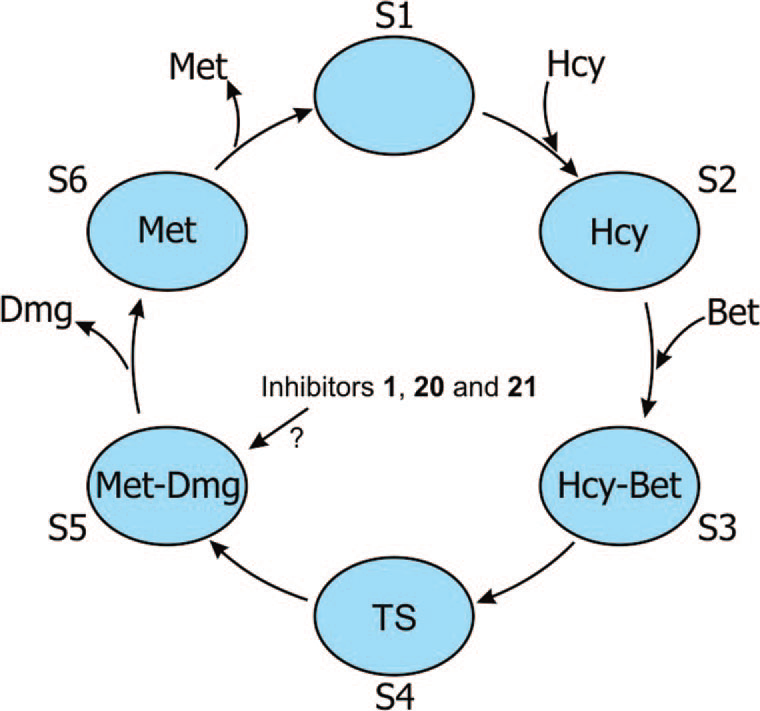
Schematic diagram showing the possible structural changes of BHMT during the binding process with substrates and products. The blue ovals (S1-S6) represent the different structural states of BMHT monomers. Hcy represents homocysteine, Bet represents betaine, Met represents methionine, Dmg represents dimethylglycine, and TS represents the assumed transition state of the substrate.
CAS number: 603-35-0
Triphenylphosphine is a member of the class of tertiary phosphines that is phosphane in which the three hydrogens are replaced by phenyl groups. It has a role as a reducing agent. It is a member of benzenes and a tertiary phosphine.
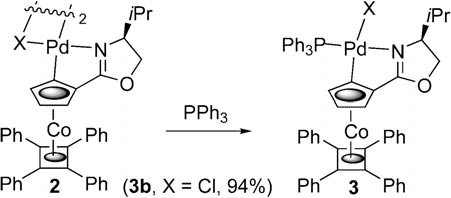
Synthesis of palladacycle–triphenylphosphine adducts 3.
CAS number: 603-76-9
1-Methylindole, also known as N-methylindole or methylindole, is a methylated derivative of indole, featuring a methyl group attached to the nitrogen atom of the indole ring.
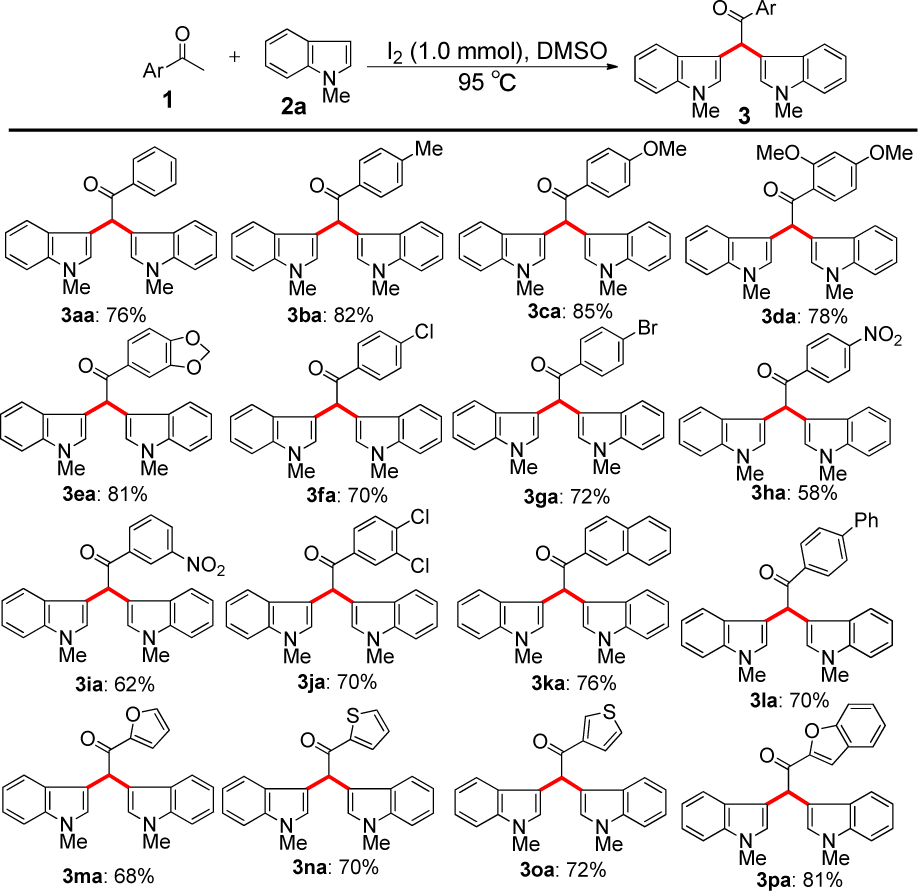
Scope of Aryl Methyl Ketones and N-Methylindole