Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 287-92-3
Cyclopentane is a cycloalkane that consists of five carbons each bonded with two hydrogens above and below the plane. The parent of the class of cyclopentanes. It has a role as a non-polar solvent. It is a member of cyclopentanes, a cycloalkane and a volatile organic compound.
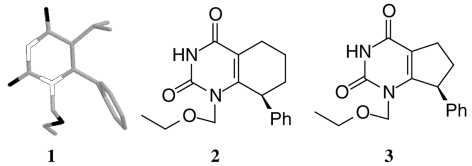
1 Crystal structure of MKC-442 when bound to RT. 2 Structure of cyclohexane-annelated MKC-442 analogue. 3 Structure of cyclopentane-annelated MKC-442 analogue.
CAS number: 288-13-1
Pyrazole is a heterocyclic organic compound characterized by a ring structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms in adjacent positions.
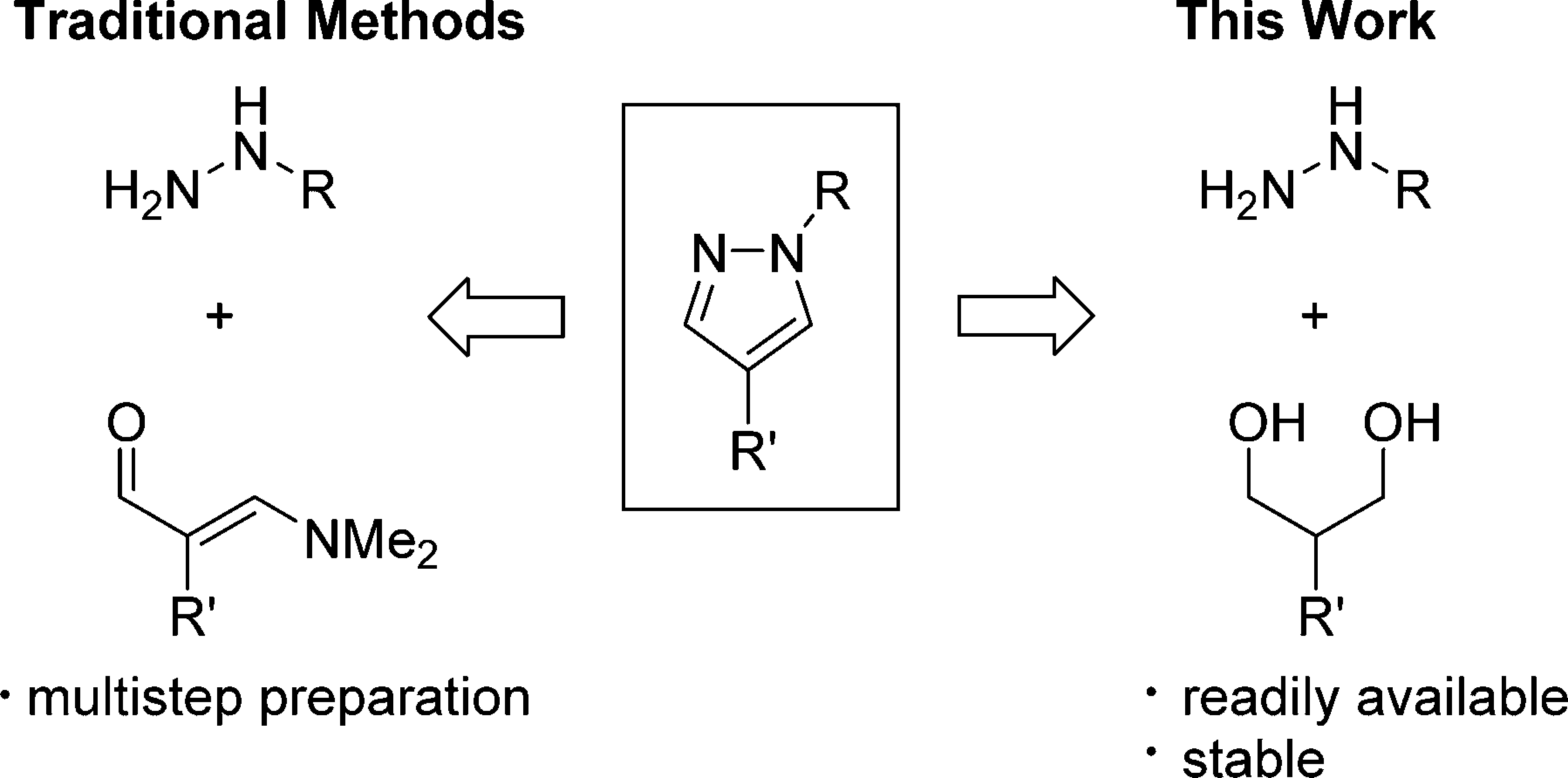
Pyrazoles from masked dialdehydes vs diols
CAS number: 288-14-2
Isoxazole is a monocyclic heteroarene with a structure consisting of a 5-membered ring containing three carbon atoms and an oxygen and nitrogen atom adjacent to each other. It is the parent of the class of isoxazoles. It is a mancude organic heteromonocyclic parent, a monocyclic heteroarene and a member of isoxazoles.
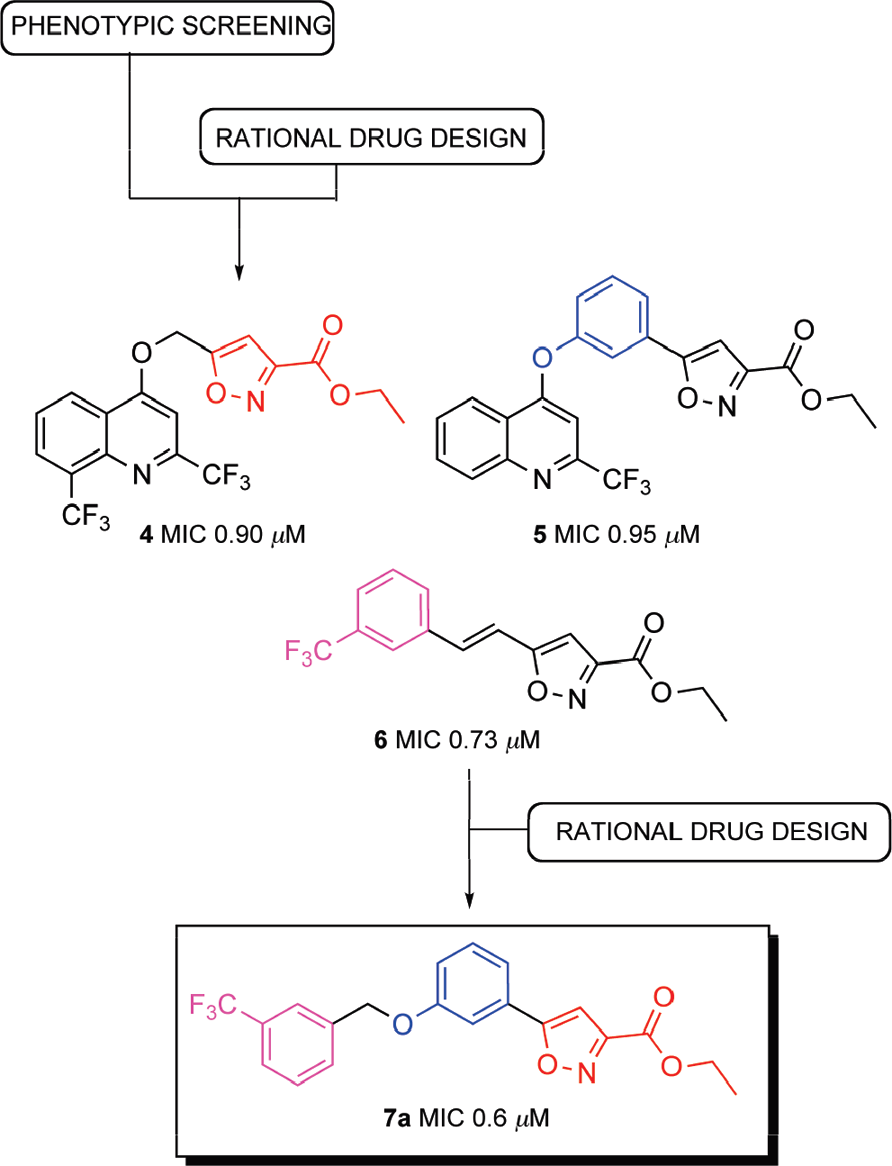
Evolution of isoxazole-based anti-TB agents
![Synthesis of isoxazoles 6 via [3 + 2] cycloaddition of nitrile oxide 4 onto vinyl ether 2.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/2812959_05.png)
Synthesis of isoxazoles 6 via [3 + 2] cycloaddition of nitrile oxide 4 onto vinyl ether 2.
![Synthesis of isoxazoles 10 via Suzuki coupling and [3 + 2] cycloaddition of nitrile oxides onto vinyl ether 2.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/2812959_10.png)
Synthesis of isoxazoles 10 via Suzuki coupling and [3 + 2] cycloaddition of nitrile oxides onto vinyl ether 2.
CAS number: 288-16-4
Isothiazole is a mancude organic heteromonocyclic parent, a monocyclic heteroarene and a member of 1,2-thiazoles.
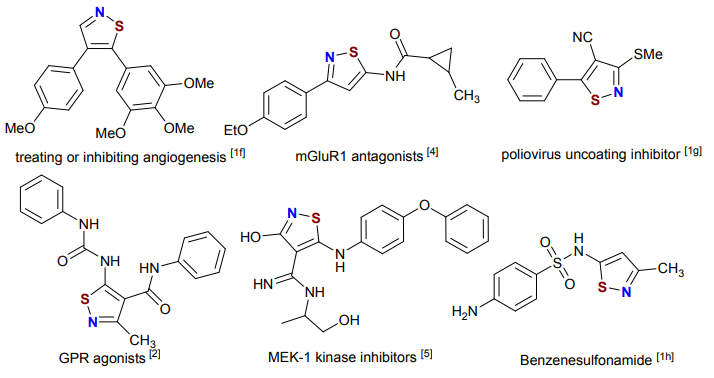
Bioactive compounds containing isothiazole-based heterocycles
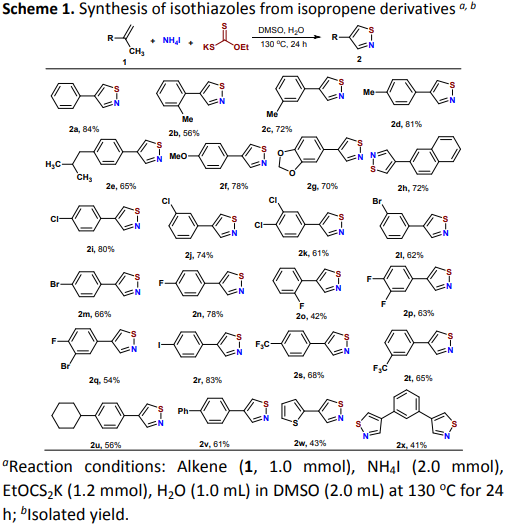
Synthesis of isothiazoles from isopropene derivatives
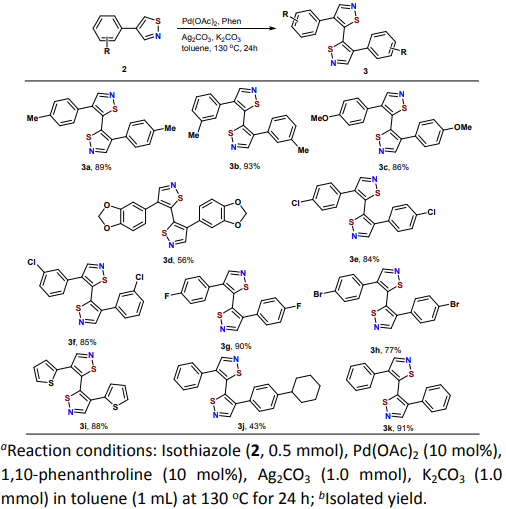
Synthesis of 5,5'-bisisothiazoles from 4-substituted isothiazole derivatives
CAS number: 288-32-4
1H-imidazole is an imidazole tautomer which has the migrating hydrogen at position 1. It is a conjugate base of an imidazolium cation. It is a conjugate acid of an imidazolide. It is a tautomer of a 4H-imidazole.
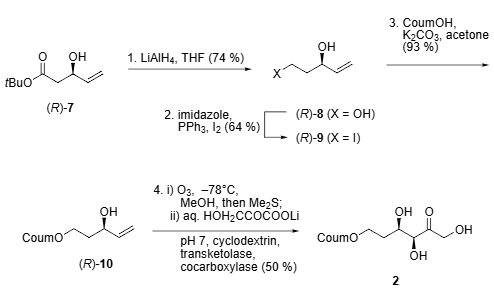
Biocatalytic stereoselective synthesis of fluorogenic substrate 2.
CAS number: 288-36-8
1H-1,2,3-Triazole is one of the four aromatic heterocyclic compounds with two carbon atoms, three nitrogen atoms, and two double bonds.
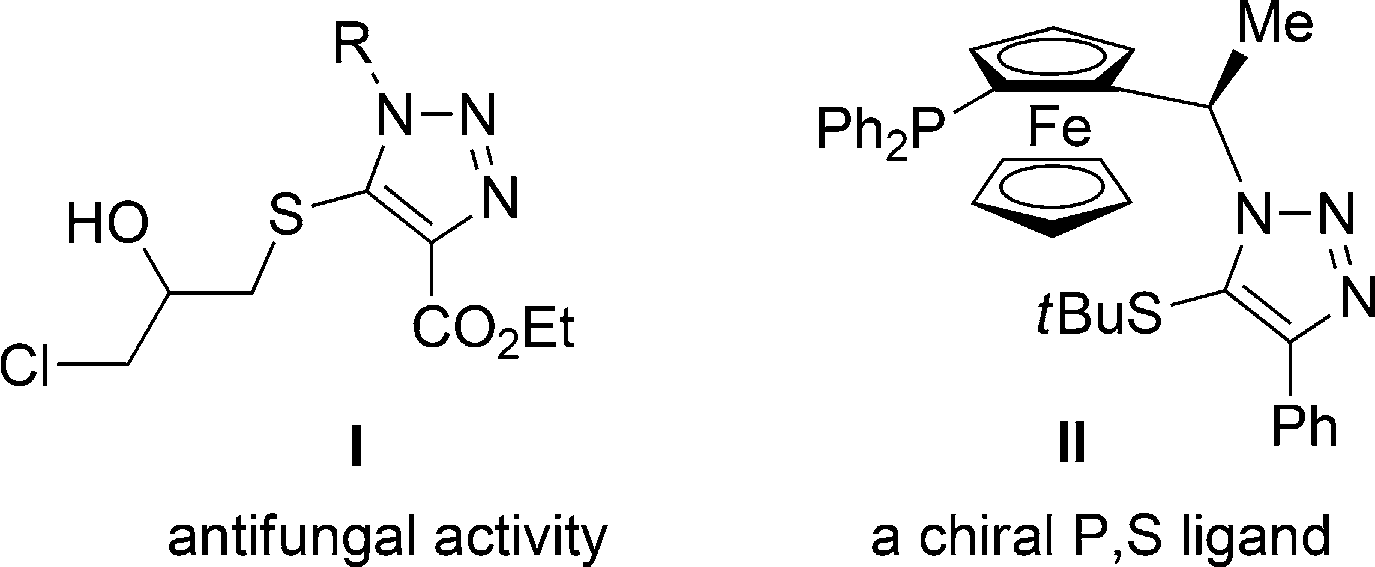
Selected useful 1,2,3-triazoles with a 5-sulfur substituent.
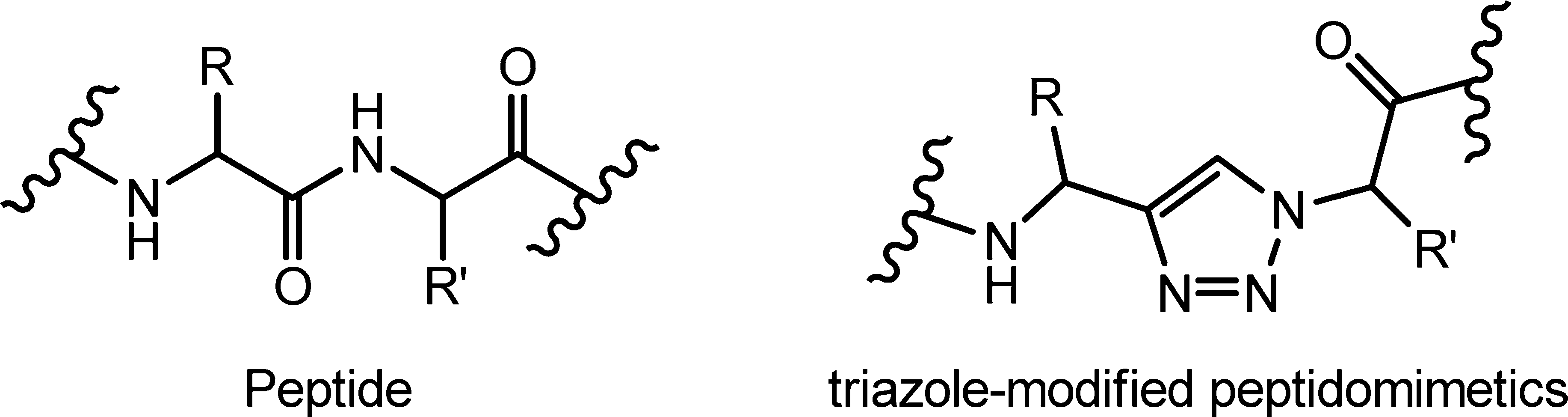
General structures of (a) a peptide and (b) a 1H-1,2,3-triazole-modified peptidomimetics.
CAS number: 288-42-6
Oxazole is a vital heterocycle moiety, devouring effective healing action with three loci for substitution.
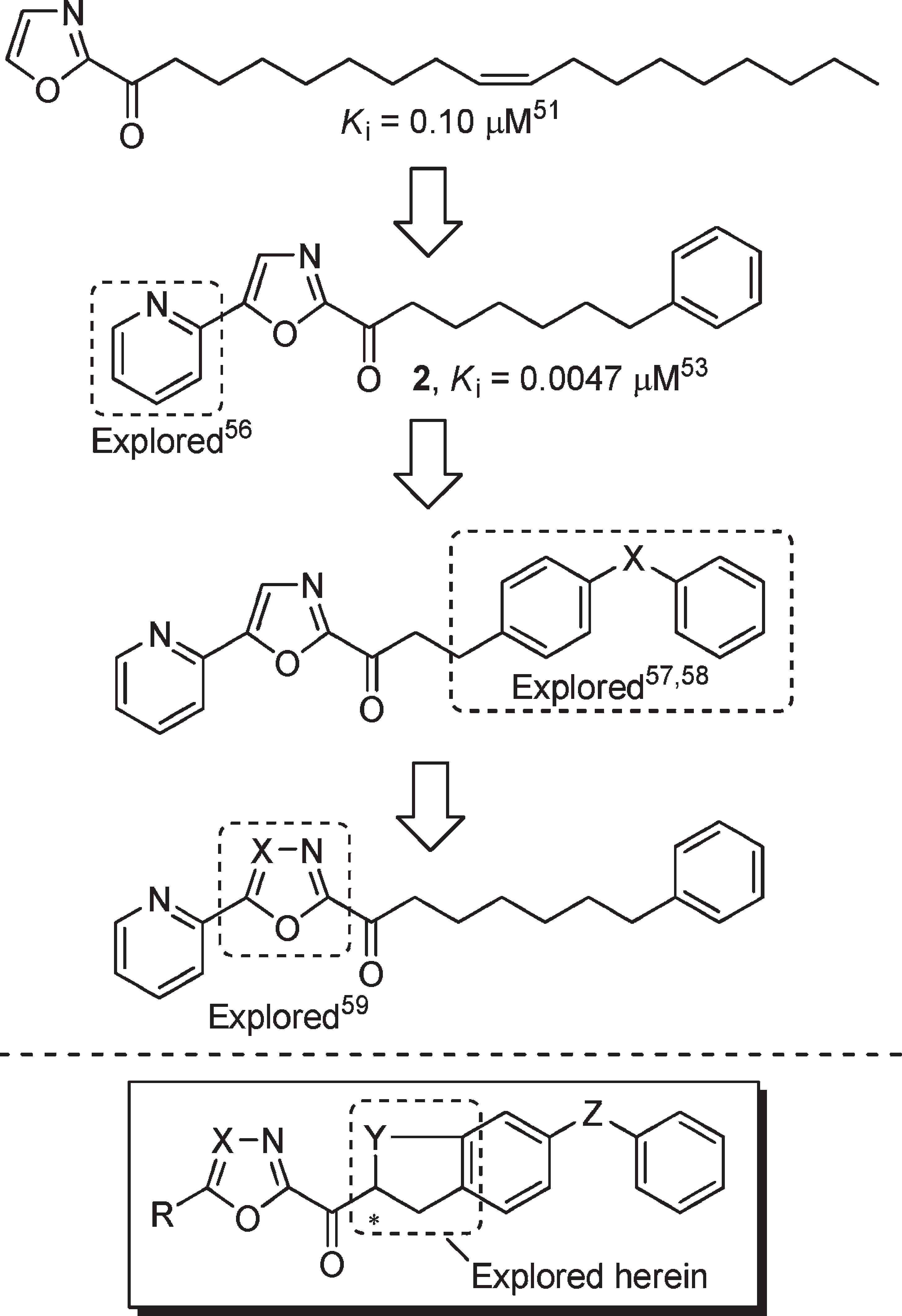
We performed a series of systematic structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies on 2 , exploring the 4- and 5-positions of the central oxazole, the C2 acyl side chain, and the central heterocyclic ring, and found that each independently affects the potency or selectivity of the inhibitor, Figure 2 .
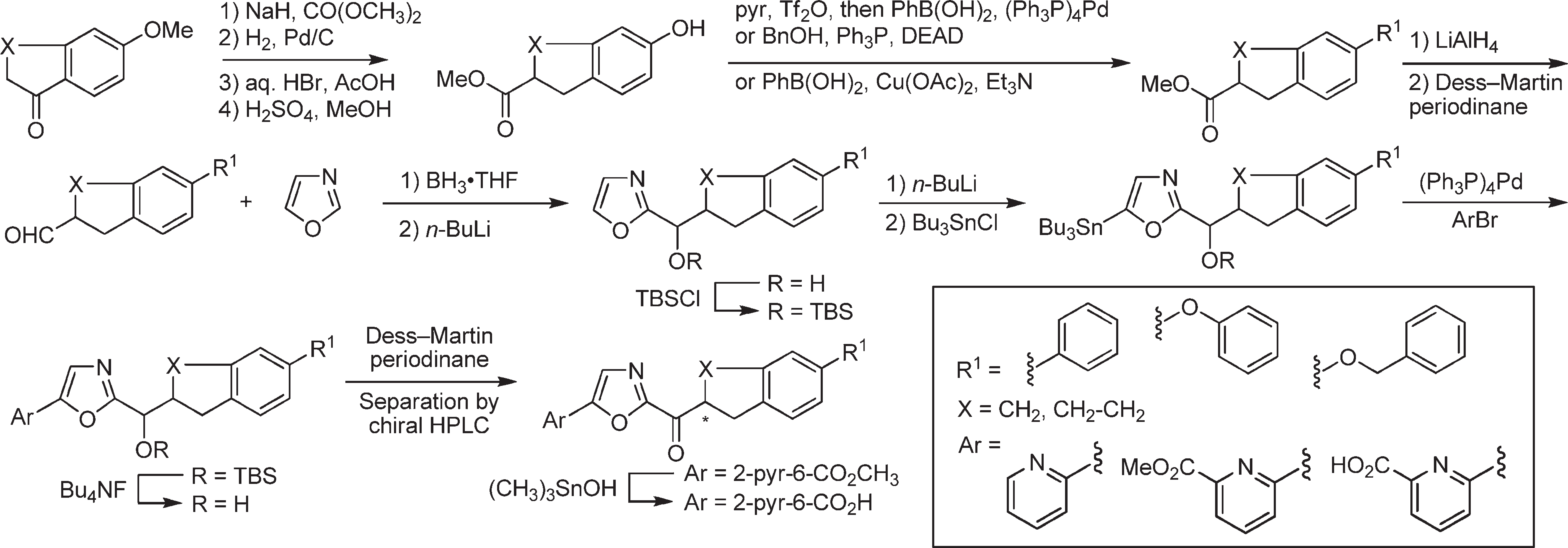
Synthesis of oxazole-based inhibitors bearing a C5 aryl substituent and containing additional conformational constraints in the C2 acyl side chain.
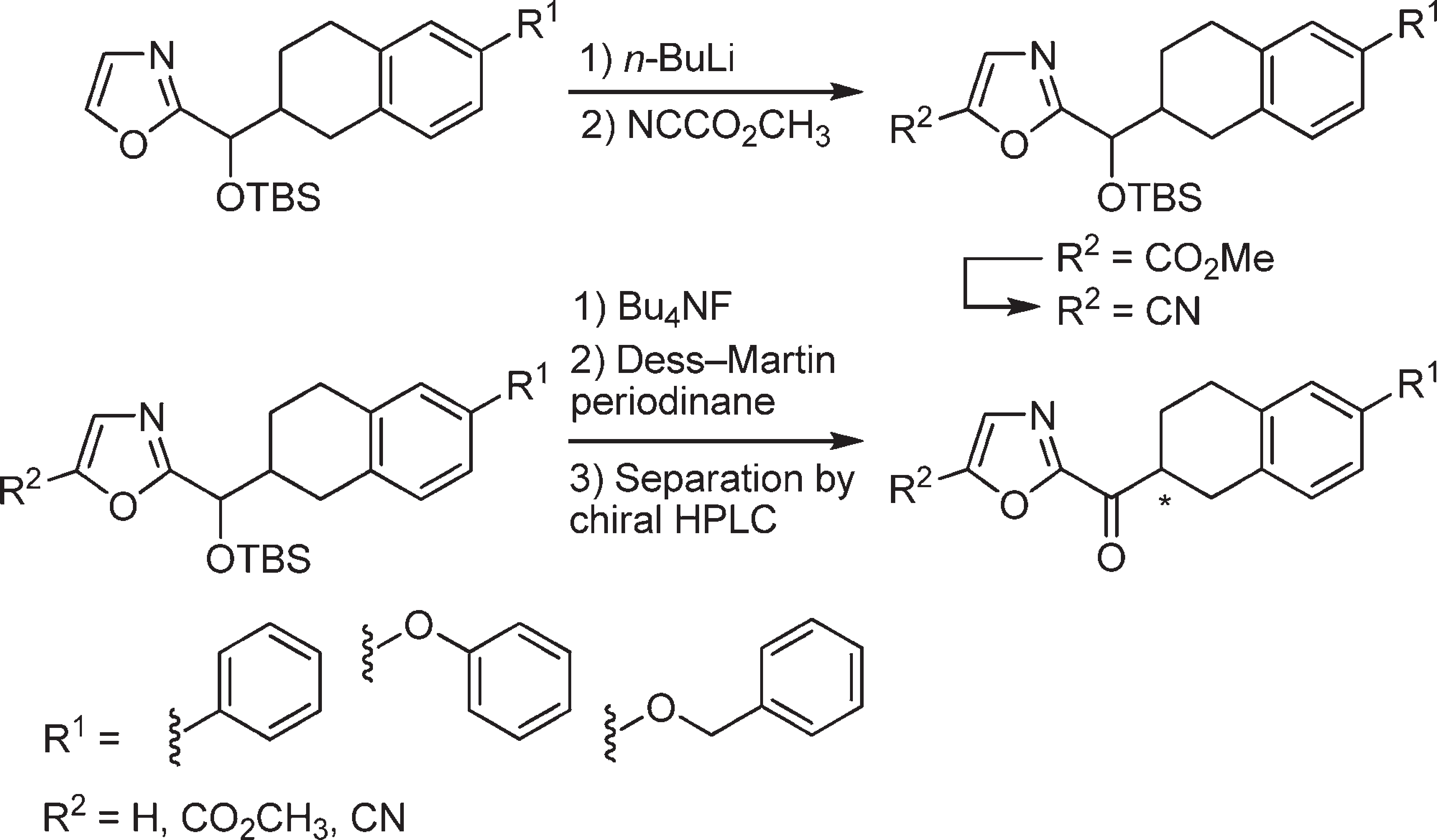
The synthesis of candidate inhibitors that bear a nonaro-matic oxazole C5-substituent.
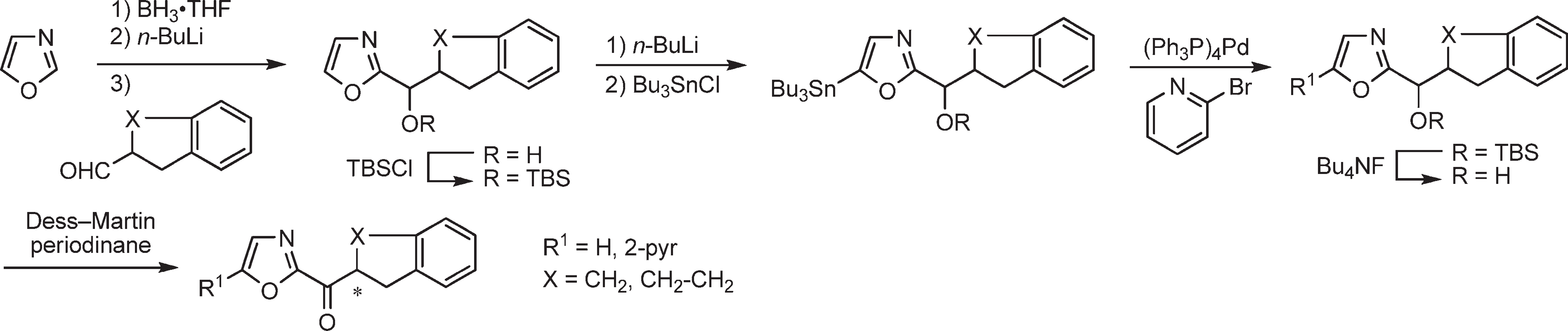
Stille coupling with 2-bromopyridine produced the C5-substituted oxazoles, which were converted to the corresponding ketones by TBS ether deprotection (Bu4NF) and oxidation of the liberated alcohols using Dess-Martin Periodinane.
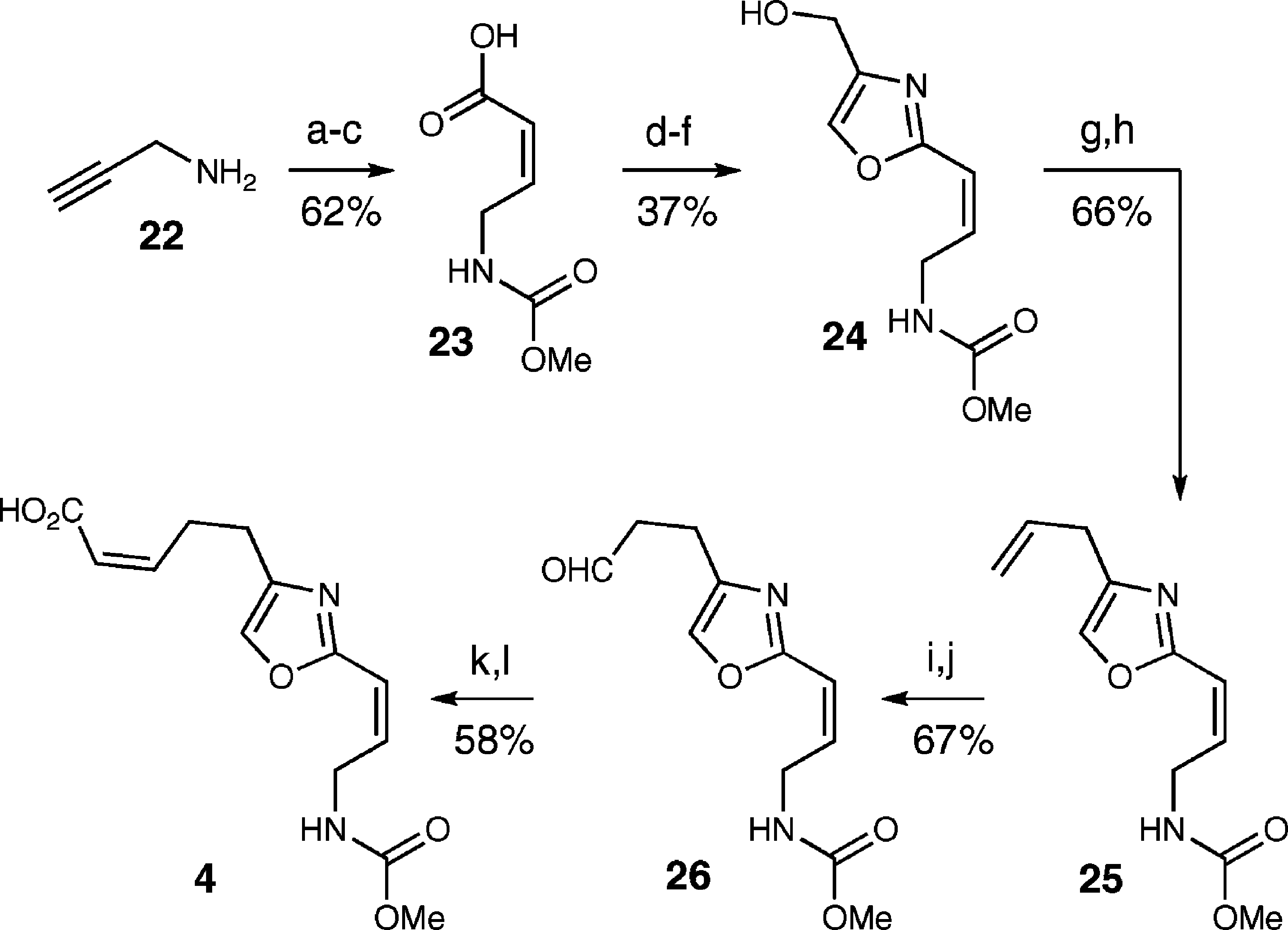
Oxazole Fragment Synthesis
CAS number: 288-47-1
Thiazole is a mancude organic heteromonocyclic parent, a member of 1,3-thiazoles and a monocyclic heteroarene.
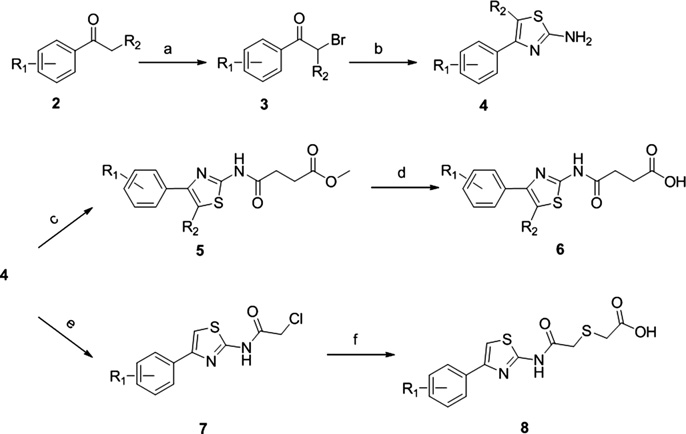
General synthesis of thiazole-based derivatives.
CAS number: 288-88-0
1H-1,2,4-triazole is a 1,2,4-triazole. It is a tautomer of a 3H-1,2,4-triazole and a 4H-1,2,4-triazole.
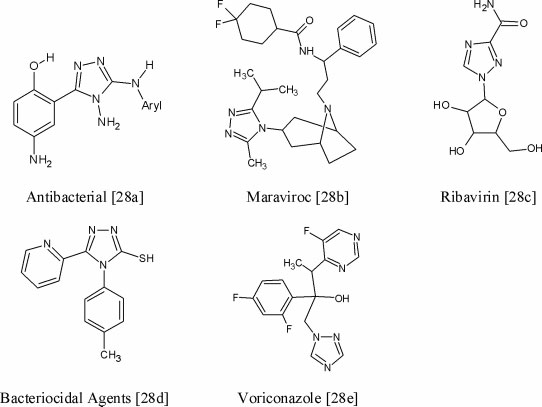
Examples of some bioactive compounds containing 1,2,4-triazole moiety.
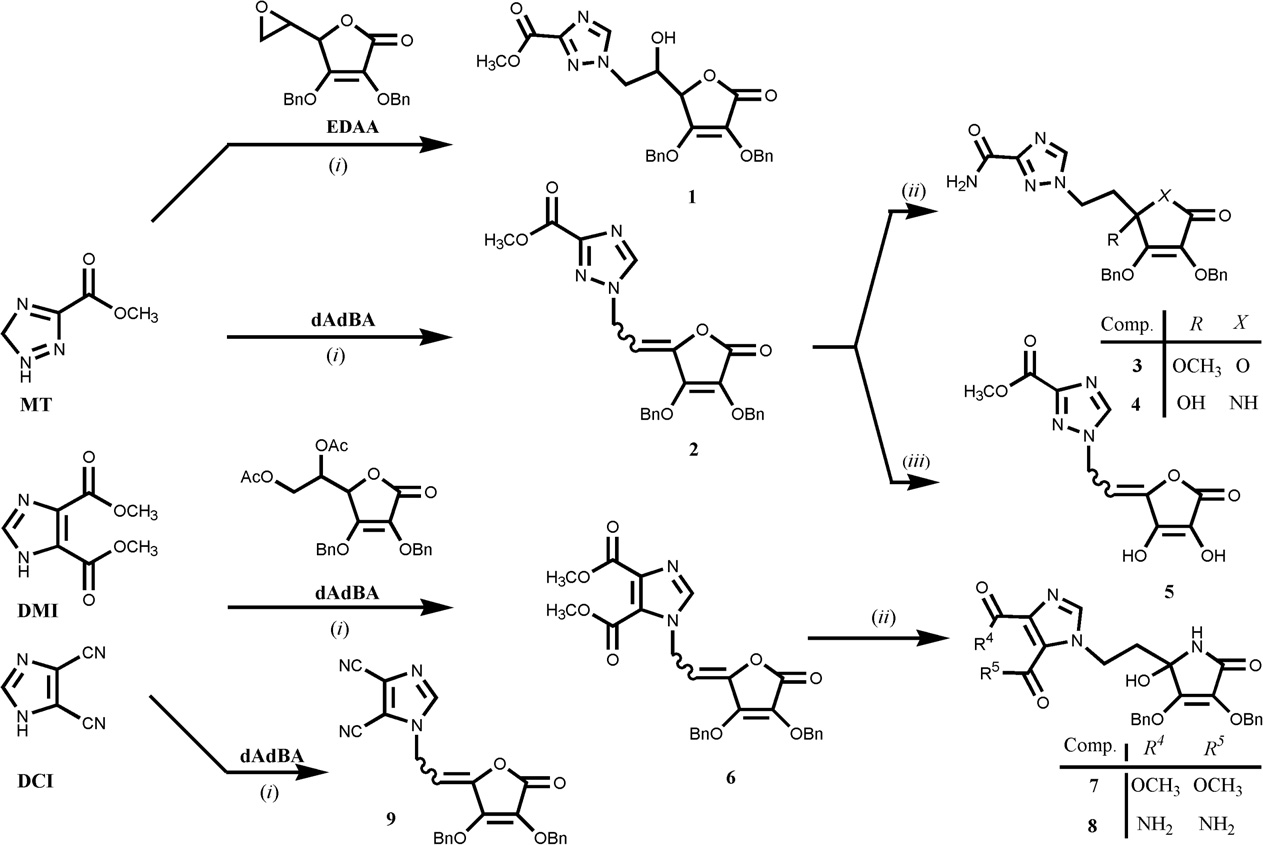
Synthesis of 1,2,4-triazole and 4,5-disubstituted-imidazole L-ascorbic acid (1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 9) and imino-ascorbic acid (4, 7 and 8) derivatives.
CAS number: 288-90-4
1,2,4-Oxadiazole is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring containing two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It's a versatile scaffold in medicinal chemistry due to its unique properties and wide range of biological activities.
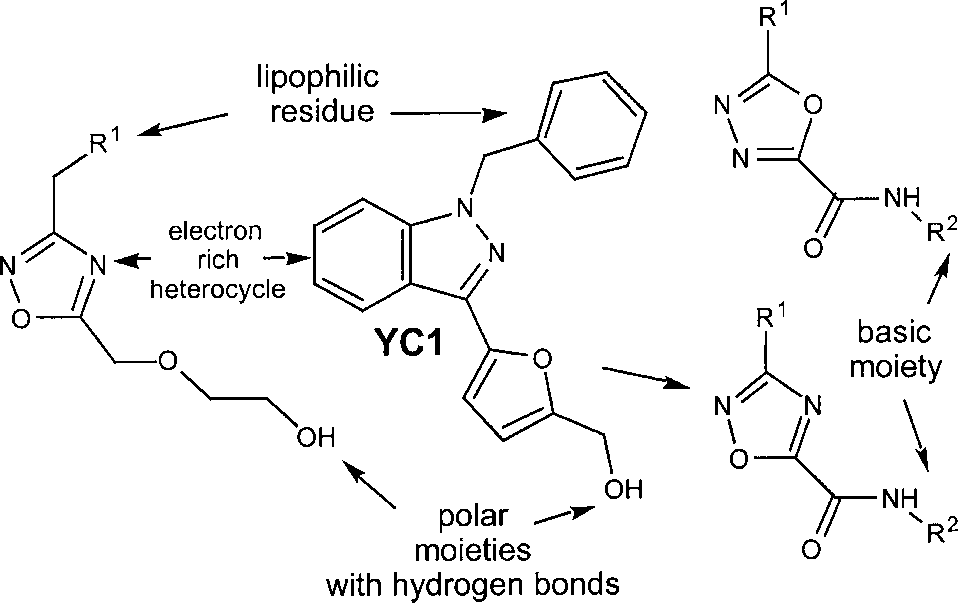
1,2,4-Oxadiazoles and 1,3,4-oxadiazoles derived from YC-1.
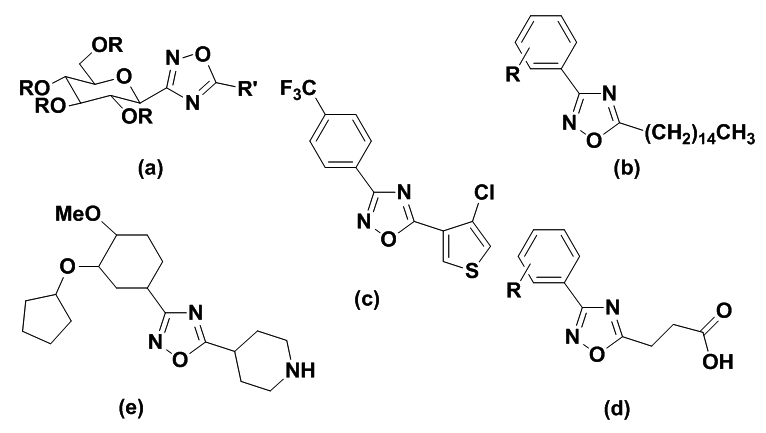
Examples of biologically active 1,2,4-oxadiazoles.