Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 21291-40-7
ε-Fructoselysine, also known as fructosyl-lysine, is a compound formed through the Maillard reaction, a chemical reaction between reducing sugars and the amino group of lysine residues in proteins or free amino acids. It's an Amadori product, meaning it's an early intermediate in the Maillard reaction.
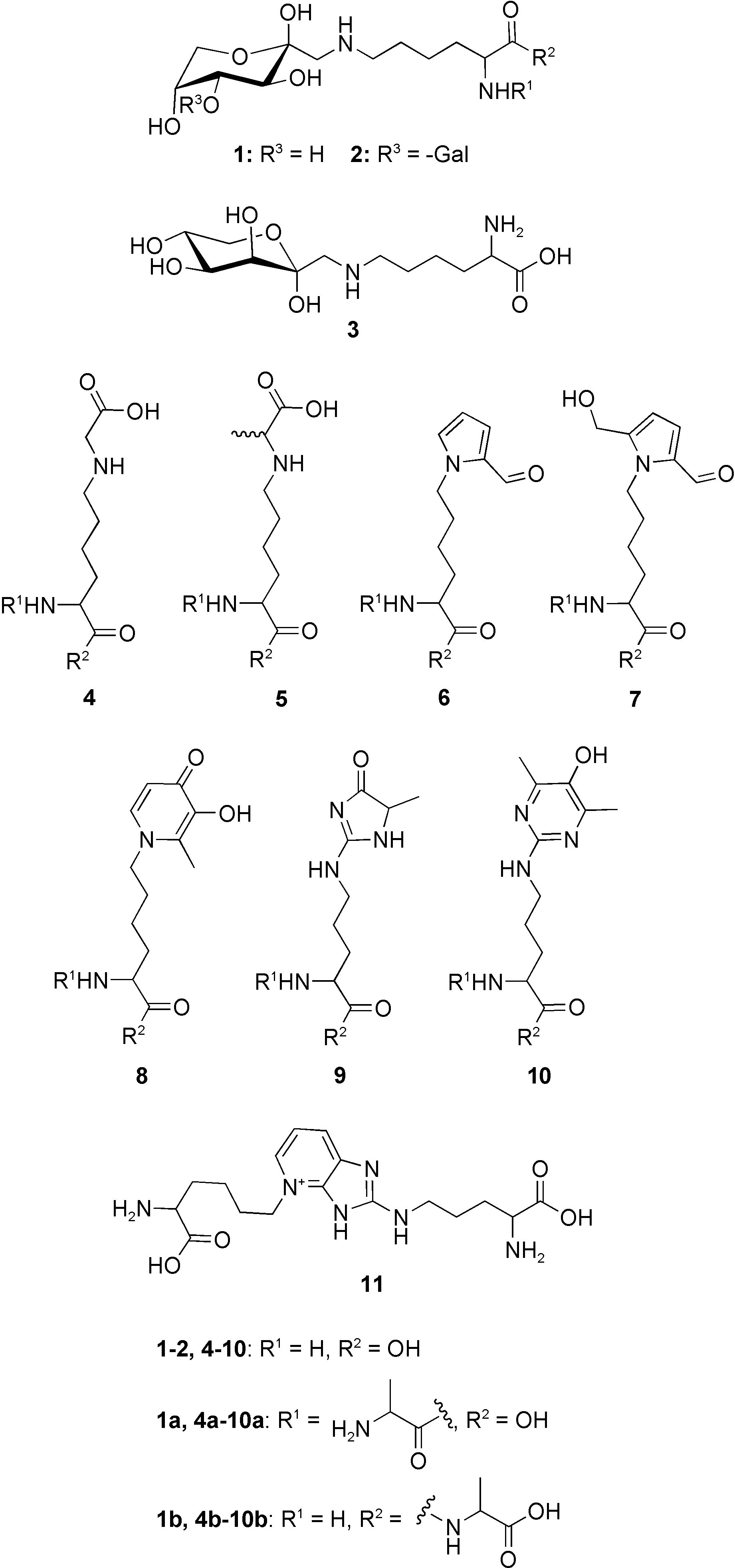
Chemical structures of the investigated Maillard reaction prod- ucts fructoselysine (1), lactuloselysine (2), tagatoselysine (3), CML (4), CEL (5), formyline (6), pyrraline (7), maltosine (8), MG-H1 (9), argpyrimidine (10), and pentosidine (11).
CAS number: 2140-95-6
(-)-β-Aminoisobutyric acid (also known as L-β-Aminoisobutyric acid or L-BAIBA) is a naturally occurring, non-proteinogenic β-amino acid derived from thymine catabolism. It is the L-enantiomer of β-aminoisobutyric acid and plays a role as a signaling molecule, particularly in metabolic regulation.
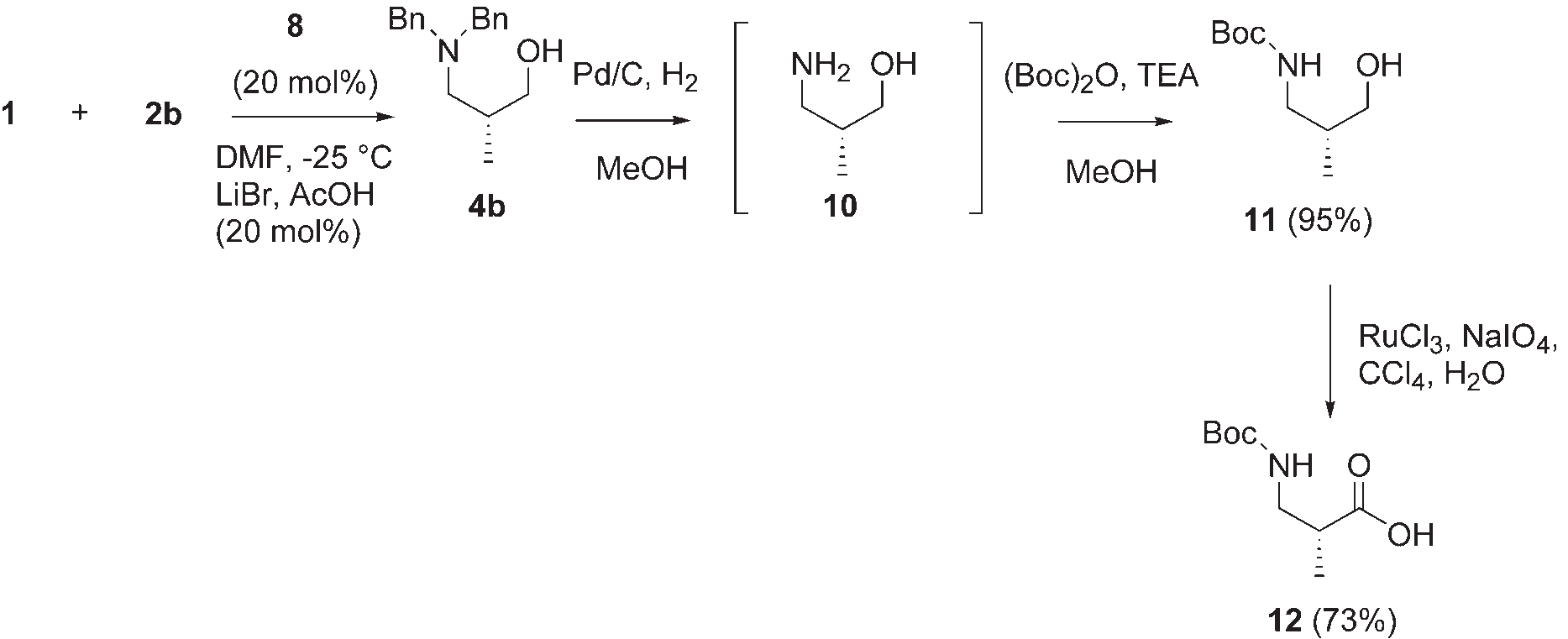
Asymmetric synthesis of Boc-protected (R)-3-amino-2-methyl-propanoic acid 12.
CAS number: 2143-68-2
Methyloxidanyl is an organic radical derived from methanol. It is functionally related to a methanol.
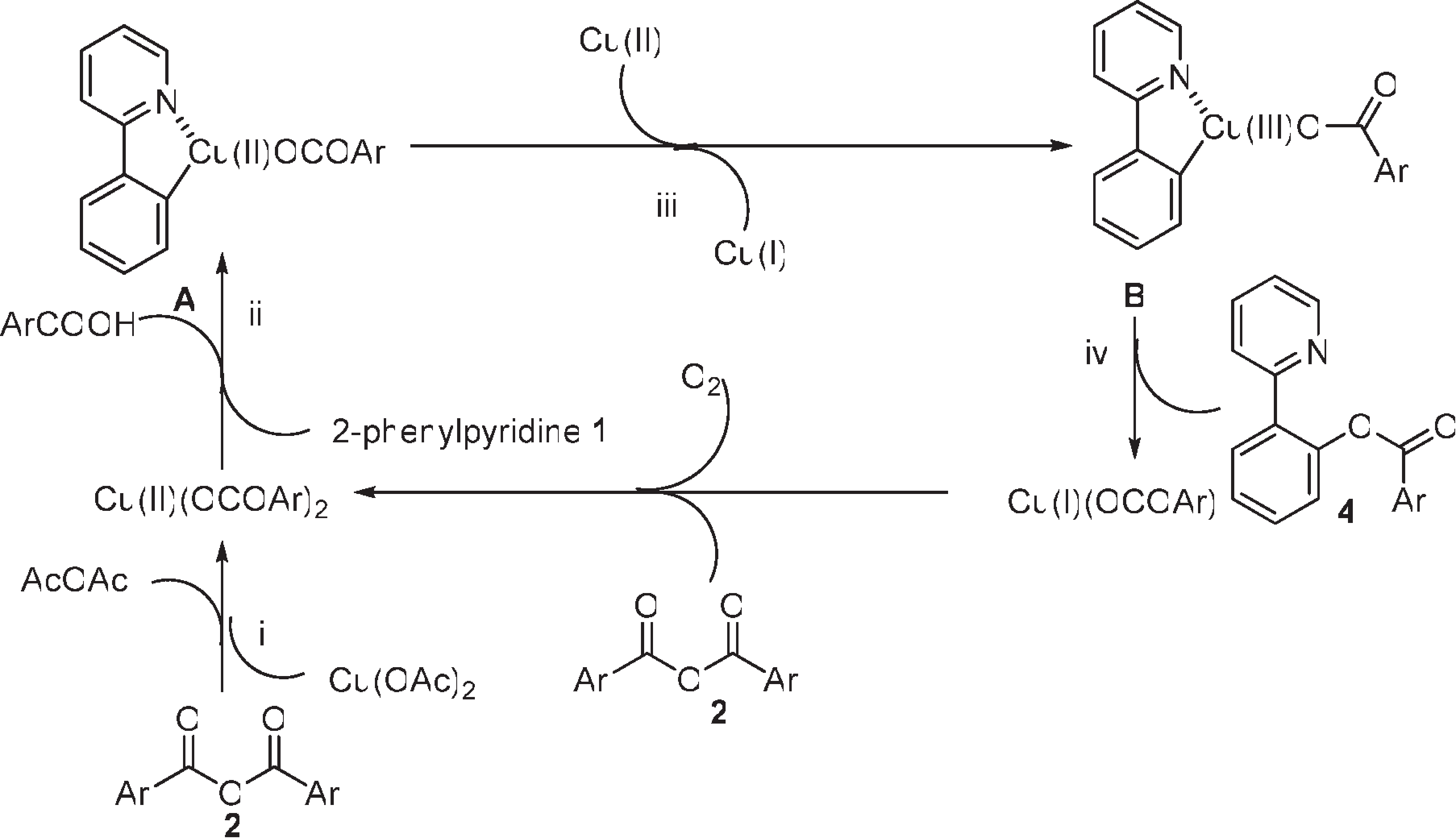
On the basis of the experimental results and Stahl's seminal work on mechanistic study of copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative coupling of arylboronic esters and methanol, a plausible mechanism for this transformation is outlined in Scheme 3.
CAS number: 214348-67-1
Somatostatin receptor subtype 2 agonist
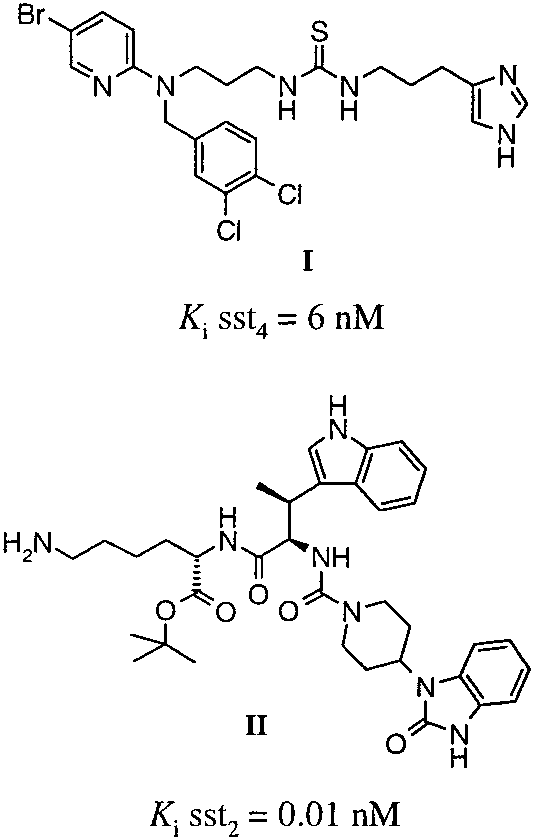
Chemical structures of I (NNC 26-9100) and II (L-054,522) and their inhibition constants (Ki) on somatostatin receptor subtypes.
CAS number: 215-58-7
Dibenz[a,c]anthracene is a carbopolycyclic compound.
![Synthesis of substituted benzo[b]triphenylene 2.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3955533_02.png)
Synthesis of substituted benzo[b]triphenylene 2.
CAS number: 215-95-2
Tetrabenzo[a,c,j,l]naphthacene is a specific type of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) known for its unique structure and properties. It's essentially a naphthacene molecule with four benzene rings fused onto its periphery.
![Synthesis of substituted tetrabenzo[a,c,j,l]tetracene 3.](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/3955533_04.png)
Synthesis of substituted tetrabenzo[a,c,j,l]tetracene 3.
CAS number: 2150-43-8
Methyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate is a methyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid with methanol. It has a role as an antioxidant, a neuroprotective agent and a plant metabolite. It is a methyl ester and a member of catechols. It is functionally related to a 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid.
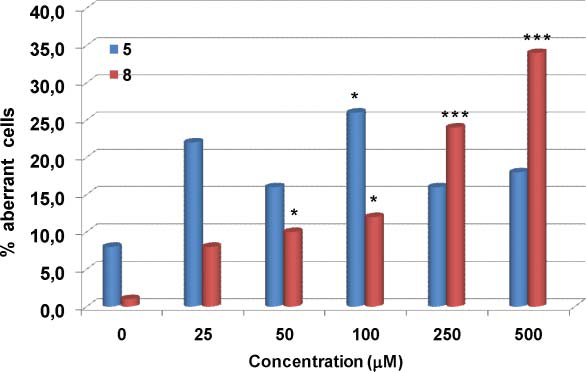
Frequency of aberration-bearing cells induced by the monolignol methyl vanillate 5 and its catechol derivative methyl protocatechuate 8 in V79 cells in vitro.
CAS number: 2161-85-5
4,6-Diacetylresorcinol (also known as resodiacetophenone) is a bifunctional molecule, meaning it has two acetyl groups (CH3CO-) attached to a resorcinol (a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups) at the 4 and 6 positions.
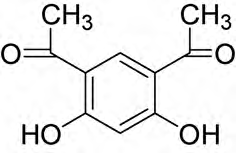
Structure of 4,6-diacetylresorcinol (H2-DAR) ligand.
CAS number: 21679-14-1
Fludarabine is a chemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of hematological malignancies. It is commonly marketed under the brand name Fludara.
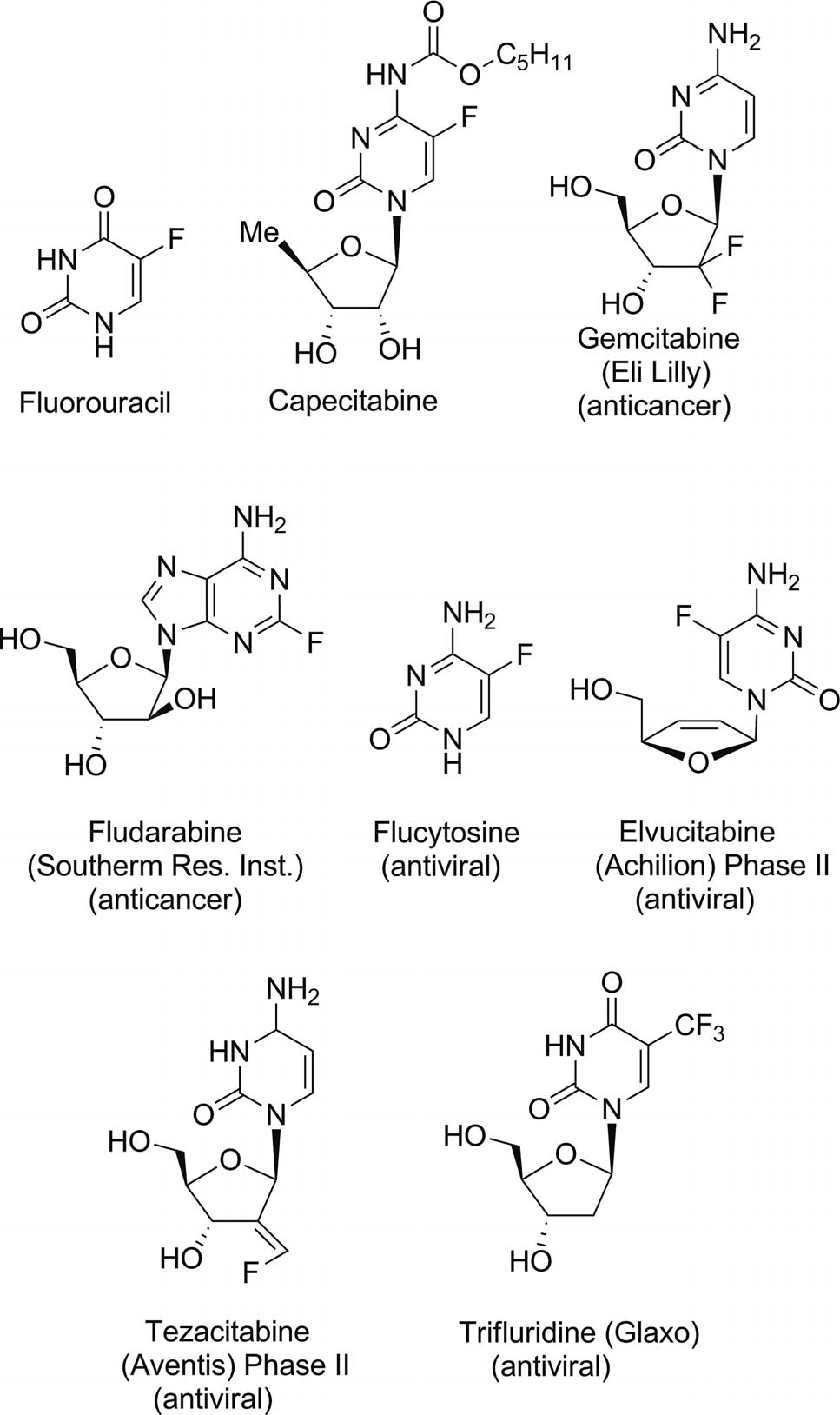
Fluorinated purine and pyrimidine antimetabolites clinically used for the treatment of numerous cancers and viral infections: Fluorouracil, capecitabine, gemcitabine, fludarabine, flucytosine, elvucitabine, tezacitabine, trifluridine.
CAS number: 217-59-4
Triphenylene is an ortho-fused polycyclic arene consisting of four fused benzene rings.
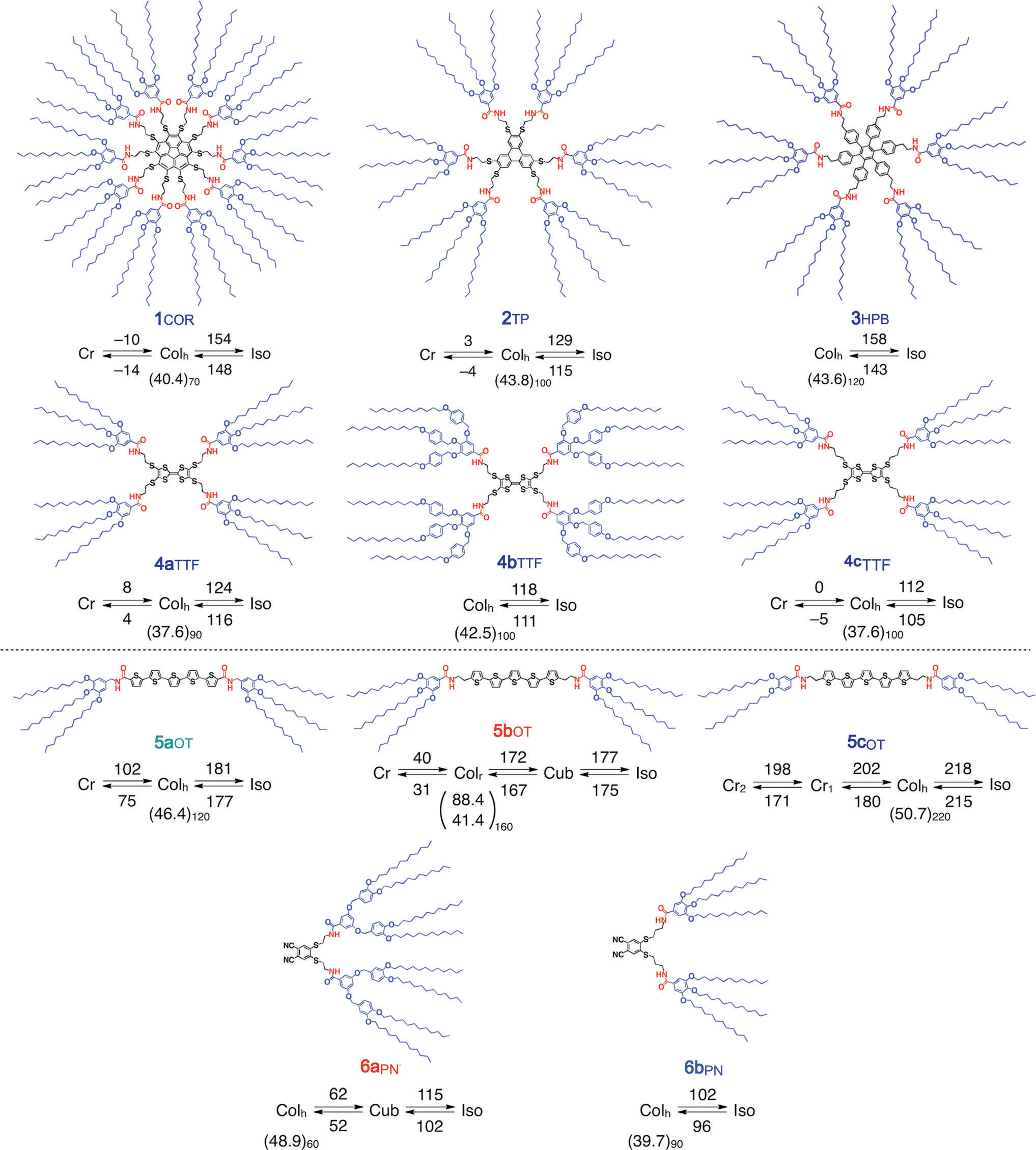
Structures and phase diagrams of LC compounds derived form corannulene (1COR), triphenylene (2TP), hexaphenylbenzene (3HPB), tetrathiafluvalene (4aTTF, 4bTTF, and 4cTTF), oligothiophene (5aOT, 5bOT, and 5cOT), and phthalonitrile (6aPN and 6bPN).
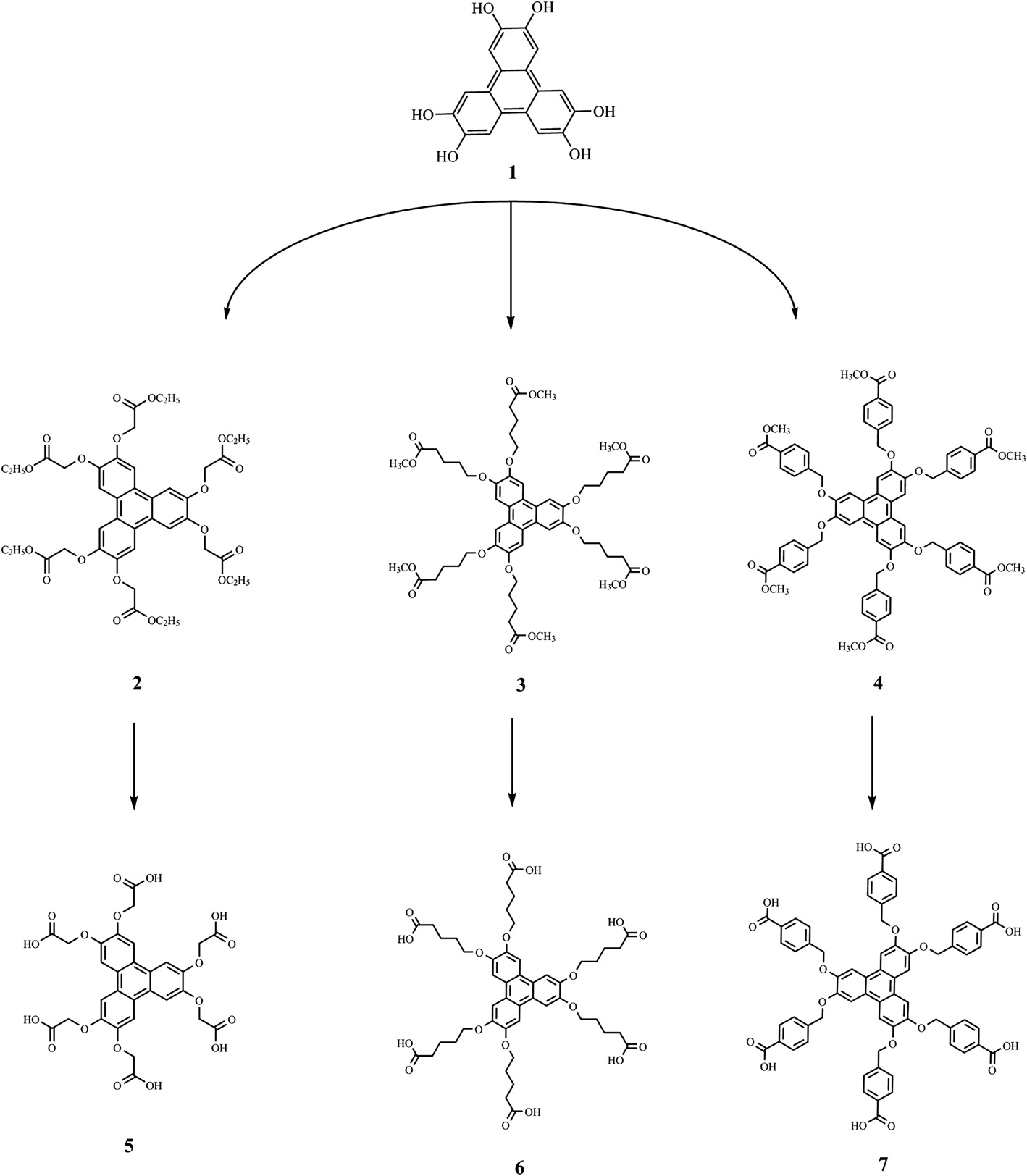
Synthesis of the carboxylic acid derivatives of triphenylene.