Chemicals list & Research Gallery
CAS number: 151-56-4
Aziridine is a saturated organic heteromonocyclic parent, a member of aziridines and an azacycloalkane. It has a role as an alkylating agent. It is a conjugate base of an aziridinium.
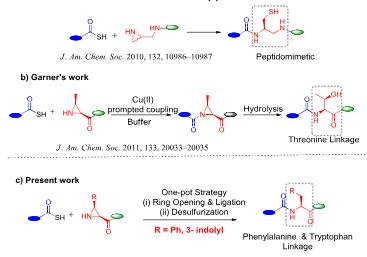
Previous and present work on aziridine-mediated ligation.
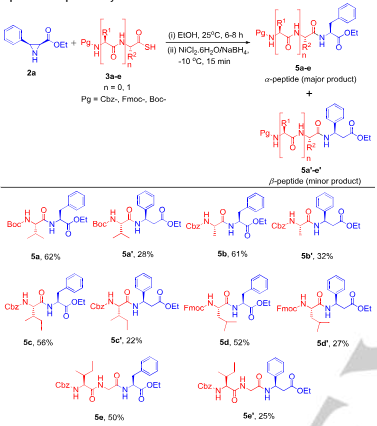
Substrate scope for aziridine-mediated ligation at phenylalanine site.
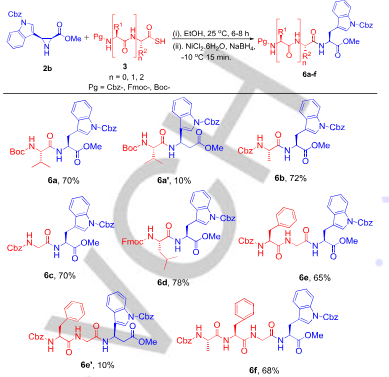
Substrate scope for aziridine-mediated ligation at tryptophan site.
CAS number: 15159-40-7
4-Morpholinecarbonyl chloride may be used in the preparation of a versatile fluorogenic label for biomolecular imaging. It may be used in the synthesis of: morpholine-4-carboxylic acid [4-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)thiazol-2-yl]amide.
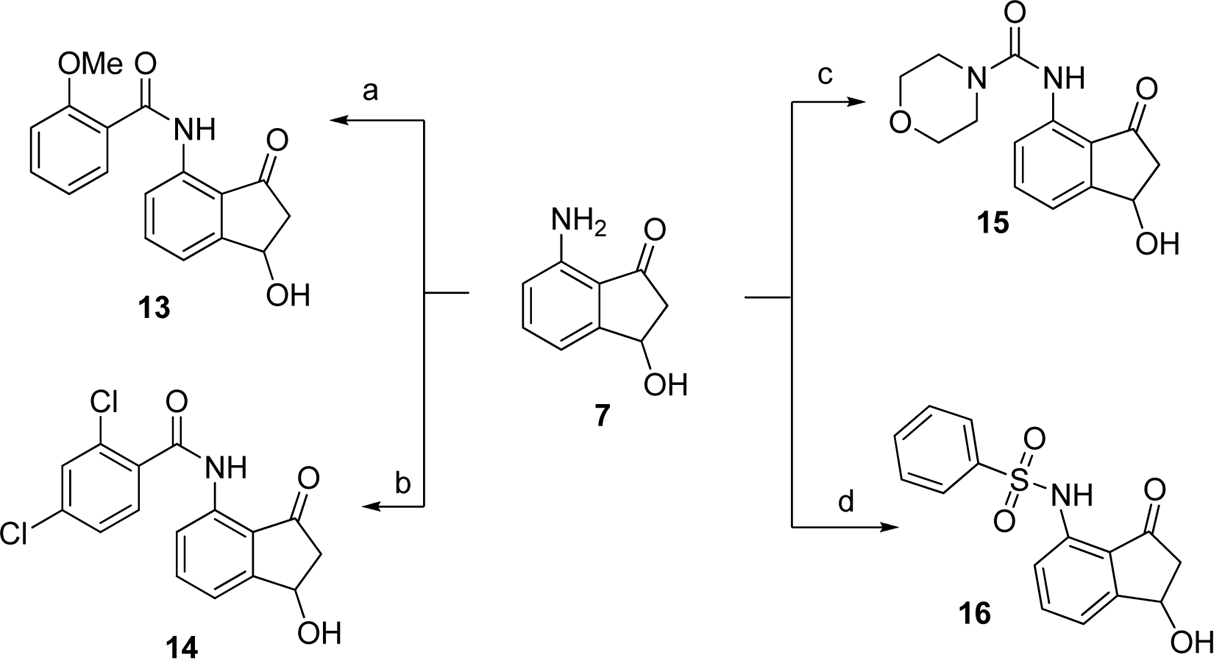
Reagents and conditions: (a) 2-methoxbenzoyl chloride, DIEA, DCE, room temperature; (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl chloride, DIEA, DCE, room tempera- ture; (c) 4-morpholinecarbonyl chloride, DIEA, DCE, room temperature; (d) phenylsulfonyl chloride, DIEA, DCE, room temperature.
CAS number: 15186-48-8
(R)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolane-4-carbaldehyde, also known as D-glyceraldehyde acetonide, is a chiral organic compound used as a versatile building block in organic synthesis. It functions as a reactant in various chemical reactions, including aldol condensations, Henry condensation reactions, and the synthesis of complex molecules like chiral aziridines and fluorescent dyes. Its specific (R) stereochemistry makes it valuable for creating enantiomerically pure compounds with specific biological or catalytic activities.
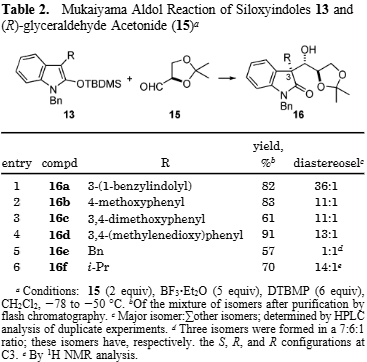
Mukaiyama Aldol Reaction of Siloxyindoles 13 and (R)-glyceraldehyde Acetonide
CAS number: 151864-96-9
Calonyctin A-2d is one of two components of the plant growth regulator known as calonyctin. It's a glycoside, meaning it's a molecule made up of a sugar (specifically, a tetrasaccharide) and a non-sugar component called an aglycone. The aglycone in calonyctin A-2d is composed of two hydroxy fatty acid residues. It's a macrocyclic structure, meaning it has a large ring.
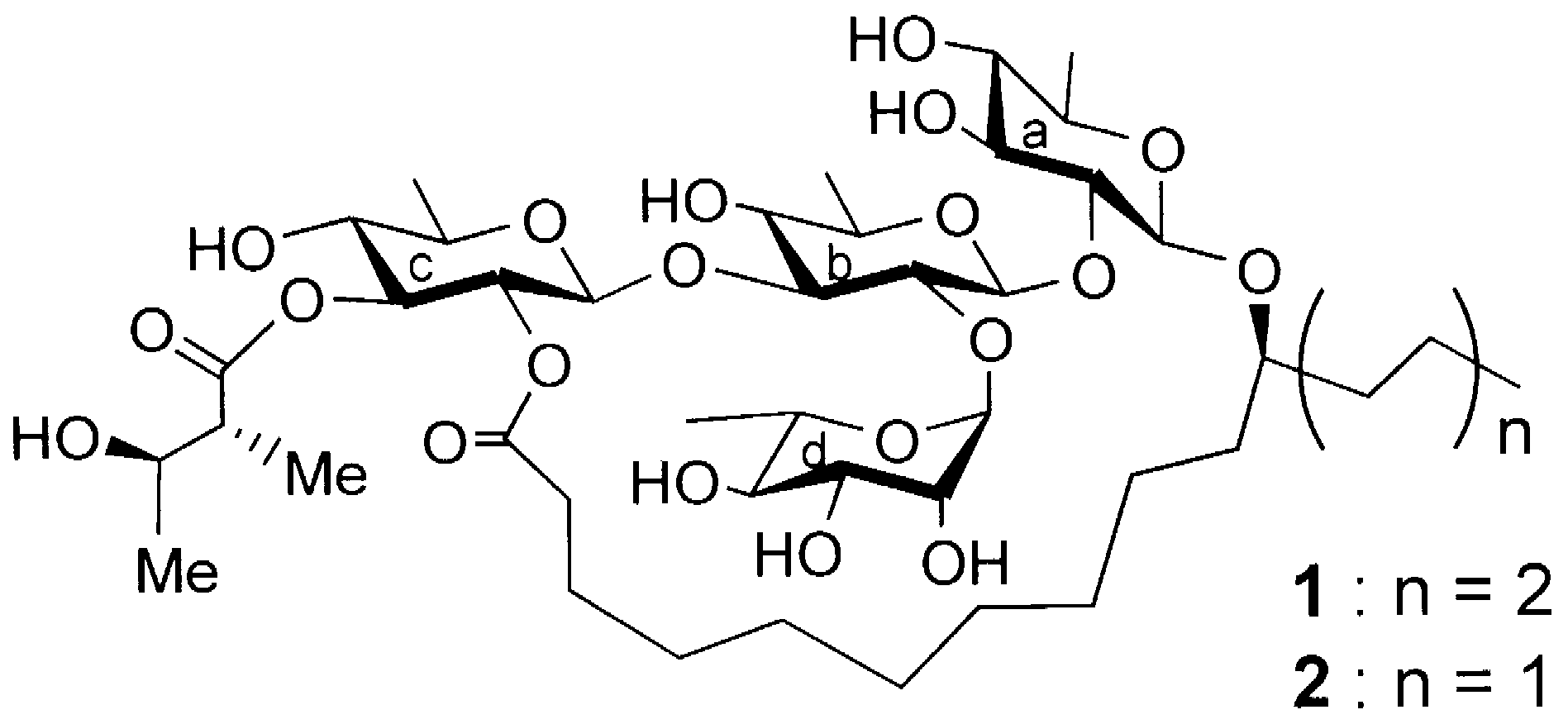
Calonyctin is a mixture of homologous glycolipids consisting of a common deoxygenated tetrasaccharide residue and 11-hydroxy fatty acids, which are named calonyctin A1 (1) and A2 (2), respectively (Fig. 1).
CAS number: 151923-84-1
Aplyronine A is a macrolide isolated from Aplysia kurodai. By monitoring fluorescent intensity of pyrenyl-actin, it was found that aplyronine A inhibited both the velocity and the degree of actin polymerization. Aplyronine A also quickly depolymerized F-actin.
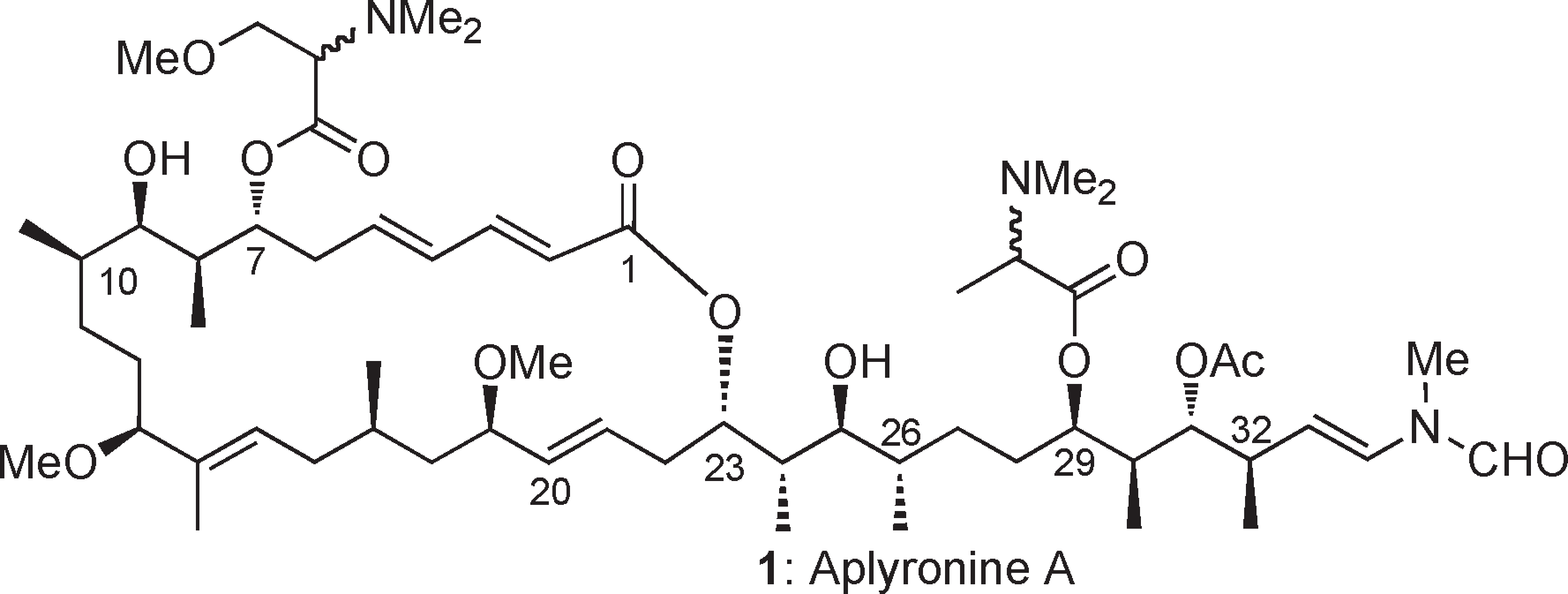
Aplyronine A: mixture of four side chain diastereomers.
CAS number: 152406-28-5
Agelastatin A is a marine alkaloid with potent biological activity.
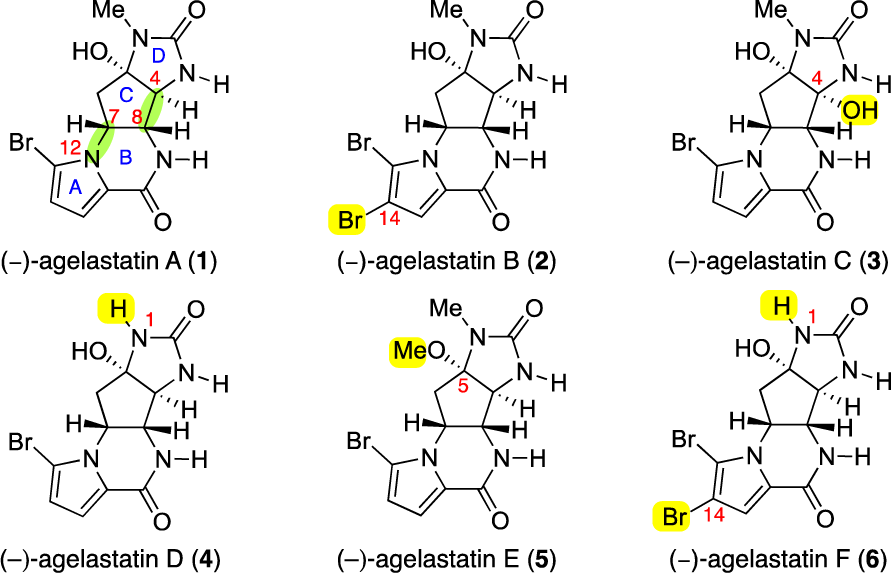
Structures of (−)-agelastatins A−F (1−6).
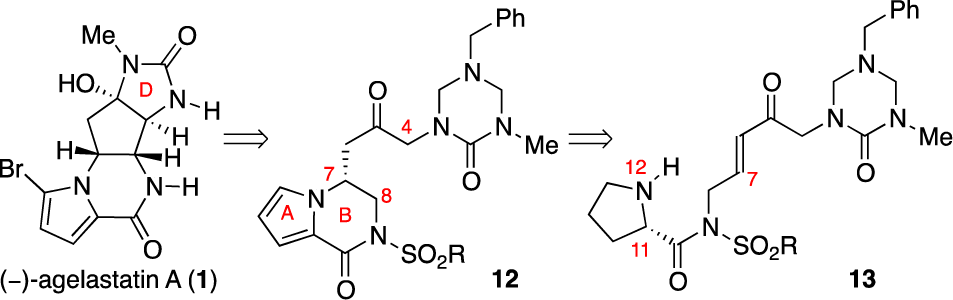
Early Approach toward (−)-Agelastatin A (1)
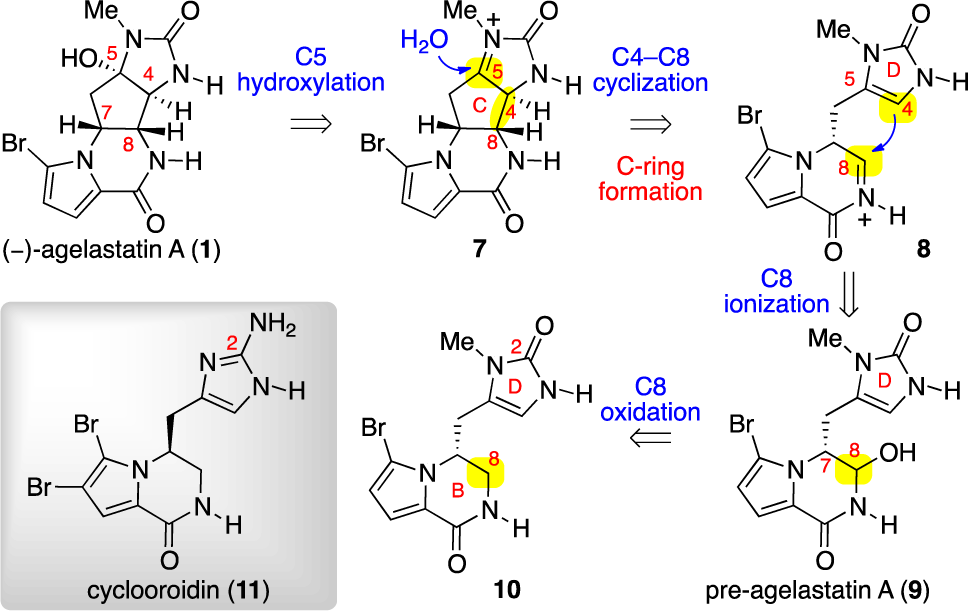
Retrobiosynthetic Analysis of (−)-Agelastatin A (1)
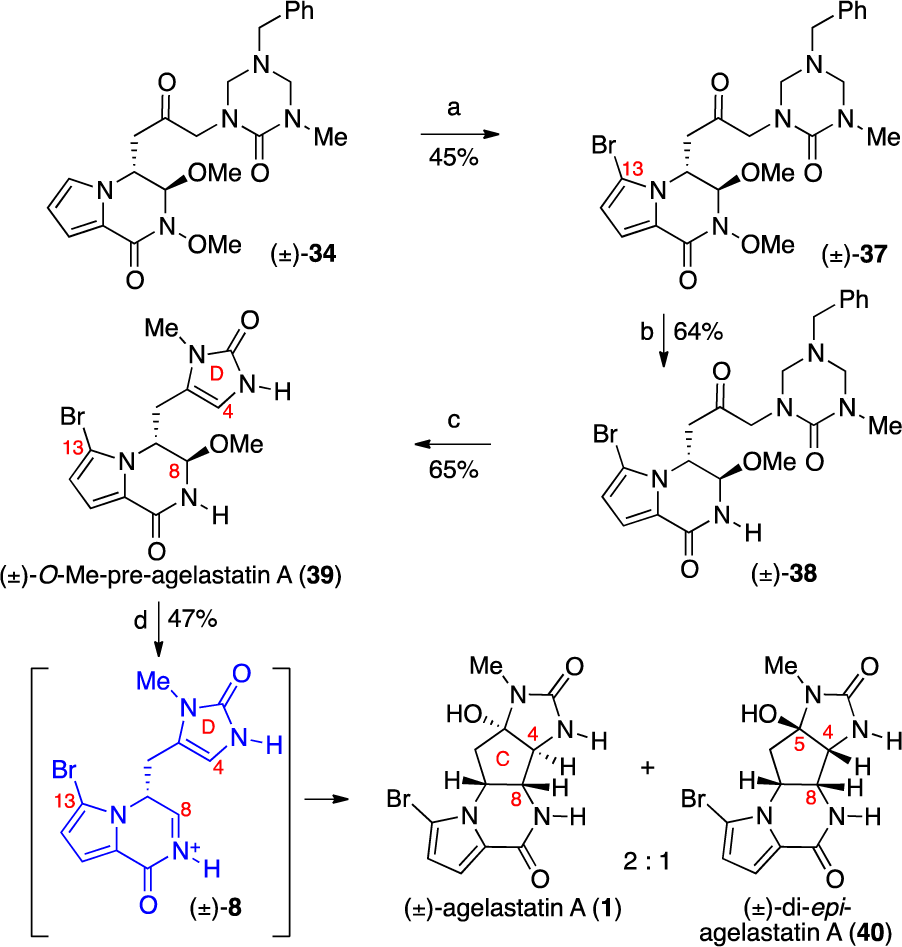
Our First-Generation Total Synthesis of ( )-Agelastatin A (1)
CAS number: 152459-95-5
Imatinib is in a class of medications called kinase inhibitors. It works by blocking the action of an abnormal protein in cancer cells.

(Left) Interaction of STI-571 and (right) 11b from MCPRO+ calculations. Only nearby residues and water with H-bonding interactions with the ligand are shown. Images were created with PYMOL v1.5.0.4
CAS number: 152918-18-8
CF 101 (known generically as IB-MECA) is an anti-inflammatory drug for rheumatoid arthritis patients. Its novel mechanism of action relies on antagonism of adenoside A3 receptors. CF101 is supplied as an oral drug and has an excellent safety profile. It is also being considered for the treatment of other autoimmune-inflammatory disorders, such as Crohn's disease, psorasis and dry eye syndrome.
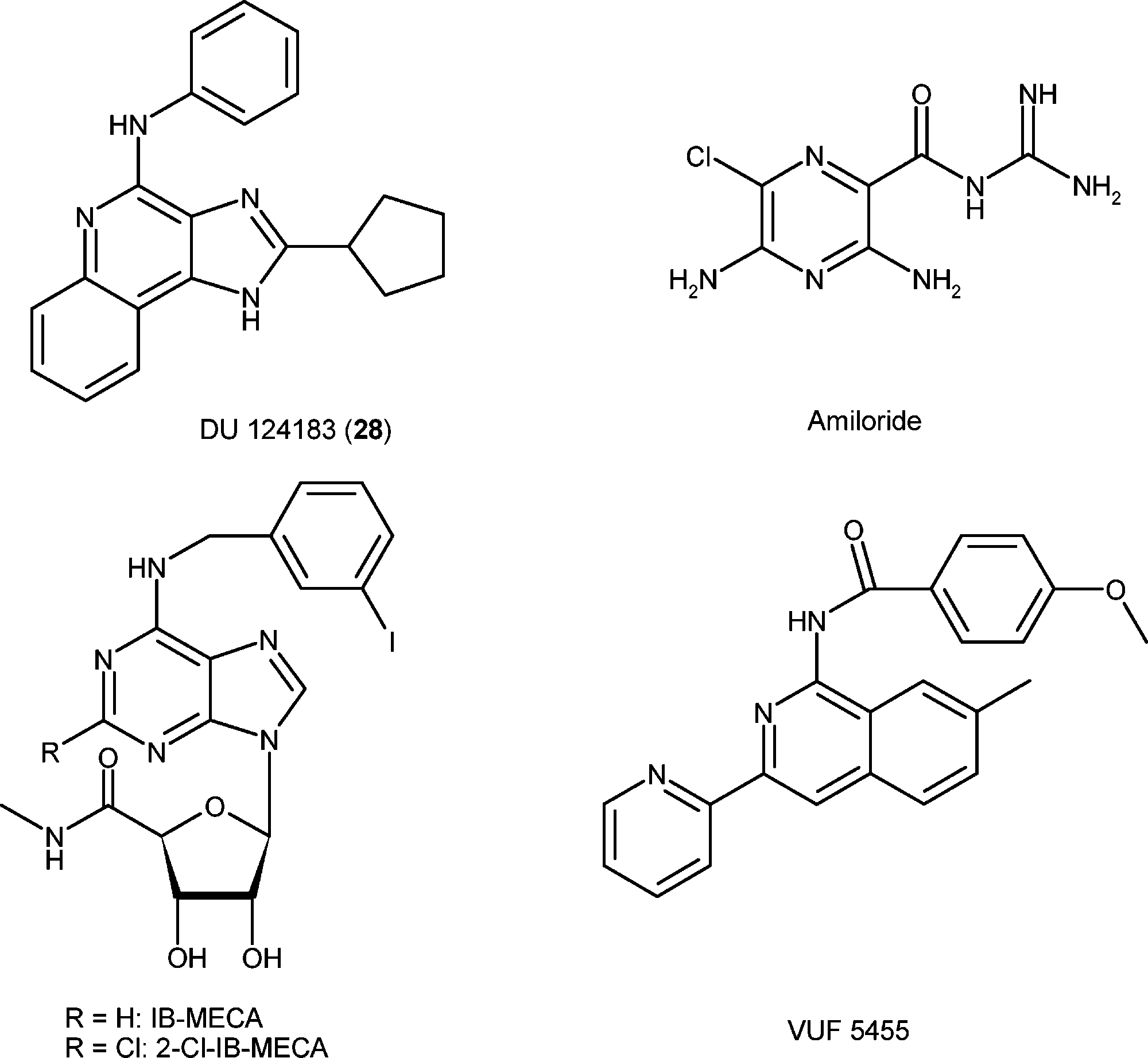
Structures of reference agonists (IB-MECA and 2-Cl-IB-MECA) and allosteric modulators (DU 124183, amiloride, and VUF5455) of the A3AR.
CAS number: 153420-96-3
LU-53439 (Atibeprone) is a selective MAO-B inhibitor with antidepressant potential in early research, but it showed no anticonvulsant efficacy in key animal models and was never advanced to the market.
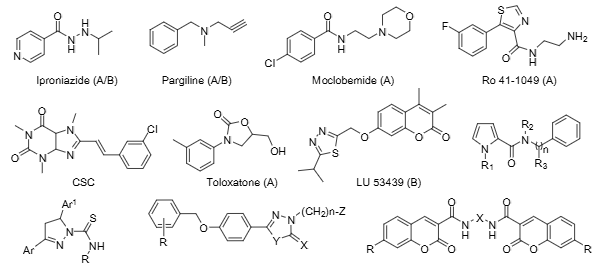
Some representative structures of MAO inhibitors used in research or clinical practice: Iproniazide, Pargiline, Moclobemide, Ro 41-1049, CSC, Toloxatone, LU-53439.
CAS number: 153436-54-5
PD-153035 is a member of the class of quinazolines carrying a 3-bromophenylamino substituent at position 4 and two methoxy substituents at positions 6 and 7. It has a role as an EC 2.7.10.1 (receptor protein-tyrosine kinase) inhibitor and an epidermal growth factor receptor antagonist. It is a member of quinazolines, an aromatic amine, a secondary amino compound, a member of bromobenzenes and an aromatic ether. It is a conjugate base of a PD-153035(1+).
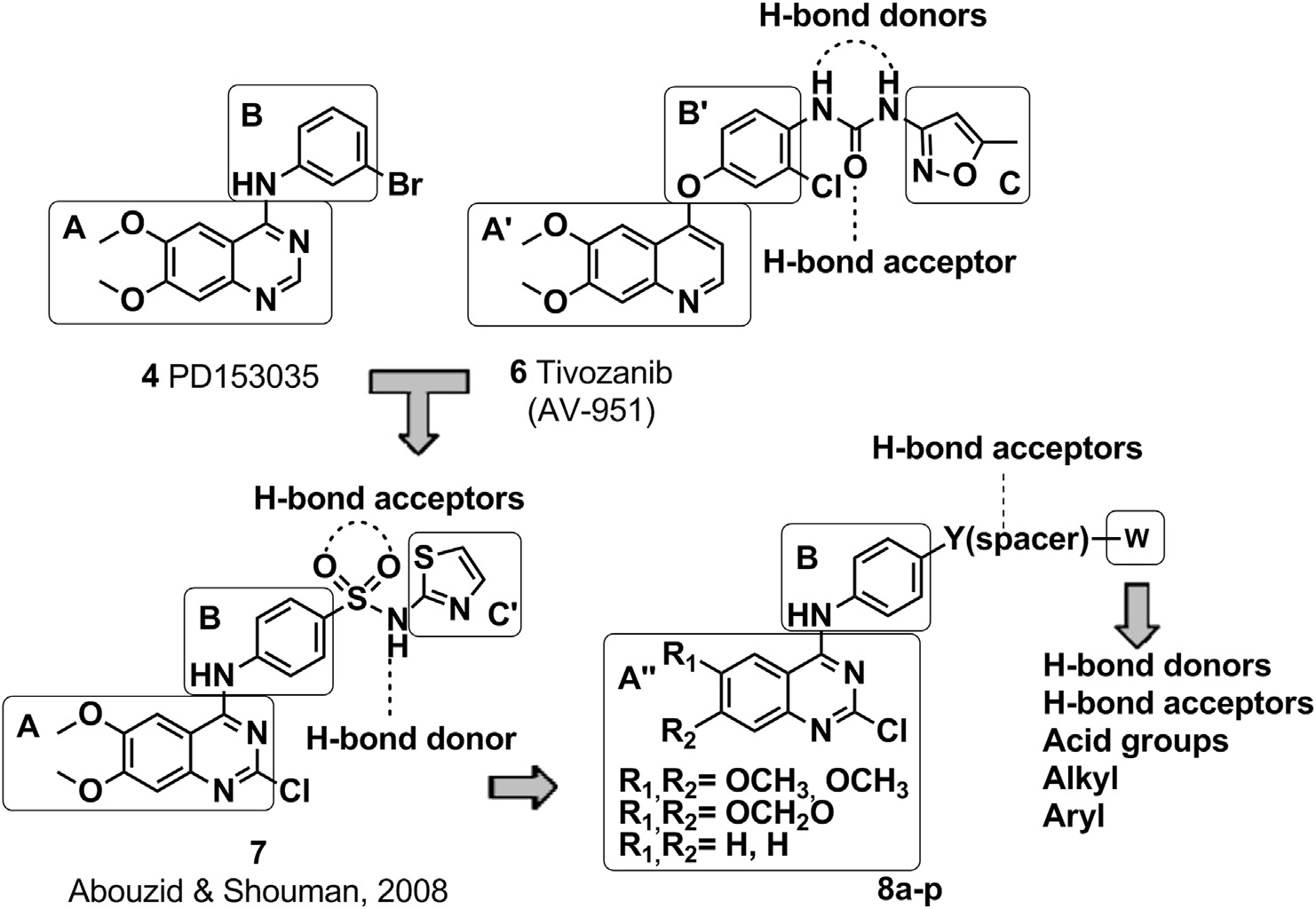
Structural design of the target 2-chloro-4-anilino-quinazoline derivatives 8aep.