Titanocene
CAS number: 1271-29-0
Titanocene is an organotitanium compound in which a titanium atom is sandwiched between two cyclopentadienyl (C₅H₅⁻) rings in a metallocene structure. It is a dark-colored, air-sensitive solid that is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as benzene or toluene. The compound is typically prepared by reacting sodium cyclopentadienide with titanium tetrachloride, producing titanocene dichloride as a precursor, which can then be reduced to titanocene itself. Titanocene’s structure and bonding are of significant interest in organometallic chemistry due to its symmetry, stability in inert atmospheres, and potential as a starting material for catalytic and polymerization processes.
Related images
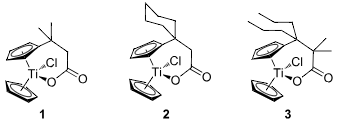
Carboxylates employed as titanocene starting materials for azide-substituted complexes.
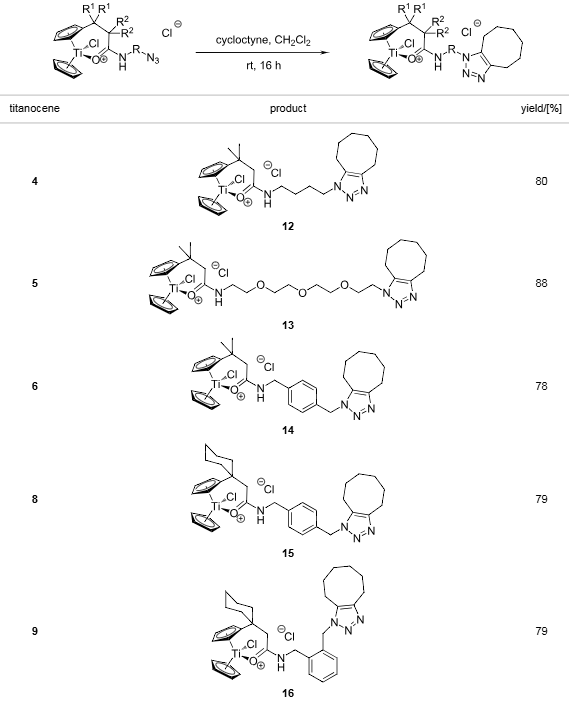
Strain-driven 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions between cyclooctyne and azide-functionalized titanocenes in CH2Cl2 (0.1 M).
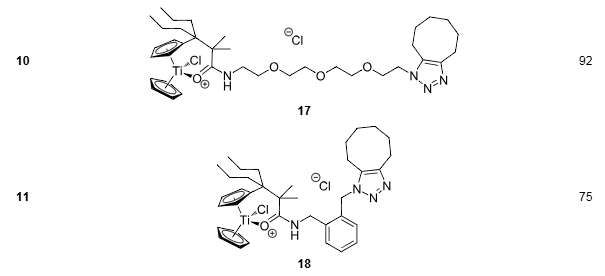
Strain-driven 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions between cyclooctyne and azide-functionalized titanocenes in CH2Cl2 (0.1 M). (continued)
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet
![Modular titanocene synthesis via acylation reactions [24].](http://www.wlxkc.cn/picture/bjoc.10.169_1.png)