SGI-1776
CAS number: 1025065-69-3
PIM Kinase Inhibitor SGI-1776 is a small-molecule pan-PIM protein kinase inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. PIM kinase inhibitor SGI-1776 binds to and inhibits the activities of PIM-1, -2 and -3 serine/threonine kinases, which may result in the interruption of the G1/S phase cell cycle transition, the expression of pro-apoptotic Bcl2 proteins and tumor cell apoptosis. PIM kinases play key roles in cell cycle progression and apoptosis inhibition and may be overexpressed in various malignancies.
Related images
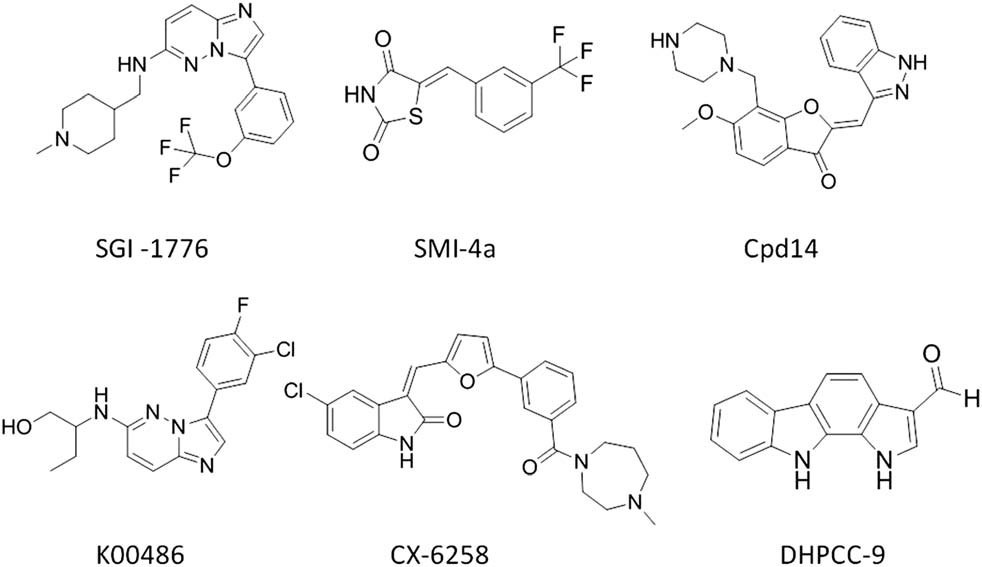
Small molecule inhibitors targeting Pim family kinases: SGI-1776, SMI-4a, K00486, CX-6258, DHPCC-9
Related Questions and Answers
A: SGI-1776 treatment does not significantly affect normal PBMCs, unlike MCL cells. In normal PBMCs, SGI-1776 does not consistently reduce the phosphorylation of Pim kinase targets or the levels of short-lived proteins like Mcl-1 and cyclin D1. Additionally, apoptosis is not induced in normal PBMCs after SGI-1776 treatment, suggesting that the drug selectively targets MCL cells without affecting healthy cells.
A: SGI-1776 treatment reduces the phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62 and 4E-BP1 at Thr37/46 in MCL cell lines such as JeKo-1 and Mino. In JeKo-1 cells, phospho-c-Myc (Ser62) and phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) levels decrease in a dose-dependent manner. In Mino cells, phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) levels also decline, but phospho-c-Myc (Ser62) levels are less affected. This inhibition of phosphorylation disrupts transcriptional and translational processes, contributing to cell death.
A: SGI-1776 treatment leads to a dose- and time-dependent decrease in Mcl-1 and cyclin D1 protein levels in MCL cell lines such as JeKo-1 and Mino. In JeKo-1 cells, Mcl-1 protein levels decrease significantly at 3 µM and higher concentrations, while in Mino cells, a more pronounced decrease is observed at 10 µM. Cyclin D1 levels also decline in JeKo-1 cells but increase in Mino cells, possibly due to cell cycle changes. This suggests that SGI-1776-induced degradation of these proteins contributes to cell death in MCL cells.
A: SGI-1776 significantly reduces global RNA synthesis in MCL cell lines such as JeKo-1, Mino, Granta 519, and SP-53. In JeKo-1 cells, RNA synthesis decreases to 75%, 57%, and 28% of control at 3, 5, and 10 µM of SGI-1776, respectively. In Mino cells, RNA synthesis slightly increases at lower concentrations but decreases by 40% at 10 µM. This reduction in RNA synthesis is associated with decreased levels of short-lived mRNA and proteins like Mcl-1 and cyclin D1, contributing to cell death.
A: SGI-1776 selectively binds to the ATP-binding site of Pim-1 and inhibits all three Pim kinases (Pim-1, Pim-2, and Pim-3) with IC50 values of 7 nM, 363 nM, and 69 nM, respectively. It induces apoptosis in MCL cell lines and primary cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of key Pim kinase targets such as c-Myc (Ser62), Histone H3 (Ser10), Bad (Ser112), and 4E-BP1 (Thr37/46). This inhibition disrupts transcriptional and translational processes, leading to decreased levels of short-lived proteins like Mcl-1 and cyclin D1, ultimately promoting cell death.
A: SGI-1776 treatment leads to mitochondrial depolarization in SACC cells, as indicated by a decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). This depolarization is a hallmark of early apoptosis and contributes to the induction of apoptosis in SACC cells.
A: SGI-1776 induces apoptosis in SACC cells, as shown by increased early apoptosis rates and elevated caspase-3 activity. This effect is dose-dependent, with higher concentrations of SGI-1776 leading to greater induction of apoptosis.
A: SGI-1776 treatment significantly reduces the migration and invasive potential of SACC cells. This is demonstrated by a slower rate of wound healing in scratch assays and reduced cell invasion in transwell assays.
A: SGI-1776 treatment significantly reduces cell proliferation in SACC cells, as evidenced by decreased DNA synthesis (measured by BrdU incorporation) and reduced colony formation. The cell cycle is also arrested, with an increase in the percentage of cells in the G0/G1 and G2/M phases and a decrease in the S phase.
A: SGI-1776 down-regulates Pim-1 protein expression and inhibits Pim-1 kinase activity in a dose-dependent manner in SACC cells. This inhibition leads to reduced cell proliferation, decreased invasive ability, and increased apoptosis.