Huperzine A
CAS number: 102518-79-6
Huperzine A, is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid found in the extracts of the firmoss Huperzia serrata. The botanical has been used in China for centuries for the treatment of swelling, fever and blood disorders. Recently in clinical trials in China, it has demonstrated neuroprotective effects. It is currently being investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly Alzheimer’s disease.
Related images
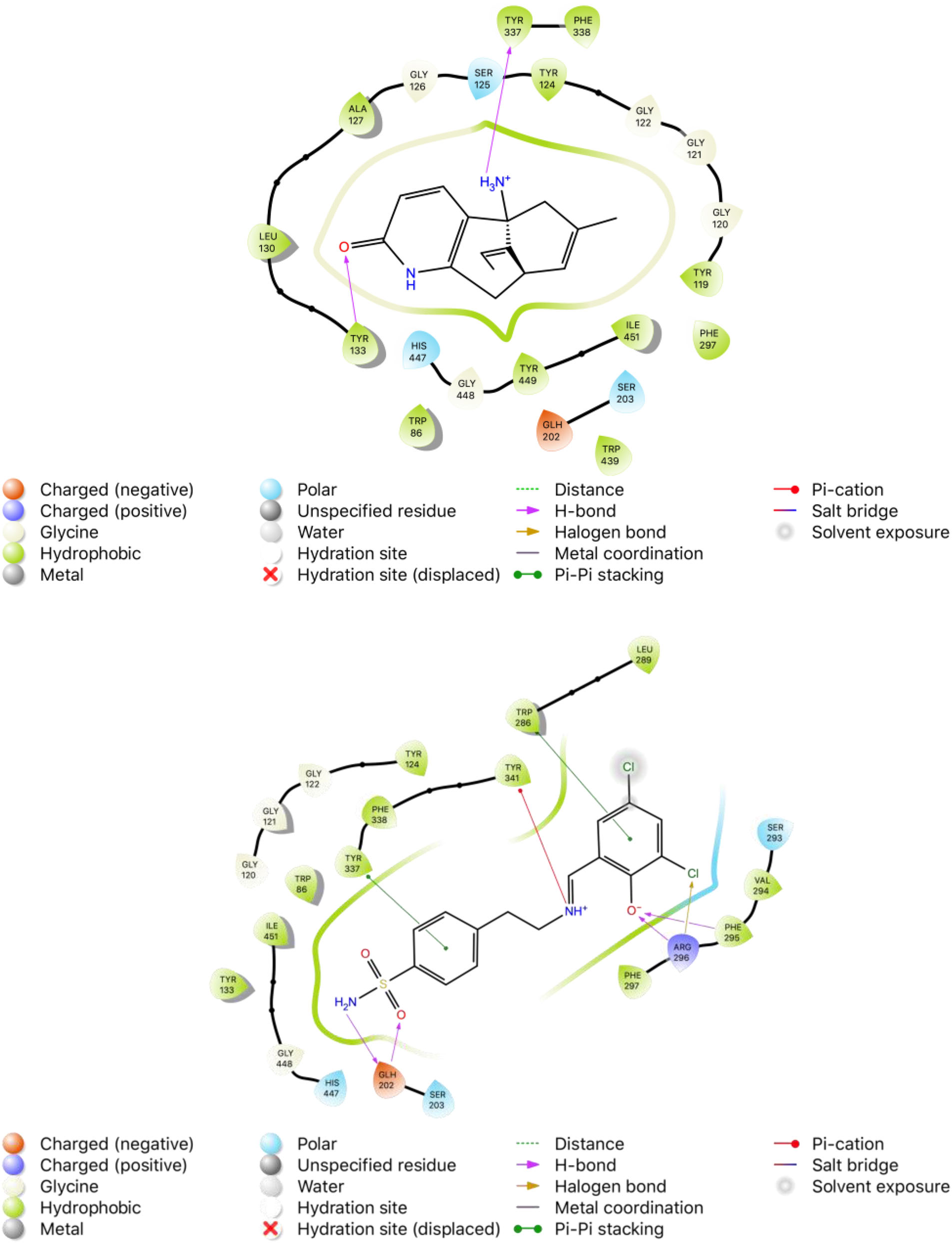
2D binding modes of native ligand huperzine A (HUP) and compound 10 in the active site of AChE (PDB ID: 4EY5), respectively.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Huperzine-A significantly improves neuronal behavior in cadmium chloride-induced Drosophila melanogaster, as evidenced by enhanced feeding, climbing, and reduced rough eye phenotype. This suggests that huperzine-A has a neuroprotective effect by mitigating the behavioral deficits caused by cadmium chloride.
A: Huperzine-A significantly reduces acetylcholinesterase activity in cadmium chloride-induced models. This suggests that huperzine-A may help maintain higher levels of acetylcholine, thereby supporting cognitive functions and reducing neurodegenerative symptoms.
Q: What is the role of huperzine-A in modulating Wnt signaling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases?
A: Huperzine-A significantly reduces the mRNA levels of Wnt3a and CAMK2A in cadmium chloride-treated SH-SY5Y cells. This suggests that huperzine-A may help normalize Wnt signaling pathways, thereby reducing neurotoxicity and protecting against neurodegenerative effects.
A: Huperzine-A protects against cadmium chloride-induced cytotoxicity by reducing lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. It also helps maintain the levels of antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing oxidative damage and enhancing cell survival.
A: Huperzine-A significantly increases dopamine and serotonin levels in cadmium chloride-induced models. This suggests that huperzine-A may help restore normal neurotransmitter balance, thereby mitigating the neurotoxic effects of cadmium chloride.
A: Huperzine-A binds to the huntingtin protein with a binding energy of −7.85 kcal/mol, interacting with amino acids LYS2236, TYR2576, and HIS2574. This interaction suggests that huperzine-A may help stabilize the huntingtin protein or modulate its effects, potentially reducing neurodegenerative symptoms.
A: Huperzine-A significantly reduces oxidative stress in cadmium chloride-induced neurotoxicity by decreasing ROS levels and restoring antioxidant enzyme activities such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This helps protect neurons from oxidative damage.