Calpastatin
CAS number: 79079-11-1
A calpain inhibitor is a substance that blocks or inhibits the activity of calpains, which are a family of calcium-dependent enzymes (proteases) involved in various cellular processes.
Related images
Related Questions and Answers
A: Calpastatin overexpression in podocytes prevents Angiotensin II-induced autophagy inhibition and podocyte injury. This is achieved by reducing calpain activity, thereby maintaining autophagy flux. Calpastatin overexpression also limits albuminuria and glomerulosclerosis, highlighting its protective role in hypertension-associated nephropathies.
A: Calpastatin prevents Angiotensin II-mediated podocyte injury by inhibiting calpain activity. Overexpression of calpastatin in podocytes maintains autophagy flux, thereby protecting podocytes from AngII-induced damage. This suggests that calpastatin could be a potential therapeutic target for preventing podocyte injury in hypertension-associated nephropathies.
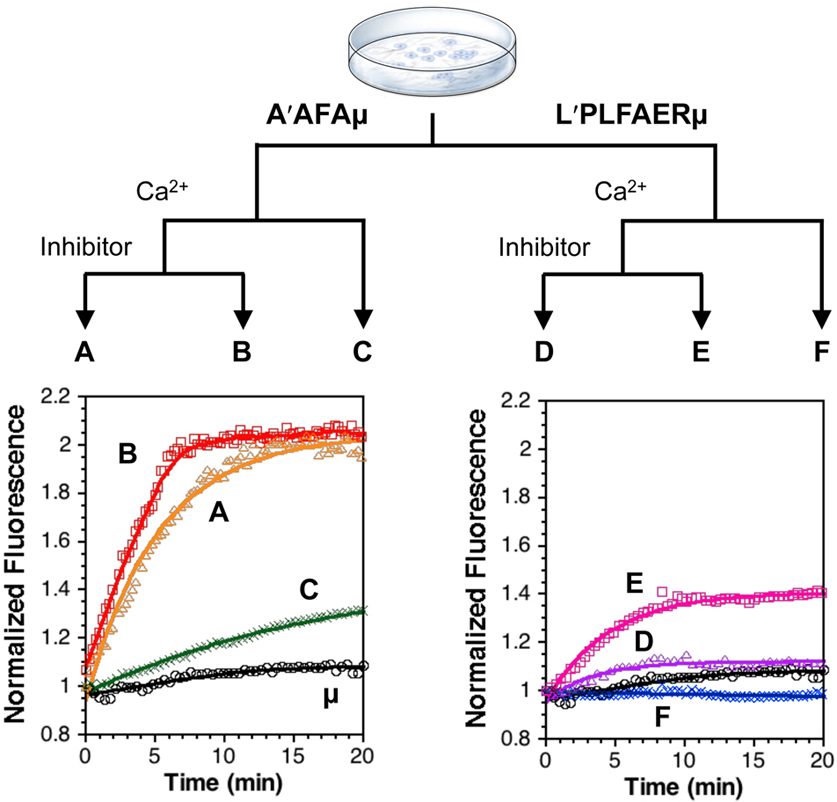
Q: What is the effect of hcast 3-25 on calpain-1 activity in the presence of inhibitory calpastatins?
A: hcast 3-25 does not interfere with the inhibitory activity of calpastatins but enhances the activity of calpain-1. When hcast 3-25 is present with calpain-1 and inhibitory calpastatins (e.g., cast600), it protects calpain-1 from degradation, allowing the inhibitory calpastatins to effectively regulate calpain-1 activity. The study concludes that hcast 3-25 is essential for maintaining the appropriate amount of active calpain-1 molecules that can be modulated by inhibitory calpastatins.
A: hcast 3-25 can interact with calpain-1 in the absence of Ca2+. This interaction is Ca2+-independent and occurs when calpain-1 is in its native inactive conformation. The study demonstrates that hcast 3-25 binds to calpain-1 and protects it from degradation by activated calpain-1 molecules, even in the absence of Ca2+. This interaction is crucial for maintaining the catalytic activity of calpain-1.
A: hcast 3-25 acts as a positive modulator of calpain-1 activity. It prevents the degradation of calpain-1 by activated calpain-1 molecules and blocks the binding of inhibitory calpastatins to calpain-1. This results in the protection of calpain-1 from inactivation and degradation, allowing it to maintain its catalytic activity. The study concludes that hcast 3-25 is a novel member of the calpain/calpastatin system that modulates calpain-1 activity through a mechanism different from classical inhibition.