Milrinone
CAS number: 78415-72-2
Milrinone is a member of the class of bipyridines that is 2-pyridone which is substituted at positions 3, 5, and 6 by cyano, pyrid-4-yl, and methyl groups, respectively. It is used (particularly intravenously, as the lactate) for the short-term management of severe heart failure. It has a role as an EC 3.1.4.17 (3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase) inhibitor, a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a vasodilator agent and a cardiotonic drug. It is a pyridone, a nitrile and a member of bipyridines.
Related images
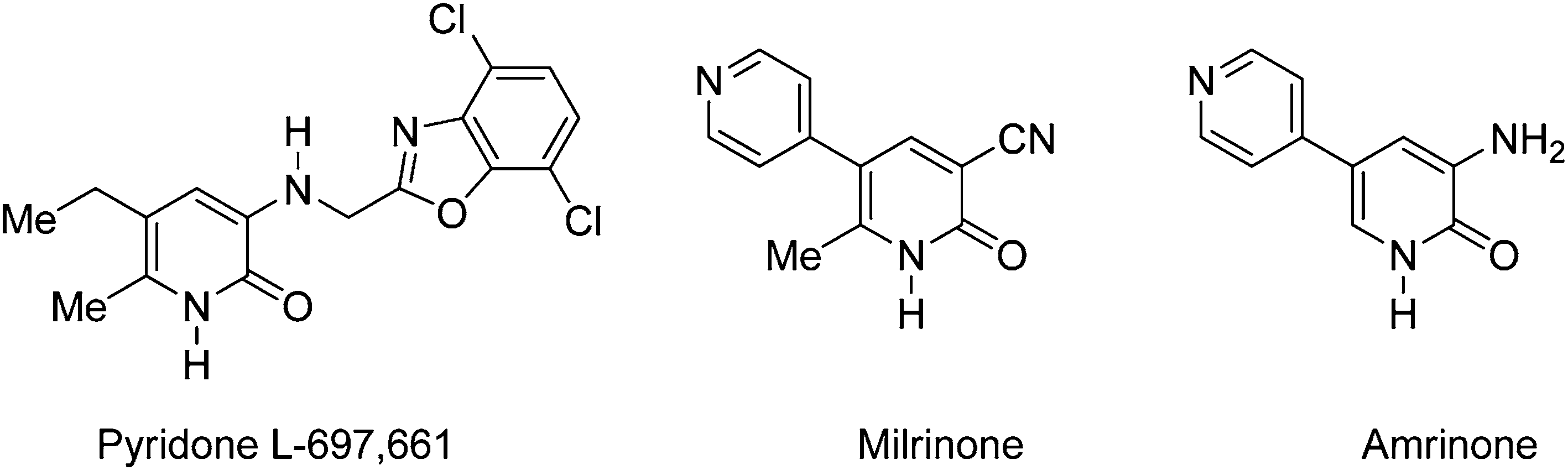
2-Pyridones possessing pharmacological properties: Amrinone, milrinone, L-697,661
Related Questions and Answers
A: The study observed an interaction between AKI and the treatment effect of milrinone compared to dobutamine. Patients without AKI treated with milrinone had a lower risk of primary outcomes and death compared to those treated with dobutamine. In contrast, patients with AKI did not show a significant difference in outcomes between milrinone and dobutamine treatment.
A: The study found that baseline renal function (eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73m²) did not significantly modulate the treatment effect of milrinone compared to dobutamine. However, the presence of AKI significantly influenced the treatment effect, with milrinone showing a lower risk of primary outcomes and death in patients without AKI compared to those with AKI.
A: Milrinone is used to improve cardiac function in patients with cardiogenic shock. However, its efficacy may be influenced by renal function, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). The study suggests that milrinone may offer therapeutic benefits in patients without AKI, but these benefits are attenuated in patients who develop AKI.
Q: How does milrinone help in the management of cardiogenic shock in Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TTC)?
A: Milrinone was used to support the patient's circulatory function in this case of TTC-related cardiogenic shock. It improved hemodynamics and allowed for the discontinuation of norepinephrine, contributing to the patient's recovery.
A: Milrinone is used to improve vessel diameter and reduce vasospasm in patients with severe refractory VSP following aSAH. It is administered intraarterially in combination with Nimodipine to enhance vasodilation and improve clinical outcomes.
A: Milrinone may promote apoptosis and reduce tumor growth by increasing cAMP levels. It also has potential anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties, which could make it a useful adjuvant therapy in oncology. Further research is needed to confirm its efficacy and safety in cancer patients.